UlzhanKamila Energy transfer between organisms.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 13

Energy exchange among organisms

Energy • Remember that all energy starts in the sun. • Producers can convert light energy from the sun into chemical energy stored in food.

Energy transfer • We will look at 3 ways of representing energy as it flows from the sun to producers, and from producers to consumers. – Energy Pyramids – Food Chains – Food Webs
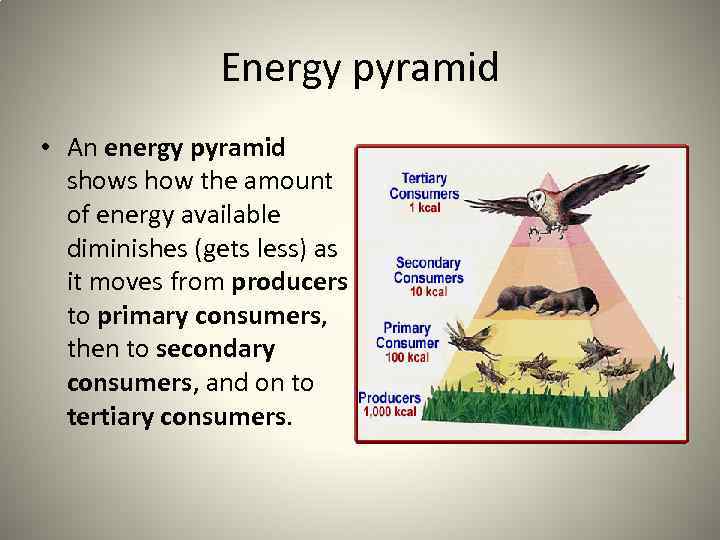
Energy pyramid • An energy pyramid shows how the amount of energy available diminishes (gets less) as it moves from producers to primary consumers, then to secondary consumers, and on to tertiary consumers.
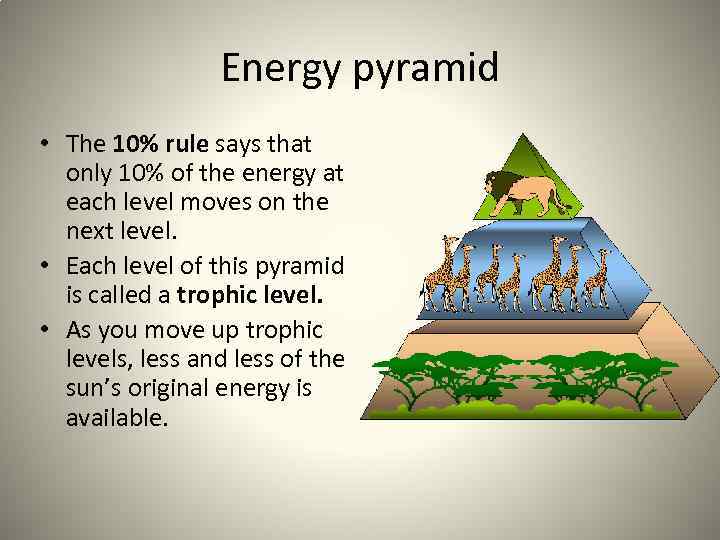
Energy pyramid • The 10% rule says that only 10% of the energy at each level moves on the next level. • Each level of this pyramid is called a trophic level. • As you move up trophic levels, less and less of the sun’s original energy is available.

Energy pyramid • What happens to the other 90% of the energy at each level? – Most of it is used by the organism, or lost as heat. – Humans radiate about 100 joules of heat per second. That’s the same amount of heat that is radiated from a 100 watt lightbulb!
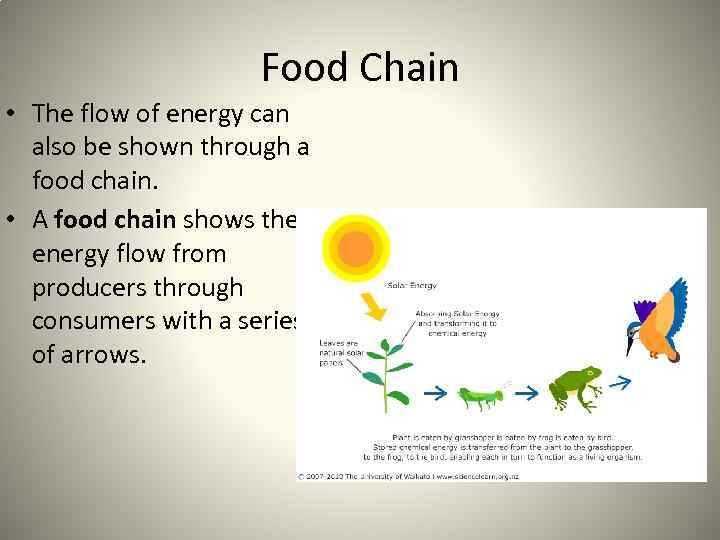
Food Chain • The flow of energy can also be shown through a food chain. • A food chain shows the energy flow from producers through consumers with a series of arrows.
8
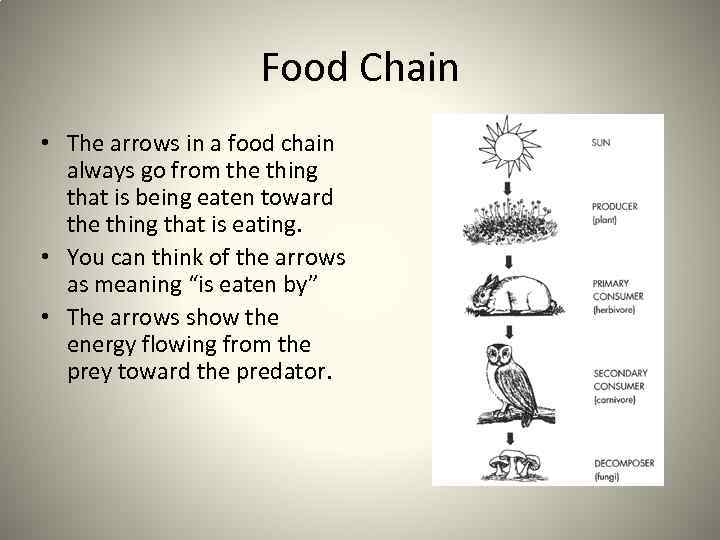
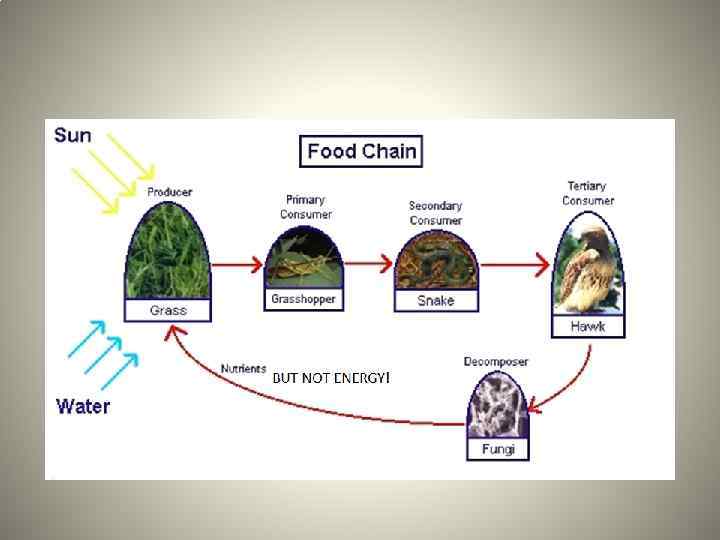
Food Chain • The arrows in a food chain always go from the thing that is being eaten toward the thing that is eating. • You can think of the arrows as meaning “is eaten by” • The arrows show the energy flowing from the prey toward the predator.
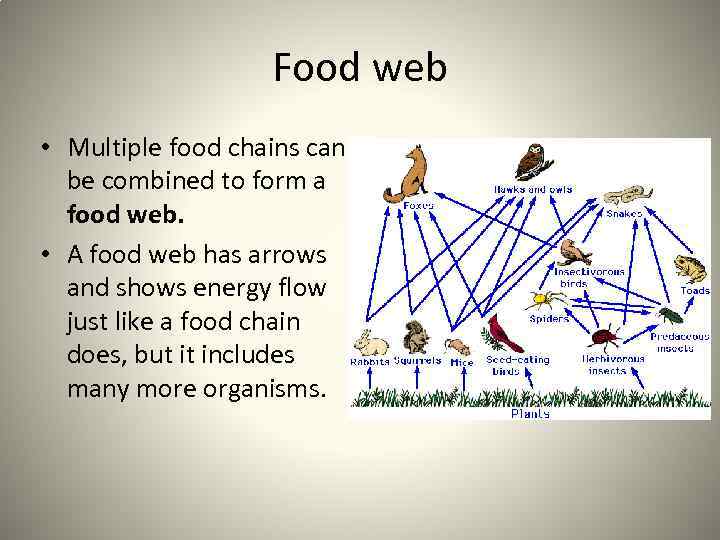
Food web • Multiple food chains can be combined to form a food web. • A food web has arrows and shows energy flow just like a food chain does, but it includes many more organisms.
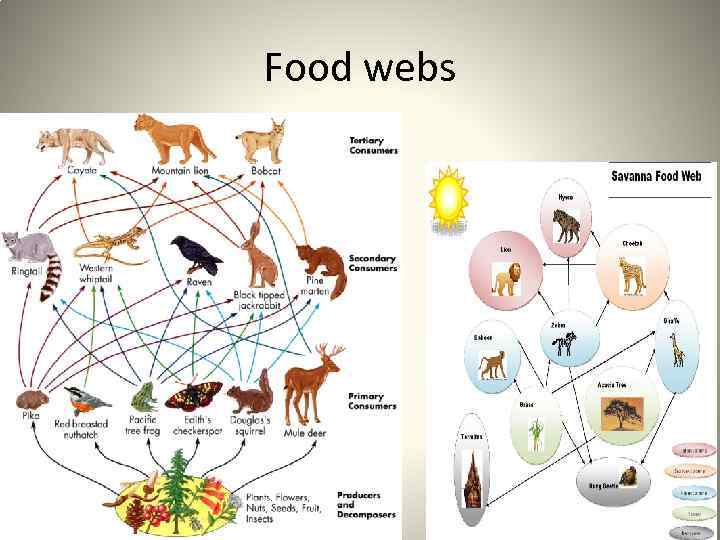
Food webs

Transfer of Energy When a lion eats a zebra, it does not get all of the energy from the zebra. Energy lost is usually in form of heat Energy lost from chain “link” to “link” is significant! 12

Energy lost from one trophic level (energy level) to th ♦ Each level above only gets 10% of the energy from b CONSUMERS − Ex: 10, 000 J of producers (plants) only give 10% of energy to prim > > 1, 000 J to primary consumers (snails, minnows, dra 100 J to secondary consumers (small fish) 10 J to tertiary consumers (big fish) 1 J to quaternary consumers (fish hawk) 13
UlzhanKamila Energy transfer between organisms.pptx