b32da46cf4d04ee8811aac06be824a9e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 14
 Energy Efficiency for the Consumers April 10, 2010 Anuradha Bhattacharji Bureau of Energy Efficiency 1
Energy Efficiency for the Consumers April 10, 2010 Anuradha Bhattacharji Bureau of Energy Efficiency 1
 Bureau of Energy Efficiency • Established in 2002, under the Energy Conservation Act, 2001. • Improve energy efficiency through various regulatory and promotional instruments – Plan, manage and implement provisions the EC Act • Appliance standards and labeling • Industrial energy benchmarks • Energy Conservation Building Codes • Monitor energy use in high energy-consumption units • Certify and accredit energy auditors and energy managers – Provide a policy framework and direction to national energy conservation activities – Disseminate information and knowledge, and facilitate pilot and demonstration projects – Establish EE delivery systems through Public-Private Partnerships (PPP). 2
Bureau of Energy Efficiency • Established in 2002, under the Energy Conservation Act, 2001. • Improve energy efficiency through various regulatory and promotional instruments – Plan, manage and implement provisions the EC Act • Appliance standards and labeling • Industrial energy benchmarks • Energy Conservation Building Codes • Monitor energy use in high energy-consumption units • Certify and accredit energy auditors and energy managers – Provide a policy framework and direction to national energy conservation activities – Disseminate information and knowledge, and facilitate pilot and demonstration projects – Establish EE delivery systems through Public-Private Partnerships (PPP). 2
 Energy Efficiency – Action Plan Ø Bachat Lamp Yojana to promote energy efficient and high quality CFLs as replacement for incandescent bulbs in households. Ø Standards & Labeling Scheme targets high energy end use equipment and appliances to lay down minimum energy performance standards. Ø Energy Conservation Building Code (ECBC) sets minimum energy performance standards for new commercial buildings. Ø Agricultural and Municipal DSM targeting replacement of inefficient pumpsets, street lighting, etc. Ø Operationalising EC Act by Strengthening Institutional Capacity of State Designated Agencies (SDAs) : The scheme seeks to build institutional capacity of the newly created SDAs to perform their regulatory, enforcement and facilitative functions in the respective States. Ø Energy Efficiency Improvement in Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs): To stimulate energy efficiency measures in 25 high energy consuming small and medium enterprise clusters. 3
Energy Efficiency – Action Plan Ø Bachat Lamp Yojana to promote energy efficient and high quality CFLs as replacement for incandescent bulbs in households. Ø Standards & Labeling Scheme targets high energy end use equipment and appliances to lay down minimum energy performance standards. Ø Energy Conservation Building Code (ECBC) sets minimum energy performance standards for new commercial buildings. Ø Agricultural and Municipal DSM targeting replacement of inefficient pumpsets, street lighting, etc. Ø Operationalising EC Act by Strengthening Institutional Capacity of State Designated Agencies (SDAs) : The scheme seeks to build institutional capacity of the newly created SDAs to perform their regulatory, enforcement and facilitative functions in the respective States. Ø Energy Efficiency Improvement in Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs): To stimulate energy efficiency measures in 25 high energy consuming small and medium enterprise clusters. 3
 Bachat Lamp Yojna (CDM Based Lighting Project for House hold) ü First pilot project registered by UNFCCC in September 2008. (National Roll out to be take place shortly) ü Targeted 400 Millions incandescent Lamps and its replacement to CFLs at the price of incandescent bulbs to avoid 4000 MW Capacity Addition. ü The difference in cost would be recovered through the carbon credits CERs that accrue because of their lower energy use. ü CFLs distribution by Private-sector companies and DISCOMs 4
Bachat Lamp Yojna (CDM Based Lighting Project for House hold) ü First pilot project registered by UNFCCC in September 2008. (National Roll out to be take place shortly) ü Targeted 400 Millions incandescent Lamps and its replacement to CFLs at the price of incandescent bulbs to avoid 4000 MW Capacity Addition. ü The difference in cost would be recovered through the carbon credits CERs that accrue because of their lower energy use. ü CFLs distribution by Private-sector companies and DISCOMs 4
 Mission- S&L Programme • To reduce overall energy consumption by use of Energy Efficient equipments/ appliances 18 BU by 2012 (~3000 MW). • Targeted an avoided capacity addition of over 3000 MW during XI plan of Govt. of India 5
Mission- S&L Programme • To reduce overall energy consumption by use of Energy Efficient equipments/ appliances 18 BU by 2012 (~3000 MW). • Targeted an avoided capacity addition of over 3000 MW during XI plan of Govt. of India 5
 Products covered under Indian S&L Program Current List 1. Frost-free Refrigerators 2. Tubular Fluorescent Lamps (TFL) 3. Air-conditioners 4. Direct cool /Frost Free Refrigerators 5. Distribution Transformers 6. Motors 7. Pump sets 8. Ceiling fans 9. LPG Stoves 10. Colour TVs 11. Storage Water Geysers Launched on 18 th May 2006 , for 4 products by BEE 6
Products covered under Indian S&L Program Current List 1. Frost-free Refrigerators 2. Tubular Fluorescent Lamps (TFL) 3. Air-conditioners 4. Direct cool /Frost Free Refrigerators 5. Distribution Transformers 6. Motors 7. Pump sets 8. Ceiling fans 9. LPG Stoves 10. Colour TVs 11. Storage Water Geysers Launched on 18 th May 2006 , for 4 products by BEE 6
 Future - Equipments / appliances for S&L Programme Home Appliances üWashing Machines üElectronic Ballast üComputer Monitors üKerosene Stoves üConsumer Electronics Industrial Equipments üIndustrial Fans & Blowers üDiesel Generating sets üBoilers üCompressors Other Appliances üUninterrupted Power Supply (UPS) üExternal Power Supplies (EPS) üBattery Chargers (BCs) üStandby Power equipments Refrigerator &AC Systems üAdaptive Defrost üCommercial Freezers üVisi Coolers üChocolate Coolers üChest Coolers üHeat Pumps üMulti Split Systems 7
Future - Equipments / appliances for S&L Programme Home Appliances üWashing Machines üElectronic Ballast üComputer Monitors üKerosene Stoves üConsumer Electronics Industrial Equipments üIndustrial Fans & Blowers üDiesel Generating sets üBoilers üCompressors Other Appliances üUninterrupted Power Supply (UPS) üExternal Power Supplies (EPS) üBattery Chargers (BCs) üStandby Power equipments Refrigerator &AC Systems üAdaptive Defrost üCommercial Freezers üVisi Coolers üChocolate Coolers üChest Coolers üHeat Pumps üMulti Split Systems 7
 Indian Comparative Label Features • Stars (1 -5) display the relative efficiency of the product. • Daily/annual Power consumption is used for comparing the actual energy use between different models. • Important product specifications like brand, model, type, capacity, efficiency (EER), etc. Logo 8
Indian Comparative Label Features • Stars (1 -5) display the relative efficiency of the product. • Daily/annual Power consumption is used for comparing the actual energy use between different models. • Important product specifications like brand, model, type, capacity, efficiency (EER), etc. Logo 8
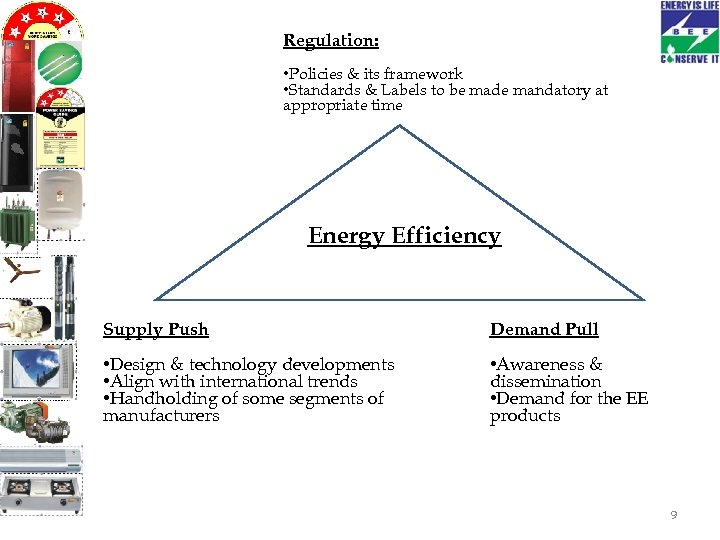 Regulation: • Policies & its framework • Standards & Labels to be made mandatory at appropriate time Energy Efficiency Supply Push Demand Pull • Design & technology developments • Align with international trends • Handholding of some segments of manufacturers • Awareness & dissemination • Demand for the EE products 9
Regulation: • Policies & its framework • Standards & Labels to be made mandatory at appropriate time Energy Efficiency Supply Push Demand Pull • Design & technology developments • Align with international trends • Handholding of some segments of manufacturers • Awareness & dissemination • Demand for the EE products 9
 Institutional frame work for regulation • BIS – National Standards Body Ø Formulation & Implementation of National Standards Ø Production certification, Quality system certification, EMS certification etc. • Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE) Ø BEE is established to implement & monitor the Energy Conservation Act, 2001 Ø One of the key thrust areas of EC Act, 2001 is Standards & Labeling Programme Ø Formulation of Energy Efficiency Standards. • Laboratories accredited by National Accreditation Board of Laboratories • Educational Institutions. • Manufacturers and Manufacturing Associations • Consumer Organizations • Ministries and key stakeholders. 10
Institutional frame work for regulation • BIS – National Standards Body Ø Formulation & Implementation of National Standards Ø Production certification, Quality system certification, EMS certification etc. • Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE) Ø BEE is established to implement & monitor the Energy Conservation Act, 2001 Ø One of the key thrust areas of EC Act, 2001 is Standards & Labeling Programme Ø Formulation of Energy Efficiency Standards. • Laboratories accredited by National Accreditation Board of Laboratories • Educational Institutions. • Manufacturers and Manufacturing Associations • Consumer Organizations • Ministries and key stakeholders. 10
 Energy Savings through Standards and Labeling Programme Standards and Labeling (07 -08) Standards and Labeling(08 -09) Electricity Saved (MUs) Equivalent million MTOE Avoided Thermal Capacity (MW) Total Fuel Saved (mtoe) 1425. 8 0. 48 260. 48 2111 0. 717 568 0. 917 The avoided capacity addition achieved during 2008 -09 was 237% higher than the previous year and exceeded the target of 1200 MW set by Ministry of Power. It has also resulted in CO 2 emission reduction of 5. 2 million tones as against 2. 95 million tonnes in 2007 -08. 11
Energy Savings through Standards and Labeling Programme Standards and Labeling (07 -08) Standards and Labeling(08 -09) Electricity Saved (MUs) Equivalent million MTOE Avoided Thermal Capacity (MW) Total Fuel Saved (mtoe) 1425. 8 0. 48 260. 48 2111 0. 717 568 0. 917 The avoided capacity addition achieved during 2008 -09 was 237% higher than the previous year and exceeded the target of 1200 MW set by Ministry of Power. It has also resulted in CO 2 emission reduction of 5. 2 million tones as against 2. 95 million tonnes in 2007 -08. 11
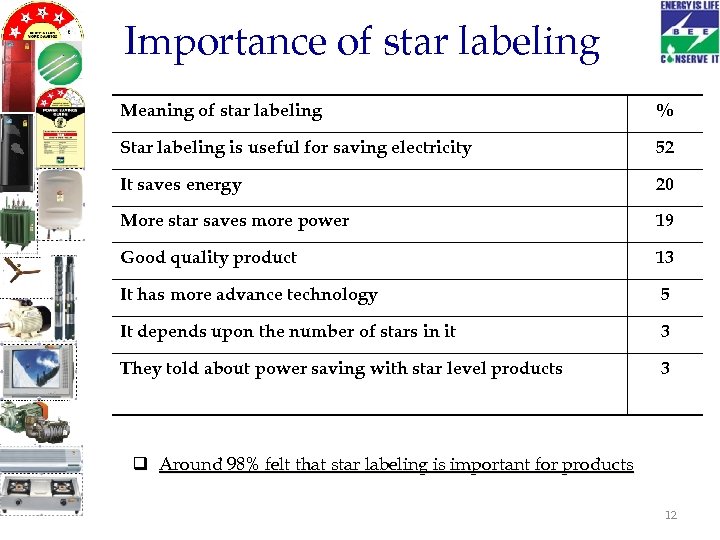 Importance of star labeling Meaning of star labeling % Star labeling is useful for saving electricity 52 It saves energy 20 More star saves more power 19 Good quality product 13 It has more advance technology 5 It depends upon the number of stars in it 3 They told about power saving with star level products 3 q Around 98% felt that star labeling is important for products 12
Importance of star labeling Meaning of star labeling % Star labeling is useful for saving electricity 52 It saves energy 20 More star saves more power 19 Good quality product 13 It has more advance technology 5 It depends upon the number of stars in it 3 They told about power saving with star level products 3 q Around 98% felt that star labeling is important for products 12
 Role of Consumer • Look for star label, even for non – mandatory products • Use of CFL (home and commercial) • Role of RWA’s in raising awareness • Life cost over original cost 13
Role of Consumer • Look for star label, even for non – mandatory products • Use of CFL (home and commercial) • Role of RWA’s in raising awareness • Life cost over original cost 13
 Contact information: Anuradha Bhattacharji (abhattacharji@beenet. in) Bureau of Energy Efficiency (Ministry of Power, Govt. of India) 4 th Floor, Sewa Bhawan R. K. Puram New Delhi – 110066 www. bee-india. nic. in 14
Contact information: Anuradha Bhattacharji (abhattacharji@beenet. in) Bureau of Energy Efficiency (Ministry of Power, Govt. of India) 4 th Floor, Sewa Bhawan R. K. Puram New Delhi – 110066 www. bee-india. nic. in 14


