b55fe0f88d41f3da3420814bdd3547a0.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26
 Energy Chapter 4
Energy Chapter 4
 Energy l Any and every change that occurs, involves energy
Energy l Any and every change that occurs, involves energy
 Kinetic Energy l The energy a moving object has because of its motion l Kinetic energy of a moving object depends on: objects mass and its speed
Kinetic Energy l The energy a moving object has because of its motion l Kinetic energy of a moving object depends on: objects mass and its speed
 Kinetic Energy Equation l Kinetic energy (in joules) = ½ mass (kg) x [speed/velocity (in m/s)]² l KE = ½ mv²
Kinetic Energy Equation l Kinetic energy (in joules) = ½ mass (kg) x [speed/velocity (in m/s)]² l KE = ½ mv²
 Try It l. A jogger with a mass of 50 kg is moving at a speed of 3. 0 m/s. What is the joggers kinetic energy?
Try It l. A jogger with a mass of 50 kg is moving at a speed of 3. 0 m/s. What is the joggers kinetic energy?
 Potential Energy l Stored energy due to position l Ex: Rock on top of hill Vase on edge of shelf Ball ready to be dropped
Potential Energy l Stored energy due to position l Ex: Rock on top of hill Vase on edge of shelf Ball ready to be dropped
 Elastic Potential Energy stored by something that can stretch or compress l Ex: Rubber band Spring Bouncy ball Basket ball
Elastic Potential Energy stored by something that can stretch or compress l Ex: Rubber band Spring Bouncy ball Basket ball
 Chemical Potential Energy stored in chemical bonds between atoms l Ex: Carbon dioxide Water
Chemical Potential Energy stored in chemical bonds between atoms l Ex: Carbon dioxide Water
 Gravitational Potential Energy stored by objects due to their position above the Earth’s surface l GPE depends on objects mass and height above the ground
Gravitational Potential Energy stored by objects due to their position above the Earth’s surface l GPE depends on objects mass and height above the ground
 GPE Equation l Gravitational potential energy (J) = mass(kg) x accel. due to gravity(m/s²) x height (m) • GPE = mgh
GPE Equation l Gravitational potential energy (J) = mass(kg) x accel. due to gravity(m/s²) x height (m) • GPE = mgh
 Try It l What is the gravitational potential energy of a ceiling fan that has a mass of 8. 0 kg and is 4. 0 meters above the ground
Try It l What is the gravitational potential energy of a ceiling fan that has a mass of 8. 0 kg and is 4. 0 meters above the ground
 Conservation of Energy l “Energy is not created or destroyed. ” l Energy is only transformed or transferred l PE can change to KE and back l Ex: Roller Coaster
Conservation of Energy l “Energy is not created or destroyed. ” l Energy is only transformed or transferred l PE can change to KE and back l Ex: Roller Coaster
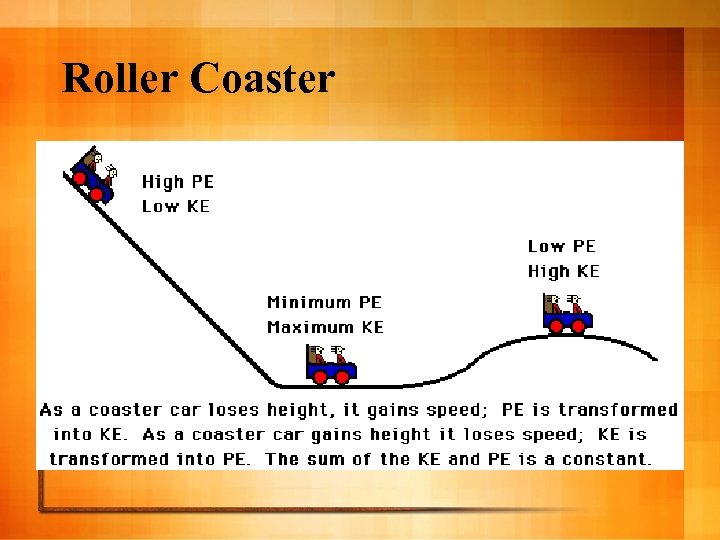 Roller Coaster
Roller Coaster
 Mechanical Energy l The total amount of potential and kinetic energy in a system l Ex: mech. Energy = pot. Energy + kin. energy
Mechanical Energy l The total amount of potential and kinetic energy in a system l Ex: mech. Energy = pot. Energy + kin. energy
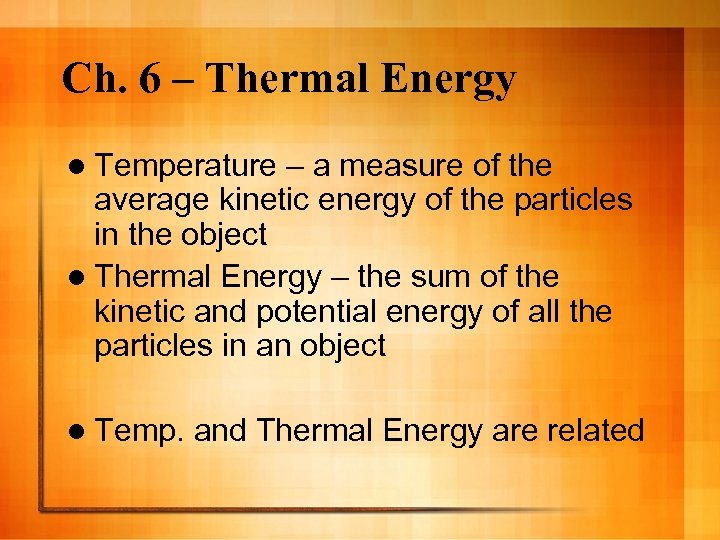 Ch. 6 – Thermal Energy l Temperature – a measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles in the object l Thermal Energy – the sum of the kinetic and potential energy of all the particles in an object l Temp. and Thermal Energy are related
Ch. 6 – Thermal Energy l Temperature – a measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles in the object l Thermal Energy – the sum of the kinetic and potential energy of all the particles in an object l Temp. and Thermal Energy are related
 Heat l Transfer of energy from object at higher temperature to an object of lower temperature l Hotter object to colder object l Ex: Hand to ice, fire to hand
Heat l Transfer of energy from object at higher temperature to an object of lower temperature l Hotter object to colder object l Ex: Hand to ice, fire to hand
 Specific Heat l The amount of heat that is needed to raise the temperature of 1 kg of a material by 1◦C l Measured in [J/(kg◦C)] l Temperature change depends on the nature of the substance and amt of heat added
Specific Heat l The amount of heat that is needed to raise the temperature of 1 kg of a material by 1◦C l Measured in [J/(kg◦C)] l Temperature change depends on the nature of the substance and amt of heat added
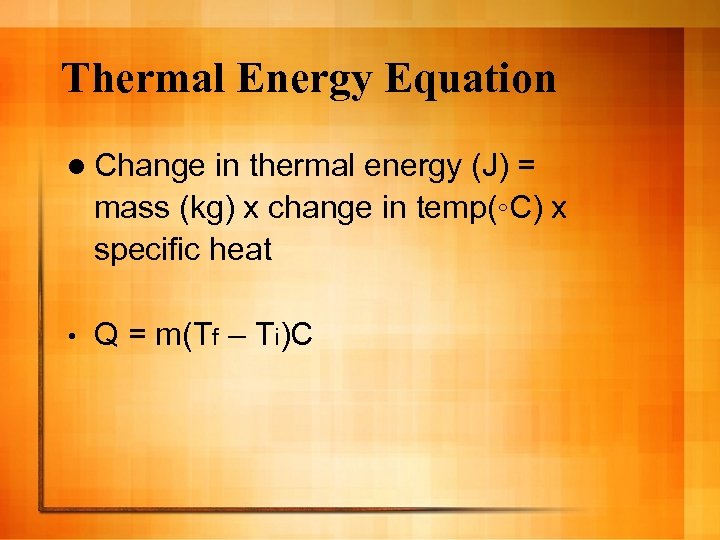 Thermal Energy Equation l Change in thermal energy (J) = mass (kg) x change in temp(◦C) x specific heat • Q = m(Tf – Ti)C
Thermal Energy Equation l Change in thermal energy (J) = mass (kg) x change in temp(◦C) x specific heat • Q = m(Tf – Ti)C
 Try It l. A wooden block has a mass of 20. 0 kg and specific heat of 1, 700 J/(kg◦C). Find the change in thermal energy of the block as it warms from 20◦C to 30◦C.
Try It l. A wooden block has a mass of 20. 0 kg and specific heat of 1, 700 J/(kg◦C). Find the change in thermal energy of the block as it warms from 20◦C to 30◦C.
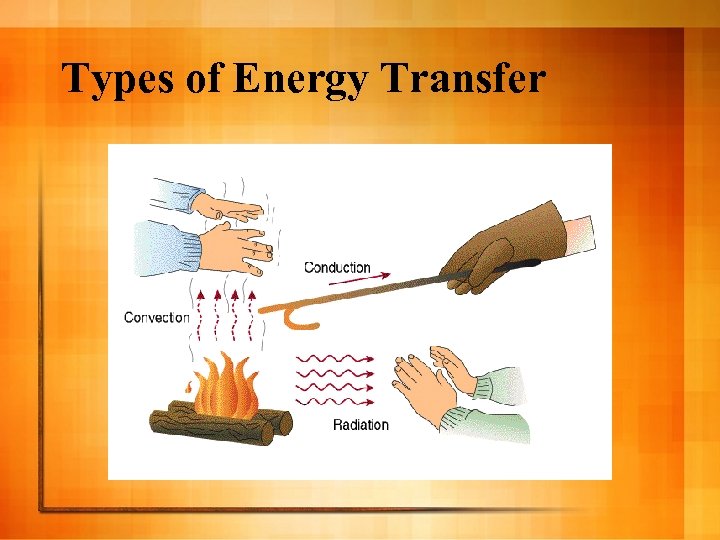
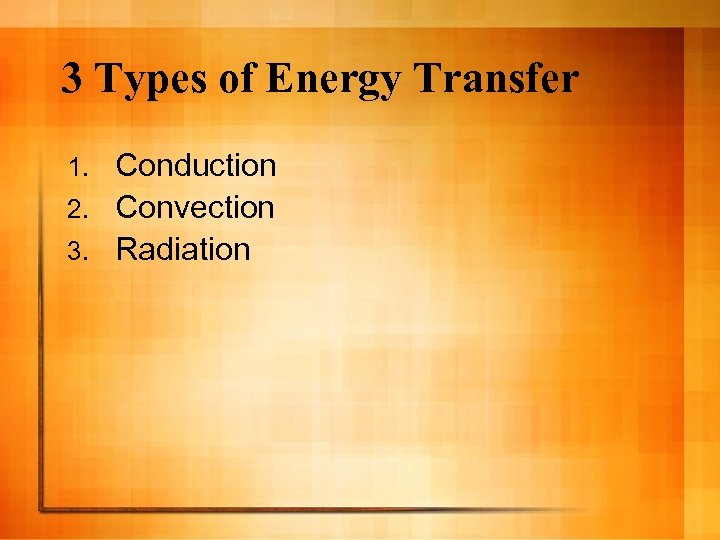 3 Types of Energy Transfer Conduction 2. Convection 3. Radiation 1.
3 Types of Energy Transfer Conduction 2. Convection 3. Radiation 1.
 Conduction Heat transfer between 2 touching objects l Exs: Touching hot metal, pot on stove l
Conduction Heat transfer between 2 touching objects l Exs: Touching hot metal, pot on stove l
 Convection Heating a fluid (liquid or gas) l Exs: boiling water, hot air balloon l Hot gas/liquid rises l
Convection Heating a fluid (liquid or gas) l Exs: boiling water, hot air balloon l Hot gas/liquid rises l
 Radiation Heat thru electromagnetic waves (microwave, sun, uv, etc. ) l Doesn’t need solid, liquid, or gas to work l
Radiation Heat thru electromagnetic waves (microwave, sun, uv, etc. ) l Doesn’t need solid, liquid, or gas to work l
 Types of Energy Transfer
Types of Energy Transfer
 Conductors & Insulators l Conductor – transfer heat well l Exs: metal l Insulators – hinders heat transfer l Exs: rubber, plastic, clothing
Conductors & Insulators l Conductor – transfer heat well l Exs: metal l Insulators – hinders heat transfer l Exs: rubber, plastic, clothing
 Conductor & Insulator l House Insulation insulator l Copper Wire Conductor
Conductor & Insulator l House Insulation insulator l Copper Wire Conductor


