863e2adab3f8da9fe279127804080744.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 15
 Energy and power part II
Energy and power part II
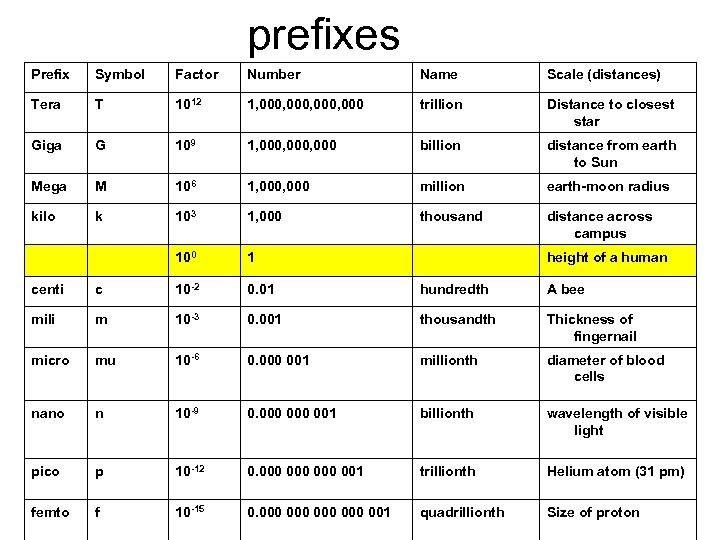 prefixes Prefix Symbol Factor Number Name Scale (distances) Tera T 1012 1, 000, 000 trillion Distance to closest star Giga G 109 1, 000, 000 billion distance from earth to Sun Mega M 106 1, 000 million earth-moon radius kilo k 103 1, 000 thousand distance across campus 100 1 height of a human centi c 10 -2 0. 01 hundredth A bee mili m 10 -3 0. 001 thousandth Thickness of fingernail micro mu 10 -6 0. 000 001 millionth diameter of blood cells nano n 10 -9 0. 000 001 billionth wavelength of visible light pico p 10 -12 0. 000 000 001 trillionth Helium atom (31 pm) femto f 10 -15 0. 000 000 001 quadrillionth Size of proton
prefixes Prefix Symbol Factor Number Name Scale (distances) Tera T 1012 1, 000, 000 trillion Distance to closest star Giga G 109 1, 000, 000 billion distance from earth to Sun Mega M 106 1, 000 million earth-moon radius kilo k 103 1, 000 thousand distance across campus 100 1 height of a human centi c 10 -2 0. 01 hundredth A bee mili m 10 -3 0. 001 thousandth Thickness of fingernail micro mu 10 -6 0. 000 001 millionth diameter of blood cells nano n 10 -9 0. 000 001 billionth wavelength of visible light pico p 10 -12 0. 000 000 001 trillionth Helium atom (31 pm) femto f 10 -15 0. 000 000 001 quadrillionth Size of proton
 A MWh is a unit of: A) Charge B) Energy C) Current D) Power E) Cost
A MWh is a unit of: A) Charge B) Energy C) Current D) Power E) Cost
 Cost of energy I burn 2000 light bulbs for 10 hours. How much does this cost? ($0. 10/k. Wh) A) $0. 20 B) $2. 00 C) $20. 00 D) $200. 00 E) $2000. 00
Cost of energy I burn 2000 light bulbs for 10 hours. How much does this cost? ($0. 10/k. Wh) A) $0. 20 B) $2. 00 C) $20. 00 D) $200. 00 E) $2000. 00
 Cost of energy I burn 2000 light bulbs for 10 hours. How much does this cost? ($0. 10/k. Wh) A) $0. 20 Flourescent lights = about 4 x more efficient! B) $2. 00 That’s why CU uses flourescent lights instead of incandescent bulbs! C) $20. 00 D) $200. 00 E) $2000. 00
Cost of energy I burn 2000 light bulbs for 10 hours. How much does this cost? ($0. 10/k. Wh) A) $0. 20 Flourescent lights = about 4 x more efficient! B) $2. 00 That’s why CU uses flourescent lights instead of incandescent bulbs! C) $20. 00 D) $200. 00 E) $2000. 00
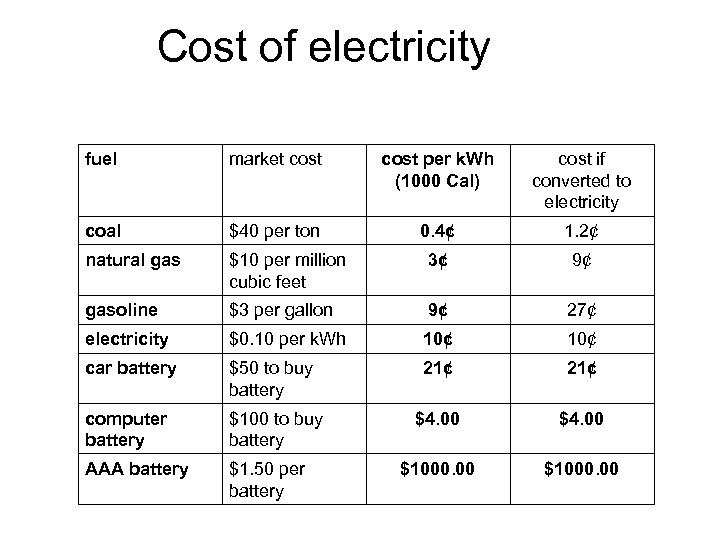 Cost of electricity fuel market cost per k. Wh (1000 Cal) cost if converted to electricity coal $40 per ton 0. 4¢ 1. 2¢ natural gas $10 per million cubic feet 3¢ 9¢ gasoline $3 per gallon 9¢ 27¢ electricity $0. 10 per k. Wh 10¢ car battery $50 to buy battery 21¢ computer battery $100 to buy battery $4. 00 AAA battery $1. 50 per battery $1000. 00
Cost of electricity fuel market cost per k. Wh (1000 Cal) cost if converted to electricity coal $40 per ton 0. 4¢ 1. 2¢ natural gas $10 per million cubic feet 3¢ 9¢ gasoline $3 per gallon 9¢ 27¢ electricity $0. 10 per k. Wh 10¢ car battery $50 to buy battery 21¢ computer battery $100 to buy battery $4. 00 AAA battery $1. 50 per battery $1000. 00
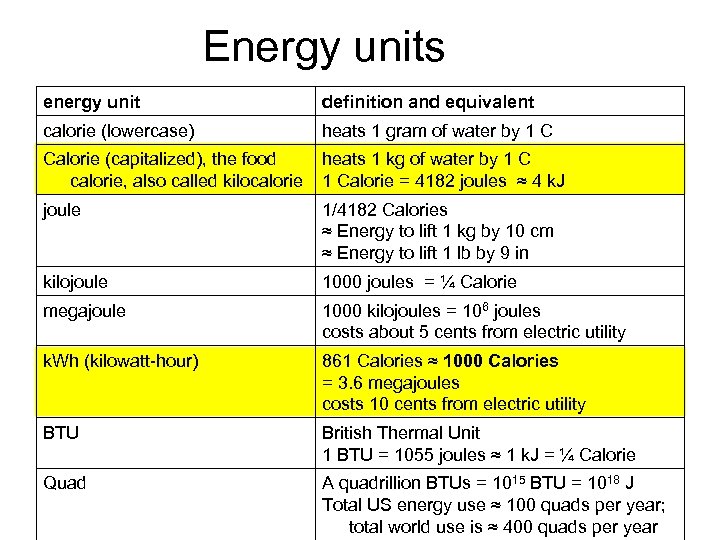 Energy units energy unit definition and equivalent calorie (lowercase) heats 1 gram of water by 1 C Calorie (capitalized), the food calorie, also called kilocalorie heats 1 kg of water by 1 Calorie = 4182 joules ≈ 4 k. J joule 1/4182 Calories ≈ Energy to lift 1 kg by 10 cm ≈ Energy to lift 1 lb by 9 in kilojoule 1000 joules = ¼ Calorie megajoule 1000 kilojoules = 106 joules costs about 5 cents from electric utility k. Wh (kilowatt-hour) 861 Calories ≈ 1000 Calories = 3. 6 megajoules costs 10 cents from electric utility BTU British Thermal Unit 1 BTU = 1055 joules ≈ 1 k. J = ¼ Calorie Quad A quadrillion BTUs = 1015 BTU = 1018 J Total US energy use ≈ 100 quads per year; total world use is ≈ 400 quads per year
Energy units energy unit definition and equivalent calorie (lowercase) heats 1 gram of water by 1 C Calorie (capitalized), the food calorie, also called kilocalorie heats 1 kg of water by 1 Calorie = 4182 joules ≈ 4 k. J joule 1/4182 Calories ≈ Energy to lift 1 kg by 10 cm ≈ Energy to lift 1 lb by 9 in kilojoule 1000 joules = ¼ Calorie megajoule 1000 kilojoules = 106 joules costs about 5 cents from electric utility k. Wh (kilowatt-hour) 861 Calories ≈ 1000 Calories = 3. 6 megajoules costs 10 cents from electric utility BTU British Thermal Unit 1 BTU = 1055 joules ≈ 1 k. J = ¼ Calorie Quad A quadrillion BTUs = 1015 BTU = 1018 J Total US energy use ≈ 100 quads per year; total world use is ≈ 400 quads per year
 Power Is a Mega. Watt a lot? A) A horse can output about a MW B) A Ferrari could output a MW at peak acceleration C) That’s about the entire power output of the sun D) A nuclear power plant produces about a MW
Power Is a Mega. Watt a lot? A) A horse can output about a MW B) A Ferrari could output a MW at peak acceleration C) That’s about the entire power output of the sun D) A nuclear power plant produces about a MW
 Power Is a Mega. Watt a lot? A) A horse can output about a MW – 1 k. W is about a hp (+34%) B) A Ferrari could output a MW at peak acceleration – 750 k. W max… C) That’s about the entire power output of the sun – 173, 000 TW hits the earth D) A nuclear power plant produces about a MW – about a GW
Power Is a Mega. Watt a lot? A) A horse can output about a MW – 1 k. W is about a hp (+34%) B) A Ferrari could output a MW at peak acceleration – 750 k. W max… C) That’s about the entire power output of the sun – 173, 000 TW hits the earth D) A nuclear power plant produces about a MW – about a GW
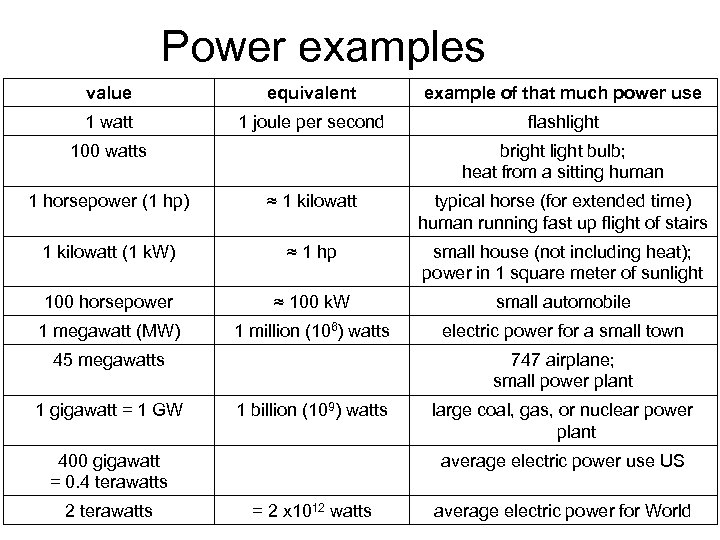 Power examples value equivalent example of that much power use 1 watt 1 joule per second flashlight 100 watts bright light bulb; heat from a sitting human 1 horsepower (1 hp) ≈ 1 kilowatt typical horse (for extended time) human running fast up flight of stairs 1 kilowatt (1 k. W) ≈ 1 hp small house (not including heat); power in 1 square meter of sunlight 100 horsepower ≈ 100 k. W small automobile 1 megawatt (MW) 1 million (106) watts electric power for a small town 45 megawatts 747 airplane; small power plant 1 gigawatt = 1 GW 1 billion (109) watts large coal, gas, or nuclear power plant 400 gigawatt = 0. 4 terawatts average electric power use US 2 terawatts = 2 x 1012 watts average electric power for World
Power examples value equivalent example of that much power use 1 watt 1 joule per second flashlight 100 watts bright light bulb; heat from a sitting human 1 horsepower (1 hp) ≈ 1 kilowatt typical horse (for extended time) human running fast up flight of stairs 1 kilowatt (1 k. W) ≈ 1 hp small house (not including heat); power in 1 square meter of sunlight 100 horsepower ≈ 100 k. W small automobile 1 megawatt (MW) 1 million (106) watts electric power for a small town 45 megawatts 747 airplane; small power plant 1 gigawatt = 1 GW 1 billion (109) watts large coal, gas, or nuclear power plant 400 gigawatt = 0. 4 terawatts average electric power use US 2 terawatts = 2 x 1012 watts average electric power for World
 Solar power 1 square meter 1 kilowatt of sunlight 150 – 400 watts electric using solar cells 1 square kilometer 1 Gigawatt of sunlight 150 – 400 Megawatts electric
Solar power 1 square meter 1 kilowatt of sunlight 150 – 400 watts electric using solar cells 1 square kilometer 1 Gigawatt of sunlight 150 – 400 Megawatts electric
 Fossils Levels (amount in ground): Coal: 4. 4 Tboe Oil: 1. 2 Tboe Natural gas: 1. 2 Tboe Flows (daily production): Coal: 52 Mboe/day Oil: 84 Mboe/day Natural gas: 19 Mboe/day Years of production left (using current #s most optimistic): Coal: 231 417 years Oil: 39 43 years Natural gas: 173 167 years In 2008, the U. S. energy use was: 84% fossils 9% Nuclear 7% Renewables
Fossils Levels (amount in ground): Coal: 4. 4 Tboe Oil: 1. 2 Tboe Natural gas: 1. 2 Tboe Flows (daily production): Coal: 52 Mboe/day Oil: 84 Mboe/day Natural gas: 19 Mboe/day Years of production left (using current #s most optimistic): Coal: 231 417 years Oil: 39 43 years Natural gas: 173 167 years In 2008, the U. S. energy use was: 84% fossils 9% Nuclear 7% Renewables
 Extra clickers… Didn’t get to these 31 Aug 2010
Extra clickers… Didn’t get to these 31 Aug 2010
 In Chapter 1, “smart rock” refers to: A) a kind of low-calorie food B) the asteroid that killed the dinosaurs C) a method for shooting down missiles D) uranium ore
In Chapter 1, “smart rock” refers to: A) a kind of low-calorie food B) the asteroid that killed the dinosaurs C) a method for shooting down missiles D) uranium ore
 A disadvantage of hydrogen fuel is that: a) it contains less energy per pound than gasoline. b) it cannot be made into a liquid, even at low temperature. c) it is highly poisonous and corrosive. d) it can’t be mined, but must be “manufactured. ”
A disadvantage of hydrogen fuel is that: a) it contains less energy per pound than gasoline. b) it cannot be made into a liquid, even at low temperature. c) it is highly poisonous and corrosive. d) it can’t be mined, but must be “manufactured. ”


