148e813f5b08f1d13502e3ec624fd2f5.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20
 Energiesystemen, Exergie analyse, Cascades en Ruimtelijke integratie. Prof. dr. H. C. Moll, Centrum voor Energie en Milieukunde, IVEM, Rijksuniversiteit Groningen Presentatie 8 oktober 2011 Open Universiteit, Natuurwetenschappen Utrecht VEM Energie, Exergie, Cascades in de Ruimte H. C. Moll, OU-NW, Utrecht, 8 oktober 2011
Energiesystemen, Exergie analyse, Cascades en Ruimtelijke integratie. Prof. dr. H. C. Moll, Centrum voor Energie en Milieukunde, IVEM, Rijksuniversiteit Groningen Presentatie 8 oktober 2011 Open Universiteit, Natuurwetenschappen Utrecht VEM Energie, Exergie, Cascades in de Ruimte H. C. Moll, OU-NW, Utrecht, 8 oktober 2011
 Energiesystemen, Exergie analyse, Cascades en Ruimtelijke integratie. Inhoud van de presentatie 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Energie en energiesystemen. Efficiëntie en exergie. Energiecascades om exergie te besparen Energie, exergiecascades en ruimtegebruik. Toepassingen en voorbeelden VEM Energie, Exergie, Cascades in de Ruimte H. C. Moll, OU-NW, Utrecht, 8 oktober 2011
Energiesystemen, Exergie analyse, Cascades en Ruimtelijke integratie. Inhoud van de presentatie 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Energie en energiesystemen. Efficiëntie en exergie. Energiecascades om exergie te besparen Energie, exergiecascades en ruimtegebruik. Toepassingen en voorbeelden VEM Energie, Exergie, Cascades in de Ruimte H. C. Moll, OU-NW, Utrecht, 8 oktober 2011
 The influence of energy use on the three spheres Economy Exploitation of energy sources generates economic benefits Energy is an essential resource for production and service delivery by all economic sectors Social Energy is directly and indirectly a source of health and wealth Ecological Extraction of energy may have several ecological effects Emissions due to energy use cause severe environmental problems VEM Energie, Exergie, Cascades in de Ruimte H. C. Moll, OU-NW, Utrecht, 8 oktober 2011
The influence of energy use on the three spheres Economy Exploitation of energy sources generates economic benefits Energy is an essential resource for production and service delivery by all economic sectors Social Energy is directly and indirectly a source of health and wealth Ecological Extraction of energy may have several ecological effects Emissions due to energy use cause severe environmental problems VEM Energie, Exergie, Cascades in de Ruimte H. C. Moll, OU-NW, Utrecht, 8 oktober 2011
 Some important energy issues. The most important environmental effect of present-day energy use is the emission of gases contributing to the increased radiative forcing of the atmosphere (the greenhouse effect) that causes global warming. (a) Carbondioxide and methane are the relevant emissions. (b) To almost stabilise the atmospheric concentrations the global use of energy from fossil carbon sources and the related emissions should be halved. (c) Therefore it is necessary that the energy requirements of lifestyles are diminished, carbon-neutral energy sources are developed, and carbon dioxide is removed from tail gas. VEM Energie, Exergie, Cascades in de Ruimte H. C. Moll, OU-NW, Utrecht, 8 oktober 2011
Some important energy issues. The most important environmental effect of present-day energy use is the emission of gases contributing to the increased radiative forcing of the atmosphere (the greenhouse effect) that causes global warming. (a) Carbondioxide and methane are the relevant emissions. (b) To almost stabilise the atmospheric concentrations the global use of energy from fossil carbon sources and the related emissions should be halved. (c) Therefore it is necessary that the energy requirements of lifestyles are diminished, carbon-neutral energy sources are developed, and carbon dioxide is removed from tail gas. VEM Energie, Exergie, Cascades in de Ruimte H. C. Moll, OU-NW, Utrecht, 8 oktober 2011
 Additional energy issues Global distribution of energy use World-wide average annual use of energy 65 GJ/capita Average annual use of energy in EU 150 GJ/capita Present-day trends of EU energy use Energy use is increasing for electricity and transport, and is at a stable level for heating and the total of production Slow development of renewable energy sources Waste combustion (including organic waste and biomass) is important. Wind energy is stimulated in the North. Solar energy (PV and solar collectors) is developing in the South. VEM Energie, Exergie, Cascades in de Ruimte H. C. Moll, OU-NW, Utrecht, 8 oktober 2011
Additional energy issues Global distribution of energy use World-wide average annual use of energy 65 GJ/capita Average annual use of energy in EU 150 GJ/capita Present-day trends of EU energy use Energy use is increasing for electricity and transport, and is at a stable level for heating and the total of production Slow development of renewable energy sources Waste combustion (including organic waste and biomass) is important. Wind energy is stimulated in the North. Solar energy (PV and solar collectors) is developing in the South. VEM Energie, Exergie, Cascades in de Ruimte H. C. Moll, OU-NW, Utrecht, 8 oktober 2011
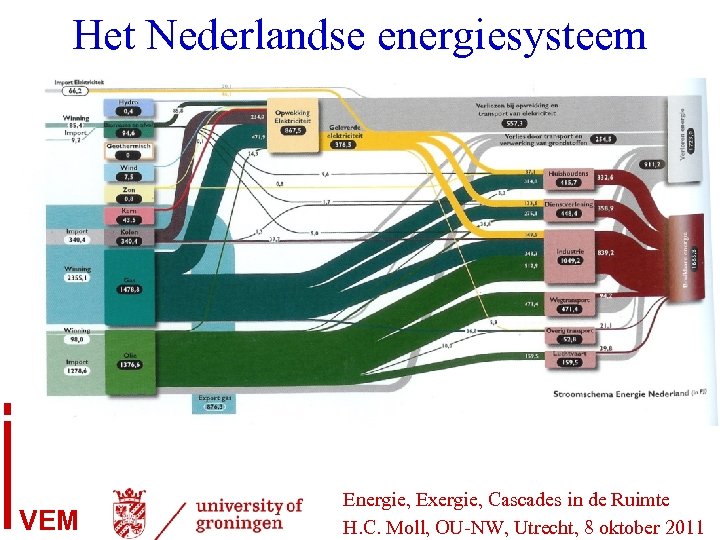 Het Nederlandse energiesysteem VEM Energie, Exergie, Cascades in de Ruimte H. C. Moll, OU-NW, Utrecht, 8 oktober 2011
Het Nederlandse energiesysteem VEM Energie, Exergie, Cascades in de Ruimte H. C. Moll, OU-NW, Utrecht, 8 oktober 2011
 A typology of approaches to reduce nonsustainable energy use: The Trias Energetica. Consider FIRST the fundamental needs to be satisfied PREVENTION Use renewable sources maximally Use non renewable sources highly efficiently VEM Energie, Exergie, Cascades in de Ruimte H. C. Moll, OU-NW, Utrecht, 8 oktober 2011
A typology of approaches to reduce nonsustainable energy use: The Trias Energetica. Consider FIRST the fundamental needs to be satisfied PREVENTION Use renewable sources maximally Use non renewable sources highly efficiently VEM Energie, Exergie, Cascades in de Ruimte H. C. Moll, OU-NW, Utrecht, 8 oktober 2011
 Energy system analysis Energy system: A social/economic system consisting out of installations, institutions, arrangements and practices that is able to meet the demand for an energy service. Examples • The transport system • The electricity system • The heating system VEM Energie, Exergie, Cascades in de Ruimte H. C. Moll, OU-NW, Utrecht, 8 oktober 2011
Energy system analysis Energy system: A social/economic system consisting out of installations, institutions, arrangements and practices that is able to meet the demand for an energy service. Examples • The transport system • The electricity system • The heating system VEM Energie, Exergie, Cascades in de Ruimte H. C. Moll, OU-NW, Utrecht, 8 oktober 2011
 Some common features of energy systems. • Diversity of ways to produce the supply and of installations associated with the production and distribution. • Diversity of the demand of the final consumers of the energy service. • Strategies to guarantee the sufficiency of the supply: the expected total demand should be met by the energy system. • Strategies to guarantee the reliability of the supply: notwithstanding variation in the demand, the demand should be met at any time and at any place as much as possible. VEM Energie, Exergie, Cascades in de Ruimte H. C. Moll, OU-NW, Utrecht, 8 oktober 2011
Some common features of energy systems. • Diversity of ways to produce the supply and of installations associated with the production and distribution. • Diversity of the demand of the final consumers of the energy service. • Strategies to guarantee the sufficiency of the supply: the expected total demand should be met by the energy system. • Strategies to guarantee the reliability of the supply: notwithstanding variation in the demand, the demand should be met at any time and at any place as much as possible. VEM Energie, Exergie, Cascades in de Ruimte H. C. Moll, OU-NW, Utrecht, 8 oktober 2011
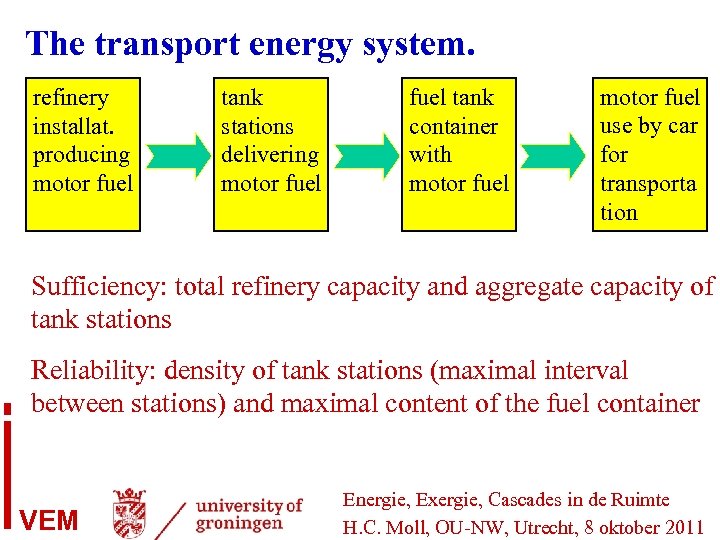 The transport energy system. refinery installat. producing motor fuel tank stations delivering motor fuel tank container with motor fuel use by car for transporta tion Sufficiency: total refinery capacity and aggregate capacity of tank stations Reliability: density of tank stations (maximal interval between stations) and maximal content of the fuel container VEM Energie, Exergie, Cascades in de Ruimte H. C. Moll, OU-NW, Utrecht, 8 oktober 2011
The transport energy system. refinery installat. producing motor fuel tank stations delivering motor fuel tank container with motor fuel use by car for transporta tion Sufficiency: total refinery capacity and aggregate capacity of tank stations Reliability: density of tank stations (maximal interval between stations) and maximal content of the fuel container VEM Energie, Exergie, Cascades in de Ruimte H. C. Moll, OU-NW, Utrecht, 8 oktober 2011
 Changing the transport energy system. • Changing the transport fuel may require changes at all steps in the system (production, tank stations, storage in cars and use in cars). Past successful example lead-free gasoline. Failures until now: electrical cars and CNG cars. • Changing the system in one step is feasible - reformulated gasoline, energy-efficient cars - but depends on the investment and replacement rate in that step. • Complex changes may facilitated by a hybrid strategy: double storage (gasoline and LPG), a dual drive system (electric and engine-driven), or a conversion system may guarantee the sufficiency and the reliability of the system. VEM Energie, Exergie, Cascades in de Ruimte H. C. Moll, OU-NW, Utrecht, 8 oktober 2011
Changing the transport energy system. • Changing the transport fuel may require changes at all steps in the system (production, tank stations, storage in cars and use in cars). Past successful example lead-free gasoline. Failures until now: electrical cars and CNG cars. • Changing the system in one step is feasible - reformulated gasoline, energy-efficient cars - but depends on the investment and replacement rate in that step. • Complex changes may facilitated by a hybrid strategy: double storage (gasoline and LPG), a dual drive system (electric and engine-driven), or a conversion system may guarantee the sufficiency and the reliability of the system. VEM Energie, Exergie, Cascades in de Ruimte H. C. Moll, OU-NW, Utrecht, 8 oktober 2011
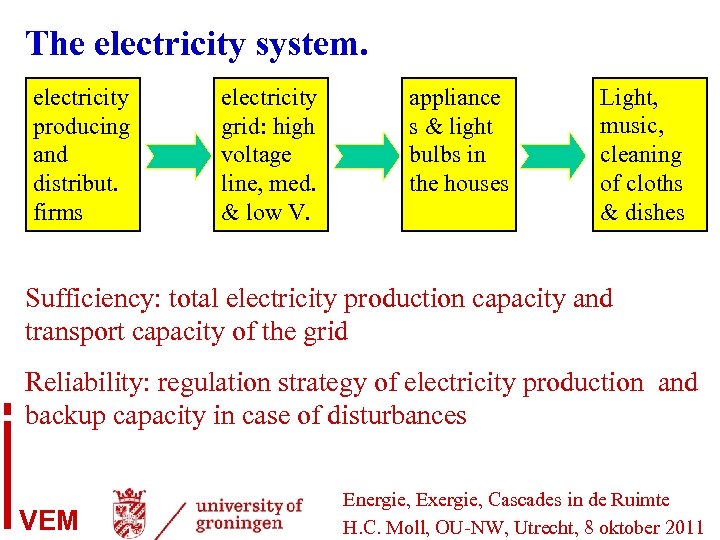 The electricity system. electricity producing and distribut. firms electricity grid: high voltage line, med. & low V. appliance s & light bulbs in the houses Light, music, cleaning of cloths & dishes Sufficiency: total electricity production capacity and transport capacity of the grid Reliability: regulation strategy of electricity production and backup capacity in case of disturbances VEM Energie, Exergie, Cascades in de Ruimte H. C. Moll, OU-NW, Utrecht, 8 oktober 2011
The electricity system. electricity producing and distribut. firms electricity grid: high voltage line, med. & low V. appliance s & light bulbs in the houses Light, music, cleaning of cloths & dishes Sufficiency: total electricity production capacity and transport capacity of the grid Reliability: regulation strategy of electricity production and backup capacity in case of disturbances VEM Energie, Exergie, Cascades in de Ruimte H. C. Moll, OU-NW, Utrecht, 8 oktober 2011
 Specific features of the electricity system and possibilities for change. • Diversity of electricity production methods: Regular sources coal, oil, natural gas, nuclear; other sources waste, wind, solar PV; Technologies gas turbine, steam turbine, combustion engines, combined heat and power systems. • Technologies differ with regard to efficiency, to flexibility, and to the ability to regulate the output, and to predictability. The technology mix determines the overall reliability of the system. VEM Energie, Exergie, Cascades in de Ruimte H. C. Moll, OU-NW, Utrecht, 8 oktober 2011
Specific features of the electricity system and possibilities for change. • Diversity of electricity production methods: Regular sources coal, oil, natural gas, nuclear; other sources waste, wind, solar PV; Technologies gas turbine, steam turbine, combustion engines, combined heat and power systems. • Technologies differ with regard to efficiency, to flexibility, and to the ability to regulate the output, and to predictability. The technology mix determines the overall reliability of the system. VEM Energie, Exergie, Cascades in de Ruimte H. C. Moll, OU-NW, Utrecht, 8 oktober 2011
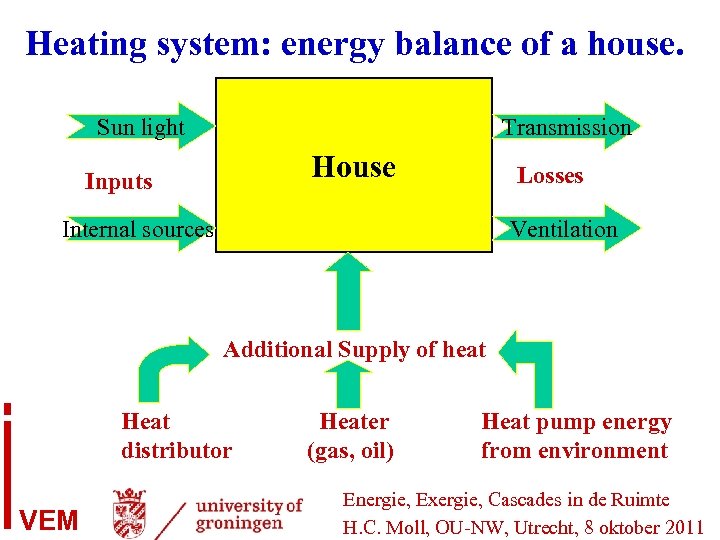 Heating system: energy balance of a house. Sun light Transmission House Inputs Losses Internal sources Ventilation Additional Supply of heat Heat distributor VEM Heater (gas, oil) Heat pump energy from environment Energie, Exergie, Cascades in de Ruimte H. C. Moll, OU-NW, Utrecht, 8 oktober 2011
Heating system: energy balance of a house. Sun light Transmission House Inputs Losses Internal sources Ventilation Additional Supply of heat Heat distributor VEM Heater (gas, oil) Heat pump energy from environment Energie, Exergie, Cascades in de Ruimte H. C. Moll, OU-NW, Utrecht, 8 oktober 2011
 Grenzen aan energiesysteem analyses Interactie tussen deelsystemen complex in de analyse Bij voorbeeld warmtepomp voor verwarming draait op elektriciteit, net als de elektrische auto Alleen de hoeveelheid energie wordt beschouwd, maar niet de kwaliteit. Een elektrische waterkoker is zeer energie efficiënt, maar gebruikt energie van hoge kwaliteit. VEM Energie, Exergie, Cascades in de Ruimte H. C. Moll, OU-NW, Utrecht, 8 oktober 2011
Grenzen aan energiesysteem analyses Interactie tussen deelsystemen complex in de analyse Bij voorbeeld warmtepomp voor verwarming draait op elektriciteit, net als de elektrische auto Alleen de hoeveelheid energie wordt beschouwd, maar niet de kwaliteit. Een elektrische waterkoker is zeer energie efficiënt, maar gebruikt energie van hoge kwaliteit. VEM Energie, Exergie, Cascades in de Ruimte H. C. Moll, OU-NW, Utrecht, 8 oktober 2011
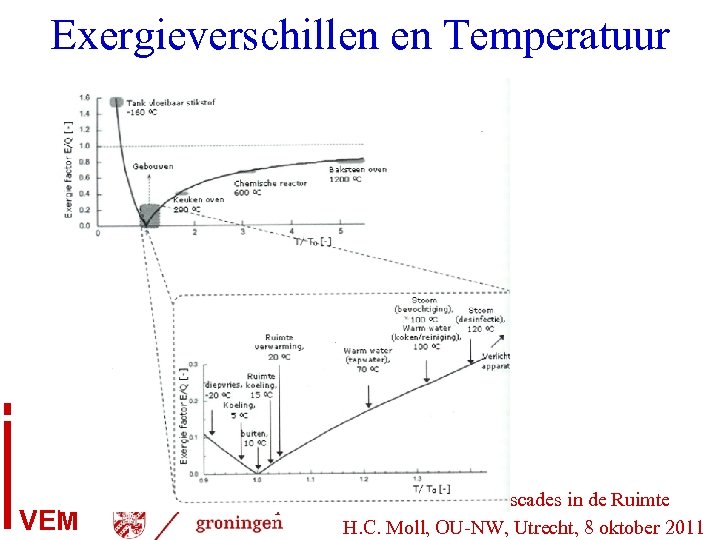 Exergieverschillen en Temperatuur VEM Energie, Exergie, Cascades in de Ruimte H. C. Moll, OU-NW, Utrecht, 8 oktober 2011
Exergieverschillen en Temperatuur VEM Energie, Exergie, Cascades in de Ruimte H. C. Moll, OU-NW, Utrecht, 8 oktober 2011
 De Nederlandse energiehuishouding VEM Energie, Exergie, Cascades in de Ruimte H. C. Moll, OU-NW, Utrecht, 8 oktober 2011
De Nederlandse energiehuishouding VEM Energie, Exergie, Cascades in de Ruimte H. C. Moll, OU-NW, Utrecht, 8 oktober 2011
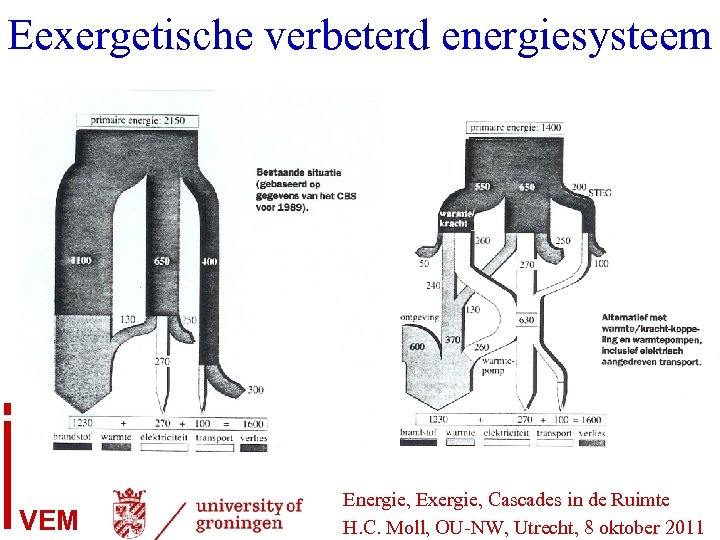 Eexergetische verbeterd energiesysteem VEM Energie, Exergie, Cascades in de Ruimte H. C. Moll, OU-NW, Utrecht, 8 oktober 2011
Eexergetische verbeterd energiesysteem VEM Energie, Exergie, Cascades in de Ruimte H. C. Moll, OU-NW, Utrecht, 8 oktober 2011
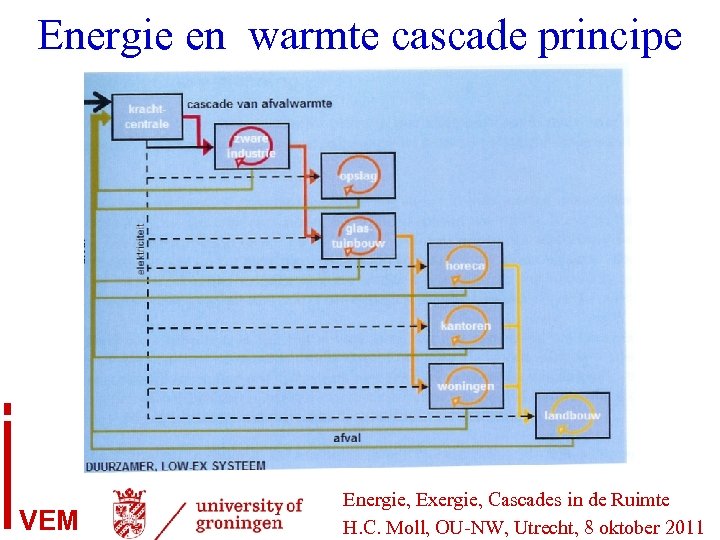 Energie en warmte cascade principe VEM Energie, Exergie, Cascades in de Ruimte H. C. Moll, OU-NW, Utrecht, 8 oktober 2011
Energie en warmte cascade principe VEM Energie, Exergie, Cascades in de Ruimte H. C. Moll, OU-NW, Utrecht, 8 oktober 2011
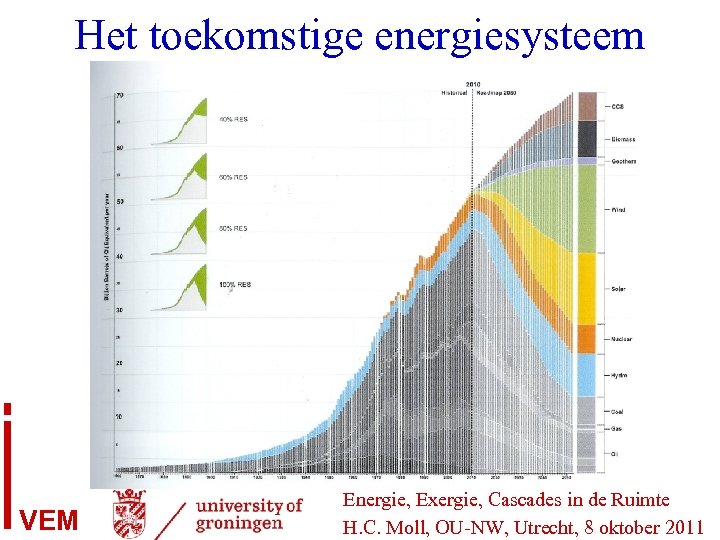 Het toekomstige energiesysteem VEM Energie, Exergie, Cascades in de Ruimte H. C. Moll, OU-NW, Utrecht, 8 oktober 2011
Het toekomstige energiesysteem VEM Energie, Exergie, Cascades in de Ruimte H. C. Moll, OU-NW, Utrecht, 8 oktober 2011


