4_lesson_8_th_grade2.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 20
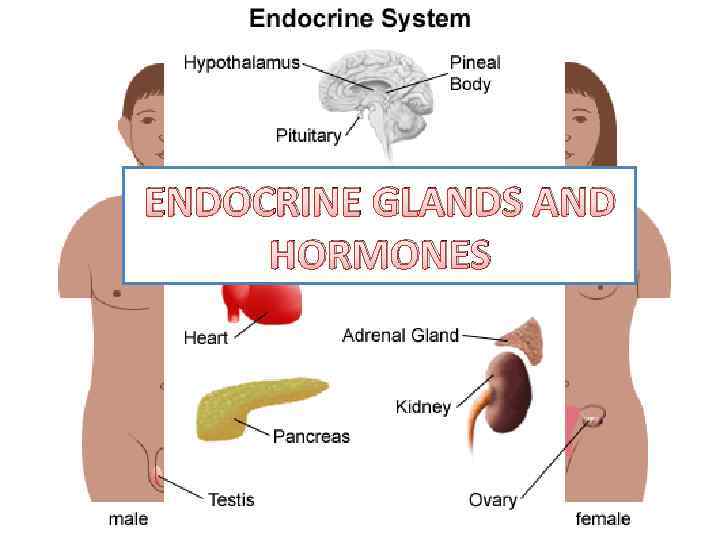 ENDOCRINE GLANDS AND HORMONES
ENDOCRINE GLANDS AND HORMONES
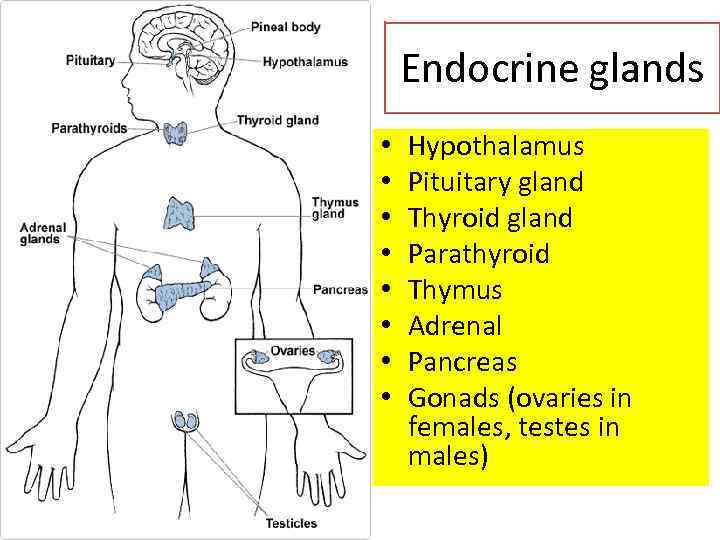 Endocrine glands • • Hypothalamus Pituitary gland Thyroid gland Parathyroid Thymus Adrenal Pancreas Gonads (ovaries in females, testes in males)
Endocrine glands • • Hypothalamus Pituitary gland Thyroid gland Parathyroid Thymus Adrenal Pancreas Gonads (ovaries in females, testes in males)
 Hypothalamus The area of the brain that coordinates the activities of the nervous and endocrine systems. It controls body temperature, blood pressure and emotions. It receives information about external and internal conditions from other brain regions. It responds by giving instructions—in the form of hormones—to the pituitary gland.
Hypothalamus The area of the brain that coordinates the activities of the nervous and endocrine systems. It controls body temperature, blood pressure and emotions. It receives information about external and internal conditions from other brain regions. It responds by giving instructions—in the form of hormones—to the pituitary gland.
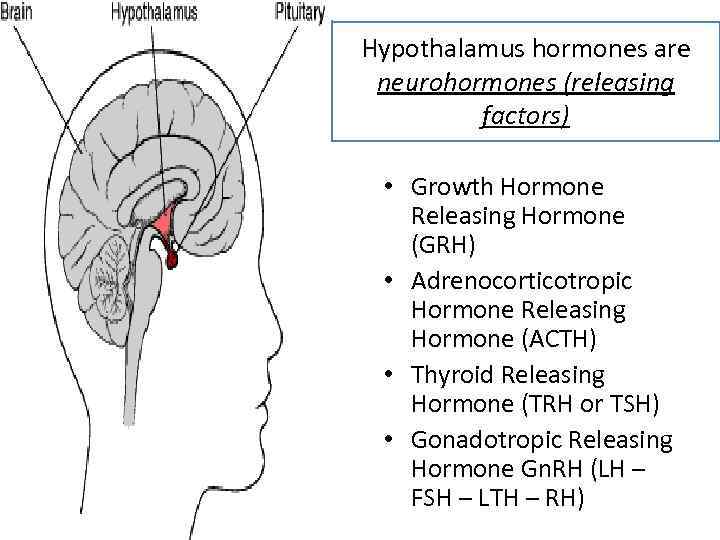 Hypothalamus hormones are neurohormones (releasing factors) • Growth Hormone Releasing Hormone (GRH) • Adrenocorticotropic Hormone Releasing Hormone (ACTH) • Thyroid Releasing Hormone (TRH or TSH) • Gonadotropic Releasing Hormone Gn. RH (LH – FSH – LTH – RH)
Hypothalamus hormones are neurohormones (releasing factors) • Growth Hormone Releasing Hormone (GRH) • Adrenocorticotropic Hormone Releasing Hormone (ACTH) • Thyroid Releasing Hormone (TRH or TSH) • Gonadotropic Releasing Hormone Gn. RH (LH – FSH – LTH – RH)
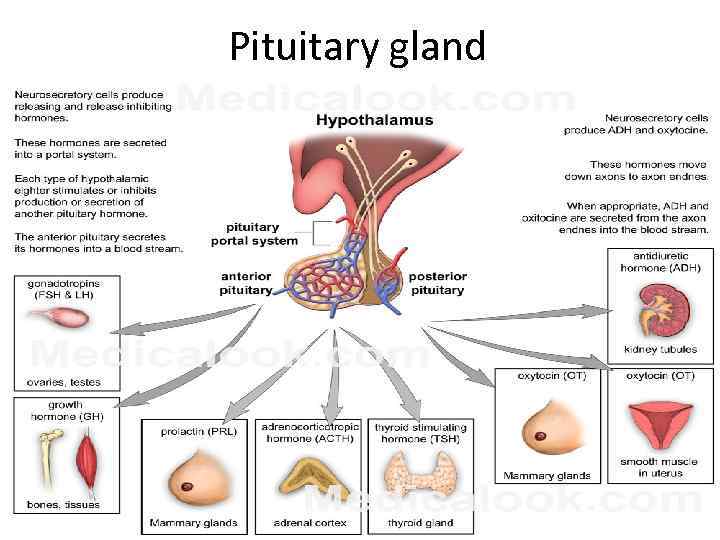 Pituitary gland
Pituitary gland
 Tropic Hormones Stimulate the secretions of other hormones Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH): Thyroid Gland Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH): adrenal glands Gonadotropic Hormones (LH, FSH, GTH): gonads. Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH): Growth and maturation of the egg in the follicle. In the testes, it stimulates the production of sperm. Luteinizing hormone (LH): the release of ovum (яйцеклетка) and secretion of progesterone and in males stimulates the secretion of testosterone.
Tropic Hormones Stimulate the secretions of other hormones Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH): Thyroid Gland Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH): adrenal glands Gonadotropic Hormones (LH, FSH, GTH): gonads. Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH): Growth and maturation of the egg in the follicle. In the testes, it stimulates the production of sperm. Luteinizing hormone (LH): the release of ovum (яйцеклетка) and secretion of progesterone and in males stimulates the secretion of testosterone.
 • GH (growth hormone) • Is released during life time • Increases the rate of cell division ADH – antiduiretic hormone (Vasopressin): regulates the water balance of the body by controlling reabsorption of water in the kidneys. OXYTOCIN: stimulates the smooth muscle fibers of the uterus (матка) to contract during labor. It causes contractions of the channel cells of the mammary glands so that milk can be secreted.
• GH (growth hormone) • Is released during life time • Increases the rate of cell division ADH – antiduiretic hormone (Vasopressin): regulates the water balance of the body by controlling reabsorption of water in the kidneys. OXYTOCIN: stimulates the smooth muscle fibers of the uterus (матка) to contract during labor. It causes contractions of the channel cells of the mammary glands so that milk can be secreted.
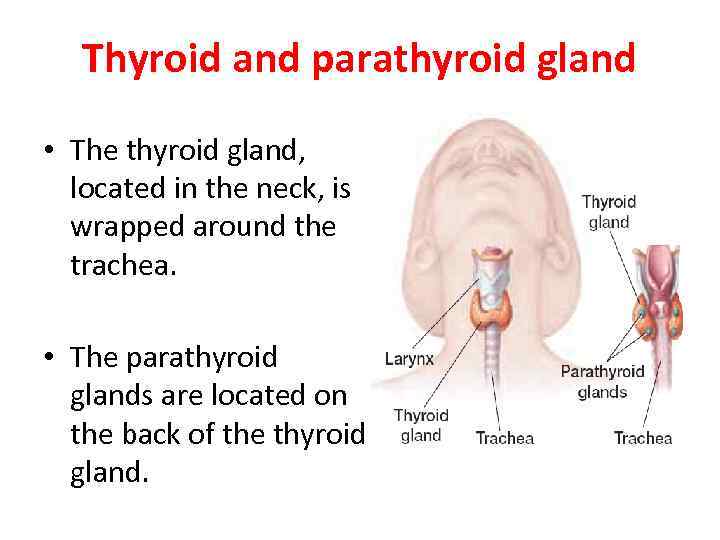 Thyroid and parathyroid gland • The thyroid gland, located in the neck, is wrapped around the trachea. • The parathyroid glands are located on the back of the thyroid gland.
Thyroid and parathyroid gland • The thyroid gland, located in the neck, is wrapped around the trachea. • The parathyroid glands are located on the back of the thyroid gland.
 Hormones • Thyroid hormone thyroxin has iodine in its structure • They regulate the body’s metabolic rate and promote normal growth of the brain, bones, and muscles during childhood.
Hormones • Thyroid hormone thyroxin has iodine in its structure • They regulate the body’s metabolic rate and promote normal growth of the brain, bones, and muscles during childhood.
 • A high level of calcium in the blood stimulates the thyroid gland to produce a hormone called calcitonin. Calcitonin causes calcium to be deposited in bone tissue rapidly, lowering the blood-calcium level. • Parathyroid hormone (PTH) or parathormone released by parathyroid gland. • PTH increases the calcium blood level.
• A high level of calcium in the blood stimulates the thyroid gland to produce a hormone called calcitonin. Calcitonin causes calcium to be deposited in bone tissue rapidly, lowering the blood-calcium level. • Parathyroid hormone (PTH) or parathormone released by parathyroid gland. • PTH increases the calcium blood level.
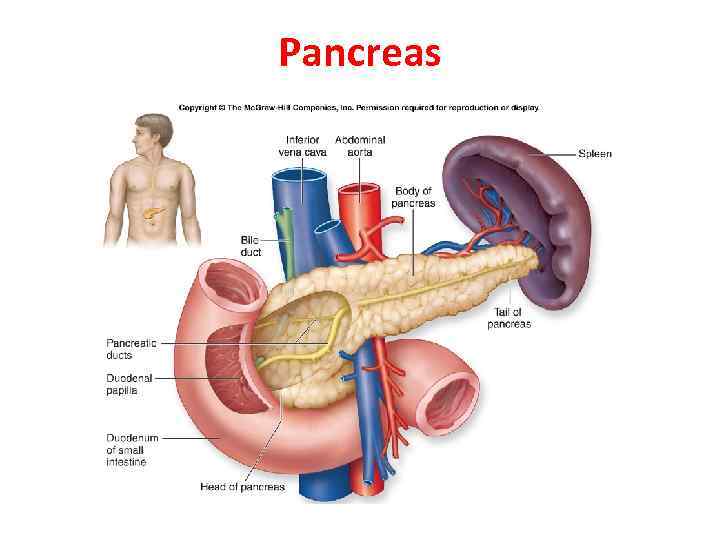 Pancreas
Pancreas
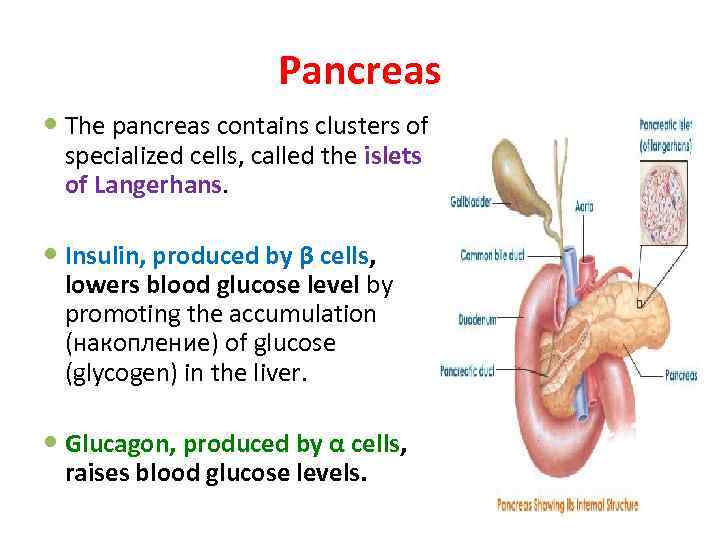 Pancreas The pancreas contains clusters of specialized cells, called the islets of Langerhans. Insulin, produced by β cells, lowers blood glucose level by promoting the accumulation (накопление) of glucose (glycogen) in the liver. Glucagon, produced by α cells, raises blood glucose levels.
Pancreas The pancreas contains clusters of specialized cells, called the islets of Langerhans. Insulin, produced by β cells, lowers blood glucose level by promoting the accumulation (накопление) of glucose (glycogen) in the liver. Glucagon, produced by α cells, raises blood glucose levels.
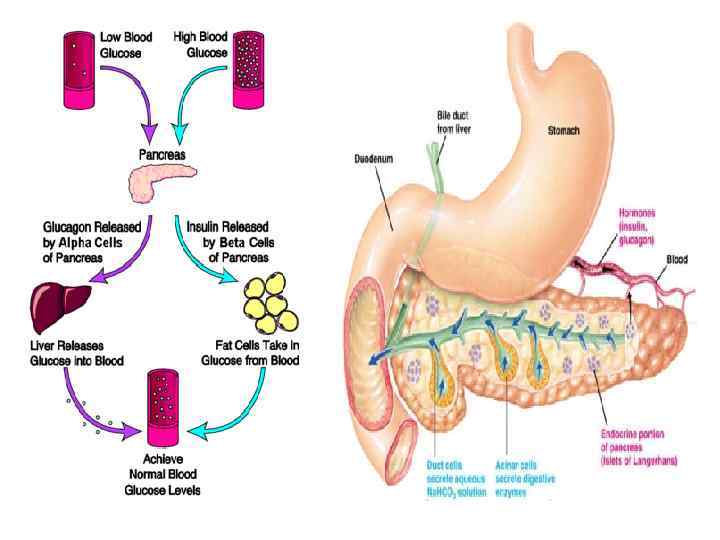
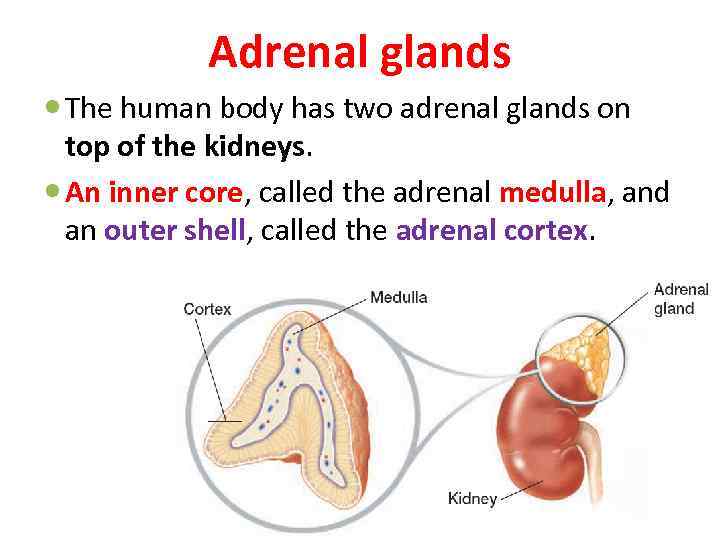 Adrenal glands The human body has two adrenal glands on top of the kidneys. An inner core, called the adrenal medulla, and an outer shell, called the adrenal cortex.
Adrenal glands The human body has two adrenal glands on top of the kidneys. An inner core, called the adrenal medulla, and an outer shell, called the adrenal cortex.
 Adrenal gland hormones ADRENAL MEDULLA: It produces epinephrine (adrenalin) and norepinephrine (noradrenalin) as a response to stress situations (fear, danger, cold…) They increase heart rate, blood pressure, blood glucose level, blood flow into heart and lungs (Fight or Flight response) ADRENAL CORTEX: Produces cortisol, aldosterone, small amounts of testosterone Cortisol makes more energy available to the body. Aldosterone helps reabsorb sodium (Na+) ions from the fluids removed by the kidneys. Involved in the excretion of excess potassium (K+).
Adrenal gland hormones ADRENAL MEDULLA: It produces epinephrine (adrenalin) and norepinephrine (noradrenalin) as a response to stress situations (fear, danger, cold…) They increase heart rate, blood pressure, blood glucose level, blood flow into heart and lungs (Fight or Flight response) ADRENAL CORTEX: Produces cortisol, aldosterone, small amounts of testosterone Cortisol makes more energy available to the body. Aldosterone helps reabsorb sodium (Na+) ions from the fluids removed by the kidneys. Involved in the excretion of excess potassium (K+).
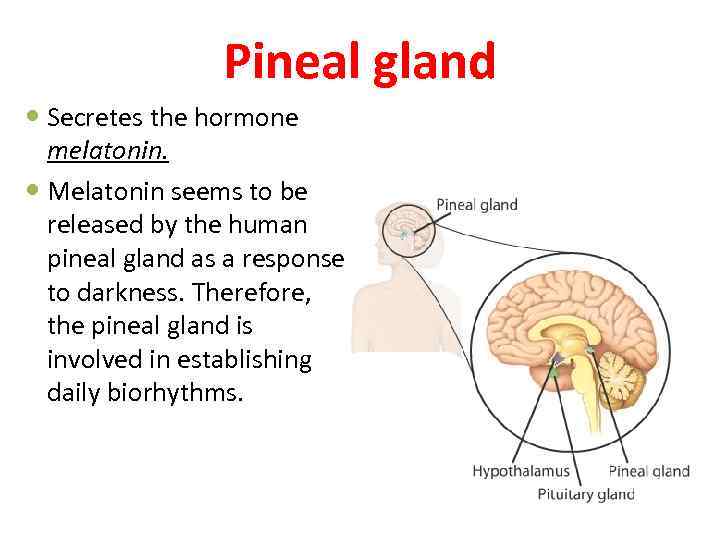 Pineal gland Secretes the hormone melatonin. Melatonin seems to be released by the human pineal gland as a response to darkness. Therefore, the pineal gland is involved in establishing daily biorhythms.
Pineal gland Secretes the hormone melatonin. Melatonin seems to be released by the human pineal gland as a response to darkness. Therefore, the pineal gland is involved in establishing daily biorhythms.
 Thymus • The thymus is a lymphoid organ. • It is involved in the immune system by stimulating lymphocyte production by its hormones. • Begins to disappear at puberty
Thymus • The thymus is a lymphoid organ. • It is involved in the immune system by stimulating lymphocyte production by its hormones. • Begins to disappear at puberty
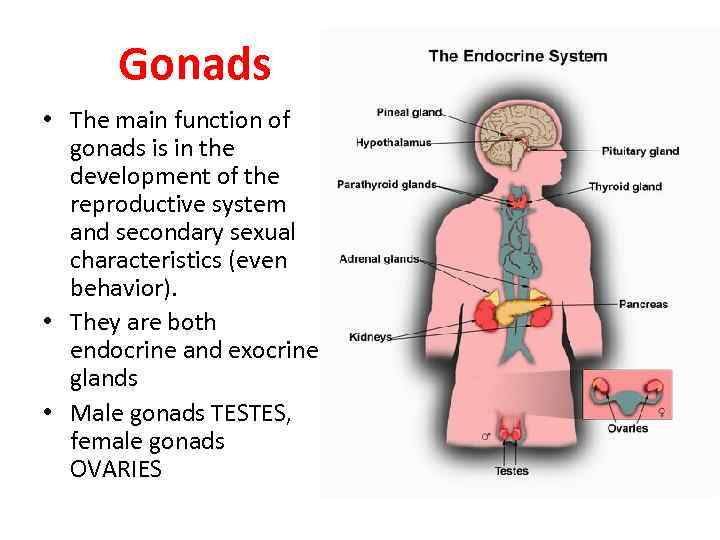 Gonads • The main function of gonads is in the development of the reproductive system and secondary sexual characteristics (even behavior). • They are both endocrine and exocrine glands • Male gonads TESTES, female gonads OVARIES
Gonads • The main function of gonads is in the development of the reproductive system and secondary sexual characteristics (even behavior). • They are both endocrine and exocrine glands • Male gonads TESTES, female gonads OVARIES
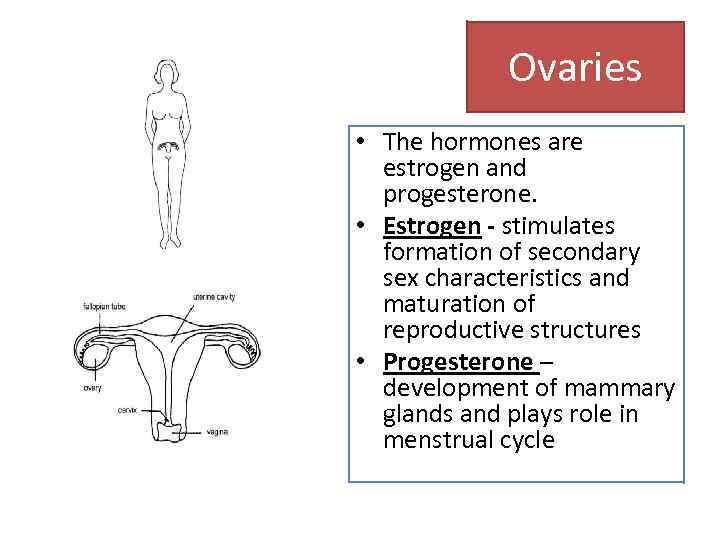 Ovaries • The hormones are estrogen and progesterone. • Estrogen - stimulates formation of secondary sex characteristics and maturation of reproductive structures • Progesterone – development of mammary glands and plays role in menstrual cycle
Ovaries • The hormones are estrogen and progesterone. • Estrogen - stimulates formation of secondary sex characteristics and maturation of reproductive structures • Progesterone – development of mammary glands and plays role in menstrual cycle
 Testes • Hormone is testosterone. • Function: stimulates production of sperm, development of male reproductive organs and secondary sex characteristics.
Testes • Hormone is testosterone. • Function: stimulates production of sperm, development of male reproductive organs and secondary sex characteristics.


