53a881471b20731e542f7de266c37d82.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 46
 Endocrine 3 Part 2
Endocrine 3 Part 2
 Acute complications of DM • Hypoglycemia • Diabetic Ketoacidosis • Hyperglycemia Hyperosmolar Non-ketonic Syndrome
Acute complications of DM • Hypoglycemia • Diabetic Ketoacidosis • Hyperglycemia Hyperosmolar Non-ketonic Syndrome
 Hypoglycemia • AKA Insulin reaction • Definition: When blood glucose levels fall below 70 mg/dl • < 50 mg/dl = severe
Hypoglycemia • AKA Insulin reaction • Definition: When blood glucose levels fall below 70 mg/dl • < 50 mg/dl = severe
 Hypoglycemia: Etiology • • • Any time Skip meal Under-eating Eating late Unplanned exercise Excess insulin or oral hypoglycemic meds
Hypoglycemia: Etiology • • • Any time Skip meal Under-eating Eating late Unplanned exercise Excess insulin or oral hypoglycemic meds
 Hypoglycemia: Signs & Symptoms • Mild – – – Diaphoresis Pallor Paresthesia Palpitations Tremors Anxiety • Adrenal Medulla
Hypoglycemia: Signs & Symptoms • Mild – – – Diaphoresis Pallor Paresthesia Palpitations Tremors Anxiety • Adrenal Medulla
 Hypoglycemia: Signs & Symptoms • Moderate: – Confusion/disorientation – Behavioral Changes
Hypoglycemia: Signs & Symptoms • Moderate: – Confusion/disorientation – Behavioral Changes
 Hypoglycemia: Signs & Symptoms • Severe – Seizures – Loss of Consciousness – Shallow respirations
Hypoglycemia: Signs & Symptoms • Severe – Seizures – Loss of Consciousness – Shallow respirations
 Hypoglycemia: Diagnosis • • Signs & Symptoms SMBG FSBS
Hypoglycemia: Diagnosis • • Signs & Symptoms SMBG FSBS
 Hypoglycemia: Medical Management • Follow protocol • P blood sugar level • Admin. fast sugar
Hypoglycemia: Medical Management • Follow protocol • P blood sugar level • Admin. fast sugar
 Hypoglycemic Protocol: Sample • For BG <60 mg/d. L – If patient can take PO, give 15 g of fast acting carbohydrate. (4 oz fruit juice/non diet soda, 8 oz nonfat milk, or 3 -4 glucose tablets) – If patient cannot take PO, give 25 m. L of D 50 as IV push – Check FSBG q 15 minutes and repeat above if BG<80.
Hypoglycemic Protocol: Sample • For BG <60 mg/d. L – If patient can take PO, give 15 g of fast acting carbohydrate. (4 oz fruit juice/non diet soda, 8 oz nonfat milk, or 3 -4 glucose tablets) – If patient cannot take PO, give 25 m. L of D 50 as IV push – Check FSBG q 15 minutes and repeat above if BG<80.
 Glucose Fast! 10 -15 mg fast acting carbohydrate • Glucose tabs • 4 -6 oz. Juice or soda • 6 -10 lifesaver candies • 2 -3 tsp honey/sugar
Glucose Fast! 10 -15 mg fast acting carbohydrate • Glucose tabs • 4 -6 oz. Juice or soda • 6 -10 lifesaver candies • 2 -3 tsp honey/sugar
 Rules to remember Do not add sugar to OJ Recheck FSBS q 15 min until WNL Avoid high fat slows absorption of glucose Instruct: carry fast sugar If meal is >1 hr away, follow with a protein and complex carbohydrate • NPO if “unconscious” or confused • • •
Rules to remember Do not add sugar to OJ Recheck FSBS q 15 min until WNL Avoid high fat slows absorption of glucose Instruct: carry fast sugar If meal is >1 hr away, follow with a protein and complex carbohydrate • NPO if “unconscious” or confused • • •
 Protein Sources • 1 Tbsp peanut butter • 1 oz cheese • 1 oz meat
Protein Sources • 1 Tbsp peanut butter • 1 oz cheese • 1 oz meat
 Hypoglycemia treatment Unconscious • IV 25 -50 mm of 50% dextrose in water • Glucagon 1 mg Sub-Q or IM – Action: (hormone) raises BS levels – Onset: 10 minutes – Duration 25 minutes – S/E: N/V • Position: side lying
Hypoglycemia treatment Unconscious • IV 25 -50 mm of 50% dextrose in water • Glucagon 1 mg Sub-Q or IM – Action: (hormone) raises BS levels – Onset: 10 minutes – Duration 25 minutes – S/E: N/V • Position: side lying
 Hypoglycemia Gerontological Consideration • Cognitive deficits – not recognize S&S • Decreased renal function – oral hypoglycemic meds stay in body longer • More likely to _____a meal – Skip • Vision problems – inaccurate insulin draws
Hypoglycemia Gerontological Consideration • Cognitive deficits – not recognize S&S • Decreased renal function – oral hypoglycemic meds stay in body longer • More likely to _____a meal – Skip • Vision problems – inaccurate insulin draws
 Hypoglycemia Nursing measures • Follow protocol • Teach – Carry simple sugar at all times – S&S or hypoglycemia – How to prevent Hypoglycemia – Check FSBS if you suspect NOW!
Hypoglycemia Nursing measures • Follow protocol • Teach – Carry simple sugar at all times – S&S or hypoglycemia – How to prevent Hypoglycemia – Check FSBS if you suspect NOW!
 Hypoglycemia Nursing measures • Enc. to wear ID bracelet • Teach family that belligerence is sign of hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia Nursing measures • Enc. to wear ID bracelet • Teach family that belligerence is sign of hypoglycemia
 Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) • Serious complication of hyperglycemia due to lack of insulin • Usually occurs with type I DM
Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) • Serious complication of hyperglycemia due to lack of insulin • Usually occurs with type I DM
 DKA: Etiology • #1 cause illness, infection, stress • Absence or inadequate insulin • Initial or undiagnosed diabetes
DKA: Etiology • #1 cause illness, infection, stress • Absence or inadequate insulin • Initial or undiagnosed diabetes
 Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) 4 main clinical features 1. 2. 3. 4. Hyperglycemia Dehydration Electrolyte loss Metabolic Acidosis
Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) 4 main clinical features 1. 2. 3. 4. Hyperglycemia Dehydration Electrolyte loss Metabolic Acidosis
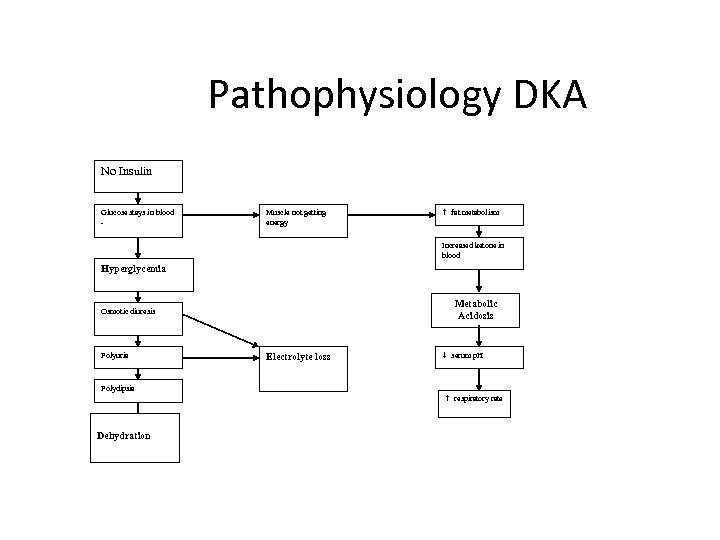 Pathophysiology DKA No Insulin Glucose stays in blood - Muscle not getting energy h fat metabolism Increased ketone in blood Hyperglycemia Metabolic Acidosis Osmotic diuresis Polyuria Electrolyte loss i serum p. H Polydipsia h respiratory rate Dehydration
Pathophysiology DKA No Insulin Glucose stays in blood - Muscle not getting energy h fat metabolism Increased ketone in blood Hyperglycemia Metabolic Acidosis Osmotic diuresis Polyuria Electrolyte loss i serum p. H Polydipsia h respiratory rate Dehydration
 S&S of DKA • Hyperglycemia – ↑blood glucose – Tired – Polyphagia – Decreased attention, confusion – N/V, abdominal pain – Blurred vision
S&S of DKA • Hyperglycemia – ↑blood glucose – Tired – Polyphagia – Decreased attention, confusion – N/V, abdominal pain – Blurred vision
 S&S of DKA • Dehydration – Polydipsia – Polyuria – Dry/flushed skin – Orthostatic hypotension – Tachycardia – Headaches – Decreased Na+ and K+ levels
S&S of DKA • Dehydration – Polydipsia – Polyuria – Dry/flushed skin – Orthostatic hypotension – Tachycardia – Headaches – Decreased Na+ and K+ levels
 S&S of DKA • Acidosis – ↑Resp. rate Kussmaul’s – Fruity breath, acetone breath – Serum p. H • Decreased – Normal Serum p. H 7. 35 – 7. 45 – i p. H = acidic / acidosis – h p. H = alkaline/ alkalosis
S&S of DKA • Acidosis – ↑Resp. rate Kussmaul’s – Fruity breath, acetone breath – Serum p. H • Decreased – Normal Serum p. H 7. 35 – 7. 45 – i p. H = acidic / acidosis – h p. H = alkaline/ alkalosis
 DKA: diagnosis • Blood sugar levels – Elevated • Serum p. H – Decreased (< 7. 35) • BUN Blood Urea Nitrate – increased = dehydration
DKA: diagnosis • Blood sugar levels – Elevated • Serum p. H – Decreased (< 7. 35) • BUN Blood Urea Nitrate – increased = dehydration
 DKA: diagnosis • Urine – Ketones • + – Specific gravity of urine • i • Serum Osmolality – h – thick
DKA: diagnosis • Urine – Ketones • + – Specific gravity of urine • i • Serum Osmolality – h – thick
 DKA: diagnosis • Hemoglobin – Normal • Female : 12 -16 g/d. L • Male: 14 -18 g/d. L – Elevated • Dehydration • COPD – Decreased • Anemia, hemorrhaging, over-hydration
DKA: diagnosis • Hemoglobin – Normal • Female : 12 -16 g/d. L • Male: 14 -18 g/d. L – Elevated • Dehydration • COPD – Decreased • Anemia, hemorrhaging, over-hydration
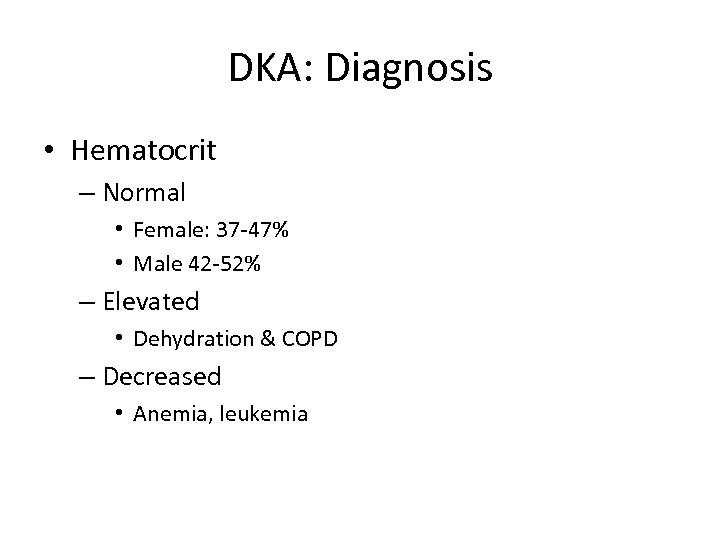 DKA: Diagnosis • Hematocrit – Normal • Female: 37 -47% • Male 42 -52% – Elevated • Dehydration & COPD – Decreased • Anemia, leukemia
DKA: Diagnosis • Hematocrit – Normal • Female: 37 -47% • Male 42 -52% – Elevated • Dehydration & COPD – Decreased • Anemia, leukemia
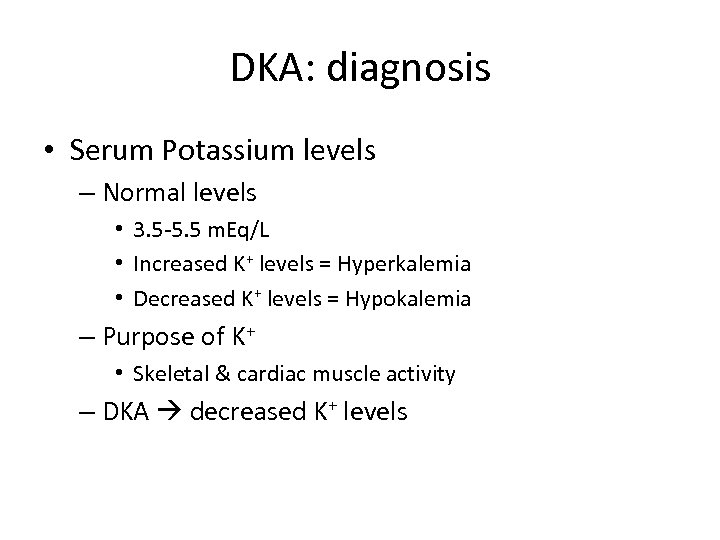 DKA: diagnosis • Serum Potassium levels – Normal levels • 3. 5 -5. 5 m. Eq/L • Increased K+ levels = Hyperkalemia • Decreased K+ levels = Hypokalemia – Purpose of K+ • Skeletal & cardiac muscle activity – DKA decreased K+ levels
DKA: diagnosis • Serum Potassium levels – Normal levels • 3. 5 -5. 5 m. Eq/L • Increased K+ levels = Hyperkalemia • Decreased K+ levels = Hypokalemia – Purpose of K+ • Skeletal & cardiac muscle activity – DKA decreased K+ levels
 Hypokalemia S&S • • • Fatigue Anorexia N/V Muscle weakness Leg cramps Dysrhythmias ↑sensitivity to digitalis
Hypokalemia S&S • • • Fatigue Anorexia N/V Muscle weakness Leg cramps Dysrhythmias ↑sensitivity to digitalis
 Treatment of DKA • Focus on the four main clinical features – Hyperglycemia – Dehydration – Electrolyte loss – Acidosis
Treatment of DKA • Focus on the four main clinical features – Hyperglycemia – Dehydration – Electrolyte loss – Acidosis
 Treatment of DKA • Hyperglycemia – Give insulin IV
Treatment of DKA • Hyperglycemia – Give insulin IV
 Treatment of DKA • Dehydration – Rehydrate • • • IV, push fluids I&O Check vital signs Check Lung sounds Monitor lab values
Treatment of DKA • Dehydration – Rehydrate • • • IV, push fluids I&O Check vital signs Check Lung sounds Monitor lab values
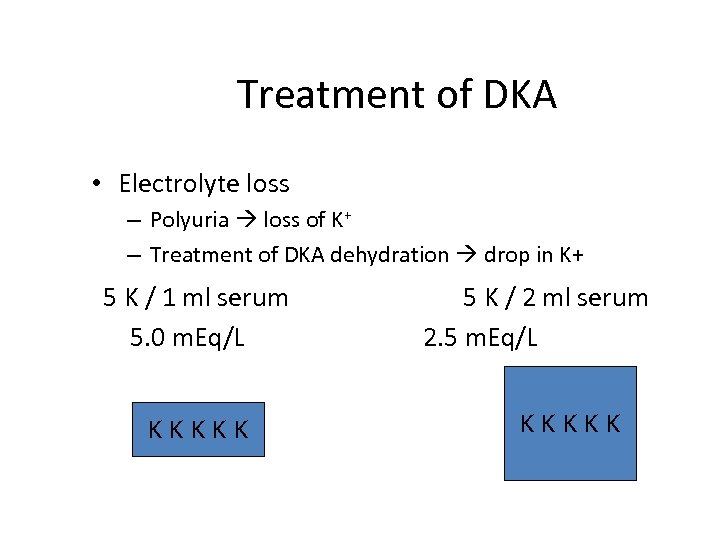 Treatment of DKA • Electrolyte loss – Polyuria loss of K+ – Treatment of DKA dehydration drop in K+ 5 K / 1 ml serum 5. 0 m. Eq/L KKKKK 5 K / 2 ml serum 2. 5 m. Eq/L KKKKK
Treatment of DKA • Electrolyte loss – Polyuria loss of K+ – Treatment of DKA dehydration drop in K+ 5 K / 1 ml serum 5. 0 m. Eq/L KKKKK 5 K / 2 ml serum 2. 5 m. Eq/L KKKKK
 Treatment of DKA: • Electrolyte loss – Replace K+ – Monitor lab values closely
Treatment of DKA: • Electrolyte loss – Replace K+ – Monitor lab values closely
 Treatment of DKA • Acidosis – Reversed with insulin • • • Insulin glucose enters muscles i fat metabolism i in Ketones acidosis reversed
Treatment of DKA • Acidosis – Reversed with insulin • • • Insulin glucose enters muscles i fat metabolism i in Ketones acidosis reversed
 Prevention of DKA • #1 cause of DKA? – Illness • Sick Day Rules
Prevention of DKA • #1 cause of DKA? – Illness • Sick Day Rules
 Sick Day Protocol/Rules • Never omit insulin • If you are unable to eat normally, DO NOT stop taking insulin • Sliding scale • Test blood sugar every 3 -4 hours • Test urine for ketones every 3 -4 hours • Take liquid/fluids q hour
Sick Day Protocol/Rules • Never omit insulin • If you are unable to eat normally, DO NOT stop taking insulin • Sliding scale • Test blood sugar every 3 -4 hours • Test urine for ketones every 3 -4 hours • Take liquid/fluids q hour
 Sick Day Protocol/Rules • If you can not eat your usual meal, substitute soft foods • Have “sick day” food in house • If vomiting, diarrhea or fever persists, take liquids q half hour • If miss or replace 4 meals with fluids, call MD
Sick Day Protocol/Rules • If you can not eat your usual meal, substitute soft foods • Have “sick day” food in house • If vomiting, diarrhea or fever persists, take liquids q half hour • If miss or replace 4 meals with fluids, call MD
 Sick Day Protocol/Rules • Go to bed and keep warm • Friends: good to have someone around who understands and knows about insulin reactions and diabetes
Sick Day Protocol/Rules • Go to bed and keep warm • Friends: good to have someone around who understands and knows about insulin reactions and diabetes
 Hyperglycemia Hyperosmolar Nonketonic Syndrome - HHNK • Definition – HHNK occurs when there is insufficient insulin to prevent hyperglycemia, but there is enough insulin to prevent Ketoacidosis – Occurs in all types of diabetes
Hyperglycemia Hyperosmolar Nonketonic Syndrome - HHNK • Definition – HHNK occurs when there is insufficient insulin to prevent hyperglycemia, but there is enough insulin to prevent Ketoacidosis – Occurs in all types of diabetes
 Hyperglycemia Hyperosmolar Nonketonic Syndrome - HHNK • Etiology – Overeating – Stress – Illness – Too little insulin
Hyperglycemia Hyperosmolar Nonketonic Syndrome - HHNK • Etiology – Overeating – Stress – Illness – Too little insulin
 S&S of HHNK syndrome • • Polyuria Polydipsia Polyphagia Skin, hot, dry, decreased turgor Dehydration Seizures Blurred vision Weakness • Headache • Mental status changes • Lab values: FSBS 600 – 2, 000 mg/dl • Serum osmolality h • Urine neg. for ketone
S&S of HHNK syndrome • • Polyuria Polydipsia Polyphagia Skin, hot, dry, decreased turgor Dehydration Seizures Blurred vision Weakness • Headache • Mental status changes • Lab values: FSBS 600 – 2, 000 mg/dl • Serum osmolality h • Urine neg. for ketone
 Medical Management/treatment • Confirm with glucose meter • If greater than 300 mg/dl check urine for ketones • Fluid and electrolyte replacement – Especially K+ • Insulin • Treat precipitating factors
Medical Management/treatment • Confirm with glucose meter • If greater than 300 mg/dl check urine for ketones • Fluid and electrolyte replacement – Especially K+ • Insulin • Treat precipitating factors
 Nursing Responsibility • Same as with DKA – Insulin – Hydration – Electrolyte replacement and monitoring – Treat underlying cause
Nursing Responsibility • Same as with DKA – Insulin – Hydration – Electrolyte replacement and monitoring – Treat underlying cause
 Summary • Acute complications of DM – Hypoglycemia – Diabetic Ketoacidosis – Hyperglycemia Hyperosmolar Non-ketonic Syndrome
Summary • Acute complications of DM – Hypoglycemia – Diabetic Ketoacidosis – Hyperglycemia Hyperosmolar Non-ketonic Syndrome


