603918d67295c6f8de522c0130c14b1c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 37
 End-User Analysis with PROOF P. Malzacher@gsi. de Physics at the Terascale, Kick-off Workshop 4. 12. 2007, DESY
End-User Analysis with PROOF P. Malzacher@gsi. de Physics at the Terascale, Kick-off Workshop 4. 12. 2007, DESY
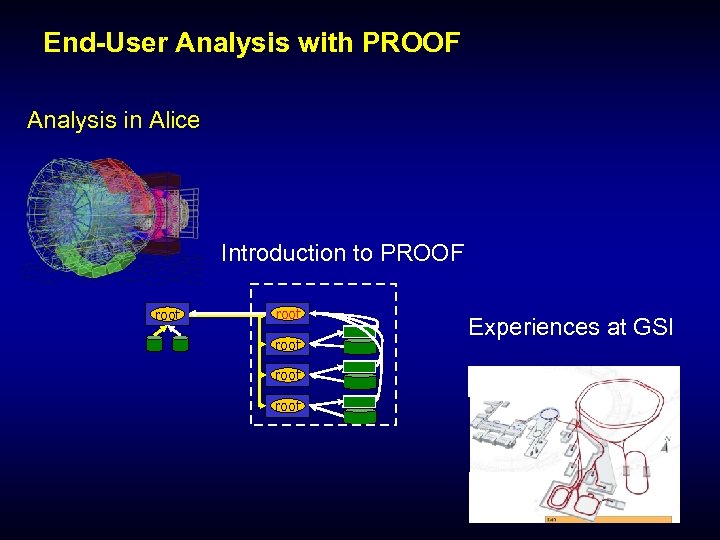 End-User Analysis with PROOF Analysis in Alice Introduction to PROOF root root Experiences at GSI
End-User Analysis with PROOF Analysis in Alice Introduction to PROOF root root Experiences at GSI
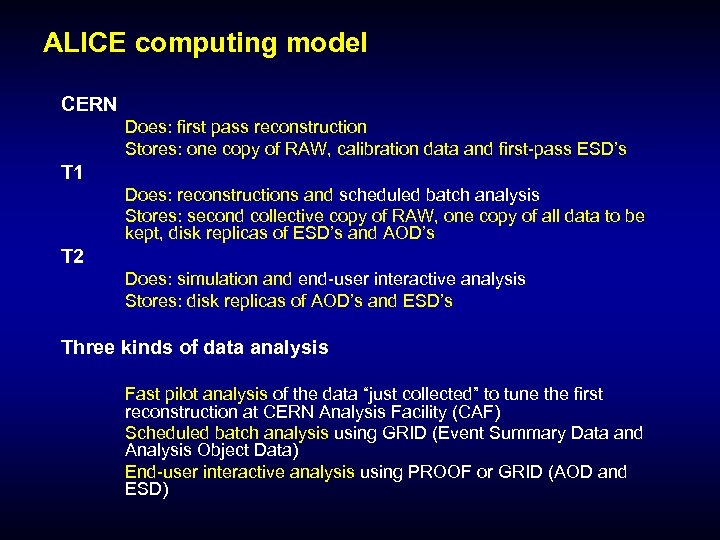 ALICE computing model CERN Does: first pass reconstruction Stores: one copy of RAW, calibration data and first-pass ESD’s T 1 Does: reconstructions and scheduled batch analysis Stores: second collective copy of RAW, one copy of all data to be kept, disk replicas of ESD’s and AOD’s T 2 Does: simulation and end-user interactive analysis Stores: disk replicas of AOD’s and ESD’s Three kinds of data analysis Fast pilot analysis of the data “just collected” to tune the first reconstruction at CERN Analysis Facility (CAF) Scheduled batch analysis using GRID (Event Summary Data and Analysis Object Data) End-user interactive analysis using PROOF or GRID (AOD and ESD)
ALICE computing model CERN Does: first pass reconstruction Stores: one copy of RAW, calibration data and first-pass ESD’s T 1 Does: reconstructions and scheduled batch analysis Stores: second collective copy of RAW, one copy of all data to be kept, disk replicas of ESD’s and AOD’s T 2 Does: simulation and end-user interactive analysis Stores: disk replicas of AOD’s and ESD’s Three kinds of data analysis Fast pilot analysis of the data “just collected” to tune the first reconstruction at CERN Analysis Facility (CAF) Scheduled batch analysis using GRID (Event Summary Data and Analysis Object Data) End-user interactive analysis using PROOF or GRID (AOD and ESD)
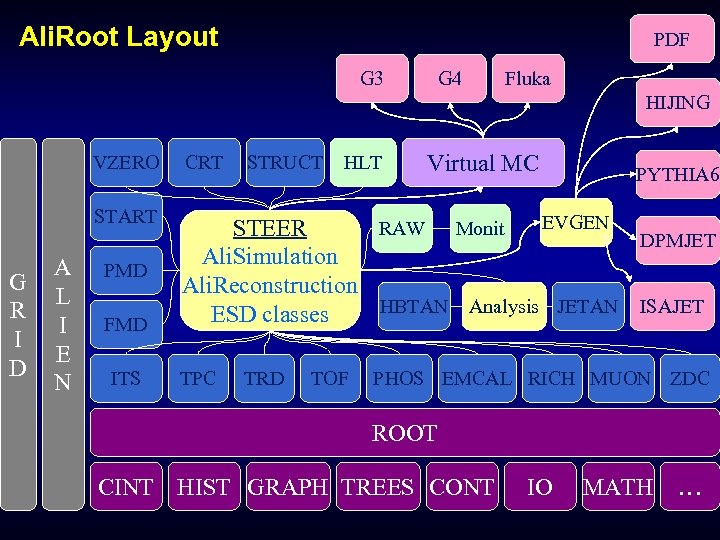 Ali. Root Layout PDF G 3 G 4 Fluka HIJING G R I D CRT START A L I E N EVGEN RAW Monit STEER DPMJET Ali. Simulation Ali. Reconstruction HBTAN Analysis JETAN ISAJET ESD classes PMD FMD ITS TPC STRUCT TRD HLT Virtual MC VZERO TOF PYTHIA 6 PHOS EMCAL RICH MUON ZDC ROOT CINT HIST GRAPH TREES CONT IO MATH …
Ali. Root Layout PDF G 3 G 4 Fluka HIJING G R I D CRT START A L I E N EVGEN RAW Monit STEER DPMJET Ali. Simulation Ali. Reconstruction HBTAN Analysis JETAN ISAJET ESD classes PMD FMD ITS TPC STRUCT TRD HLT Virtual MC VZERO TOF PYTHIA 6 PHOS EMCAL RICH MUON ZDC ROOT CINT HIST GRAPH TREES CONT IO MATH …
 Analysis requires only a few libraries on top of ROOT: lib. Steer. Base, lib. ESD, lib. AOD, . . . Ali. En for the File/Tag DB G R I D A L I E N ESD classes HBTAN Analysis JETAN ROOT CINT HIST GRAPH TREES CONT IO MATH …
Analysis requires only a few libraries on top of ROOT: lib. Steer. Base, lib. ESD, lib. AOD, . . . Ali. En for the File/Tag DB G R I D A L I E N ESD classes HBTAN Analysis JETAN ROOT CINT HIST GRAPH TREES CONT IO MATH …
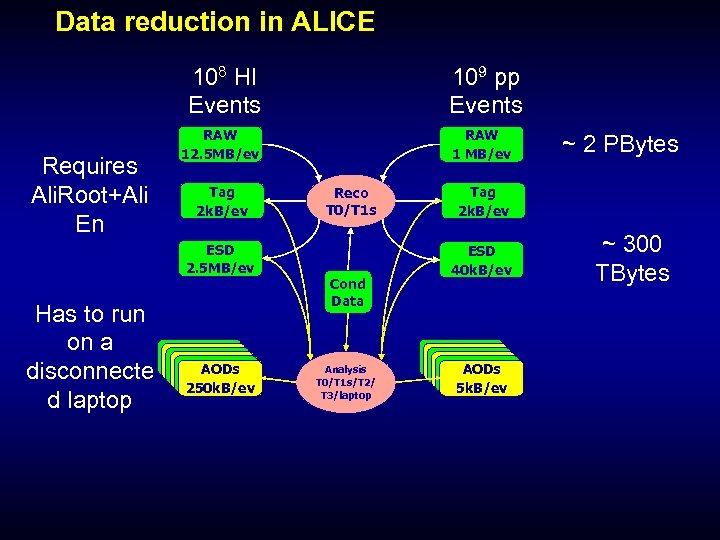 Data reduction in ALICE 108 HI Events Requires Ali. Root+Ali En RAW 12. 5 MB/ev Tag 2 k. B/ev ESD 2. 5 MB/ev Has to run on a disconnecte d laptop 109 pp Events AODs 250 k. B/ev RAW 1 MB/ev Reco T 0/T 1 s Cond Data Analysis T 0/T 1 s/T 2/ T 3/laptop ~ 2 PBytes Tag 2 k. B/ev ESD 40 k. B/ev AODs 5 k. B/ev ~ 300 TBytes
Data reduction in ALICE 108 HI Events Requires Ali. Root+Ali En RAW 12. 5 MB/ev Tag 2 k. B/ev ESD 2. 5 MB/ev Has to run on a disconnecte d laptop 109 pp Events AODs 250 k. B/ev RAW 1 MB/ev Reco T 0/T 1 s Cond Data Analysis T 0/T 1 s/T 2/ T 3/laptop ~ 2 PBytes Tag 2 k. B/ev ESD 40 k. B/ev AODs 5 k. B/ev ~ 300 TBytes
 End-User Analysis with PROOF Analysis in Alice Introduction to PROOF root root Experiences at GSI
End-User Analysis with PROOF Analysis in Alice Introduction to PROOF root root Experiences at GSI
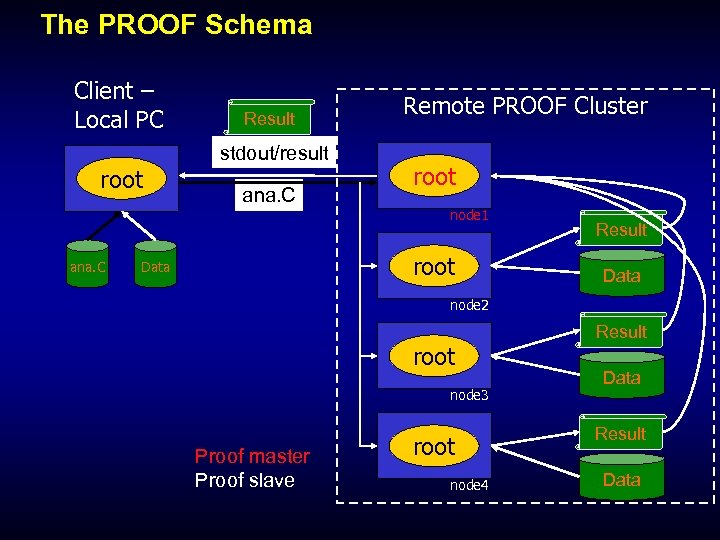 The PROOF Schema Client – Local PC root ana. C Result stdout/result ana. C Remote PROOF Cluster root node 1 root Data Result Data node 2 root node 3 Proof master Proof slave root node 4 Result Data
The PROOF Schema Client – Local PC root ana. C Result stdout/result ana. C Remote PROOF Cluster root node 1 root Data Result Data node 2 root node 3 Proof master Proof slave root node 4 Result Data
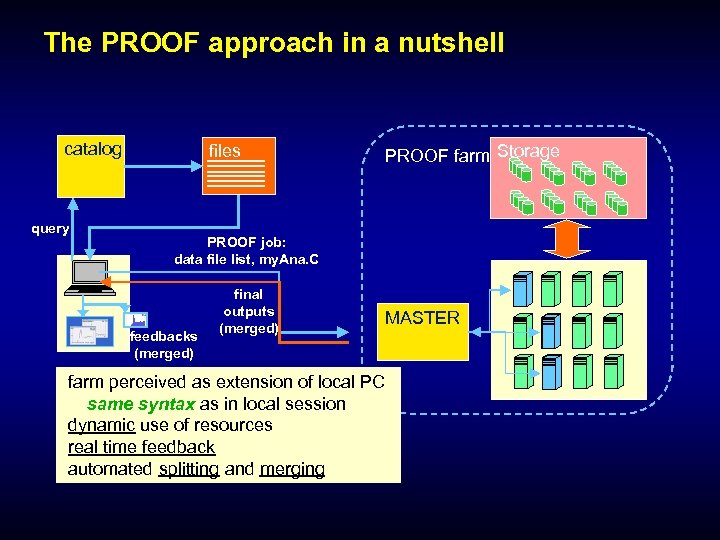 The PROOF approach in a nutshell catalog query files PROOF farm Storage PROOF job: data file list, my. Ana. C feedbacks (merged) final outputs (merged) MASTER farm perceived as extension of local PC same syntax as in local session dynamic use of resources real time feedback automated splitting and merging
The PROOF approach in a nutshell catalog query files PROOF farm Storage PROOF job: data file list, my. Ana. C feedbacks (merged) final outputs (merged) MASTER farm perceived as extension of local PC same syntax as in local session dynamic use of resources real time feedback automated splitting and merging
 PROOF: Parallel ROOT Facility Interactive parallel analysis on a local cluster Parallel processing of (local) data (trivial parallelism) Fast Feedback Output handling with direct visualization Not a batch system, no Grid The usage of PROOF is transparent The same code can be run locally and in a PROOF system (certain rules have to be followed) ~ 1997 : First Prototype Fons Rademakers 2000…: Further developed by MIT Phobos group Maarten Ballintijn, . . . 2005…: Alice sees PROOF as strategic tool Gerri Ganis, . . .
PROOF: Parallel ROOT Facility Interactive parallel analysis on a local cluster Parallel processing of (local) data (trivial parallelism) Fast Feedback Output handling with direct visualization Not a batch system, no Grid The usage of PROOF is transparent The same code can be run locally and in a PROOF system (certain rules have to be followed) ~ 1997 : First Prototype Fons Rademakers 2000…: Further developed by MIT Phobos group Maarten Ballintijn, . . . 2005…: Alice sees PROOF as strategic tool Gerri Ganis, . . .
 http: //root. cern. ch/root/PROOF 2007/ ~ 60 participants majority from Alice individuals from other experiments
http: //root. cern. ch/root/PROOF 2007/ ~ 60 participants majority from Alice individuals from other experiments
 Terminology Client Your machine running a ROOT session that is connected to a PROOF master Master PROOF machine coordinating work between slaves Slave/Worker PROOF machine that processes data Query A job submitted from the client to the PROOF system. A query consists of a selector and a chain Selector A class containing the analysis code In ALICE we use the Analysis Framework, therefore a Ali. Analysis. Task is sufficient Chain A list of files (trees) to process
Terminology Client Your machine running a ROOT session that is connected to a PROOF master Master PROOF machine coordinating work between slaves Slave/Worker PROOF machine that processes data Query A job submitted from the client to the PROOF system. A query consists of a selector and a chain Selector A class containing the analysis code In ALICE we use the Analysis Framework, therefore a Ali. Analysis. Task is sufficient Chain A list of files (trees) to process
 TSelector Classes derived from TSelector can run locally and in PROOF – Begin() – Slave. Begin() – Init(TTree* tree) – Process(Long 64_t entry) – Slave. Terminate() – Terminate() once on your client once on each Slave for each tree for each event
TSelector Classes derived from TSelector can run locally and in PROOF – Begin() – Slave. Begin() – Init(TTree* tree) – Process(Long 64_t entry) – Slave. Terminate() – Terminate() once on your client once on each Slave for each tree for each event
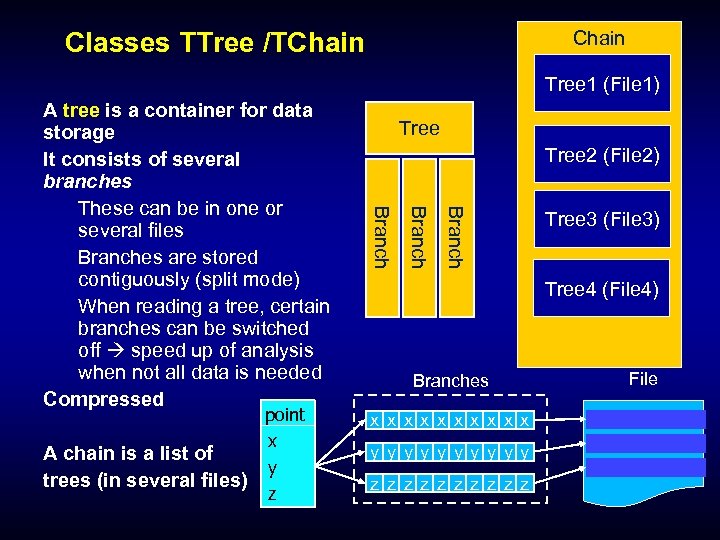 Chain Classes TTree /TChain Tree 1 (File 1) Tree 2 (File 2) Branch point x A chain is a list of y trees (in several files) z Tree Branch A tree is a container for data storage It consists of several branches These can be in one or several files Branches are stored contiguously (split mode) When reading a tree, certain branches can be switched off speed up of analysis when not all data is needed Compressed Tree 3 (File 3) Tree 4 (File 4) Branches x x x x x y y y y y z z z z z File
Chain Classes TTree /TChain Tree 1 (File 1) Tree 2 (File 2) Branch point x A chain is a list of y trees (in several files) z Tree Branch A tree is a container for data storage It consists of several branches These can be in one or several files Branches are stored contiguously (split mode) When reading a tree, certain branches can be switched off speed up of analysis when not all data is needed Compressed Tree 3 (File 3) Tree 4 (File 4) Branches x x x x x y y y y y z z z z z File
 Loading packages PAR file – Proof ARchive. Like Java JAR GZipped tar file PROOF-INF directory: BUILD. sh, building the package, executed per Slave SETUP. C, set environment, load libraries, executed per Slave API to manage and activate packages: Upload. Package(“package. par”) Enable. Package(“package”) Show. Packages() Clear. Packages()
Loading packages PAR file – Proof ARchive. Like Java JAR GZipped tar file PROOF-INF directory: BUILD. sh, building the package, executed per Slave SETUP. C, set environment, load libraries, executed per Slave API to manage and activate packages: Upload. Package(“package. par”) Enable. Package(“package”) Show. Packages() Clear. Packages()
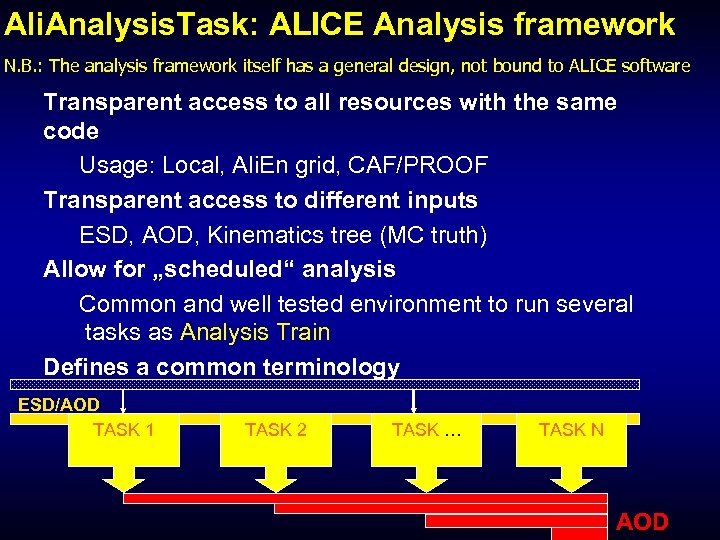 Ali. Analysis. Task: ALICE Analysis framework N. B. : The analysis framework itself has a general design, not bound to ALICE software Transparent access to all resources with the same code Usage: Local, Ali. En grid, CAF/PROOF Transparent access to different inputs ESD, AOD, Kinematics tree (MC truth) Allow for „scheduled“ analysis Common and well tested environment to run several tasks as Analysis Train Defines a common terminology ESD/AOD TASK 1 TASK 2 TASK … TASK N AOD
Ali. Analysis. Task: ALICE Analysis framework N. B. : The analysis framework itself has a general design, not bound to ALICE software Transparent access to all resources with the same code Usage: Local, Ali. En grid, CAF/PROOF Transparent access to different inputs ESD, AOD, Kinematics tree (MC truth) Allow for „scheduled“ analysis Common and well tested environment to run several tasks as Analysis Train Defines a common terminology ESD/AOD TASK 1 TASK 2 TASK … TASK N AOD
 Ali. Analysis. Task Classes derived from Ali. Analysis. Task can run locally and in PROOF and Ali. En – "Constructor" – Create. Output. Objects() – Connect. Input. Data() – Exec() – Terminate() once on your client once on each Slave for each tree for each event
Ali. Analysis. Task Classes derived from Ali. Analysis. Task can run locally and in PROOF and Ali. En – "Constructor" – Create. Output. Objects() – Connect. Input. Data() – Exec() – Terminate() once on your client once on each Slave for each tree for each event
 Run a task locally (from ALICE Offline Tutorial) • Start ROOT • Try the following lines and once they work add them to a macro run. C (enclose in {}) • Load needed libraries Ø g. System->Load("lib. Tree"); Ø g. System->Load("lib. STEERBase"); Ø g. System->Load("lib. AOD"); Ø g. System->Load("lib. ESD"); Ø g. System->Load("lib. ANALYSIS");
Run a task locally (from ALICE Offline Tutorial) • Start ROOT • Try the following lines and once they work add them to a macro run. C (enclose in {}) • Load needed libraries Ø g. System->Load("lib. Tree"); Ø g. System->Load("lib. STEERBase"); Ø g. System->Load("lib. AOD"); Ø g. System->Load("lib. ESD"); Ø g. System->Load("lib. ANALYSIS");
 Run a task locally (2) • Create the analysis manager Ø mgr = new Ali. Analysis. Manager("mgr"); • Create the analysis task and add it to the manager Ø g. ROOT->Load. Macro("Ali. Analysis. Task. Pt. cxx++g"); • "+" means compile; "g" means debug Ø task = new Ali. Analysis. Task. Pt; Ø mgr->Add. Task(task); • Add the ESD handler (to access the ESD) Ø Ali. ESDInput. Handler* esd. H = new Ali. ESDInput. Handler; Ø mgr->Set. Input. Event. Handler(esd. H);
Run a task locally (2) • Create the analysis manager Ø mgr = new Ali. Analysis. Manager("mgr"); • Create the analysis task and add it to the manager Ø g. ROOT->Load. Macro("Ali. Analysis. Task. Pt. cxx++g"); • "+" means compile; "g" means debug Ø task = new Ali. Analysis. Task. Pt; Ø mgr->Add. Task(task); • Add the ESD handler (to access the ESD) Ø Ali. ESDInput. Handler* esd. H = new Ali. ESDInput. Handler; Ø mgr->Set. Input. Event. Handler(esd. H);
 Run a task locally (3) • Create a chain Ø g. ROOT->Load. Macro("Create. ESDChain. C"); Ø chain = Create. ESDChain("ESD 82 XX_30 K. txt", 20); • Attach the input (the chain) Ø c. Input = mgr->Create. Container("c. Input", TChain: : Class(), Ali. Analysis. Manager: : k. Input. Container); Ø mgr->Connect. Input(task, 0, c. Input); • Create a place for the output (a histogram: TH 1) Ø c. Output = mgr->Create. Container("c. Output", TH 1: : Class(), Ali. Analysis. Manager: : k. Output. Container, "Pt. root"); Ø mgr->Connect. Output(task, 0, c. Output); • Enable debug (optional) Ø mgr->Set. Debug. Level(2);
Run a task locally (3) • Create a chain Ø g. ROOT->Load. Macro("Create. ESDChain. C"); Ø chain = Create. ESDChain("ESD 82 XX_30 K. txt", 20); • Attach the input (the chain) Ø c. Input = mgr->Create. Container("c. Input", TChain: : Class(), Ali. Analysis. Manager: : k. Input. Container); Ø mgr->Connect. Input(task, 0, c. Input); • Create a place for the output (a histogram: TH 1) Ø c. Output = mgr->Create. Container("c. Output", TH 1: : Class(), Ali. Analysis. Manager: : k. Output. Container, "Pt. root"); Ø mgr->Connect. Output(task, 0, c. Output); • Enable debug (optional) Ø mgr->Set. Debug. Level(2);
 Run a task locally (4) • Initialize the manager Ø mgr->Init. Analysis(); • Print the status (optional) Ø mgr->Print. Status(); • Run the analysis Ø mgr->Start. Analysis("local" , chain);
Run a task locally (4) • Initialize the manager Ø mgr->Init. Analysis(); • Print the status (optional) Ø mgr->Print. Status(); • Run the analysis Ø mgr->Start. Analysis("local" , chain);
 Running a task in PROOF • Copy run. C to run. Proof. C • Add connecting to the cluster 20 files Ø TProof: : Open("lxb 6046") • Replace the loading of the libraries with uploading the packages Ø g. Proof->Upload. Package("STEERBase") Ø g. Proof->Enable. Package("STEERBase") –Same with AOD, ESD, ANALYSIS • Replace the loading of the task with Ø g. Proof->Load("Ali. Analysis. Task. Pt. cxx++g") • Replace in Start. Analysis Ø "local" with "proof" • Run it! • Increase the number of files to 200 files
Running a task in PROOF • Copy run. C to run. Proof. C • Add connecting to the cluster 20 files Ø TProof: : Open("lxb 6046") • Replace the loading of the libraries with uploading the packages Ø g. Proof->Upload. Package("STEERBase") Ø g. Proof->Enable. Package("STEERBase") –Same with AOD, ESD, ANALYSIS • Replace the loading of the task with Ø g. Proof->Load("Ali. Analysis. Task. Pt. cxx++g") • Replace in Start. Analysis Ø "local" with "proof" • Run it! • Increase the number of files to 200 files
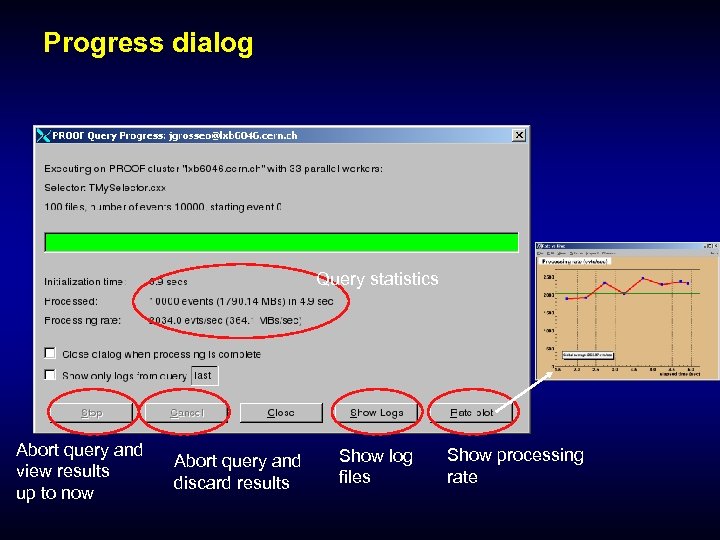 Progress dialog Query statistics Abort query and view results up to now Abort query and discard results Show log files Show processing rate
Progress dialog Query statistics Abort query and view results up to now Abort query and discard results Show log files Show processing rate
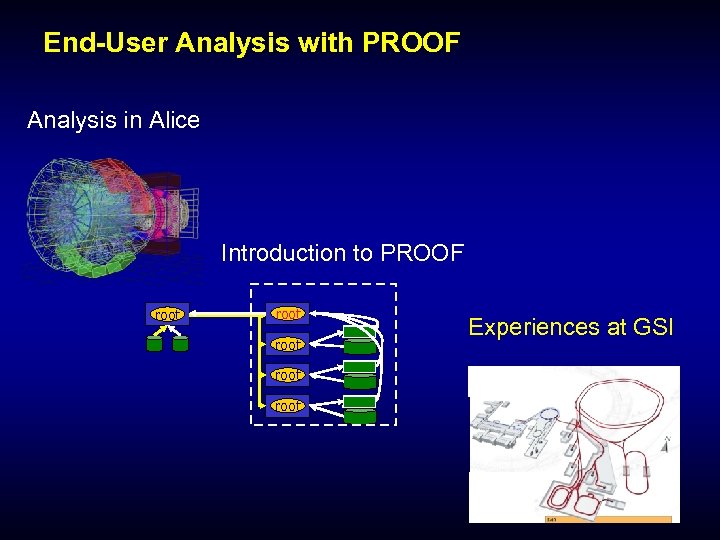 End-User Analysis with PROOF Analysis in Alice Introduction to PROOF root root Experiences at GSI
End-User Analysis with PROOF Analysis in Alice Introduction to PROOF root root Experiences at GSI
 FAIR GSI as of today
FAIR GSI as of today
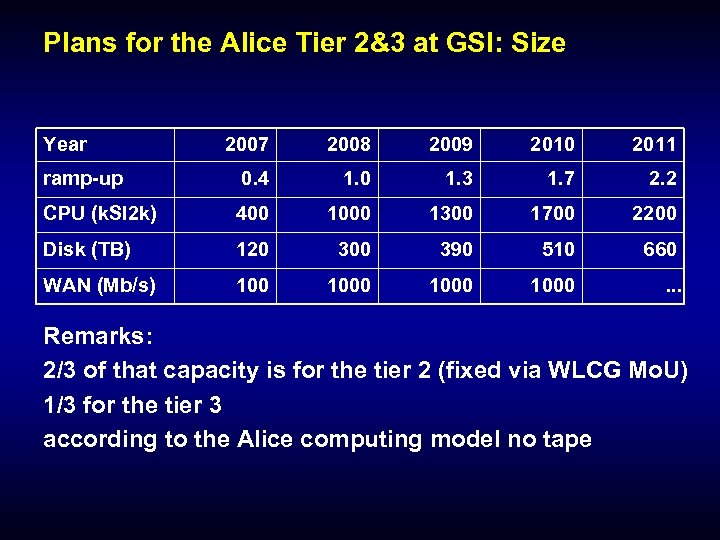 Plans for the Alice Tier 2&3 at GSI: Size Year 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 ramp-up 0. 4 1. 0 1. 3 1. 7 2. 2 CPU (k. SI 2 k) 400 1000 1300 1700 2200 Disk (TB) 120 300 390 510 660 WAN (Mb/s) 1000 . . . Remarks: 2/3 of that capacity is for the tier 2 (fixed via WLCG Mo. U) 1/3 for the tier 3 according to the Alice computing model no tape
Plans for the Alice Tier 2&3 at GSI: Size Year 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 ramp-up 0. 4 1. 0 1. 3 1. 7 2. 2 CPU (k. SI 2 k) 400 1000 1300 1700 2200 Disk (TB) 120 300 390 510 660 WAN (Mb/s) 1000 . . . Remarks: 2/3 of that capacity is for the tier 2 (fixed via WLCG Mo. U) 1/3 for the tier 3 according to the Alice computing model no tape
 Status today: Alice Tier 2 @ GSI 120 TB disk on fileserver 20 fileserver 3 U 15*500 GB disks RAID 5 6 TB user space per server 15 boxes, funded by D-Grid: each 2*2 core 2. 67 GHz Xeon, 8 GB RAM 2. 1 TB local disk space on 3 disks + system disk 24 boxes: each 2*4 core 2. 67 GHz Xeon, 16 GB RAM 2. 0 TB local disk space on 4 disks including system Status end of this year: D-Grid for FAIR + 54 boxes, 2*4 core 2. 67 GHz Xeon, 32 GB RAM + 35 fileserver, 6 TB netto per server
Status today: Alice Tier 2 @ GSI 120 TB disk on fileserver 20 fileserver 3 U 15*500 GB disks RAID 5 6 TB user space per server 15 boxes, funded by D-Grid: each 2*2 core 2. 67 GHz Xeon, 8 GB RAM 2. 1 TB local disk space on 3 disks + system disk 24 boxes: each 2*4 core 2. 67 GHz Xeon, 16 GB RAM 2. 0 TB local disk space on 4 disks including system Status end of this year: D-Grid for FAIR + 54 boxes, 2*4 core 2. 67 GHz Xeon, 32 GB RAM + 35 fileserver, 6 TB netto per server
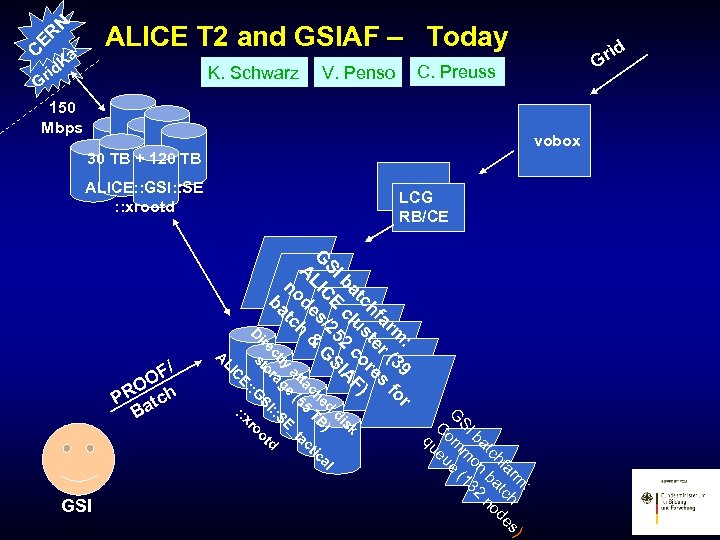 vobox 150 Mbps : r m 39 fo ar r ( s hf ste re ) o tc : ) m ar h es hf tc d tc ba no ba on 32 SI m 1 G om e ( C ueu q u c F sk ba cl 2 IA di SI E 25 S al ed B) G C / G tic LI s ch T A de h & ta 5 ac at (5 _t no tc ly ge : SE ct ra ba d I: ire to GS oot D s : r E: : : x C LI GSI A / OF O PR atch B C. Preuss V. Penso K. Schwarz rid G N ER C Ka LCG RB/CE ALICE: : GSI: : SE : : xrootd rid G ALICE T 2 and GSIAF – Today 30 TB + 120 TB
vobox 150 Mbps : r m 39 fo ar r ( s hf ste re ) o tc : ) m ar h es hf tc d tc ba no ba on 32 SI m 1 G om e ( C ueu q u c F sk ba cl 2 IA di SI E 25 S al ed B) G C / G tic LI s ch T A de h & ta 5 ac at (5 _t no tc ly ge : SE ct ra ba d I: ire to GS oot D s : r E: : : x C LI GSI A / OF O PR atch B C. Preuss V. Penso K. Schwarz rid G N ER C Ka LCG RB/CE ALICE: : GSI: : SE : : xrootd rid G ALICE T 2 and GSIAF – Today 30 TB + 120 TB
 ALICE Tier 2 and GSIAF On all machines Debian Etch, 64 bit. Installation via shared NFS directory visible on all nodes. xrootd 2. 7. 0 ROOT 5. 17/04 Ali. ROOT (head) Study the coexistence of interactive and batch processes: PROOF analysis on staged data, Grid and local batch jobs. Currently up to 4 concurrent PROOF user. Study data access posibilities: local disk, file server, xrd, lustre, . . .
ALICE Tier 2 and GSIAF On all machines Debian Etch, 64 bit. Installation via shared NFS directory visible on all nodes. xrootd 2. 7. 0 ROOT 5. 17/04 Ali. ROOT (head) Study the coexistence of interactive and batch processes: PROOF analysis on staged data, Grid and local batch jobs. Currently up to 4 concurrent PROOF user. Study data access posibilities: local disk, file server, xrd, lustre, . . .
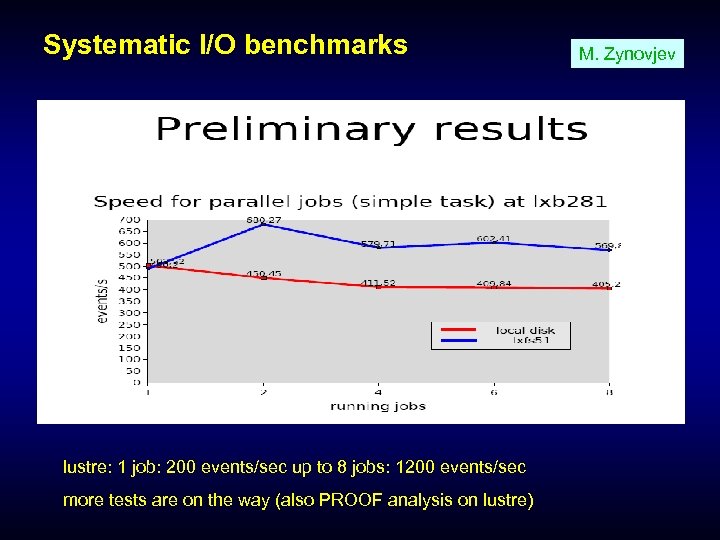 Systematic I/O benchmarks lustre: 1 job: 200 events/sec up to 8 jobs: 1200 events/sec more tests are on the way (also PROOF analysis on lustre) M. Zynovjev
Systematic I/O benchmarks lustre: 1 job: 200 events/sec up to 8 jobs: 1200 events/sec more tests are on the way (also PROOF analysis on lustre) M. Zynovjev
 Improving Debugging: Memory consumption monitoring A. Kreshuk An easy way to access logfiles after a session crashed. Workers monitor their memory usage and save info in the log file. New button in the dialog box to display the evolution of memory usage per node in real time. Client get warned of high usage: The session may be eventually killed Prototype being tested
Improving Debugging: Memory consumption monitoring A. Kreshuk An easy way to access logfiles after a session crashed. Workers monitor their memory usage and save info in the log file. New button in the dialog box to display the evolution of memory usage per node in real time. Client get warned of high usage: The session may be eventually killed Prototype being tested
 g. Lite. PROOF – a g. Lite PROOF package A. Manafov A number of utilities and configuration files to implement a PROOF distributed data analysis on the g. Lite Grid. Built on top of RGlite: TGrid. XXX interface are implemented in RGLite for g. Lite MW. ROOT team accepted our suggestions to TGrid. XXX interface. g. Lite. PROOF package – alpha release (tested against FZK and GSI WMSs). It setups “on-the-fly” a PROOF cluster on g. Lite Grid. It works with mixed type of g. Lite worker nodes (x 86_64, i 686. . . ) It supports reconnection.
g. Lite. PROOF – a g. Lite PROOF package A. Manafov A number of utilities and configuration files to implement a PROOF distributed data analysis on the g. Lite Grid. Built on top of RGlite: TGrid. XXX interface are implemented in RGLite for g. Lite MW. ROOT team accepted our suggestions to TGrid. XXX interface. g. Lite. PROOF package – alpha release (tested against FZK and GSI WMSs). It setups “on-the-fly” a PROOF cluster on g. Lite Grid. It works with mixed type of g. Lite worker nodes (x 86_64, i 686. . . ) It supports reconnection.
 RGLite example // Initializing RGLite plug-in TGrid: : Connect("glite"); // Submitting a Job to g. Lite Grid TGrid. Job *job = g. Grid->Submit("JDLs/proofd. jdl"); // querying a Status of the Job TGrid. Job. Status *status = job->Get. Job. Status(); status->Get. Status(); // Getting a Job's output back to the user job->Get. Output. Sandbox("/home/anar/"); // Initializing RGLite plug-in TGrid: : Connect("glite"); // Changing current File Catalog directory to "dteam" g. Grid->Cd("dteam"); // Querying a list of files of the current FC directory TGrid. Result* result = g. Grid->Ls(); // Printing the list out Int_t i=0; while (result->Get. File. Name(i)) > printf("File %sn", result->Get. File. Name(i++)); Job submission, status querying, output retrieving. Changing file catalog directory, querying lists of files.
RGLite example // Initializing RGLite plug-in TGrid: : Connect("glite"); // Submitting a Job to g. Lite Grid TGrid. Job *job = g. Grid->Submit("JDLs/proofd. jdl"); // querying a Status of the Job TGrid. Job. Status *status = job->Get. Job. Status(); status->Get. Status(); // Getting a Job's output back to the user job->Get. Output. Sandbox("/home/anar/"); // Initializing RGLite plug-in TGrid: : Connect("glite"); // Changing current File Catalog directory to "dteam" g. Grid->Cd("dteam"); // Querying a list of files of the current FC directory TGrid. Result* result = g. Grid->Ls(); // Printing the list out Int_t i=0; while (result->Get. File. Name(i)) > printf("File %sn", result->Get. File. Name(i++)); Job submission, status querying, output retrieving. Changing file catalog directory, querying lists of files.
 End-User Analysis with PROOF Summary & Observatios Analysis in Alice Introduction to PROOF root root Experiences at GSI
End-User Analysis with PROOF Summary & Observatios Analysis in Alice Introduction to PROOF root root Experiences at GSI
 Summary & Observations ALICE sees PROOF as strategic tool for prompt data analysis on their Central Analysis Facility. Current focus is on local farms and multi-core, multidisk desktops. The usage of PROOF is transparent, the same code can be run locally and in PROOF. Analysis based on Ali. Analysis. Task can be run transparently local, on the Grid, with PROOF and as part of an scheduled Analysis Train on the Grid.
Summary & Observations ALICE sees PROOF as strategic tool for prompt data analysis on their Central Analysis Facility. Current focus is on local farms and multi-core, multidisk desktops. The usage of PROOF is transparent, the same code can be run locally and in PROOF. Analysis based on Ali. Analysis. Task can be run transparently local, on the Grid, with PROOF and as part of an scheduled Analysis Train on the Grid.
 Summary & Observations For CPU-bound jobs we see a nearly linear speed-up. Optimal set-up in respect to IO-bound jobs still under investigations. Current version is not stable, frequent crashes of the master. Restarts in the order of days. PROOF is hard to debug. We slowly converge to a multi-user facility. There a lot of goodies in the pipeline.
Summary & Observations For CPU-bound jobs we see a nearly linear speed-up. Optimal set-up in respect to IO-bound jobs still under investigations. Current version is not stable, frequent crashes of the master. Restarts in the order of days. PROOF is hard to debug. We slowly converge to a multi-user facility. There a lot of goodies in the pipeline.


