98c62c15a3724971730994ccc5b5d993.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 33
 End of Life Care Raising an awareness…. ‘an introductory workshop for people who work in settings where Eo. LC is provided’
End of Life Care Raising an awareness…. ‘an introductory workshop for people who work in settings where Eo. LC is provided’
 Introduction & Housekeeping
Introduction & Housekeeping
 Programme • • • Welcome Learning objectives & ground rules Individual Introductions Introduction to End of Life and Palliative Care Thinking about who we support and staff involved Your role in end of life care Coffee Case Study ‘Joyce's story’ Questions and evaluation Lunch at 12. 30 – 30 mins
Programme • • • Welcome Learning objectives & ground rules Individual Introductions Introduction to End of Life and Palliative Care Thinking about who we support and staff involved Your role in end of life care Coffee Case Study ‘Joyce's story’ Questions and evaluation Lunch at 12. 30 – 30 mins
 Learning Objectives By end of this morning, you will be able to: • Explain what Palliative Care & End of Life Care means and the key principles of these approaches. • Understand who is involved in Eo. LC. • Understand & discuss how Eo. LC links to your role • Apply an End of Life Care approach to a patient’s story. • Reflect on your learning and identify further training needs
Learning Objectives By end of this morning, you will be able to: • Explain what Palliative Care & End of Life Care means and the key principles of these approaches. • Understand who is involved in Eo. LC. • Understand & discuss how Eo. LC links to your role • Apply an End of Life Care approach to a patient’s story. • Reflect on your learning and identify further training needs
 Ground Rules • • Confidentiality Shared learning One at a time Respect one another’s opinions Positive critique Sensitivity Time-out Mobile phones/pagers off please Any more? . . . .
Ground Rules • • Confidentiality Shared learning One at a time Respect one another’s opinions Positive critique Sensitivity Time-out Mobile phones/pagers off please Any more? . . . .
 Getting to know you…. • Introduce yourself, your role & where you work. • What you hope to get out of the session • Work in pairs
Getting to know you…. • Introduce yourself, your role & where you work. • What you hope to get out of the session • Work in pairs
 ‘End of Life Care’ What does this mean to you? There are no wrong answers!
‘End of Life Care’ What does this mean to you? There are no wrong answers!
 • What sort of illness & conditions might Eo. LC cover?
• What sort of illness & conditions might Eo. LC cover?
 • Where might you find people needing Eo. LC? Think outside the box!
• Where might you find people needing Eo. LC? Think outside the box!
 End of Life Care Key tools & documentation What are you aware of?
End of Life Care Key tools & documentation What are you aware of?
 End of Life Care Strategy (Do. H 2008) • Promotes high quality care across the country for all adults approaching the end of life. • Each year around 500, 000 people die in England. • Some people receive excellent care at the end of life, many do not. • Most people would prefer to die at home. In practice, only a minority manage to do so. • Services are not always joined up and as a result communication between staff and agencies can break down.
End of Life Care Strategy (Do. H 2008) • Promotes high quality care across the country for all adults approaching the end of life. • Each year around 500, 000 people die in England. • Some people receive excellent care at the end of life, many do not. • Most people would prefer to die at home. In practice, only a minority manage to do so. • Services are not always joined up and as a result communication between staff and agencies can break down.
 End of Life Care • Care that helps all those with advanced, progressive, incurable illness to live as well as possible until they die. • Draws attention to the needs of patients and their families, in the last 6 months to year or so of life. • It enables the supportive and palliative care needs of both patient and family to be identified and met through out the last phase of life and into bereavement. • Includes the management of pain and other symptoms and provision of psychological, social, spiritual and practical support’.
End of Life Care • Care that helps all those with advanced, progressive, incurable illness to live as well as possible until they die. • Draws attention to the needs of patients and their families, in the last 6 months to year or so of life. • It enables the supportive and palliative care needs of both patient and family to be identified and met through out the last phase of life and into bereavement. • Includes the management of pain and other symptoms and provision of psychological, social, spiritual and practical support’.
 Gold Standards Framework – Prognostic Indicators Provides guidance to enable better identification patients who may need supportive/ palliative care Highlights triggers for supportive/palliative care including: The ‘Surprise’ Question ‘Would you be surprised if this patient were to die in the next 6 -12 months? ’
Gold Standards Framework – Prognostic Indicators Provides guidance to enable better identification patients who may need supportive/ palliative care Highlights triggers for supportive/palliative care including: The ‘Surprise’ Question ‘Would you be surprised if this patient were to die in the next 6 -12 months? ’
 So is End Of Life Care different to Palliative Care?
So is End Of Life Care different to Palliative Care?
 Palliative Care • ‘An approach that improves quality of life of patients and their families facing the problems associated with life-threatening illness, through prevention and relief of suffering by means of early identification and impeccable assessment of pain and other problems, physical, psychological and spiritual’ WHO-2008
Palliative Care • ‘An approach that improves quality of life of patients and their families facing the problems associated with life-threatening illness, through prevention and relief of suffering by means of early identification and impeccable assessment of pain and other problems, physical, psychological and spiritual’ WHO-2008
 Coffee Break
Coffee Break
 We all have a role to play! YOU! The client and family
We all have a role to play! YOU! The client and family
 What concerns do you have in the part you play in providing End of Life Care?
What concerns do you have in the part you play in providing End of Life Care?
 Remember… • It’s OK to have concerns, most people do • It’s OK not to know the answer but remember the question and pass it on! • It’s not OK to ignore the concern either yours or client/family
Remember… • It’s OK to have concerns, most people do • It’s OK not to know the answer but remember the question and pass it on! • It’s not OK to ignore the concern either yours or client/family
 Introducing Joyce…. • Joyce, age 81, is a widow who lives alone in a 2 nd floor flat. • Has Advanced Lung Disease • In the past 3 years she has only left her flat to go into hospital (4 times) • Only family is a grandson & his family who live close by • Has told her grandson that she knows that the doctors are unable to do any more to help her. • ‘Wants it all over now’ • Now stays in bed most of the time, has no appetite and finds difficulty in taking all her tablets. • Has made it clear that she would like to die at home in her own bed.
Introducing Joyce…. • Joyce, age 81, is a widow who lives alone in a 2 nd floor flat. • Has Advanced Lung Disease • In the past 3 years she has only left her flat to go into hospital (4 times) • Only family is a grandson & his family who live close by • Has told her grandson that she knows that the doctors are unable to do any more to help her. • ‘Wants it all over now’ • Now stays in bed most of the time, has no appetite and finds difficulty in taking all her tablets. • Has made it clear that she would like to die at home in her own bed.
 If You were in this position, what would you expect from staff looking after you ? (helpful to think about Knowledge, Skills and attitudes)
If You were in this position, what would you expect from staff looking after you ? (helpful to think about Knowledge, Skills and attitudes)
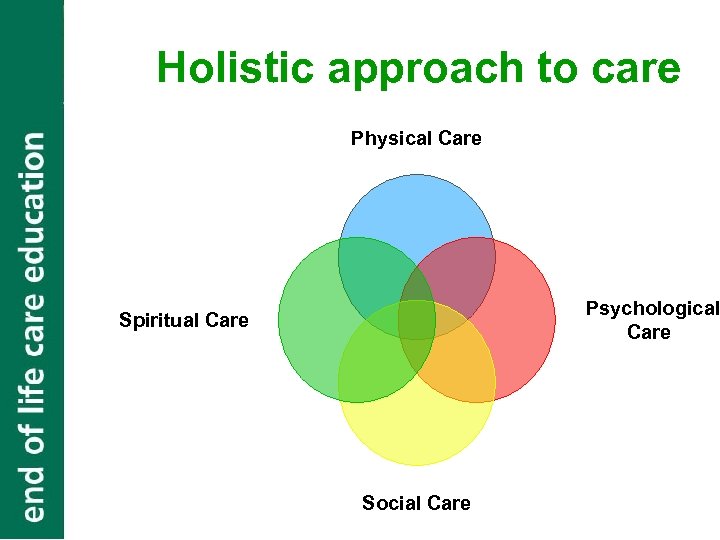 Holistic approach to care Physical Care Psychological Care Spiritual Care Social Care
Holistic approach to care Physical Care Psychological Care Spiritual Care Social Care
 Supporting Joyce… • Small group work
Supporting Joyce… • Small group work
 What do you think may help Joyce remain at home?
What do you think may help Joyce remain at home?
 What might help Joyce remain at home … • Making her wishes known to her family and professionals – Advanced Care Plan • Discussion of preferred place of death with healthcare professionals. • Ensure that Joyce is included on the Gold Standards Framework (GSF) register at her GP practice (Thomas, 2005). • Healthcare professionals have an agreed plan of how to manage her worsening breathlessness • Increased care package including Carers Allowance & Continuing Health Care funding • Involvement of specialist palliative care nurses • Hospice at Home • Having a written statement of her wishes such as an ‘Advanced Decision to Refuse Treatment’
What might help Joyce remain at home … • Making her wishes known to her family and professionals – Advanced Care Plan • Discussion of preferred place of death with healthcare professionals. • Ensure that Joyce is included on the Gold Standards Framework (GSF) register at her GP practice (Thomas, 2005). • Healthcare professionals have an agreed plan of how to manage her worsening breathlessness • Increased care package including Carers Allowance & Continuing Health Care funding • Involvement of specialist palliative care nurses • Hospice at Home • Having a written statement of her wishes such as an ‘Advanced Decision to Refuse Treatment’
 Bereavement Care Joyce dies peacefully with her family near a few days later. What may help the family at this time?
Bereavement Care Joyce dies peacefully with her family near a few days later. What may help the family at this time?
 • • Acknowledgement of what’s happened Empathy & honest communication Written & practical information Contact details of who can help now and later
• • Acknowledgement of what’s happened Empathy & honest communication Written & practical information Contact details of who can help now and later
 Reflective Learning One thing that you will take away from this morning that may change your practice
Reflective Learning One thing that you will take away from this morning that may change your practice
 Where next? • Further training within the county http: //www. gloucestershireccg. nhs. uk/? page_id=176 • • Calendar of events (via website above) E learning www. e-elca Shadowing other staff Personal reflection
Where next? • Further training within the county http: //www. gloucestershireccg. nhs. uk/? page_id=176 • • Calendar of events (via website above) E learning www. e-elca Shadowing other staff Personal reflection
 Summary & Evaluation • • • Final Questions? Revisit objectives and hopes Evaluation Handouts Certificate of attendance
Summary & Evaluation • • • Final Questions? Revisit objectives and hopes Evaluation Handouts Certificate of attendance
 References Department of Health 2008. Advanced Decisions to Refuse Treatment The National Council for Palliative Care Department of Health 2008. End Of Life Care Strategy. London: Crown Publications NHS 2008 National End of Life Care Programme. Advanced Care Planning. University of Nottingham The Gold Standards Framework; the Liverpool Care Pathway; the Preferred Priorities for Care tool: see www. endoflifecareforadults. nhs. uk WHO 2008. WHO Definition of Palliative Care Available at: www. who. int/cancer/palliative/definition/en
References Department of Health 2008. Advanced Decisions to Refuse Treatment The National Council for Palliative Care Department of Health 2008. End Of Life Care Strategy. London: Crown Publications NHS 2008 National End of Life Care Programme. Advanced Care Planning. University of Nottingham The Gold Standards Framework; the Liverpool Care Pathway; the Preferred Priorities for Care tool: see www. endoflifecareforadults. nhs. uk WHO 2008. WHO Definition of Palliative Care Available at: www. who. int/cancer/palliative/definition/en
 Lunchtime- please be back for 1 pm
Lunchtime- please be back for 1 pm


