 Encryption Nathan Helton University of Tulsa, Oklahoma
Encryption Nathan Helton University of Tulsa, Oklahoma
 What Is Encryption • Process of transforming information using an algorithm to make it unreadable to anyone except those possessing special knowledge or a key.
What Is Encryption • Process of transforming information using an algorithm to make it unreadable to anyone except those possessing special knowledge or a key.
 Why Encryption? • Helps protects user’s information from malicious people/processes. • Can protect confidentiality • Can protect integrity
Why Encryption? • Helps protects user’s information from malicious people/processes. • Can protect confidentiality • Can protect integrity
 How is Encryption Used • In the News: – Barracuda Networks • MD 5 salted
How is Encryption Used • In the News: – Barracuda Networks • MD 5 salted
 How is Encryption Used • In the News: – i. Phone • HW Encryption
How is Encryption Used • In the News: – i. Phone • HW Encryption
 How is Encryption Used • In the News: – Somebody messed with Texas • Public Server
How is Encryption Used • In the News: – Somebody messed with Texas • Public Server
 Simplistic Concepts • Steganography – “hiding in plain sight” – History – Images • Substitution / Replacement – Value Specific – Ex. Newspaper Game • Given a few characters and able to resolve the msg • Transposition – Location Specific
Simplistic Concepts • Steganography – “hiding in plain sight” – History – Images • Substitution / Replacement – Value Specific – Ex. Newspaper Game • Given a few characters and able to resolve the msg • Transposition – Location Specific
 Common Encryption Algorithms • SSL / TLS – Symmetric Key • RSA – Factorization and Asymmetric Key • AES – Transposition and Symmetric Key
Common Encryption Algorithms • SSL / TLS – Symmetric Key • RSA – Factorization and Asymmetric Key • AES – Transposition and Symmetric Key
 AES • Key Expansion • Initial Round • Rounds • Final Round – Sub. Bytes – Shift. Rows – Add. Round. Key
AES • Key Expansion • Initial Round • Rounds • Final Round – Sub. Bytes – Shift. Rows – Add. Round. Key
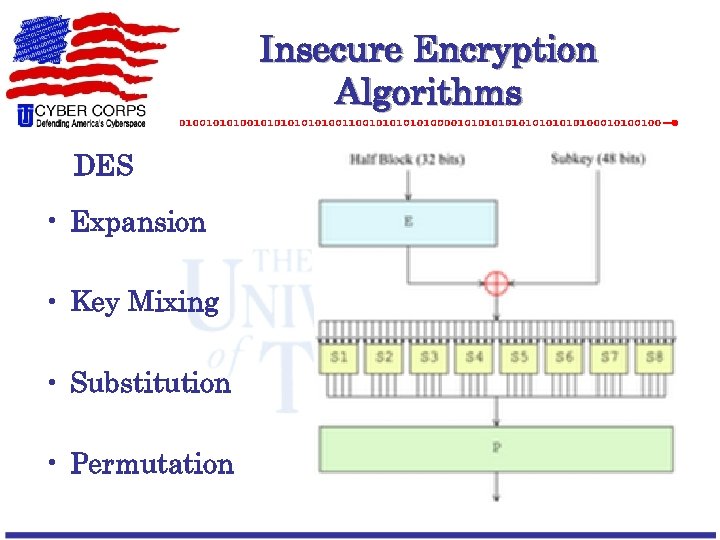 Insecure Encryption Algorithms DES • Expansion • Key Mixing • Substitution • Permutation
Insecure Encryption Algorithms DES • Expansion • Key Mixing • Substitution • Permutation
 Encryption Problems
Encryption Problems
 Encryption Problems • Constantly updating and evolving – Testing, Vulnerability Analysis Cycle • Not 100% effective • SSL Certificate Theft Example • The Human Factor
Encryption Problems • Constantly updating and evolving – Testing, Vulnerability Analysis Cycle • Not 100% effective • SSL Certificate Theft Example • The Human Factor
 Encryption and SSAC • Policies – CIA – Ex. Wi. Fi
Encryption and SSAC • Policies – CIA – Ex. Wi. Fi
 General Encryption Policy Questions • Is it allowable for a employee to encrypt their data? – Can they be forced to reveal the encryption key? Upon termination? • What type of encryption is to be used? – The latest encryption? – The most secure? – The most tested? • Should network traffic be encrypted at all times? • Should Wi-Fi be encrypted?
General Encryption Policy Questions • Is it allowable for a employee to encrypt their data? – Can they be forced to reveal the encryption key? Upon termination? • What type of encryption is to be used? – The latest encryption? – The most secure? – The most tested? • Should network traffic be encrypted at all times? • Should Wi-Fi be encrypted?
 Encryption Misunderstood • Outdated • According to the CSI Survey in 2008 – 71% encrypted traffic during transit – 53% encrypted stored data.
Encryption Misunderstood • Outdated • According to the CSI Survey in 2008 – 71% encrypted traffic during transit – 53% encrypted stored data.
 Not Just Computers Keyless Entry on Cars • Most popular version is the Kee. Loq • Non-Linear Feedback Shift Register (NLFSR) algorithm used • Uses a 64 bit key and a 32 bit block. • Most systems are networked inside the car. – IE. Sound system links to the engine control unit • Serious flaws exist to bypass the encryption. – Side-channel attack • Works on all keyless entry devices that use keyloq
Not Just Computers Keyless Entry on Cars • Most popular version is the Kee. Loq • Non-Linear Feedback Shift Register (NLFSR) algorithm used • Uses a 64 bit key and a 32 bit block. • Most systems are networked inside the car. – IE. Sound system links to the engine control unit • Serious flaws exist to bypass the encryption. – Side-channel attack • Works on all keyless entry devices that use keyloq
 The Future of Encryption • Bluetooth – Is stronger encryption needed? • Ex. Wireless mouse, hands-free for cell phones • RFID – Currently being pursued • Emerging Technologies – Also in conjunction with other methods (Biometrics)
The Future of Encryption • Bluetooth – Is stronger encryption needed? • Ex. Wireless mouse, hands-free for cell phones • RFID – Currently being pursued • Emerging Technologies – Also in conjunction with other methods (Biometrics)
 References • Researches say they’ve hacked car door locks – http: //redtape. msnbc. com/2007/08/researchers-say. html • How to steal cars (Keeloq) – http: //www. cosic. esat. kuleuven. be/keeloq-rump. pdf • Physical Cryptanalysis of Kee. Loq Code Hopping Applications – http: //eprint. iacr. org/2008/058. pdf • Policy Based Email Encryption Best Practices – http: //www. securityweek. com/best-practices-policy-basedemail-encryption
References • Researches say they’ve hacked car door locks – http: //redtape. msnbc. com/2007/08/researchers-say. html • How to steal cars (Keeloq) – http: //www. cosic. esat. kuleuven. be/keeloq-rump. pdf • Physical Cryptanalysis of Kee. Loq Code Hopping Applications – http: //eprint. iacr. org/2008/058. pdf • Policy Based Email Encryption Best Practices – http: //www. securityweek. com/best-practices-policy-basedemail-encryption