bf0df01b8c08dca281e02f83a44c2379.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25

ENCODING DIRECTIONS IN UPPER KUSKOKWIM ATHABASKAN: A CASE STUDY IN FIELD ETHNOLINGUISTICS Andrej A. Kibrik (aakibrik@gmail. com) Field Linguistics Conference Moscow, October 2009 1
2

Basic information about Upper Kuskokwim Athabaskan (UKA) § About 25 speakers left out of the population of § § § about 200 Most speakers reside in the village of Nikolai Actual use of UKA – in two or three households Prior work – Collins and Petruska 1979 Kibrik’s field trips in 1997, 2001, and 2009 As in other Athabaskan: § polysynthesis § highly complex verb morphology and morphophonemics 3

4

Welcome to Nikolai 5

Field work environment in Nikolai § Very few speakers § Very little motivation to do linguistic work § Very expensive § But very nice and hospitable people (generally) 6

Domain under consideration § Organization of spatial representation § Directional adverbs § Dimensional directionals • Riverine orientation • Elevational orientation 7

Data § Natural discourse recordings (transcribed) § § § Folk stories Personal stories Conversation (pre-arranged) Interview at school In all – about 8 hours of talk § Elicited examples 8

Abundance of directionals and locatives in discourse noygi digheloye hidenin ghelheŒ yats’in nehwdadidził ts’eŒ uphill mountain slope perhaps other. side brush. was. piled. up and notsints’eŒ nehulkanh ts’eŒ degheneŒ downhill they. were. pushing. earth Comp he. used. to. say yiŒots’ digheloye denin yihw hulkanh from. uphill mountain slope there they. ploughed. out <…> nodigw hwk’oy hwts’inh noŒin yotsin hidenin hwdinelkanh<…> uphill ridge from further downhill slope it. was. leveled. out 9
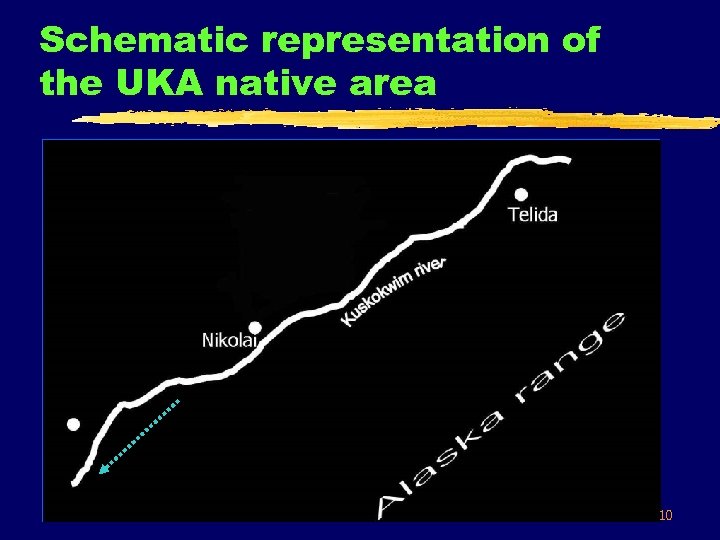
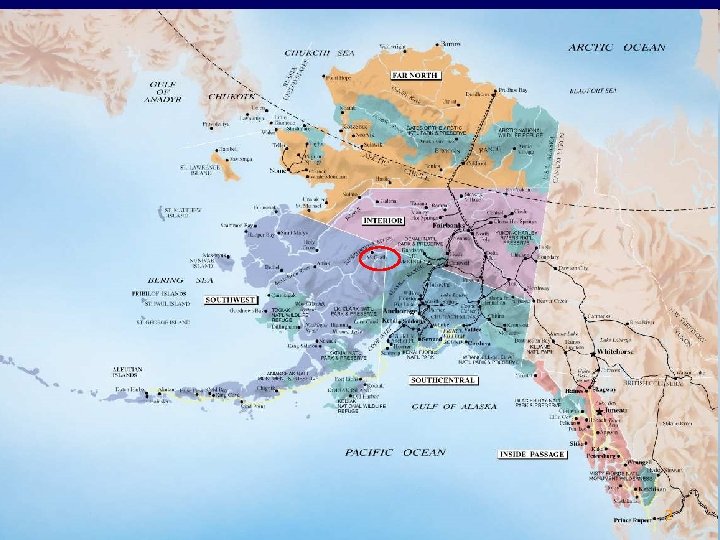
Schematic representation of the UKA native area 10

Riverine orientation: upriver vs. downriver § Roots: § -n- ‘upriver’ § -d- ‘downriver’ § Basic examples § y-o-n-aŒ Pref-upriver-Id § n-o-d-o-ts’ tekash Pref-downriver-Id-El you. paddle ‘Come this way (by boat, from downriver)’ zido ‘He lives upriver’ he. lives 11

Elevational orientation: uphill vs. downhill § Roots: § -n(w)g- ‘uphill’ § -ts- ‘downhill’ § Basic examples: § n-o-ts-in Pref-downhill-Id ‘I will go downhill’ § minh y-o-ng-w-t lake Pref-uphill-Id-Punct ‘The lake is up there’ tighisyoł I. will. go 12

Deictic orientation § X is at the river bank, Y is away from the river: § X speaks to Y: § n-o-ng-i Pref-uphill-Id tighisyoł I. will. go ‘I will go uphill’ § Y speaks to X: § y-o-ts-ets’ teyosh Pref-downhill-El you. go ‘Come here (from downhill)’ 13
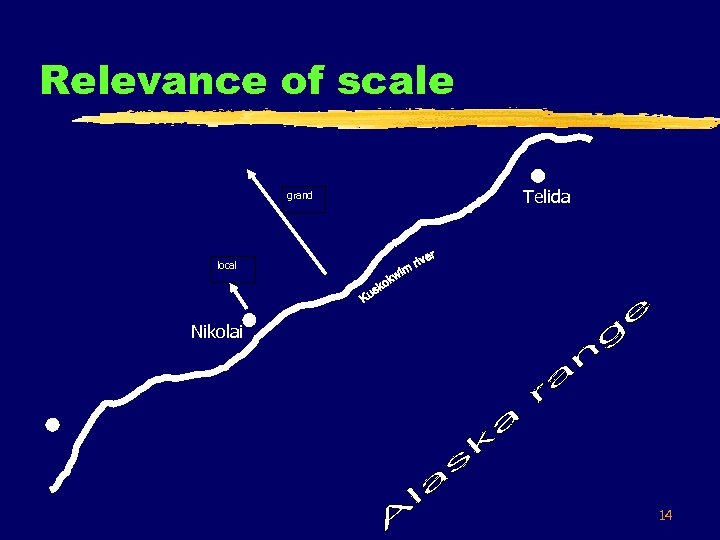
Relevance of scale grand Telida local Nikolai 14

Local vs. grand scale § § Local scale: y-o-ng-i sikayih Pref-uphill-Id my. house ‘I will go to my house’ § § Grand scale: dotron’ n-o-ts-in nonot’wh raven Pref-downhill-Id it. flies ‘A raven flies away from the mountains’ hi-ts’eŒ Ar-to notighisdoł I. will. go 15
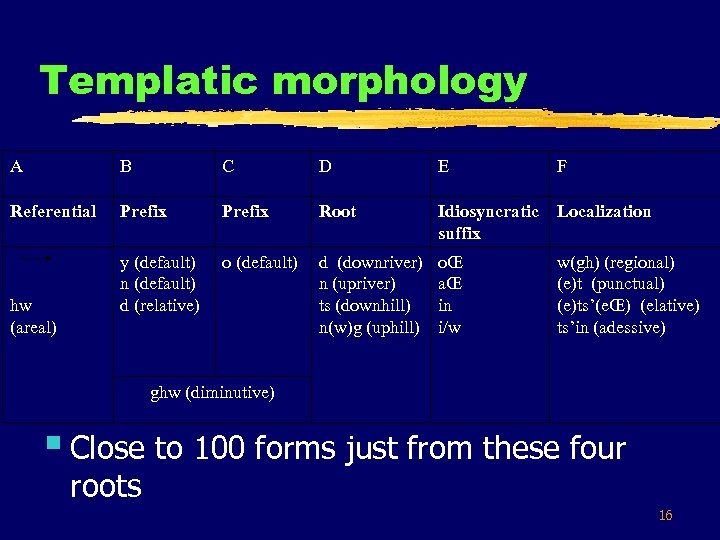
Templatic morphology A B C D E F Referential Prefix Root Idiosyncratic suffix Localization y (default) n (default) d (relative) o (default) d (downriver) n (upriver) ts (downhill) n(w)g (uphill) oŒ aŒ in i/w w(gh) (regional) (e)t (punctual) (e)ts’(eŒ) (elative) ts’in (adessive) hw (areal) ghw (diminutive) § Close to 100 forms just from these four roots 16

Examples of meaningful affixes § sichila sungha ghw-ts-et zido my. younger. brother my. older. brother dim-downhill-punct he. lives ‘My younger brother lives a little below my older brother’ § n-o-nwh-ts’eŒ tighisyoł pref-uphill-el I. will. go ‘I will go down (from an elevation)’ § y-o-n-wgh noghimał pref-upriver-reg it. is. swimming. across ‘It is swimming upriver across the river’ 17

Conclusions § Dimensional directionals display a remarkable § § § variety of forms They are semantically and morphologically highly complex They, as well as other types of directionals, are highly abundant in discourse Specification of directions and locations is a hallmark of UKA ethnic cognitive representation and constitutes an important linguistic phenomenon in this language 18

Methodological comments § This kind of complex phenomena must be preferably explored with the help of best available consultants § Criteria: age; personal life experience; gender; general intelligence 19

Bobby Esai 20

Nick Alexia 21

TsenŒan! § Thanks to all speakers of Upper Kuskokwim, both § mentioned and unmentioned above Thanks to many individuals and organizations that helped to collect and process the data, in chronological order: § § § § § Michael Krauss James Kari Raymond Collins Alaska Native Language Center Fulbright Program Endangered Language Fund Bernard Comrie MPI for Evolutionary Anthropology, Leipzig Russian Foundation for the Humanities National Science Foundation 22

23

24

25
bf0df01b8c08dca281e02f83a44c2379.ppt