fe96e9bc9188a2dfc8f9acb3166e806b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25

Enabling Technologies for EC Requirements, Standards, Problems A Min Tjoa Vienna University of Technology tjoa@ifs. tuwien. ac. at http: //www. ifs. tuwien. ac. at/ifs Gerti Kappel Johannes Kepler University of Linz gerti@ifs. uni-linz. ac. at http: //www. ifs. uni-linz. ac. at XV. IFIP World Computer Congress Vienna/Budapest, 31. 8 -4. 9. 1998

Enabling Technologies for EC Outline n Introduction n Enabling Technologies for EC u Workflow Management Systems u Database Systems and Open Hypermedia Systems u Data Mining and OLAP u EDI n Conclusion © 1998 by IFS 2

Enabling Technologies for EC Introduction (1/3) Electronic Commerce n EC comprises all selling and buying activities on the Internet u u u n Businesses in virtually every sector of economy are beginning to use the Internet to u u u n commercial transactions between businesses retail sale of tangible goods digital delivery of goods and services, etc. manage supplier relationships streamline logistics and inventory reach new and existing customers, etc. According to a study of the International Data Corporation u u © 1998 by IFS $ 8 billion worth of business was transacted in 1997 that figure will grow to $ 333 billion by 2002 3

Enabling Technologies for EC Introduction (2/3) Requirements on EC Enabling Technologies n A major challenge is to identify appropriate enabling technologies for EC and to integrate them into a common application framework u n in this respect, the existence of standards constitutes an important selection criteria Numerous requirements origin from the unique nature of EC u u distributed, autonomous and heterogenous information sources vast amounts of hypermedia data a wide range of user‘s specialties and abilities various services which should be supported e. g. , suppliers search and negotiation, establishment of initial contracts, sales, pre - and post-sales support and secure electronic payment © 1998 by IFS 4
Enabling Technologies for EC Introduction (3/3) Exemplary EC Enabling Technologies Concerning. . . n Business process aspect of EC u n Pre-sales phase of EC u n Workflow Management Systems (WFMS) could serve as the backbone of EC business processes Database Systems (DBS) and Open Hypermedia Systems (OHS) could be employed for realizing electronic catalogues Post-sales phase of EC u © 1998 by IFS Data Mining and OLAP (Online Analytical Processing) Technology could be used to establish web usage tracking 5

Enabling Technologies for EC Outline n Introduction n Enabling Technologies for EC u Workflow Management Systems u Database Systems and Open Hypermedia Systems u Data Mining and OLAP u EDI n Conclusion © 1998 by IFS 6

Enabling Technologies for EC WFMS for EC Processes (1/3) n WFMS support the design, execution and monitoring of long -lasting business processes that typically involve u u u multiple activities, multiple collaborating persons, in a distributed environment n With respect to EC, WFMS can be seen as the glue between previously independently modelled business processes of different organizations, thereby realizing inter-organizational workflows n All phases of an EC business process ranging from pre-sales via sales to post-sales activities could be supported by WFMS © 1998 by IFS 7

Enabling Technologies for EC WFMS for EC Processes (2/3) Adaptability Requirement n EC processes, especially their pre-sales and post-sales phases, are to a certain extent unstructured and unpredictable u u n therefore, deviations from a predefined workflow type capturing a sequence of tasks should be allowed at runtime meanwhile, consistency and correctness of the whole business process has to be preserved EC processes have to adapt to rapid changes in the business environment u therefore, there is a need to dynamically reengineer and optimize the workflow type itself while possibly several workflow instances of that type are active © 1998 by IFS 8

Enabling Technologies for EC WFMS for EC Processes (3/3) Interoperability Requirement n EC workflows involve multiple, possibly heterogeneous and autonomous parties u n Different levels of interoperability should be supported u u n thus, interoperability between WFMS is of major concern tight coupling with strict synchronization needs loose coupling for the electronic exchange of business documents on the basis of protocols such as EDI or OTP Two standardization groups deal with these problems u u © 1998 by IFS the Workflow Management Coalition (Wf. MC) the Object Management Group (OMG) aims at integrating a workflow management facility into CORBA 9
Enabling Technologies for EC DBS and OHS for Electronic Catalogues (1/2) Electronic Product Data Management n Clients of EC systems should quickly and easily obtain all the product data needed to make informed purchase decisions n Many existing electronic product data is stored together with HTML commands in files u n this leads to problems concerning maintenance, consistency, concurrency and authorization DBS could be employed to support the consistent multi-user management of distributed hypermedia information u u u product data can be highly structured by means of the DB schema retrieval can be done by precise Boolean queries possibly based on the SQL standard many DBS support multimedia datatypes © 1998 by IFS 10
Enabling Technologies for EC DBS and OHS for Electronic Catalogues (2/2) Interoperability of OHS n Content providers and consumers should be enabled to easily locate and acquire whatever product data they desire from other catalogues n By means of the link server functionality of OHS, every link can perform arbitrary behavior on remote catalogues such as u u u n querying controlling access presenting the remote product data in context of the original local catalogue On the basis of standard protocols, similar or complementary products can be easier located in other catalogues u cf. , e. g. , the XML and RDF initiatives of the W 3 C consortium © 1998 by IFS 11
Enabling Technologies for EC Data Mining and OLAP for Web Usage Tracking n The analysis of how users are accessing a Web site is critical for u u u n User access patterns can be discovered out of Web transactions by means of data mining techniques such as u u u n determining effective marketing strategies generating user profiles for personalizing a site optimizing the logical structure of a site path analysis association rules classification rules The analysis of access patterns may be served by OLAP techniques © 1998 by IFS 12
Enabling Technologies for EC Interfaces in EC - EDI n n Human - Human e. g. e-mail Human - Machine e. g. electronic forms (WWW) Machine - Human e. g. computer-generated e-mail Machine - Machine only EDI © 1998 by IFS 13
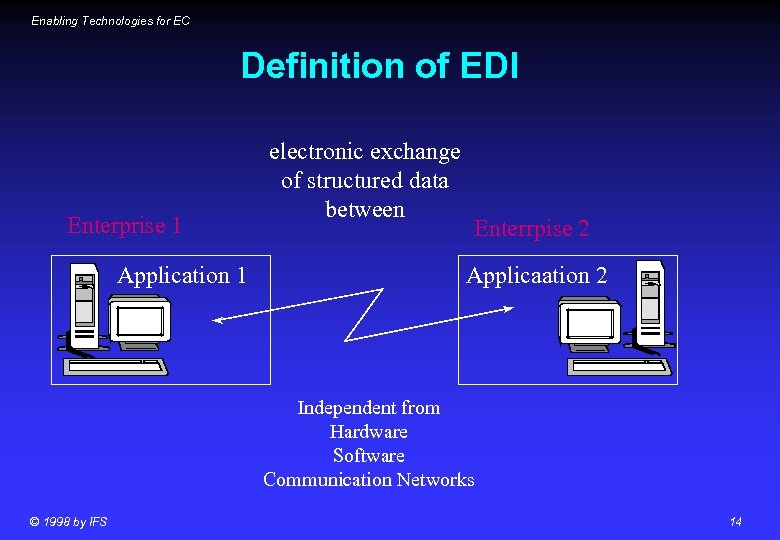
Enabling Technologies for EC Definition of EDI Enterprise 1 Application 1 electronic exchange of structured data between Enterrpise 2 Applicaation 2 Independent from Hardware Software Communication Networks © 1998 by IFS 14

Enabling Technologies for EC Definition of EDI … is the exchange of electronic business data between applications via a network based on a format which is understood by both (all) business partners © 1998 by IFS 15
Enabling Technologies for EC EDI Standard n Syntactic rules defining the allowed symbols and the sequence in which they may be used n Vocabulary of allowed words, Definition n Message design that structures the information in a defined sequence © 1998 by IFS 16
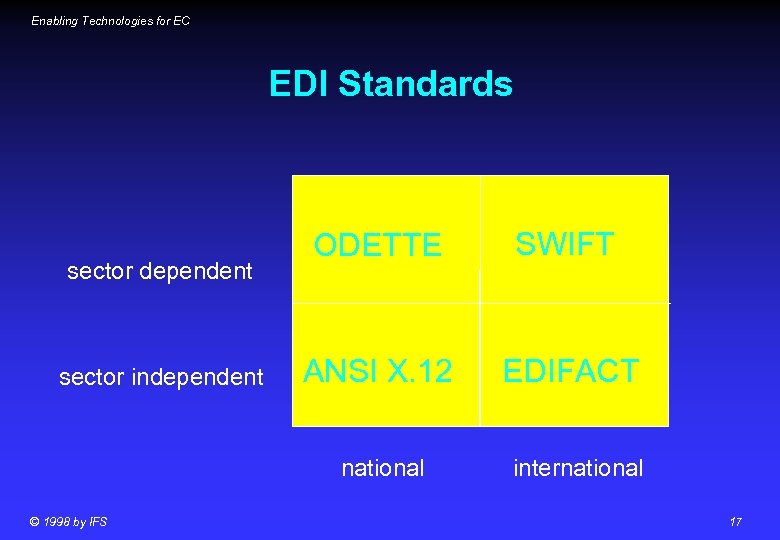
Enabling Technologies for EC EDI Standards sector dependent sector independent ODETTE SWIFT ANSI X. 12 EDIFACT national © 1998 by IFS international 17
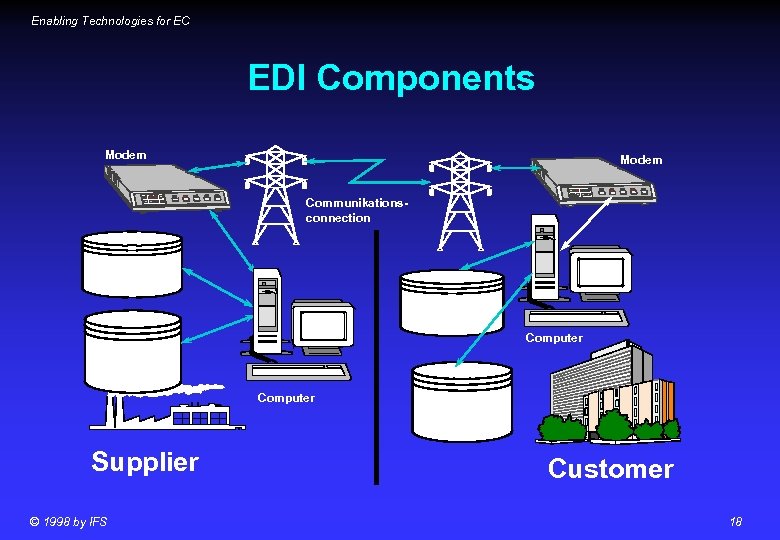
Enabling Technologies for EC EDI Components Modem Communikationsconnection Converter. Software Computer Mapping & Application Computer Supplier © 1998 by IFS Mapping & Application Customer 18
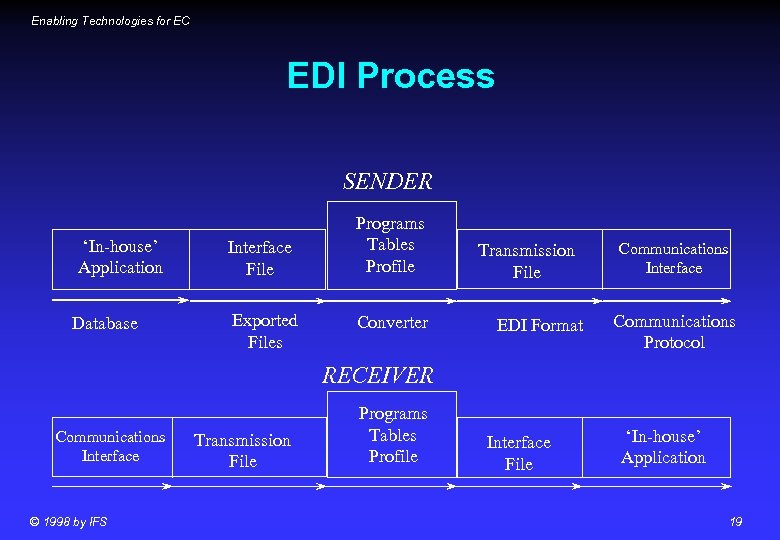
Enabling Technologies for EC EDI Process SENDER ‘In-house’ Application Database Interface File Exported Files Programs Tables Profile Converter Transmission File EDI Format Communications Interface Communications Protocol RECEIVER Communications Interface © 1998 by IFS Transmission File Programs Tables Profile Interface File ‘In-house’ Application 19

Enabling Technologies for EC Advantages of EDI n n n n More efficient use of personnel Faster transactions - shorter transaction time Recent, quickly accesible information across the whole enterprise Better planning Just-in-Time (JIT) Production Smaller amount of merchandise in the warehouses Smaller amount of interest © 1998 by IFS 20

Enabling Technologies for EC Summary n EC can largely benefit from already existing enabling technologies n A major challenge in successfully designing EC applications is to identify and combine these technologies n Thereby, standardization efforts play a major role © 1998 by IFS 21

Enabling Technologies for EC „The nice thing about standards. . . “ n n n . . . there are so many of them to choose from. . . by the time things become standards, they‘re obsolete. . . real standards are set by the market, not committees Standards - the only way that everyone can play tragedy of the common „where do you want to go today? “ © 1998 by IFS [Larry Masinter, Tutorial at the 7 th WWW Conference, April 1998] 22

Enabling Technologies for EC Standards follow Innovation, Standardization, Divergence Convergence © 1998 by IFS [Larry Masinter, Tutorial at the 7 th WWW Conference, April 1998] 23
Enabling Technologies for EC Standards vs. Design n n Design u choose between alternatives (A, B, or C) u optimize function, performance, reliability Standard u choose one, some, all, „undefined“, „implementation dependent“, „discoverable“ u optimize flexibility, interoperability, politics, extensibility, enforced operation © 1998 by IFS [Larry Masinter, Tutorial at the 7 th WWW Conference, April 1998] 24

Enabling Technologies for EC Who writes (Web/EC) standards? n n Standard organizations Consortia Companies Individuals n n n © 1998 by IFS IETF W 3 C ISO IEEE ANSI [Larry Masinter, Tutorial at the 7 th WWW Conference, April 1998] 25
fe96e9bc9188a2dfc8f9acb3166e806b.ppt