5cf5ffabe247a7b9cd0d2d9148bf8d4d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 18

Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E South East Europe resources in EGEE and next steps Emanouil Atanassov, Todor Gurov, Vladimir Dimitrov - IPP-BAS, Bulgaria Ognjen Prnjat, Kostas Koumantaros, Ioannis Liabotis - GRNET, Greece www. eu-egee. org INFSO-RI-222667 Introduction to Grid Computing, EGEE and Bulgarian Grid Initiatives, Sofia, 8. 07. 2009

Overview Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E • • Organization of EGEE project Organization of EGEE SEE ROC Authorization/Authentication resources Information system resources Workload Management System resources Monitoring Tools Bulgarian sites in EGEE Conclusions INFSO-RI-222667 Introduction to Grid Computing, EGEE and Bulgarian Grid Initiatives, Sofia, 8. 07. 2009 2

Organization of the EGEE project Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E • • • The EGEE project brings together experts from 50 countries with the common aim of building on recent advances in Grid technology and developing a service Grid infrastructure which is available to scientists 24 hours-a-day. The project provides researchers in academia and industry with access to a production level Grid infrastructure, independent of their geographic location. The EGEE project also focuses on attracting a wide range of new users to the Grid. The EGEE III project is organized in 12 federations. Bulgaria is a member of the South Eastern Federation INFSO-RI-222667 Introduction to Grid Computing, EGEE and Bulgarian Grid Initiatives, Sofia, 8. 07. 2009 3
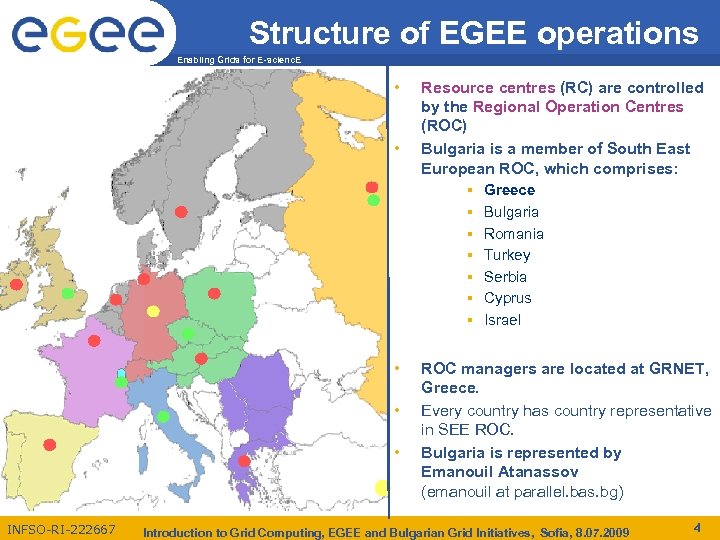
Structure of EGEE operations Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E • • • INFSO-RI-222667 Resource centres (RC) are controlled by the Regional Operation Centres (ROC) Bulgaria is a member of South East European ROC, which comprises: § Greece § Bulgaria § Romania § Turkey § Serbia § Cyprus § Israel ROC managers are located at GRNET, Greece. Every country has country representative in SEE ROC. Bulgaria is represented by Emanouil Atanassov (emanouil at parallel. bas. bg) Introduction to Grid Computing, EGEE and Bulgarian Grid Initiatives, Sofia, 8. 07. 2009 4
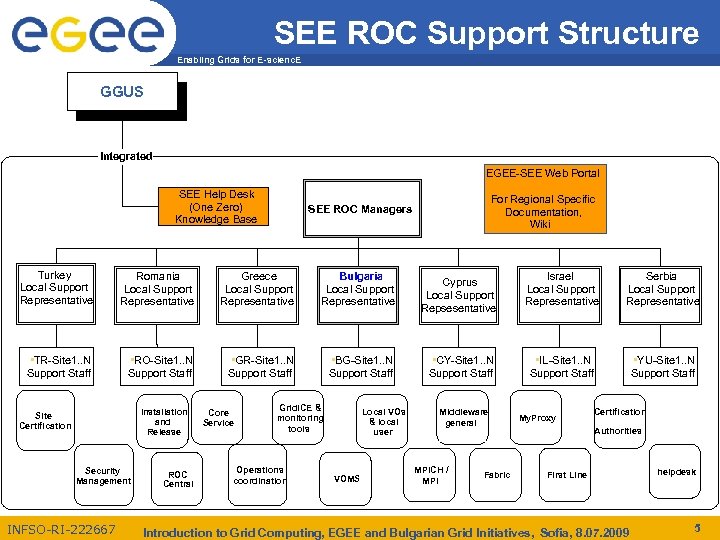
SEE ROC Support Structure Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E GGUS Integrated EGEE-SEE Web Portal SEE Help Desk (One Zero) Knowledge Base Turkey Local Support Representative Romania Local Support Representative Greece Local Support Representative Bulgaria Local Support Representative • TR-Site 1. . N Support Staff • RO-Site 1. . N Support Staff • GR-Site 1. . N Support Staff • BG-Site 1. . N Support Staff Installation and Release Site Certification Security Management INFSO-RI-222667 ROC Central Core Service For Regional Specific Documentation, Wiki SEE ROC Managers Grid. ICE & monitoring tools Operations coordination Local VOs & local user VOMS Cyprus Local Support Repsesentative • CY-Site 1. . N Support Staff Middleware general MPICH / MPI Fabric Israel Local Support Representative Serbia Local Support Representative • IL-Site 1. . N Support Staff • YU-Site 1. . N Support Staff My. Proxy Certification Authorities First Line Introduction to Grid Computing, EGEE and Bulgarian Grid Initiatives, Sofia, 8. 07. 2009 helpdesk 5

SEE ROC Support Structure Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E ØGlobal Grid User Support (GGUS): https: //gus. fzk. de ØRegional web site: http: //www. egee-see. org Ø Regional SEE helpdesk: http: //helpdesk. egee-see. org Ø SEE wiki pages: http: //wiki. egee-see. org Ø Country web site for Bulgaria: http: //www. grid. bas. bg Ø Country representative for Bulgaria: Emanouil Atanassov Ø Security contact for SEE: Christos Triantafyllidis, ctria at grid. auth. gr INFSO-RI-222667 Introduction to Grid Computing, EGEE and Bulgarian Grid Initiatives, Sofia, 8. 07. 2009 6

SEE ROC Authentication/Authorization resources Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E In order to access the Grid, every user needs a valid certificated from an accepted Certification Authority (CA), accredited by EUGrid. PMA (http: //www. eugridpma. org) Bulgarian Academic Certification Authority – BG. ACAD|CA, http: //ca. acad. bg A certificate request is created on a UI computer, using correct values for the organization’s name. Follow http: //ca. acad. bg/howto. html INFSO-RI-222667 Introduction to Grid Computing, EGEE and Bulgarian Grid Initiatives, Sofia, 8. 07. 2009 7

SEE ROC Authentication/Authorization resources Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E The certificate request is sent to the nearest RA person (Registration Authority) for Bulgaria (http: //ca. acad. bg/ra_list. html) and if approved, the user receives a certificate signed by BG. ACAD|CA. The certificate can be used for any Grid activity and access to restricted Grid related Web sites. See: http: //ca. acad. bg/policy. html and also man pkcs 12 on a Unix based User Interface machine (UI) INFSO-RI-222667 Introduction to Grid Computing, EGEE and Bulgarian Grid Initiatives, Sofia, 8. 07. 2009 8

SEE ROC Authentication/Authorization resources Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E After the user has a valid certificate, the next step is to request membership in the appropriate Virtual Organization (VO). A comprehensive list and contacts of existing EGEE-wide VOs can be obtained from: https: //cic. gridops. org/index. php? section=vo Bulgarian Virtual Organizations: biotech. grid. acad. bg bg-edu. grid. acad. bg new-energy-sources. grid. acad. bg national-heritage. grid. acad. bg Request for membership: https: //voms. ipp. acad. bg: 8443/voms/bg-edu. grid. acad. bg/Siblings. do INFSO-RI-222667 Introduction to Grid Computing, EGEE and Bulgarian Grid Initiatives, Sofia, 8. 07. 2009 9

SEE ROC Authentication/Authorization resources (contd. ) Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E • For users that can not locate an appropriate VO, we provide membership in SEE VO (a. k. a. “catch all VO”): https: //www. grid. auth. gr/services/voms/SEE/request. php • In order to join SEE VO the user must submit a description of the application that he or she is going to develop and/or use to the BG country representative in SEE ROC. INFSO-RI-222667 Introduction to Grid Computing, EGEE and Bulgarian Grid Initiatives, Sofia, 8. 07. 2009 10

SEE ROC Authentication/Authorization resources Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E • Upon approval of the request, the user joins the corresponding VO and can submit jobs and perform data management. • Users are advised to always use voms-proxy-init instead of grid-proxy-init command. • Example for SEE VO: • The VOMS server is located at: voms. grid. auth. gr The command voms-proxy-init –voms see uses automatically this VOMS server. The main myproxy server for SEE VO is located at myproxy. grid. auth. gr See: https: //www. grid. auth. gr/services/myproxy/user_guide. php Always check if the RB/WMS you are using works correctly with the My. Proxy server that you specify! INFSO-RI-222667 Introduction to Grid Computing, EGEE and Bulgarian Grid Initiatives, Sofia, 8. 07. 2009 11

SEE ROC Workload management and Information System resources Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E • In order to submit jobs in EGEE SEE sites, one can use: • The production WMS: wms. ipp. acad. bg • In order to locate resources in SEE ROC, one can use the BDII bdii. isabella. grnet. gr • Changing the BDII used on a UI (User Interface) is accomplished by editing the environment variable LCG_GFAL_INFOSYS in /etc/profile. d/lcgenv. sh and /etc/profile. d/lcgenv. csh • Example: export LCG_GFAL_INFOSYS=bdii. isabella. grnet. gr: 2170 Using the BDII for finding information about available resources: lcg-infosites –vo see ce – for computing elements lcg-infosites –vo see se – for storage resources lcg-infosistes –vo see lfc – the name of the LFC server for SEE VO INFSO-RI-222667 Introduction to Grid Computing, EGEE and Bulgarian Grid Initiatives, Sofia, 8. 07. 2009 12
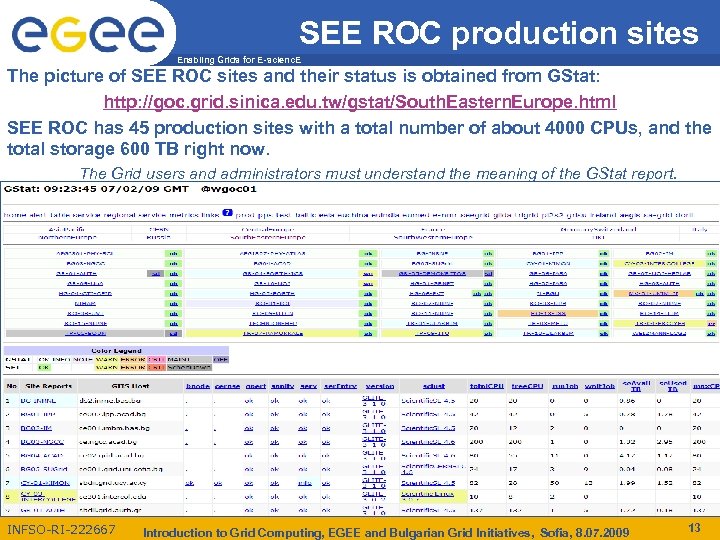
SEE ROC production sites Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E The picture of SEE ROC sites and their status is obtained from GStat: http: //goc. grid. sinica. edu. tw/gstat/South. Eastern. Europe. html SEE ROC has 45 production sites with a total number of about 4000 CPUs, and the total storage 600 TB right now. The Grid users and administrators must understand the meaning of the GStat report. INFSO-RI-222667 Introduction to Grid Computing, EGEE and Bulgarian Grid Initiatives, Sofia, 8. 07. 2009 13

Monitoring tools Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E • • GStat Grid. View Grid. ICE SEE Real Time Grid Monitor - INFSO-RI-222667 http: //goc. grid. sinica. edu. tw/gstat http: //gridview. cern. ch http: //mon. egee-see. org http: //gridportal. hep. ph. ic. ac. uk/rtm Introduction to Grid Computing, EGEE and Bulgarian Grid Initiatives, Sofia, 8. 07. 2009 14
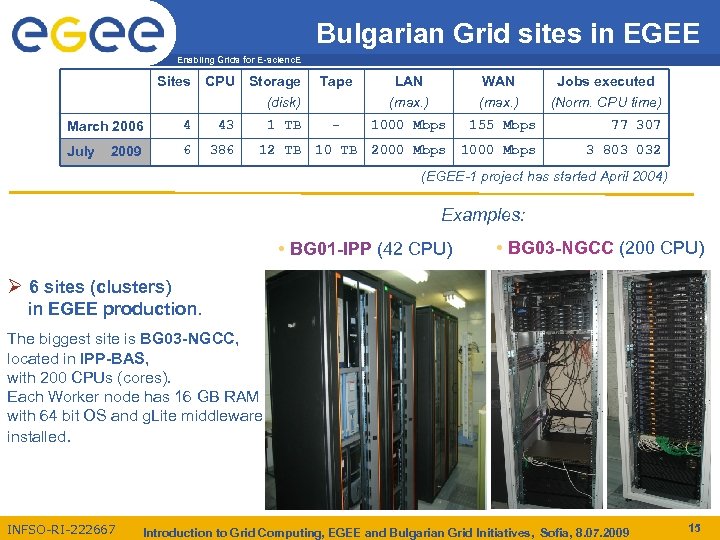
Bulgarian Grid sites in EGEE Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E Sites CPU Storage (disk) March 2006 4 43 1 TB July 6 386 12 TB 2009 Tape LAN (max. ) WAN (max. ) Jobs executed (Norm. CPU time) - 1000 Mbps 155 Mbps 77 307 10 TB 2000 Mbps 1000 Mbps 3 803 032 (EGEE-1 project has started April 2004) Examples: • BG 01 -IPP (42 CPU) • BG 03 -NGCC (200 CPU) Ø 6 sites (clusters) in EGEE production. The biggest site is BG 03 -NGCC, located in IPP-BAS, with 200 CPUs (cores). Each Worker node has 16 GB RAM with 64 bit OS and g. Lite middleware installed. INFSO-RI-222667 Introduction to Grid Computing, EGEE and Bulgarian Grid Initiatives, Sofia, 8. 07. 2009 15

Types of the Grid nodes Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E • • • • User Interface – provides user access to the Grid resources; Worker Node – basic building block, performs the computations; Computing Element – manages the received jobs inside the cluster; Workload Management System – manages the jobs between clusters; Berkerley Database Information Index – Information system; MON – Grid cluster monitoring; R-GMA – RDBMS for accounting; Storage Element (Castor, d. Cache, DPM) – reliable storage server; File Transfer Service – guaranteed fast file transfer; Logical File Catalogue – information about thedata files and their locations; AMGA – metadata file catalog; My. Proxy – storage for user certificates; HYDRA – encrypting data services; Web-portals – for easy access to the Grid resources; INFSO-RI-222667 Introduction to Grid Computing, EGEE and Bulgarian Grid Initiatives, Sofia, 8. 07. 2009 16

EGI and NGIs The future after EGEE-3 (2010) Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E European Grid Initiative (http: //web. eu-egi. eu) Objectives: ü Long-term sustainability of the European e-infrastructure; ü Coordinate the integration and interaction between NGIs; ü Production grid infrastructure for a wide range of scientific disciplines to link NGI; ü Global services and support that complement and/or coordinate national services (Authentication, VO-support, security, etc. ); ü Coordinate the Grid middleware development; ü Advise National and European Funding Agencies in establishing their programmes for future software developments based on agreed user needs and development standards; ü Integrate, test, validate and package software from leading grid middleware development projects and make it widely available; ü Provide documentation and training material; ü Take into account developments made by national e-science projects which were aimed at supporting diverse communities; ü Link the European infrastructure with similar infrastructures elsewhere; ü Promote grid interface standards, in consultation with relevant standards organizations; ü Collaborate closely with industry. INFSO-RI-222667 Introduction to Grid Computing, EGEE and Bulgarian Grid Initiatives, Sofia, 8. 07. 2009 17

Questions? Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E ? INFSO-RI-222667 Introduction to Grid Computing, EGEE and Bulgarian Grid Initiatives, Sofia, 8. 07. 2009 18
5cf5ffabe247a7b9cd0d2d9148bf8d4d.ppt