1d1749044d8f1bd73c0e894f4f23118e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 23

Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E SA 2 IPv 6 related activities overall status and on going activities Etienne Dublé - CNRS/UREC EGEE SA 2 Mario Reale – GARR EGEE SA 2 Thursday, March 26, 2009 – Rome – SA 2 All Hands Meeting www. eu-egee. org EGEE-III INFSO-RI-222667 EGEE and g. Lite are registered trademarks

content Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E • EGEE II achievements regarding IPV 6 (summary) • EGEE III achievements regarding IPV 6 (detailed) • Current status of the IPv 6 compliance of g. Lite • Next steps www. eu-egee. org EGEE-III INFSO-RI-222667 EGEE and g. Lite are registered trademarks

Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E EGEE II achievements regarding IPv 6 Summary of EGEE II SA 2 IPv 6 past work and collaborations EGEE-III INFSO-RI-222667 3

Main achievements in EGEE II Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E • Definition of a methodology for IPv 6 transition • Collaboration with ETICS (initially also with Eu. China. GRID): set up an ETICS pilot project called glite_IPv 6: – – Goal: automate IPv 6 compliance testing of g. Lite packages A static code checker was developed in order to test the packages Results are displayed as the “IPv 6 metric” on ETICS website A demonstration of automated IPv 6 regression tests was also set up • Dissemination, including programming tutorials • Development of a first IPv 6 -compliant g. Lite node: the BDII • Building of a testbed in Paris, which allowed to show – The NAT-PT protocol usage (ex. with the ported BDII) – The dual-stack environment usage (ex. with the ported BDII) • Building of a testbed in Rome • Report about IPv 6 compliance of g. Lite external dependencies EGEE-III INFSO-RI-222667 4

Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E EGEE III achievements regarding IPv 6 EGEE III SA 2 IPv 6 work and collaborations EGEE-III INFSO-RI-222667 5

A distributed IPv 6 Testbed Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E • Follow-up of the testbeds built during EGEE II • Goals: – Test IPv 6 compliance of g. Lite components – Demonstrate current g. Lite IPv 6 features – Future: IPv 4 non-regression tests (collaboration with SA 3) • One site in Rome (GARR), one site in Paris (UREC) • Site-to-site IPv 6 connectivity (through UREC / RAP / RENATER / GEANT / GARR networks) • Many relevant deployment modules installed and configured: VOMS, UI, WMS, lcg-CE, CREAM, WNs, DPM-SE, LFC, PX, BDII, LB • All nodes are dual-stack EGEE-III INFSO-RI-222667 6
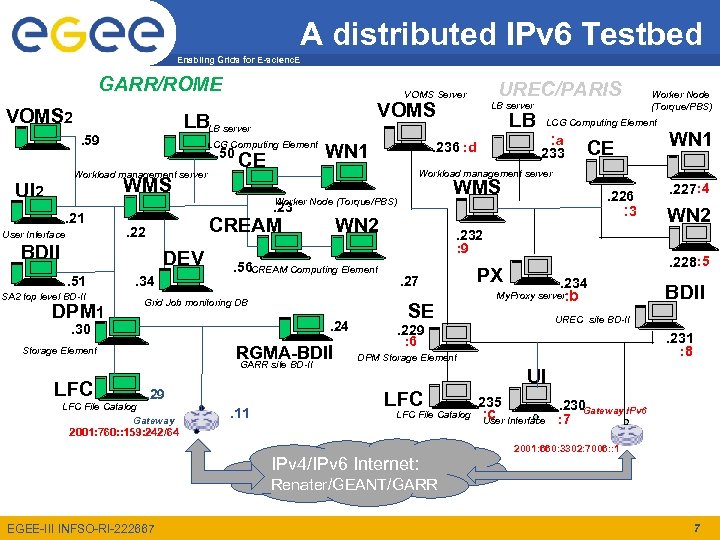
A distributed IPv 6 Testbed Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E GARR/ROME VOMS 2 LCG Computing Element Workload management server . 50 CE WMS UI 2 . 21 User Interface DEV SA 2 top level BD-II DPM 1 . 34 . 23 . 56 CREAM Computing Element LFC . 24 RGMA-BDII GARR site BD-II. 29 LFC File Catalog Gateway . 11 : a. 233 CE. 226 : 3 . 232 : 9 . 27 SE Worker Node (Torque/PBS) LCG Computing Element WMS WN 2 Grid Job monitoring DB Storage Element LB Workload management server Worker Node (Torque/PBS) . 30 LB server . 236 : d WN 1 CREAM . 22 BDII. 51 VOMS LBLB server . 59 UREC/PARIS VOMS Server WN 1. 227: 4 WN 2. 228: 5 PX . 234 : b My. Proxy server BDII UREC site BD-II . 229 . 231 : 6 : 8 DPM Storage Element UI LFC File Catalog 2001: 760: : 159: 242/64 IPv 4/IPv 6 Internet: . 235 . 230 Gateway IPv 6 : c Interface : 7 User 2001: 660: 3302: 7006: : 1 Renater/GEANT/GARR EGEE-III INFSO-RI-222667 7

IPv 6 bug reporting Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E • Analysis of the g. Lite source code – Using the IPv 6 metric (IPv 6 code checker) in ETICS – Around 110 bugs on non-compliant function calls and data structures in the code reported • This analysis effectively incited developers to work on IPv 6, and is a good metric regarding the work needed on this subject. EGEE-III INFSO-RI-222667 8
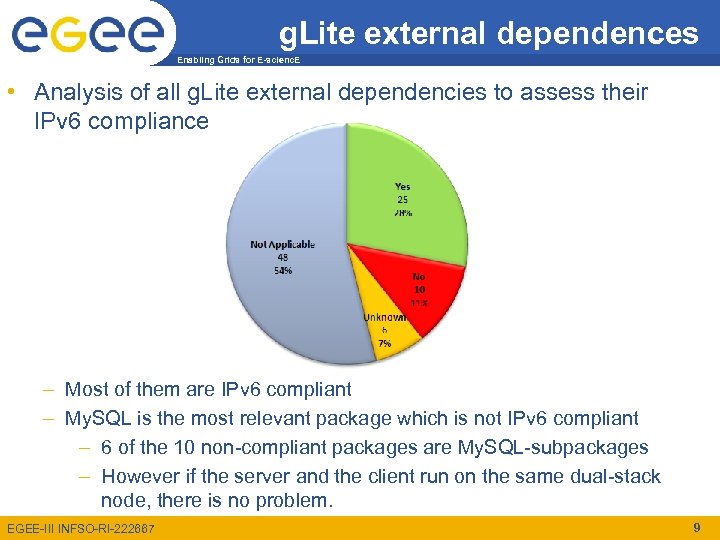
g. Lite external dependences Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E • Analysis of all g. Lite external dependencies to assess their IPv 6 compliance – Most of them are IPv 6 compliant – My. SQL is the most relevant package which is not IPv 6 compliant – 6 of the 10 non-compliant packages are My. SQL-subpackages – However if the server and the client run on the same dual-stack node, there is no problem. EGEE-III INFSO-RI-222667 9

Other Reports Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E • IPv 6 Programming methods: – Guide to IPv 6 compliant programming in C/C++, Java, Python and Perl: Provides a sample TCP client and server for each programming language Explains advantages/drawbacks/limitations of each language regarding IPv 6 • IPv 6 Testing methods: – Report explaining how to test if a TCP server is IPv 6 compliant • IPv 6 Test reports: – Selected IPv 6 compliance studies for specific packages: g. SOAP Axis and Axis 2 Boost: asio grid. FTP Python. ZSI Perl. SOAPLite – Assessment of the IPv 6 compliance of g. Lite components: DPM & LFC EGEE-III INFSO-RI-222667 10

IPv 6 CARE Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E • Developed by SA 2 • Behavior: – It monitors the execution of programs and detects networking function calls The diagnosis generated helps to assess IPv 6 compliance • Very generic: you can use it for any program, even if you don’t have the source code • Available on sourceforge: http: //sourceforge. net/projects/ipv 6 -care EGEE-III INFSO-RI-222667 11

IPv 6 CARE: Usage example Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E • Usage example: we want to test the “telnet” program – We run the program as usual except that we prefix the command by “ipv 6_care check”: $ ipv 6_care check -v telnet localhost 9876 IPV 6 CARE detected: inet_addr() with [ cp=localhost ] IPV 6 CARE detected: gethostbyname() with [ name=localhost ] IPV 6 CARE detected: inet_ntoa() with [ in=127. 0. 0. 1 ] Trying 127. 0. 0. 1. . . IPV 6 CARE detected: socket() with [ domain=AF_INET type=SOCK_STREAM protocol=ip ] IPV 6 CARE detected: connect() with [ socket=3 address. ip=127. 0. 0. 1 address. port=9876 ] telnet: Unable to connect to remote host: Connection refused ---------------------------------------IPv 6 diagnosis for 'telnet localhost 9876' was generated in: /tmp/ipv 6_diagnosis/telnet/by_pid/pid_6541 ---------------------------------------$ – The standard behavior of ‘telnet’ is not affected (it works as it should, see its output in black). – The diagnosis (network function calls log file, non-IPv 6 compliant calls detected, etc. ) can be reviewed in the mentioned directory. EGEE-III INFSO-RI-222667 12
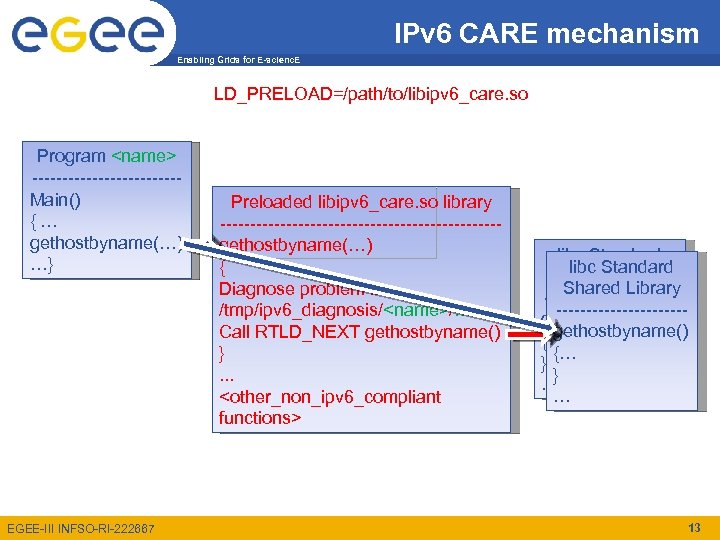
IPv 6 CARE mechanism Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E LD_PRELOAD=/path/to/libipv 6_care. so Program <name> ------------Main() {… gethostbyname(…) …} EGEE-III INFSO-RI-222667 Preloaded libipv 6_care. so library -----------------------gethostbyname(…) { Diagnose problem in /tmp/ipv 6_diagnosis/<name>/… Call RTLD_NEXT gethostbyname() }. . . <other_non_ipv 6_compliant functions> libc Standard Shared Library ---------------------gethostbyname() {… {… } } … … 13

Dissemination Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E • EGEE 08 conference, Istanbul – IPv 6 session targeted at g. Lite developers and testers • JRA 1 / SA 3 All-hands meeting, Prague – “IPv 6 Testing” session IPv 6 basics needed by developers & testers IPv 6 methods & tools for testing – “IPv 6 Programming” session Tutorial C/C++, Perl, Python, Java High-level programming topic • EGEE UF / OGF, Catania – IPv 6 session Main work done / to be done about IPv 6 in g. Lite and other middlewares Point of view of the European Commission and of RIPE about IPv 6 – A demo booth An automatic demo script running on the testbed, showing the current IPv 6 features of g. Lite (see next slide) A poster “g. Lite IPv 6 compliance” A poster “IPv 6 compliance testing: dedicated tools” An explanatory video EGEE-III INFSO-RI-222667

Dissemination: the demo script Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E • Automatic script sending commands in ssh sessions, running in the testbed environment • Content of the script: most noticeable current IPv 6 features of g. Lite – Show that g. Lite is working properly in a dual-stack environment (i. e. when IPv 6 is enabled on nodes) by submitting jobs and checking that they are run correctly – Show current IPv 6 compliant services Show that the prototype version of the BDII (Information System) is able to use IPv 6 Show that DPM & LFC (Storage Element) can be used over IPv 6 EGEE-III INFSO-RI-222667

Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E Current status of the IPv 6 compliance of g. Lite How far are we from having g. Lite fully IPv 6 compliant ? EGEE-III INFSO-RI-222667 16
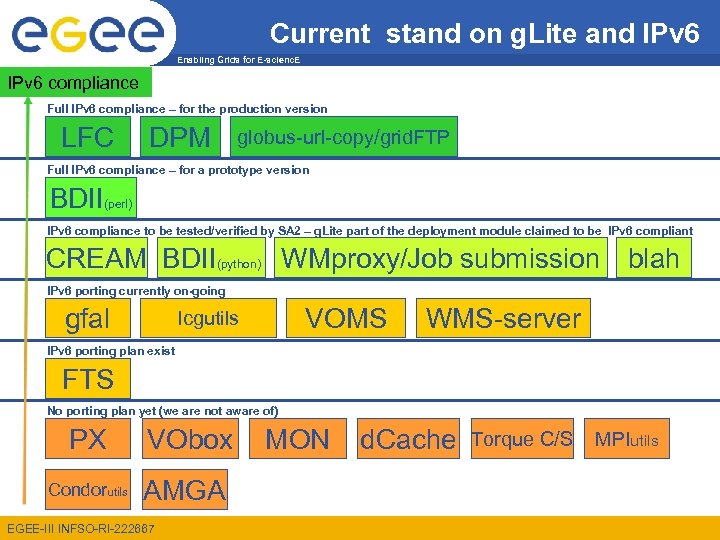
Current stand on g. Lite and IPv 6 Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E IPv 6 compliance Full IPv 6 compliance – for the production version LFC DPM globus-url-copy/grid. FTP Full IPv 6 compliance – for a prototype version BDII(perl) IPv 6 compliance to be tested/verified by SA 2 – g. Lite part of the deployment module claimed to be IPv 6 compliant CREAM BDII(python) WMproxy/Job submission blah IPv 6 porting currently on-going gfal VOMS lcgutils WMS-server IPv 6 porting plan exist FTS No porting plan yet (we are not aware of) PX Condorutils VObox AMGA EGEE-III INFSO-RI-222667 MON d. Cache Torque C/S MPIutils
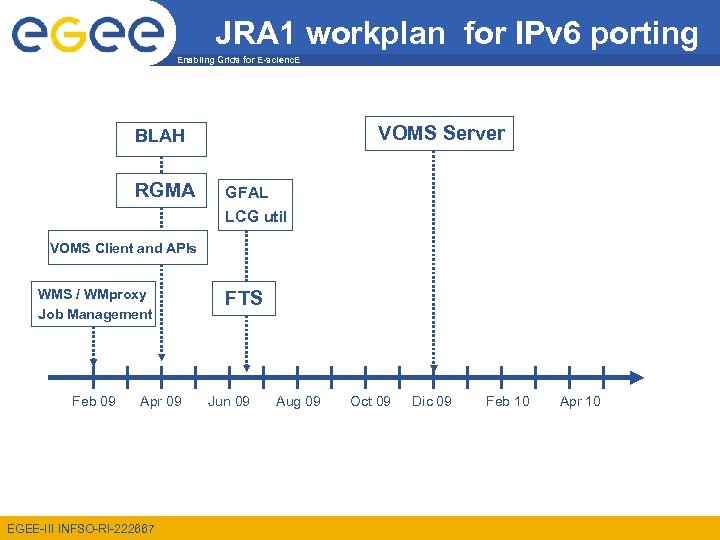
JRA 1 workplan for IPv 6 porting Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E VOMS Server BLAH RGMA GFAL LCG util VOMS Client and APIs WMS / WMproxy Job Management Feb 09 Apr 09 EGEE-III INFSO-RI-222667 FTS Jun 09 Aug 09 Oct 09 Dic 09 Feb 10 Apr 10
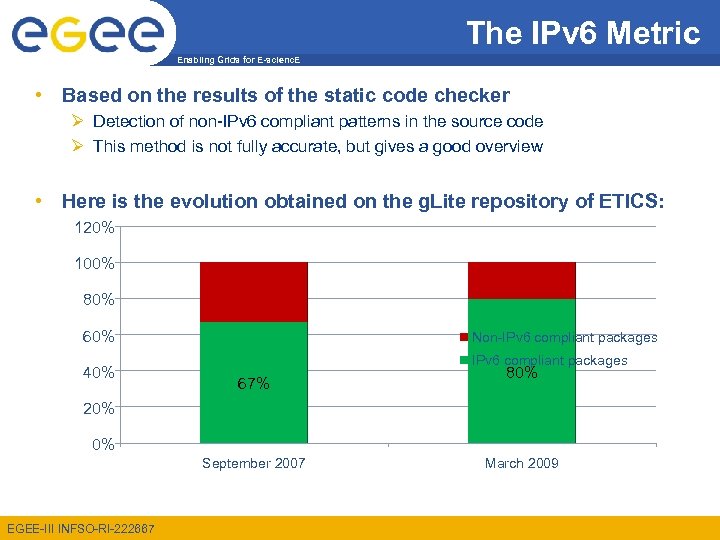
The IPv 6 Metric Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E • Based on the results of the static code checker Detection of non-IPv 6 compliant patterns in the source code This method is not fully accurate, but gives a good overview • Here is the evolution obtained on the g. Lite repository of ETICS: 120% 100% 80% 60% 40% Non-IPv 6 compliant packages 67% 80% 20% 0% September 2007 EGEE-III INFSO-RI-222667 March 2009

Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E Next steps What will keep us busy in the next months ? EGEE-III INFSO-RI-222667 20

Future work / Outlook Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E • To be considered – One goal was to provide results soon in order for JRA 1 and SA 3 to benefit from them Consequently the most relevant initial objectives are already completed The time (man power) initially planned for the IPv 6 sub-task has been already mostly used • Main foreseen tasks – – Test IPV 6 compliance of ported nodes Add an FTS node in the distributed testbed Collaboration with SA 3 for the integration of IPv 6 in the validation process Collaboration with the team responsible for the deployment tools, in order to have IPv 6 enabled on nodes at installation time – Improvement of the static code checker – New overall analysis of the g. Lite source code and update of IPv 6 non compliance bugs – Writing of the milestone document EGEE-III INFSO-RI-222667

Future work / Outlook Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E • Optional tasks: – Automation of the execution on IPv 6 CARE within the ETICS test system – Automation of the IPv 6 functional testing by means of the ETICS build system – Organization of tutorials on IPv 6 network programming and IPv 6 in general for JRA 1 and SA 3, if needed – Support to JRA 1 for specific studies on the IPv 6 compliance of packages and tools, if needed – Organization of a final demo on IPv 6 EGEE-III INFSO-RI-222667

Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E Thank You. https: //twiki. cern. ch/twiki/bin/view/EGEE/IPv 6 Follow. Up (or google “SA 2 IPv 6 follow up”) EGEE-III INFSO-RI-222667 23
1d1749044d8f1bd73c0e894f4f23118e.ppt