a800a563e496c6500033f3a347bd6afa.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 34

Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E Grid. ICE: a monitoring service for Grid Systems Giuseppe Misurelli INFN-CNAF (Italy) giuseppe. misurelli <at> cnaf. infn. it First Latin American Workshop for Grid Administrators Merida 2005, 23 November www. eu-egee. org INFSO-RI-508833

OUTLINE Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E • Grid. ICE Server Installation – – – – • Why Monitoring – – • Brief Introduction System Requirements Core Packages & Dependencies APT Installation Apache Configuration Postgre. SQL Optimization The Grid. ICE Configuration Script After The Discovery Process A Use Case Perspective VO manager viewpoint Grid Operations viewpoint Site Administrator viewpoint • The Grid. ICE Approach – Generating Events – Distributing Events – Presenting Events • Monitoring a Grid – Challenges for Data Collection – Challenges for Data Presentation • Grid. ICE@Work – VO manager utilization – Grid Operations manager utilization – Site Administrator utilization What is Grid Monitoring – – INFSO-RI-508833 Our Definition Concepts & Terminology Requirements The Four Main Phases of Monitoring First Latin American Workshop For Grid Administartor - November 23, 2005 2

Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E Grid. ICE Server Installation INFSO-RI-508833 First Latin American Workshop For Grid Administartor - November 23, 2005 3

Brief Introduction Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E Grid. ICE: – is a distributed monitoring tool for grid systems – integrates with local monitoring systems – offers a web interface for publishing monitoring data at the Grid level – fully integrated in the LCG-2 Middleware § gridice-clients data collector installation and configuration for each site ralized by the Yaim scripts. INFSO-RI-508833 First Latin American Workshop For Grid Administartor - November 23, 2005 4

System Requirements Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E • Suggested Operating system is Scientific Linux with a minimal installation • The Grid. ICE server should be installed on a performant machine – Postgre. SQL service - RAM intensive demand – Apache web server - RAM-CPU intensive demand INFSO-RI-508833 First Latin American Workshop For Grid Administartor - November 23, 2005 5
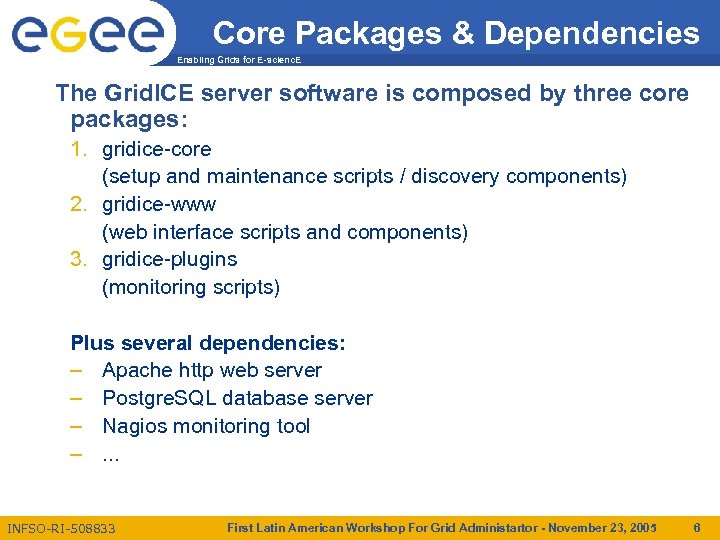
Core Packages & Dependencies Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E The Grid. ICE server software is composed by three core packages: 1. gridice-core (setup and maintenance scripts / discovery components) 2. gridice-www (web interface scripts and components) 3. gridice-plugins (monitoring scripts) Plus several dependencies: – Apache http web server – Postgre. SQL database server – Nagios monitoring tool –. . . INFSO-RI-508833 First Latin American Workshop For Grid Administartor - November 23, 2005 6

APT Installation Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E • Fully automated process thanks to APT package manager Add in the /etc/apt/source. list. d/sl. d the Grid. ICE repository: ### Grid. ICE APT Repository ### rpm http: //infnforge. cnaf. infn. it gridice/packages/sl/3. 0. 3/i 386 gridice Update your new repository list with the command: [root@localhost]#apt-get update Upgrade your system with the command: [root@localhost]# apt-get upgrade (it takes a while) Install the Grid. ICE meta-package with the command: [root@localhost]#apt-get install gridice-server INFSO-RI-508833 First Latin American Workshop For Grid Administartor - November 23, 2005 7
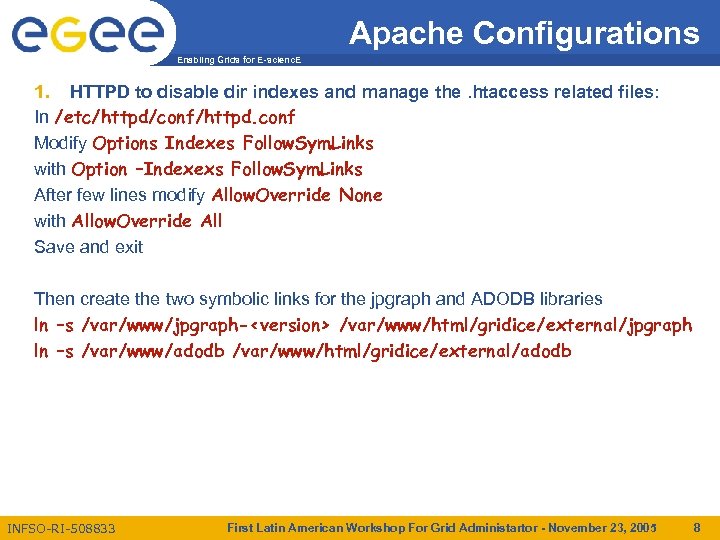
Apache Configurations Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E 1. HTTPD to disable dir indexes and manage the. htaccess related files: In /etc/httpd/conf/httpd. conf Modify Options Indexes Follow. Sym. Links with Option –Indexexs Follow. Sym. Links After few lines modify Allow. Override None with Allow. Override All Save and exit Then create the two symbolic links for the jpgraph and ADODB libraries ln –s /var/www/jpgraph-<version> /var/www/html/gridice/external/jpgraph ln –s /var/www/adodb /var/www/html/gridice/external/adodb INFSO-RI-508833 First Latin American Workshop For Grid Administartor - November 23, 2005 8

Postgre. SQL Optimization Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E 1. All Postgre. SQL databases and configurations files are locate in /var/lib/pgsql/data If this directory does not exist (or it is empty) then launch: [root@localhost]#su – postgres [root@localhost]#initdb –D /var/lib/pqsql/data 2. For a database performances optimization we suggest to set the following attibutes/values in the /var/lib/pgsql/data/postgresql. conf file as follows: listen_addresses = ‘*’ max_connections = 256 work_men = 2048 maintenance_work_men = 32768 fsync = false enable_hashjoin = true enable_indexscan = true enble_nestloop = true enable_seqscan = true enavble_tidiscan = true effective_cache_size = 10000 random_page_cost = 2 INFSO-RI-508833 First Latin American Workshop For Grid Administartor - November 23, 2005 9
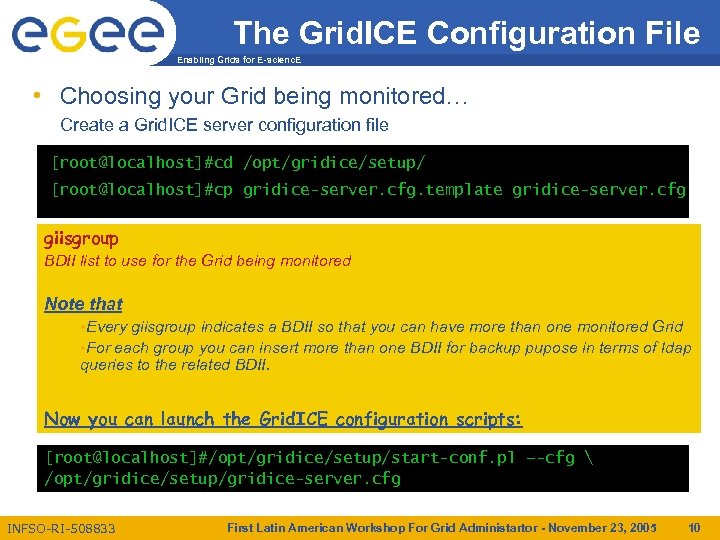
The Grid. ICE Configuration File Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E • Choosing your Grid being monitored… Create a Grid. ICE server configuration file [root@localhost]#cd /opt/gridice/setup/ [root@localhost]#cp gridice-server. cfg. template gridice-server. cfg giisgroup dbpass dbadminpass hostname Edit /opt/gridice/setup/gridice-server. cfg BDII list athe Grid. ICE server Choose topassword for the being monitored Choose the following. Grid. ICE connections FQDN of password forattributes: DB connections Modify a use for the Postgre. SQL (It refers to the ‘gridiceadmin’ Postgre. SQL user) (it refers to the‘postgres’ Linux user) addr Note that blacklist dbhost of the. Grid. ICE servera BDII so that you can have more than one monitored Grid IP address giisgroup indicates • Every Define a regular expression in order to exclude one or more sites from discovery FQDNForthe Grid. ICE server • of each group you can insert more than one BDII for backup pupose in terms of ldap process (separate each site wit “|” following the reported example) queries to the related BDII. Default is no Grid site excluded Now you can launch the Grid. ICE configuration scripts: [root@localhost]#/opt/gridice/setup/start-conf. pl –-cfg /opt/gridice/setup/gridice-server. cfg INFSO-RI-508833 First Latin American Workshop For Grid Administartor - November 23, 2005 10

Final Configurations Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E • Grid. ICE Database creation (plus patches for the new geo view) [root@localhost]#su – postgres [root@localhost]#psql –U gridiceadmin Grid. ICEdb < /opt/gridice/setup/pgsql/mondb. sql • Grid. ICE cron jobs to perform maintenance routines and periodic discovery [root@localhost]#cp /opt/gridice/utils/gridice-cronjobs /etc/cron. d • Grid. ICE discovery script to explore and collect all the monitoring data about your Grid (It queries the Information Service of your Grid and inserts into the RDMS all the data retrieved) [root@localhost]#/usr/lib/nagios/dscv/start-dscv. pl INFSO-RI-508833 First Latin American Workshop For Grid Administartor - November 23, 2005 11

After The Discovery Process Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E ü Be sure that the following services are running 1. nagios 2. postgresql 3. httpd (check also if the http port is open) ü To see your Grid monitored data, point the web browser to the URL: http: //<fqdn_of_your_gridice_server>/gridice INFSO-RI-508833 First Latin American Workshop For Grid Administartor - November 23, 2005 12

Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E Why Monitoring INFSO-RI-508833 First Latin American Workshop For Grid Administartor - November 23, 2005 13

A Use Case Perspective Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E – Grid resources availability is subject to failures. – Resources observability is necessary for the Grid utilization. Need for analyzing the usage, behavior and performance of a Grid depending on different users: 1. VO manager 2. Grid operations manager 3. Site administrator INFSO-RI-508833 First Latin American Workshop For Grid Administartor - November 23, 2005 14

VO manager viewpoint Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E • Visualization of the actual set of resources accessible to its members. • Evaluation of members’demand satisfaction on the Grid mapping functionalities. • Evaluation of the Service Level Agreement (SLA) for the global Grid service offers. INFSO-RI-508833 First Latin American Workshop For Grid Administartor - November 23, 2005 15

Grid operations manager viewpoint Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E • Detection and prediction of fault situations related to wide area distributed resources. • Coordination of the deployment and upgrade of the Grid middleware installed at several sites. • Investigation on Grid resources for statistical purpose. INFSO-RI-508833 First Latin American Workshop For Grid Administartor - November 23, 2005 16

Site Administrator viewpoint Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E • Detection of fault situations related to the own resources. • Control how the own resources are used and appear to the Grid. INFSO-RI-508833 First Latin American Workshop For Grid Administartor - November 23, 2005 17

Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E What is Grid Monitoring INFSO-RI-508833 First Latin American Workshop For Grid Administartor - November 23, 2005 18

Our Definition Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E • Grid Monitoring – the activity of measuring significant Grid resources related parameters – in order to § analyze usage, behavior and performance of the grid § detect and notify fault situations INFSO-RI-508833 First Latin American Workshop For Grid Administartor - November 23, 2005 19
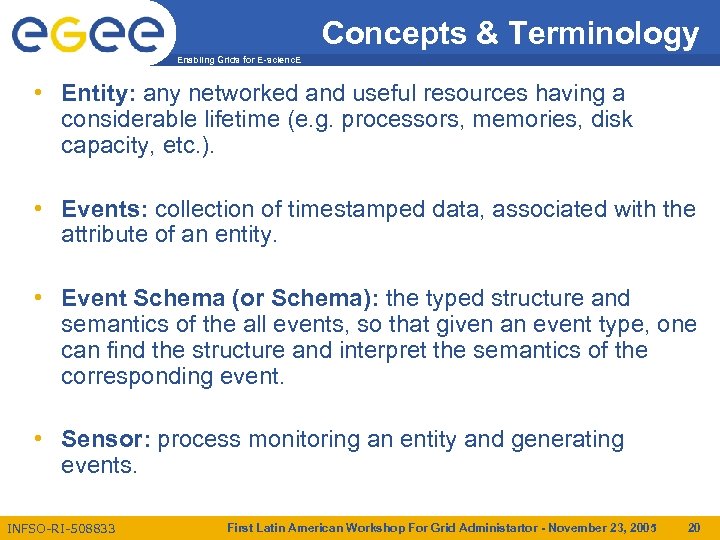
Concepts & Terminology Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E • Entity: any networked and useful resources having a considerable lifetime (e. g. processors, memories, disk capacity, etc. ). • Events: collection of timestamped data, associated with the attribute of an entity. • Event Schema (or Schema): the typed structure and semantics of the all events, so that given an event type, one can find the structure and interpret the semantics of the corresponding event. • Sensor: process monitoring an entity and generating events. INFSO-RI-508833 First Latin American Workshop For Grid Administartor - November 23, 2005 20

Requirements Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E • Scalability: monitoring systems have to cope efficiently with a growing number of resources, events and users. • Extensibility: monitoring systems must be extensible with respect to the supported resources. • Data delivery models: monitoring systems must integrate different measurement policies (e. g. periodic, on-demand). • Portability: any encapsulated measurement must be platform independent. • Security: monitoring systems must deal with security concerns such as privacy, data integration and confidentiality. INFSO-RI-508833 First Latin American Workshop For Grid Administartor - November 23, 2005 21
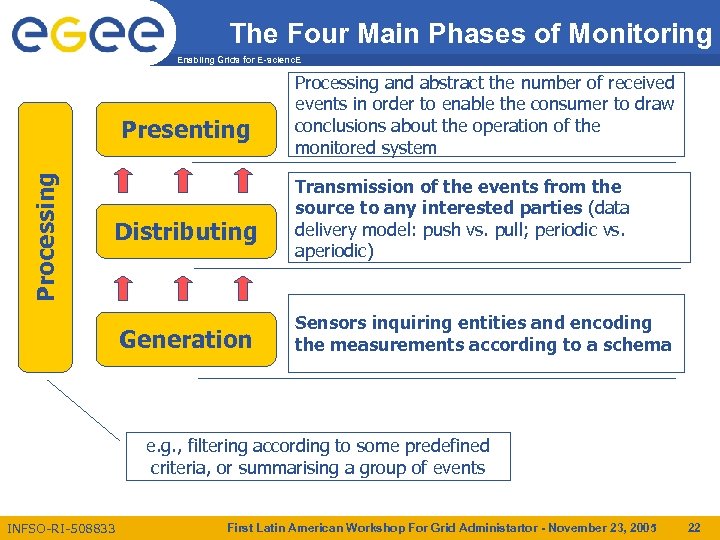
The Four Main Phases of Monitoring Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E Processing Presenting Distributing Generation Processing and abstract the number of received events in order to enable the consumer to draw conclusions about the operation of the monitored system Transmission of the events from the source to any interested parties (data delivery model: push vs. pull; periodic vs. aperiodic) Sensors inquiring entities and encoding the measurements according to a schema e. g. , filtering according to some predefined criteria, or summarising a group of events INFSO-RI-508833 First Latin American Workshop For Grid Administartor - November 23, 2005 22

Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E The Grid. ICE Approach INFSO-RI-508833 First Latin American Workshop For Grid Administartor - November 23, 2005 23

Generating Events Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E • Generation of events: – Sensors: typically perl scripts or c programs. – Schema: § GLUE Schema v. 1. 1 + Grid. ICE extension. • • System related (e. g. , CPU load, CPU Type, Memory size). Grid service related (e. g. , CE ID, queued jobs). Network related (e. g. , Packet loss). Job usage (e. g. , CPU Time, Wall Time). – All sensors are executed in a periodic fashion. INFSO-RI-508833 First Latin American Workshop For Grid Administartor - November 23, 2005 24

Distributing Events Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E • Distribution of events: – Hierarchical model. § Intra-site: by means of the local monitoring service • default choice, LEMON (http: //www. cern. ch/lemon). § Inter-site: by offering data through the Grid Information Service. § Final Consumer: depending on the client application. – Mixed data delivery model. § Intra-site: depending on the local monitoring service (push for lemon). § Inter-site: depending on the GIS (current choice, MDS 2. x, pull). § Final consumer: pull (browser/application), push (publish/subscribe notification service coming on the next release). INFSO-RI-508833 First Latin American Workshop For Grid Administartor - November 23, 2005 25

Presenting Events Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E • Data stored in a RDBMS used to build aggregated statistics. • Data retrieved from the RDBMS are encoded in XML files. • XSL to XHTML transformations to publish aggregated data in a Web context. INFSO-RI-508833 First Latin American Workshop For Grid Administartor - November 23, 2005 26

Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E Monitoring a Grid INFSO-RI-508833 First Latin American Workshop For Grid Administartor - November 23, 2005 27

Challenges for Data Collection Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E • The distribution of monitoring data is strongly characterised by significant requirements (e. g. , Scalability, Heterogeneity, Security, System Health) • None of the existing tools satisfy all of these requirements • Grid data collection should be customized depending on what are the needs of your Grid users selected INFSO-RI-508833 First Latin American Workshop For Grid Administartor - November 23, 2005 28
Challenges for Data Presentation Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E • Different Grid users are interested in different subset of Grid data and different aggregation levels • Usability principles should be taken into account to help users finding relevant Grid monitoring information • A sintetic data aggregation is crucial to permit a drilldown navigation (from the general to te detailed) of the Grid data INFSO-RI-508833 First Latin American Workshop For Grid Administartor - November 23, 2005 29

Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E Grid. ICE@Work INFSO-RI-508833 First Latin American Workshop For Grid Administartor - November 23, 2005 30

VO manager utilization Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E Mostly interested in: – Resources available to the VO § Computing elements where VO users can submit jobs. § Storage elements where VO users can store/retrieve data. – Job monitoring § How many jobs are running or queued? • For the whole VO? In each site? Submitted by a certain RB? § How many jobs have been executed? • For the whole VO? In each site? Submitted by a certain RB? INFSO-RI-508833 First Latin American Workshop For Grid Administartor - November 23, 2005 31

Grid operations manager utilization Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E Mostly interested in: – General status of the managed Grid § How many sites compose the managed Grid and where they are located. § How many resources (cpu#, WN, etc. ) are available. – Highlighted problems § Is there any Grid service (e. g. , CE, SE, BDII) which related processes have problems? § Is the Grid Information Service working properly? INFSO-RI-508833 First Latin American Workshop For Grid Administartor - November 23, 2005 32

Site administrator utilization Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E Mostly interested in: – Status of their resources § What is the cpu load at the moment? § What is the percentage of the busy storage space? § Are there any jobs running or queued in my site and in which Worker Node? – Highlighted problems § Is there any Grid service (e. g. , CE, SE, BDII) which related processes have problems? § Is the Grid Information Service working properly? INFSO-RI-508833 First Latin American Workshop For Grid Administartor - November 23, 2005 33

References Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E • Dissemination Web site: http: //grid. infn. it/gridice - S. Andreozzi, N. De Bortoli, S. Fantinel, A. Ghiselli, G. L. Rubini, G. Tortone, M. C. Vistoli Grid. ICE: a monitoring service for Grid systems, Future Generation Computer System 21 (2005) 559– 571 - B. Tierney, R. Aydt, D. Gunter, W. Smith, M. Swany, V. Taylor, R. Wolski, A Grid Monitoring Architecture, GFD-I. 7. - S. Zanikolas, R. Sakellariou, A taxonomy of grid monitoring systems, Future Generation Computer Systems 21 (2005) 163– 188. - M. Franklin, S. Zdonik, “Data In Your Face”: Push Technology in Perspective, ACM SIGMOD ’ 98, Seattle, WA, USA. - S. Andreozzi, A. Ciuffoletti, A. Ghiselli, C. Vistoli. Monitoring the connectivity of a Grid. Proceedings of the 2 nd International Workshop on Middleware for Grid Computing (MGC 2004) in conjunction with the 5 th ACM/IFIP/USENIX International Middleware Conference, Toronto, Canada, October 2004. - S. Andreozzi, N. De Bortoli, S. Fantinel, G. L. Rubini, G. Tortone. Design and Implementation of a Notification Model for Grid Monitoring Events. CHEP 04, Interlaken (CH), Sep 2004. INFSO-RI-508833 First Latin American Workshop For Grid Administartor - November 23, 2005 34
a800a563e496c6500033f3a347bd6afa.ppt