9af88b091d0f49ba8f53fb4079a895a1.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25
 “EMV-ENERGO”, Ukraine Plant Model application for design, verification and testing of Digital Control Systems at Nuclear Power Plants June 2016. Pravets, Bulgaria
“EMV-ENERGO”, Ukraine Plant Model application for design, verification and testing of Digital Control Systems at Nuclear Power Plants June 2016. Pravets, Bulgaria
 Authors • Oleksiy Sokolov (EMV-ENERGO, Ukraine) • Boris Symkin (EMV-ENERGO, Ukraine) • Volodymyr Krasnov (EMV-ENERGO, Ukraine)
Authors • Oleksiy Sokolov (EMV-ENERGO, Ukraine) • Boris Symkin (EMV-ENERGO, Ukraine) • Volodymyr Krasnov (EMV-ENERGO, Ukraine)
 Conception of Plant Model application in the process of Digital Control System implementation at NPP Realization of Digital Control System includes several stages, as follows: • Design of Modulating Control Algorithms and related to them interlocks • Verification and testing of Modulating Control Algorithms and related interlocks • Definition and setting of regulator’s optimal tuning parameters during control system commissioning at the unit • Modulating Control Systems testing at real technological equipment at following unit modes of operation: unit loading and unloading, technological equipment switching over, emergency situations
Conception of Plant Model application in the process of Digital Control System implementation at NPP Realization of Digital Control System includes several stages, as follows: • Design of Modulating Control Algorithms and related to them interlocks • Verification and testing of Modulating Control Algorithms and related interlocks • Definition and setting of regulator’s optimal tuning parameters during control system commissioning at the unit • Modulating Control Systems testing at real technological equipment at following unit modes of operation: unit loading and unloading, technological equipment switching over, emergency situations
 Directive Document for NPPs (OPB) “General Regulation on Nuclear Power Plant safety”: Clause. 8. 4. 13 Stability analysis for modulating control and control loops • According to this clause, the stability analisys is mandatory during digital control systems design and commissioning at NPPs
Directive Document for NPPs (OPB) “General Regulation on Nuclear Power Plant safety”: Clause. 8. 4. 13 Stability analysis for modulating control and control loops • According to this clause, the stability analisys is mandatory during digital control systems design and commissioning at NPPs
 Plant Model application for the NPP Directive Document demand realization Technological model application ensures the Directive Document demand realization. Besides, at all above mentioned Digital Control System development stages, additionally it gives the following results: • At the design stage it gives the possibility to choose the optimal structure of modulating control systems • During modulating control system algorithms testing with related interlocks it saves significantly the time and enhance the quality of work • It significantly simplifies and speed up the process of regulator optimal tuning parameters definition, especially for the control systems with mutual interaction and influence • It simplifies the process of regulator’s testing at unit modes of operation, related to emergency unit unloading, technological equipment switching off, emergency situations
Plant Model application for the NPP Directive Document demand realization Technological model application ensures the Directive Document demand realization. Besides, at all above mentioned Digital Control System development stages, additionally it gives the following results: • At the design stage it gives the possibility to choose the optimal structure of modulating control systems • During modulating control system algorithms testing with related interlocks it saves significantly the time and enhance the quality of work • It significantly simplifies and speed up the process of regulator optimal tuning parameters definition, especially for the control systems with mutual interaction and influence • It simplifies the process of regulator’s testing at unit modes of operation, related to emergency unit unloading, technological equipment switching off, emergency situations
 Projects of Digital Control System at “Kozloduy” NPP modernization with Plant Model application • Units 3 and 4. Feed water control system replacement for VVER-440 steam generators (Triconex hardware) • Units 5 and 6. ACYT 1000 -2 control system replacement (Ovation hardware) • Units 5 and 6. YKTC control system replacement. First and Secondary loop. (Ovation hardware) • Units 5 and 6. USB safety control system replacement (hardware of “Radiy” plant, Ukraine) • Units 5 and 6. Steam dumping device to condenser (BRU-K) algorithms modernization for leaving reactor in operation in case of both Turbine Driven Feed water Pumps trip (Ovation hardware) • Units 5 and 6. Control System modernization due to High Pressure Heaters replacement (Ovation hardware) • Units 5 and 6. Control System modernization Project: Heating up and cooling down of High Pressure Heaters tube desks (Ovation hardware) • Special Water Purification House “CK-3”. Control system replacement (Ovation hardware)
Projects of Digital Control System at “Kozloduy” NPP modernization with Plant Model application • Units 3 and 4. Feed water control system replacement for VVER-440 steam generators (Triconex hardware) • Units 5 and 6. ACYT 1000 -2 control system replacement (Ovation hardware) • Units 5 and 6. YKTC control system replacement. First and Secondary loop. (Ovation hardware) • Units 5 and 6. USB safety control system replacement (hardware of “Radiy” plant, Ukraine) • Units 5 and 6. Steam dumping device to condenser (BRU-K) algorithms modernization for leaving reactor in operation in case of both Turbine Driven Feed water Pumps trip (Ovation hardware) • Units 5 and 6. Control System modernization due to High Pressure Heaters replacement (Ovation hardware) • Units 5 and 6. Control System modernization Project: Heating up and cooling down of High Pressure Heaters tube desks (Ovation hardware) • Special Water Purification House “CK-3”. Control system replacement (Ovation hardware)
 CIS NPP Digital Control System modernization Projects with Plant Model application • South Ukrainian NPP, units 1 and 2. Feed Water Control System for VVER-1000 Steam Generators. WDPF Westinghouse hardware. • South Ukrainian NPP, unit 3. Feed Water Control System for VVER -1000 Steam Generators. “Vulkan-M” hardware, Westron, Ukraine • Armenian NPP. Feed Water Control System for VVER-440 Steam Generators. “Vulkan-M” hardware, Westron, Ukraine • South Ukrainian NPP, unit 3. Reactor Power Control Systems (ARM, ROM, UPZ). “Radiy” plant hardware, Ukraine • Rivno NPP, unit VVER-440. Reactor Power Control Systems (ARM, ROM). “Radiy” plant hardware, Ukraine
CIS NPP Digital Control System modernization Projects with Plant Model application • South Ukrainian NPP, units 1 and 2. Feed Water Control System for VVER-1000 Steam Generators. WDPF Westinghouse hardware. • South Ukrainian NPP, unit 3. Feed Water Control System for VVER -1000 Steam Generators. “Vulkan-M” hardware, Westron, Ukraine • Armenian NPP. Feed Water Control System for VVER-440 Steam Generators. “Vulkan-M” hardware, Westron, Ukraine • South Ukrainian NPP, unit 3. Reactor Power Control Systems (ARM, ROM, UPZ). “Radiy” plant hardware, Ukraine • Rivno NPP, unit VVER-440. Reactor Power Control Systems (ARM, ROM). “Radiy” plant hardware, Ukraine
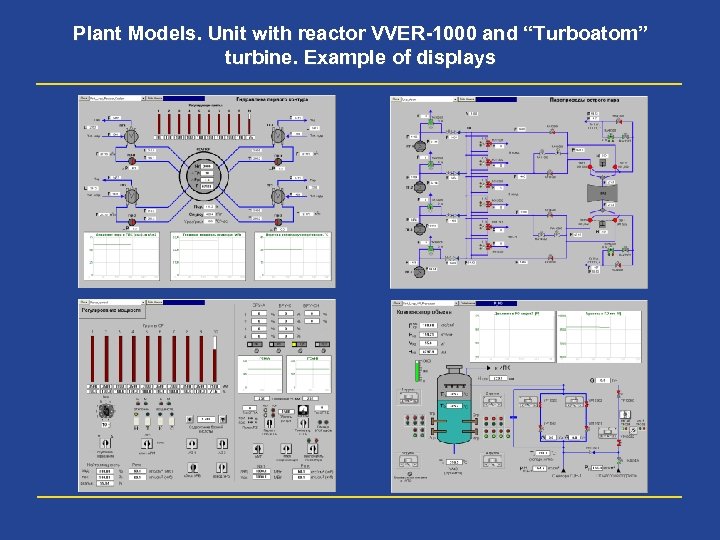 Plant Models. Unit with reactor VVER-1000 and “Turboatom” turbine. Example of displays
Plant Models. Unit with reactor VVER-1000 and “Turboatom” turbine. Example of displays
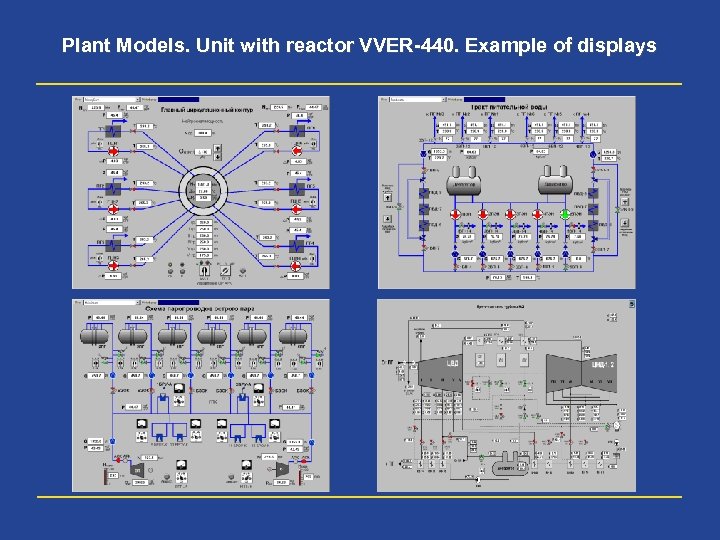 Plant Models. Unit with reactor VVER-440. Example of displays
Plant Models. Unit with reactor VVER-440. Example of displays
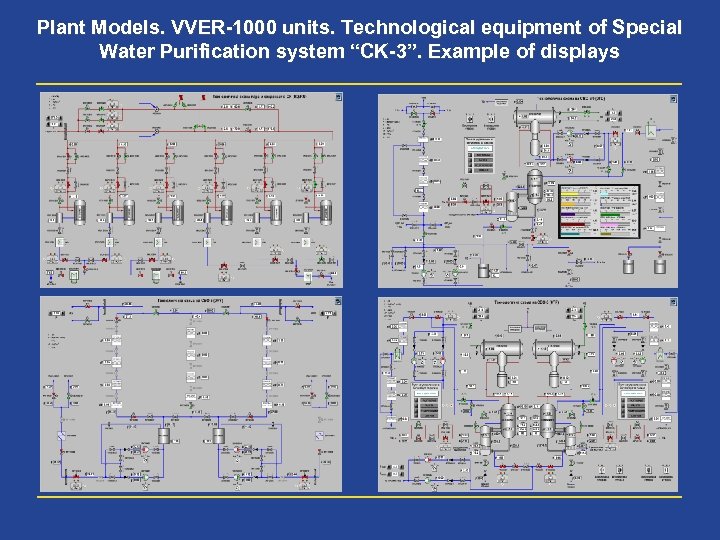 Plant Models. VVER-1000 units. Technological equipment of Special Water Purification system “CK-3”. Example of displays
Plant Models. VVER-1000 units. Technological equipment of Special Water Purification system “CK-3”. Example of displays
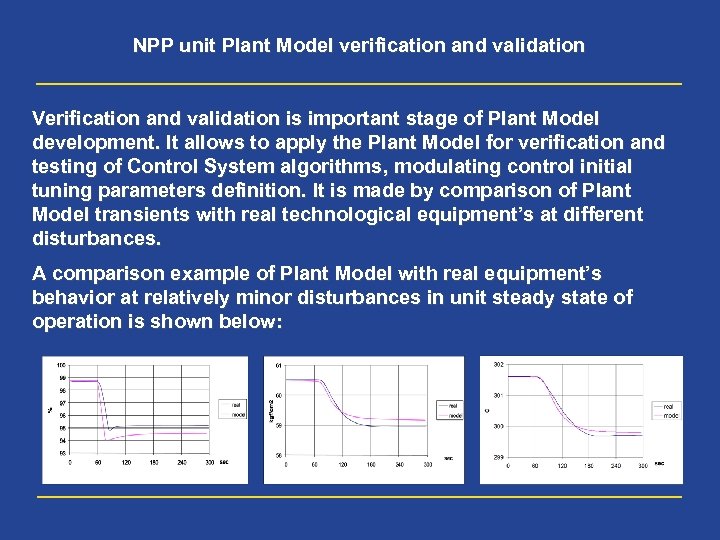 NPP unit Plant Model verification and validation Verification and validation is important stage of Plant Model development. It allows to apply the Plant Model for verification and testing of Control System algorithms, modulating control initial tuning parameters definition. It is made by comparison of Plant Model transients with real technological equipment’s at different disturbances. A comparison example of Plant Model with real equipment’s behavior at relatively minor disturbances in unit steady state of operation is shown below:
NPP unit Plant Model verification and validation Verification and validation is important stage of Plant Model development. It allows to apply the Plant Model for verification and testing of Control System algorithms, modulating control initial tuning parameters definition. It is made by comparison of Plant Model transients with real technological equipment’s at different disturbances. A comparison example of Plant Model with real equipment’s behavior at relatively minor disturbances in unit steady state of operation is shown below:
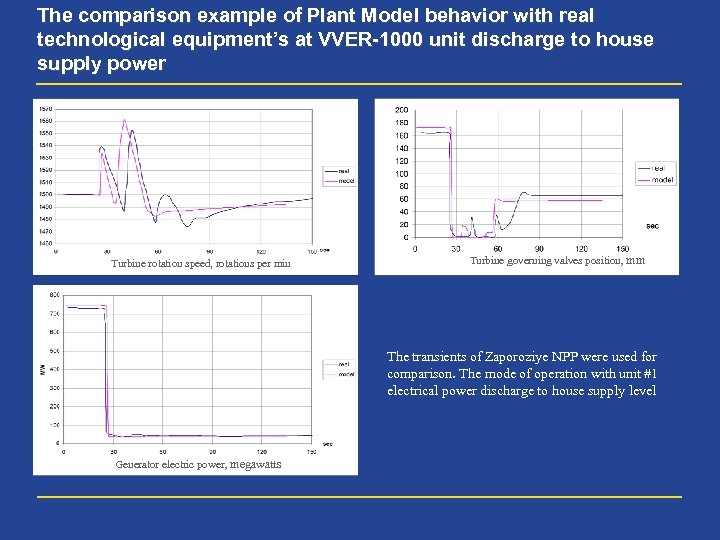 The comparison example of Plant Model behavior with real technological equipment’s at VVER-1000 unit discharge to house supply power Turbine rotation speed, rotations per min Turbine governing valves position, mm The transients of Zaporoziye NPP were used for comparison. The mode of operation with unit #1 electrical power discharge to house supply level Generator electric power, megawatts
The comparison example of Plant Model behavior with real technological equipment’s at VVER-1000 unit discharge to house supply power Turbine rotation speed, rotations per min Turbine governing valves position, mm The transients of Zaporoziye NPP were used for comparison. The mode of operation with unit #1 electrical power discharge to house supply level Generator electric power, megawatts
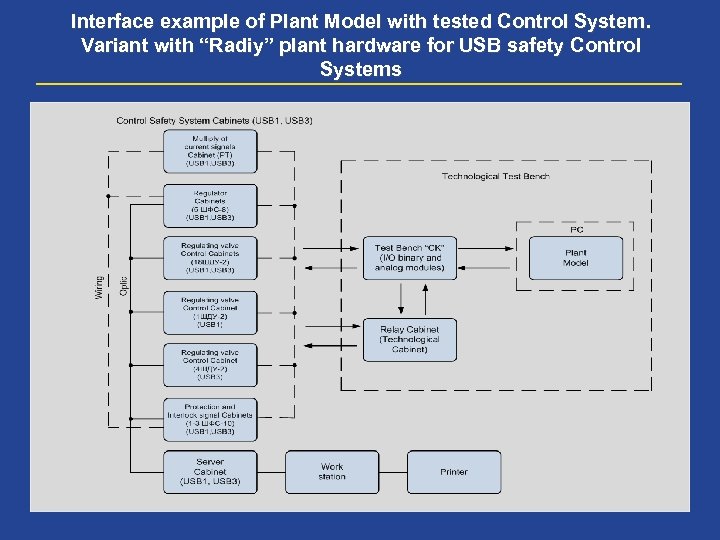 Interface example of Plant Model with tested Control System. Variant with “Radiy” plant hardware for USB safety Control Systems
Interface example of Plant Model with tested Control System. Variant with “Radiy” plant hardware for USB safety Control Systems
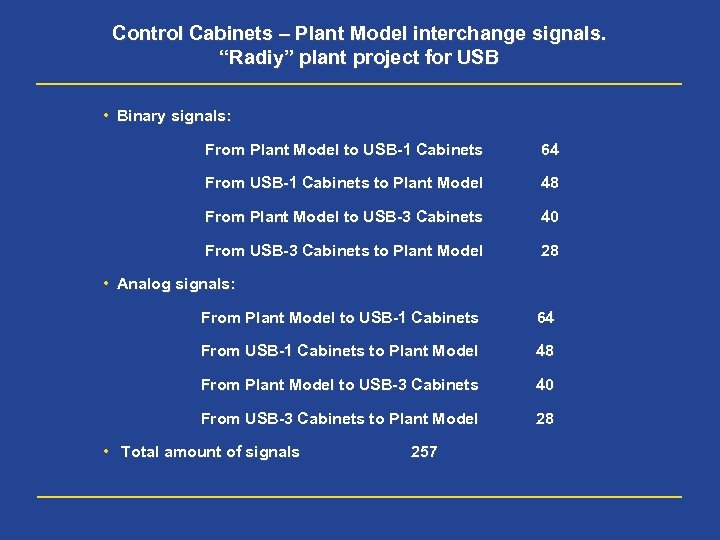 Control Cabinets – Plant Model interchange signals. “Radiy” plant project for USB • Binary signals: From Plant Model to USB-1 Cabinets 64 From USB-1 Cabinets to Plant Model 48 From Plant Model to USB-3 Cabinets 40 From USB-3 Cabinets to Plant Model 28 • Analog signals: From Plant Model to USB-1 Cabinets 64 From USB-1 Cabinets to Plant Model 48 From Plant Model to USB-3 Cabinets 40 From USB-3 Cabinets to Plant Model 28 • Total amount of signals 257
Control Cabinets – Plant Model interchange signals. “Radiy” plant project for USB • Binary signals: From Plant Model to USB-1 Cabinets 64 From USB-1 Cabinets to Plant Model 48 From Plant Model to USB-3 Cabinets 40 From USB-3 Cabinets to Plant Model 28 • Analog signals: From Plant Model to USB-1 Cabinets 64 From USB-1 Cabinets to Plant Model 48 From Plant Model to USB-3 Cabinets 40 From USB-3 Cabinets to Plant Model 28 • Total amount of signals 257
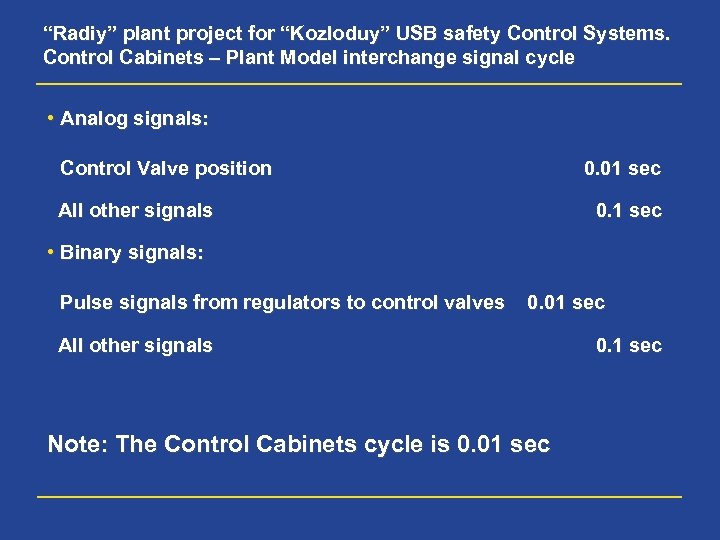 “Radiy” plant project for “Kozloduy” USB safety Control Systems. Control Cabinets – Plant Model interchange signal cycle • Analog signals: Control Valve position 0. 01 sec All other signals 0. 1 sec • Binary signals: Pulse signals from regulators to control valves 0. 01 sec All other signals Note: The Control Cabinets cycle is 0. 01 sec 0. 1 sec
“Radiy” plant project for “Kozloduy” USB safety Control Systems. Control Cabinets – Plant Model interchange signal cycle • Analog signals: Control Valve position 0. 01 sec All other signals 0. 1 sec • Binary signals: Pulse signals from regulators to control valves 0. 01 sec All other signals Note: The Control Cabinets cycle is 0. 01 sec 0. 1 sec
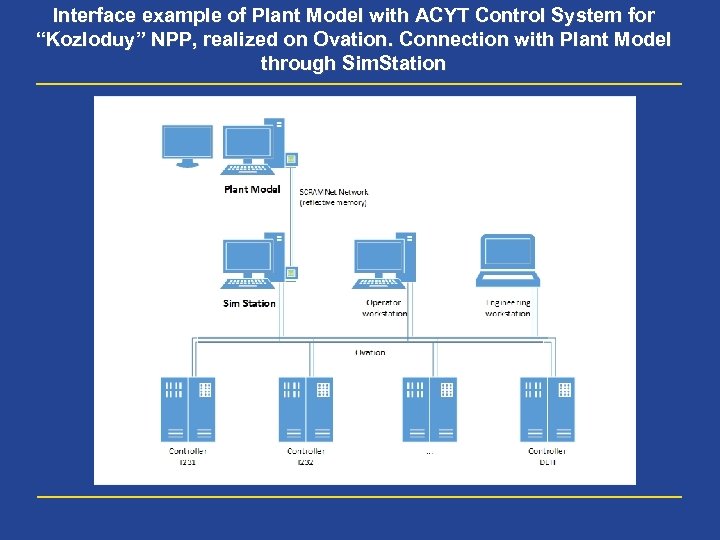 Interface example of Plant Model with ACYT Control System for “Kozloduy” NPP, realized on Ovation. Connection with Plant Model through Sim. Station
Interface example of Plant Model with ACYT Control System for “Kozloduy” NPP, realized on Ovation. Connection with Plant Model through Sim. Station
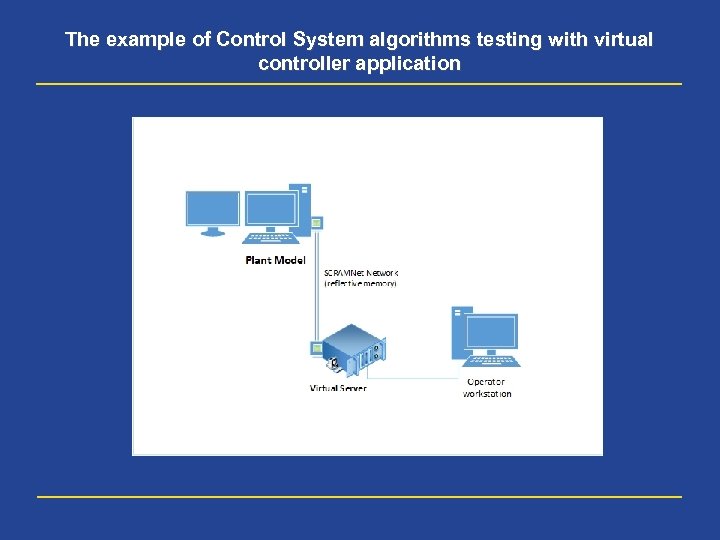 The example of Control System algorithms testing with virtual controller application
The example of Control System algorithms testing with virtual controller application
 Variants of Plant Model interface with tested Control System by “Shared memory” technology • At last two pictures there are examples of Plant Model interface with Control System software by technology “Shared memory”, realized with the help of SCRAMNet cards • At first case the controllers at Control System cabinets are switched over from data exchange with I/O modules to data exchange with the Sim. Station, for one's turn, exchanges data with the Plant Model (with time period of 100 milliseconds in the case) • At the second case the tested Control System algorithms are loaded to virtual controller, which exchanges data with the Plant Model with the help of two SCRAMNet cards. In this case operator’s interface with real Control System is ensured
Variants of Plant Model interface with tested Control System by “Shared memory” technology • At last two pictures there are examples of Plant Model interface with Control System software by technology “Shared memory”, realized with the help of SCRAMNet cards • At first case the controllers at Control System cabinets are switched over from data exchange with I/O modules to data exchange with the Sim. Station, for one's turn, exchanges data with the Plant Model (with time period of 100 milliseconds in the case) • At the second case the tested Control System algorithms are loaded to virtual controller, which exchanges data with the Plant Model with the help of two SCRAMNet cards. In this case operator’s interface with real Control System is ensured
 Control System algorithms testing during Factory Acceptance Test (FAT) Testing is made in the following modes of operation: • Regulator closed loop stability testing at unit steady state modes of operation with application of inner and outer for the system disturbances • Regulator closed loop stability testing with unit loading and unloading • Regulator closed loop stability testing in the following modes of unit operation: technological equipment switching over and switching off, emergency discharge, unit emergency modes of operation
Control System algorithms testing during Factory Acceptance Test (FAT) Testing is made in the following modes of operation: • Regulator closed loop stability testing at unit steady state modes of operation with application of inner and outer for the system disturbances • Regulator closed loop stability testing with unit loading and unloading • Regulator closed loop stability testing in the following modes of unit operation: technological equipment switching over and switching off, emergency discharge, unit emergency modes of operation
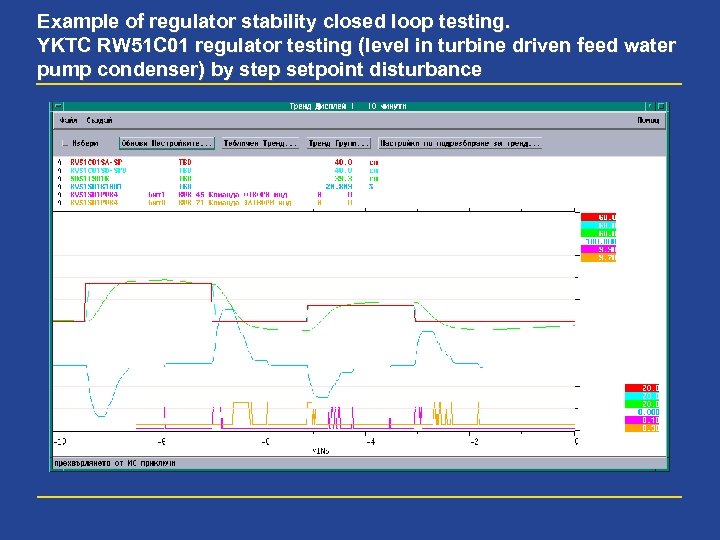 Example of regulator stability closed loop testing. YKTC RW 51 C 01 regulator testing (level in turbine driven feed water pump condenser) by step setpoint disturbance
Example of regulator stability closed loop testing. YKTC RW 51 C 01 regulator testing (level in turbine driven feed water pump condenser) by step setpoint disturbance
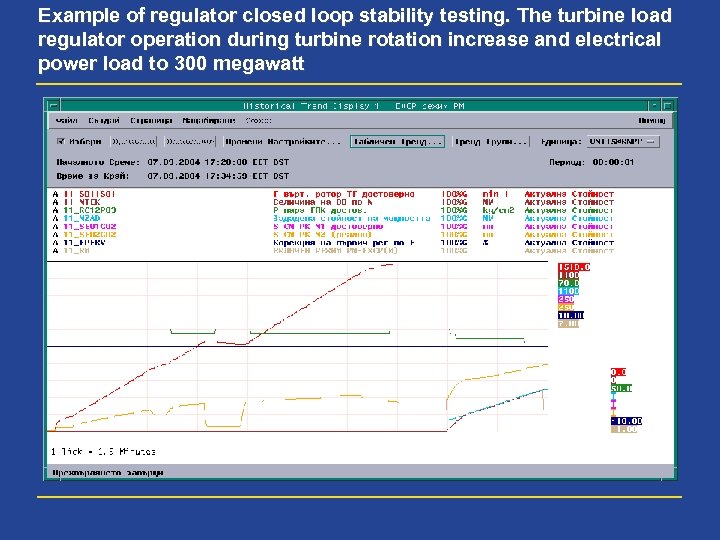 Example of regulator closed loop stability testing. The turbine load regulator operation during turbine rotation increase and electrical power load to 300 megawatt
Example of regulator closed loop stability testing. The turbine load regulator operation during turbine rotation increase and electrical power load to 300 megawatt
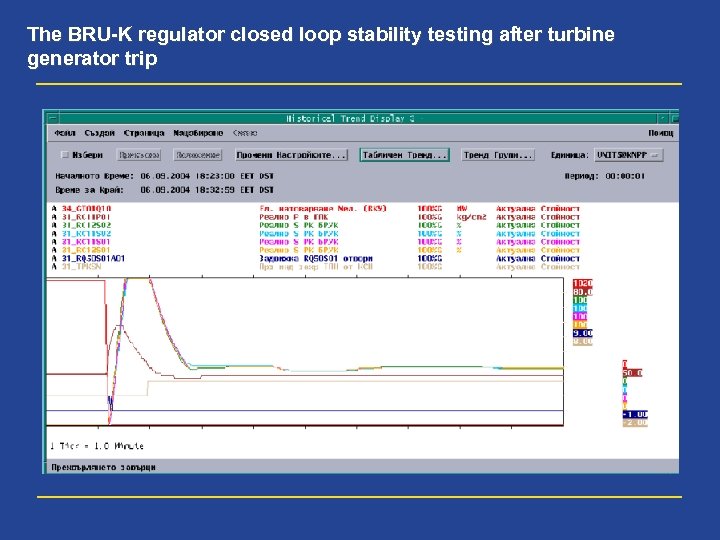 The BRU-K regulator closed loop stability testing after turbine generator trip
The BRU-K regulator closed loop stability testing after turbine generator trip
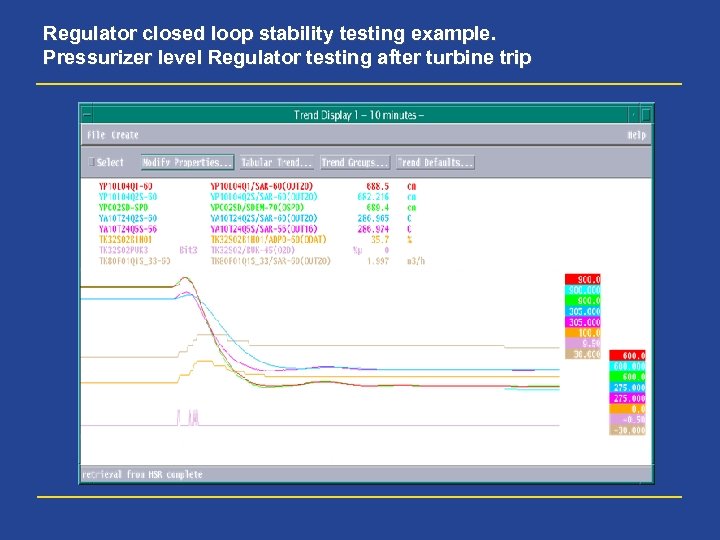 Regulator closed loop stability testing example. Pressurizer level Regulator testing after turbine trip
Regulator closed loop stability testing example. Pressurizer level Regulator testing after turbine trip
 Conclusions The Plant Model Application during Control System regulators closed loop testing allows the following: 1. Facilitates the regulator algorithms testing, significantly enhance its quality, shortens the period of testing 2. Gives the possibility to define the optimal tuning parameters of regulator control loops and set them as initial during Control System commissioning 3. Gives the possibility to test interrelated operation of regulator control loops with mutual interaction at unit steady state of operation, its abnormal and emergency situations 4. In case of successful testing of regulator control loops with the Plant Model, during the Control System commissioning at real unit it is possible to limit the number of real tests at technological equipment, especially related with equipment switching over and switching off, emergency load discharge and trip 5. In some cases: unit safety systems, emergency regulators, the Plant Model application – is the single method to test the designed regulators in closed loop operation
Conclusions The Plant Model Application during Control System regulators closed loop testing allows the following: 1. Facilitates the regulator algorithms testing, significantly enhance its quality, shortens the period of testing 2. Gives the possibility to define the optimal tuning parameters of regulator control loops and set them as initial during Control System commissioning 3. Gives the possibility to test interrelated operation of regulator control loops with mutual interaction at unit steady state of operation, its abnormal and emergency situations 4. In case of successful testing of regulator control loops with the Plant Model, during the Control System commissioning at real unit it is possible to limit the number of real tests at technological equipment, especially related with equipment switching over and switching off, emergency load discharge and trip 5. In some cases: unit safety systems, emergency regulators, the Plant Model application – is the single method to test the designed regulators in closed loop operation
 Company-partners of “EMV-ENERGO” • Energo. Service AD, Sofia, Bulgaria • Westinghouse Energy Systems OOD -Branch Bulgaria • ENERGY ORGRES Ltd, Sofia, Bulgaria • Westron LLC, Kharkiv, Ukraine • RPC “Radiy”, Kirovograd, Ukraine
Company-partners of “EMV-ENERGO” • Energo. Service AD, Sofia, Bulgaria • Westinghouse Energy Systems OOD -Branch Bulgaria • ENERGY ORGRES Ltd, Sofia, Bulgaria • Westron LLC, Kharkiv, Ukraine • RPC “Radiy”, Kirovograd, Ukraine


