 Emotions & Stress (Emotion)
Emotions & Stress (Emotion)
 Theories of Emotion • James - Lange Theory • Cannon - Bard Theory • Two Factor Theory
Theories of Emotion • James - Lange Theory • Cannon - Bard Theory • Two Factor Theory
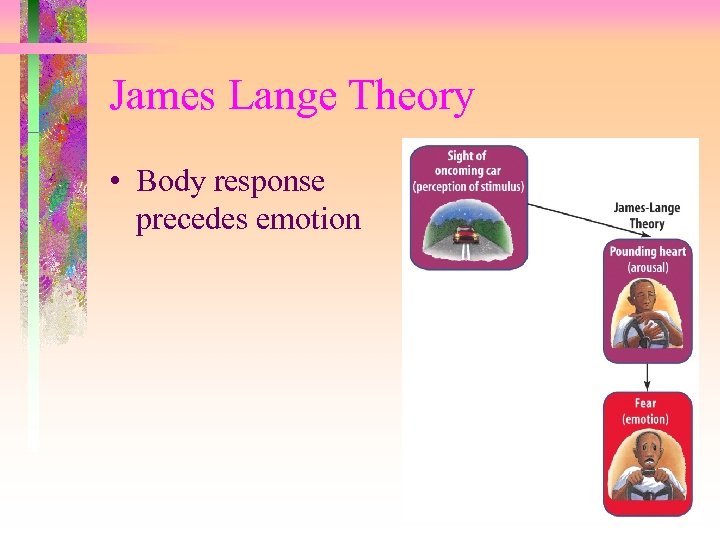 James Lange Theory • Body response precedes emotion
James Lange Theory • Body response precedes emotion
 Cannon - Bard Theory • Body response and emotion occur simultaneously
Cannon - Bard Theory • Body response and emotion occur simultaneously
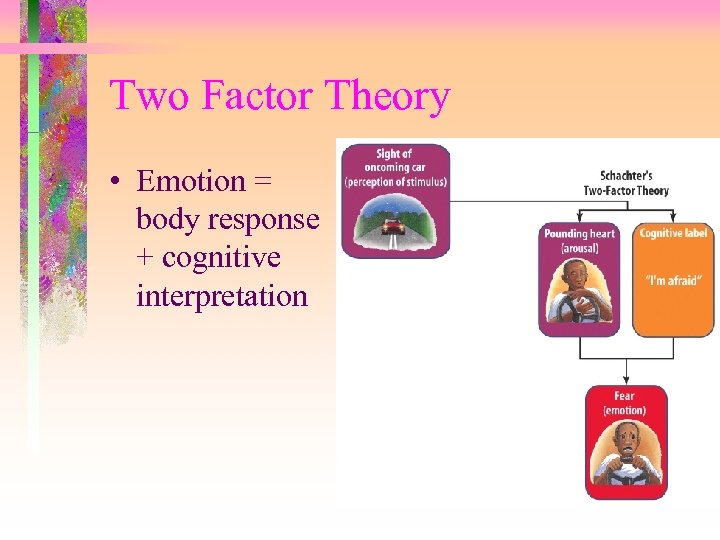 Two Factor Theory • Emotion = body response + cognitive interpretation
Two Factor Theory • Emotion = body response + cognitive interpretation
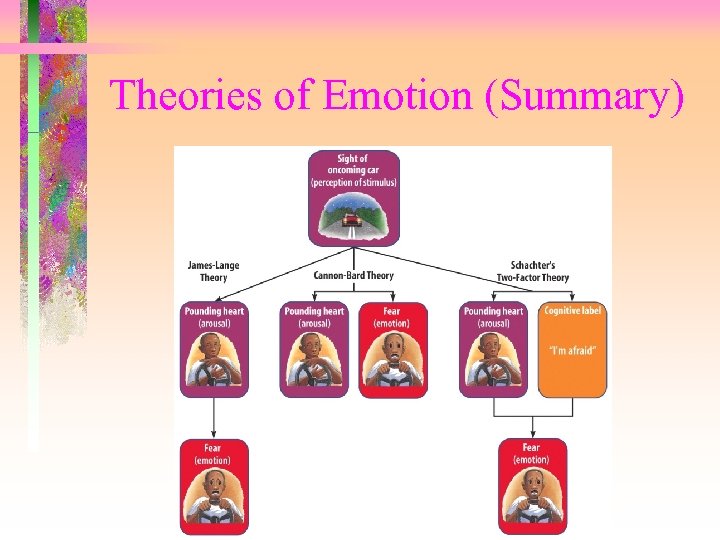 Theories of Emotion (Summary)
Theories of Emotion (Summary)
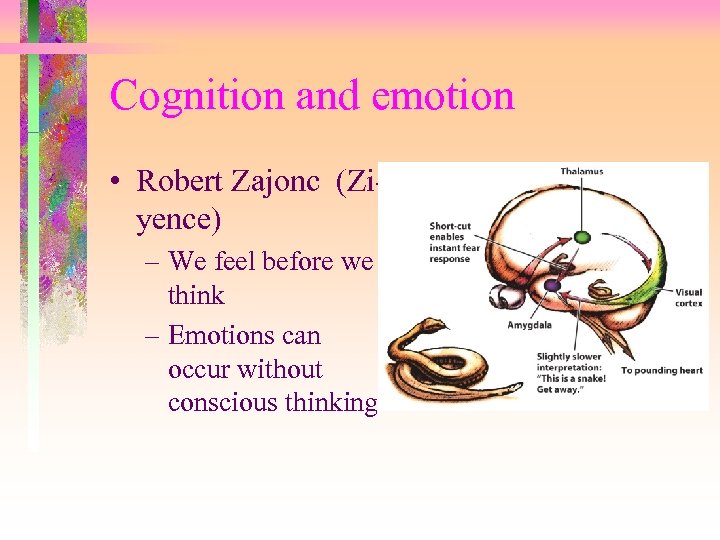 Cognition and emotion • Robert Zajonc (Ziyence) – We feel before we think – Emotions can occur without conscious thinking
Cognition and emotion • Robert Zajonc (Ziyence) – We feel before we think – Emotions can occur without conscious thinking
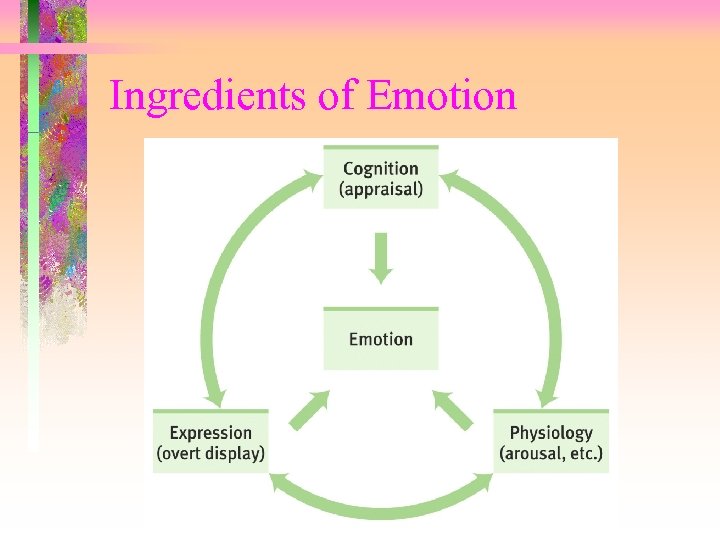 Ingredients of Emotion
Ingredients of Emotion
 Measuring Emotions
Measuring Emotions
 The polygraph • Measures changes in: – Breathing – Heart rate (Cardiovascular activity) – Perspiration • Nonverbal clues – Facial muscles - the most unambiguous clue – Other clues = hand gestures & body language
The polygraph • Measures changes in: – Breathing – Heart rate (Cardiovascular activity) – Perspiration • Nonverbal clues – Facial muscles - the most unambiguous clue – Other clues = hand gestures & body language
 FMRI (Functional MRI) • Specific parts of the brain light up when the person is lying
FMRI (Functional MRI) • Specific parts of the brain light up when the person is lying
 Observational learning of emotions • Monkeys raised in the wild fear snakes • Monkeys raised in the laboratory do not fear snakes – After observing parents and peers fear snakes, younger monkeys developed a fear of snakes
Observational learning of emotions • Monkeys raised in the wild fear snakes • Monkeys raised in the laboratory do not fear snakes – After observing parents and peers fear snakes, younger monkeys developed a fear of snakes
 Anger • Perception of anger most common when a person’s actions seemed: – Willful – Avoidable – Unjustified
Anger • Perception of anger most common when a person’s actions seemed: – Willful – Avoidable – Unjustified
 How can you handle anger? • 1. Wait (simmer down) • 2. Use a non-accusing statement of feeling (“I” statement) • 3. Avoid “You” statements
How can you handle anger? • 1. Wait (simmer down) • 2. Use a non-accusing statement of feeling (“I” statement) • 3. Avoid “You” statements
 Happiness • Our general happiness level is largely unchanged by both very positive or very negative events.
Happiness • Our general happiness level is largely unchanged by both very positive or very negative events.
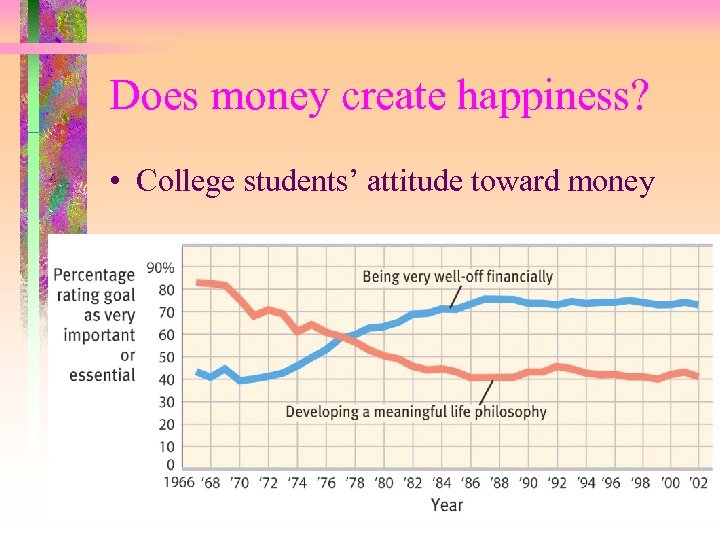 Does money create happiness? • College students’ attitude toward money
Does money create happiness? • College students’ attitude toward money
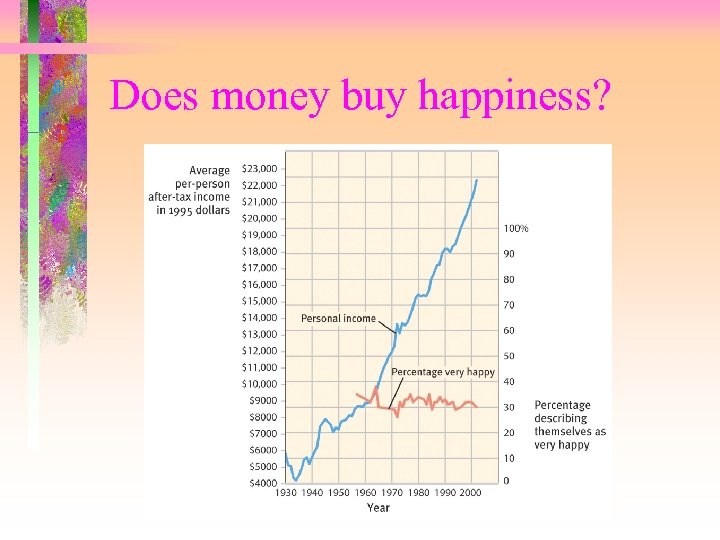 Does money buy happiness?
Does money buy happiness?
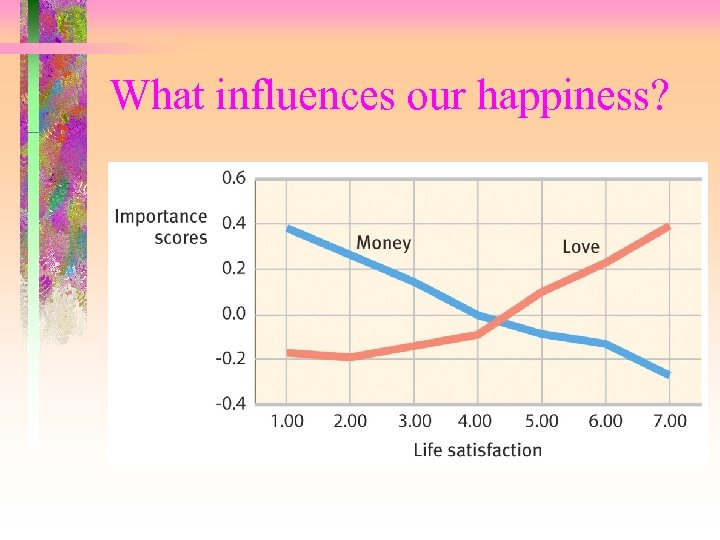 What influences our happiness?
What influences our happiness?
 Adaptation - level phenomenon • Our tendency to judge items (income, grades, sounds, lights) relative to a “neutral” (or accustomed) level based on our prior experience. – E. g. income – temperature – Grades
Adaptation - level phenomenon • Our tendency to judge items (income, grades, sounds, lights) relative to a “neutral” (or accustomed) level based on our prior experience. – E. g. income – temperature – Grades
 Relative deprivation • We often feel happy or deprived (rich or poor) relative to the people we compare ourselves to. – E. g. “Poor” in the U. S. is not poor in India – E. g. 90% on an exam feels good until you learn everyone else in the class had a score over 95%
Relative deprivation • We often feel happy or deprived (rich or poor) relative to the people we compare ourselves to. – E. g. “Poor” in the U. S. is not poor in India – E. g. 90% on an exam feels good until you learn everyone else in the class had a score over 95%
 What predicts happiness? • High self-esteem • Optimism • Having a satisfying marriage or close friends • Being happy in work and leisure • Religious faith • Enough sleep and exercise.
What predicts happiness? • High self-esteem • Optimism • Having a satisfying marriage or close friends • Being happy in work and leisure • Religious faith • Enough sleep and exercise.