01cb27f1434276bbad23fed48b1d62f9.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 36
 Emerging Infrastructure and Data Center Architecture – Principles and Practice Richard Fichera Director, Blade. Systems Strategy Blade. System & Infrastructure Software
Emerging Infrastructure and Data Center Architecture – Principles and Practice Richard Fichera Director, Blade. Systems Strategy Blade. System & Infrastructure Software
 Today’s Agenda ü The problem – complexity and physics catch up with the data center ü The building blocks – servers, storage and fabrics ü Evolution in Data Center architectures ü Infrastructure in motion – VMs, automation and orchestration ü Infrastructure and data center transformation
Today’s Agenda ü The problem – complexity and physics catch up with the data center ü The building blocks – servers, storage and fabrics ü Evolution in Data Center architectures ü Infrastructure in motion – VMs, automation and orchestration ü Infrastructure and data center transformation
 HP Blade. System c-Class Server Blade Background – Enclosure Overwhelming Complexity and Increasing Scale
HP Blade. System c-Class Server Blade Background – Enclosure Overwhelming Complexity and Increasing Scale
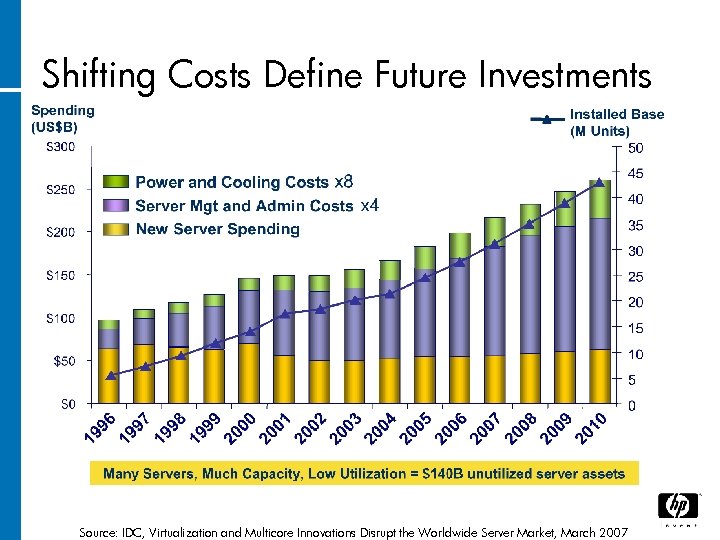 Shifting Costs Define Future Investments Source: IDC, Virtualization and Multicore Innovations Disrupt the Worldwide Server Market, March 2007
Shifting Costs Define Future Investments Source: IDC, Virtualization and Multicore Innovations Disrupt the Worldwide Server Market, March 2007
 HP Blade. System c-Class Server Blade Infrastructure Building Enclosure Blocks – Fundamental Physics and Trends
HP Blade. System c-Class Server Blade Infrastructure Building Enclosure Blocks – Fundamental Physics and Trends
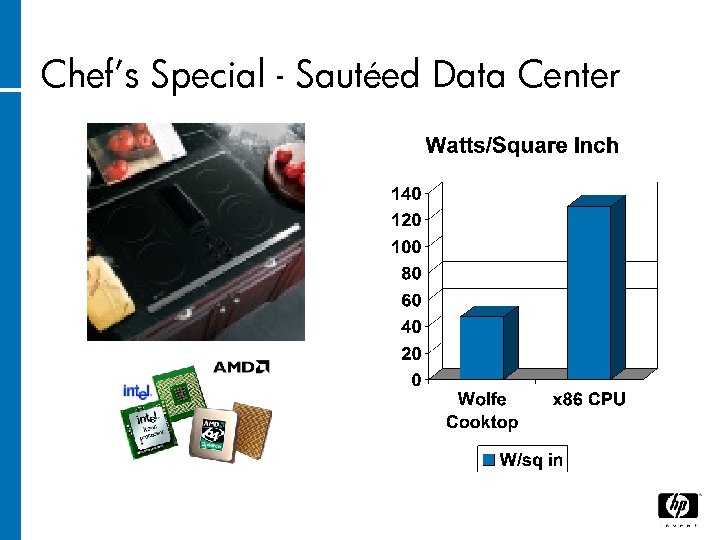 Chef’s Special - Sautéed Data Center
Chef’s Special - Sautéed Data Center
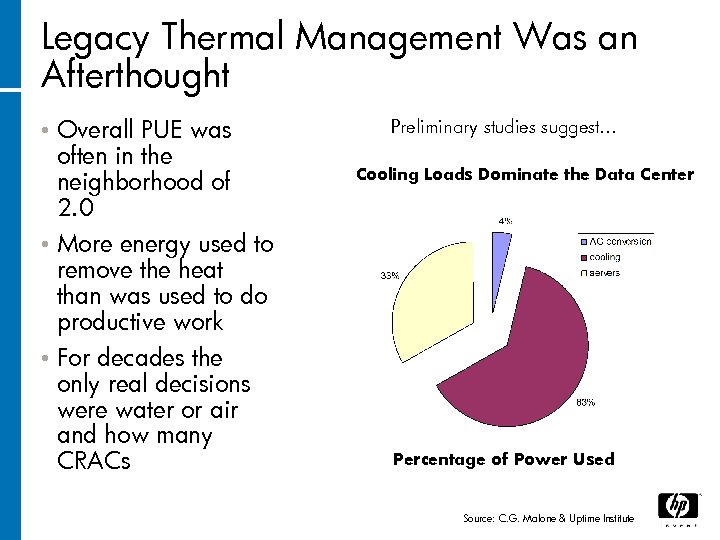 Legacy Thermal Management Was an Afterthought Overall PUE was often in the neighborhood of 2. 0 • More energy used to remove the heat than was used to do productive work • For decades the only real decisions were water or air and how many CRACs • Preliminary studies suggest… Cooling Loads Dominate the Data Center Percentage of Power Used Source: C. G. Malone & Uptime Institute
Legacy Thermal Management Was an Afterthought Overall PUE was often in the neighborhood of 2. 0 • More energy used to remove the heat than was used to do productive work • For decades the only real decisions were water or air and how many CRACs • Preliminary studies suggest… Cooling Loads Dominate the Data Center Percentage of Power Used Source: C. G. Malone & Uptime Institute
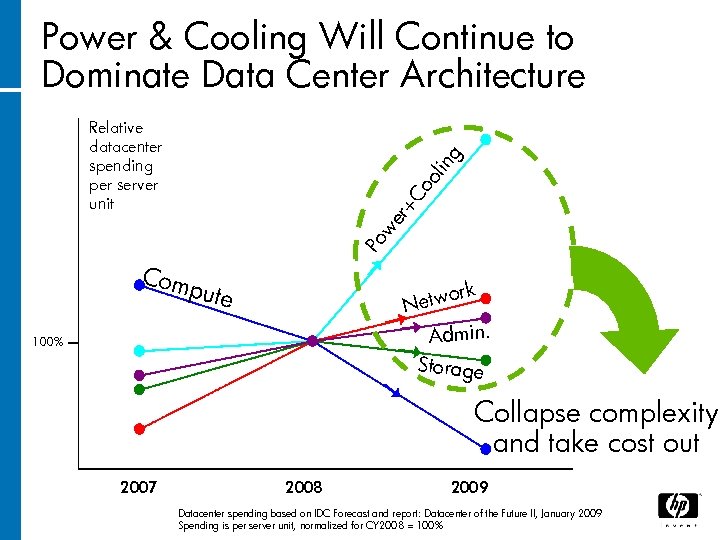 Power & Cooling Will Continue to Dominate Data Center Architecture Po we r+ Co ol in g Relative datacenter spending per server unit Com pute rk o Netw Admin. Storage 100% Collapse complexity and take cost out 2007 2008 2009 Datacenter spending based on IDC Forecast and report: Datacenter of the Future II, January 2009 Spending is per server unit, normalized for CY 2008 = 100%
Power & Cooling Will Continue to Dominate Data Center Architecture Po we r+ Co ol in g Relative datacenter spending per server unit Com pute rk o Netw Admin. Storage 100% Collapse complexity and take cost out 2007 2008 2009 Datacenter spending based on IDC Forecast and report: Datacenter of the Future II, January 2009 Spending is per server unit, normalized for CY 2008 = 100%
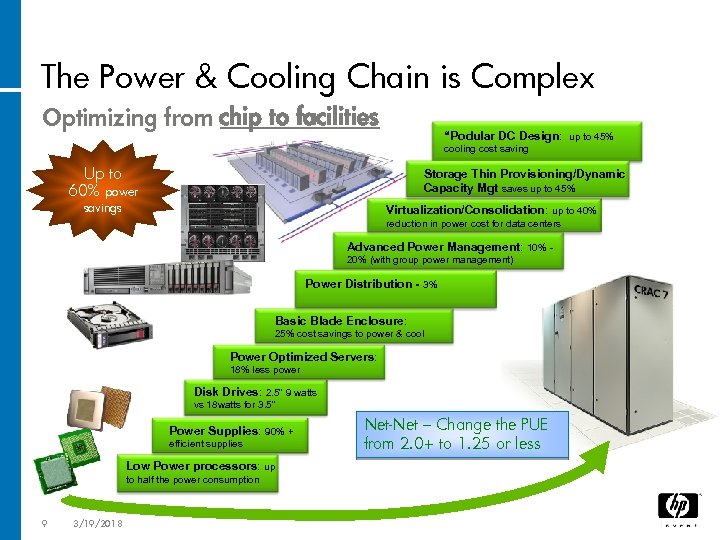 The Power & Cooling Chain is Complex Optimizing from chip to facilities “Podular DC Design: up to 45% cooling cost saving Up to 60% power Storage Thin Provisioning/Dynamic Capacity Mgt saves up to 45% savings Virtualization/Consolidation: up to 40% reduction in power cost for data centers Advanced Power Management: 10% 20% (with group power management) Power Distribution - 3% Basic Blade Enclosure: 25% cost savings to power & cool Power Optimized Servers: 18% less power Disk Drives: 2. 5” 9 watts vs 18 watts for 3. 5” Power Supplies: 90% + efficient supplies Low Power processors: up to half the power consumption 9 3/19/2018 Net-Net – Change the PUE from 2. 0+ to 1. 25 or less
The Power & Cooling Chain is Complex Optimizing from chip to facilities “Podular DC Design: up to 45% cooling cost saving Up to 60% power Storage Thin Provisioning/Dynamic Capacity Mgt saves up to 45% savings Virtualization/Consolidation: up to 40% reduction in power cost for data centers Advanced Power Management: 10% 20% (with group power management) Power Distribution - 3% Basic Blade Enclosure: 25% cost savings to power & cool Power Optimized Servers: 18% less power Disk Drives: 2. 5” 9 watts vs 18 watts for 3. 5” Power Supplies: 90% + efficient supplies Low Power processors: up to half the power consumption 9 3/19/2018 Net-Net – Change the PUE from 2. 0+ to 1. 25 or less
 Servers – Market and Drivers • Market − The x 86 server market represents approximately 8, 000 servers per year, and will remain the center of innovation and investment. − The market is split 35/50/15 in terms of the tower/rack/blade form factors, with blades and extreme scale-out as the fastestgrowing segments. • Key Drivers − Acquisition cost will always be important − Energy consumption has become a priority, but focus will shift to larger aggregates as marginal gains on servers get smaller − Total infrastructure cost, including management, becomes a focus at a system/DC level • This is the jumping off point for debates about unified fabrics, shared and virtualized I/O, new virtualization management models, etc.
Servers – Market and Drivers • Market − The x 86 server market represents approximately 8, 000 servers per year, and will remain the center of innovation and investment. − The market is split 35/50/15 in terms of the tower/rack/blade form factors, with blades and extreme scale-out as the fastestgrowing segments. • Key Drivers − Acquisition cost will always be important − Energy consumption has become a priority, but focus will shift to larger aggregates as marginal gains on servers get smaller − Total infrastructure cost, including management, becomes a focus at a system/DC level • This is the jumping off point for debates about unified fabrics, shared and virtualized I/O, new virtualization management models, etc.
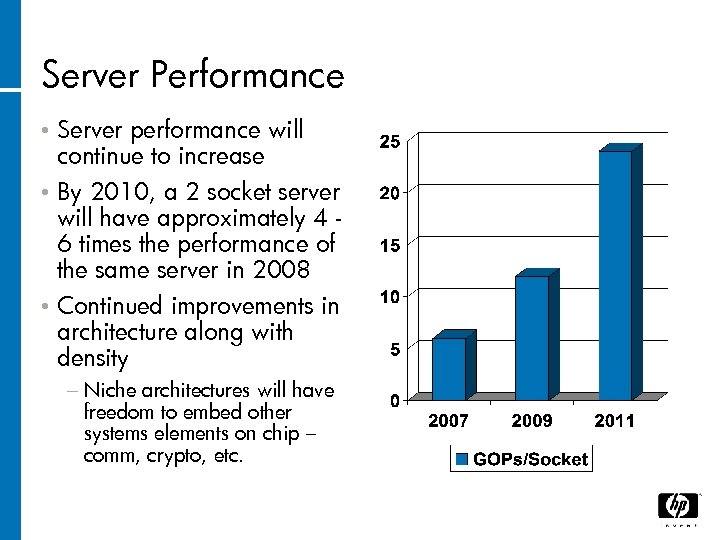 Server Performance Server performance will continue to increase • By 2010, a 2 socket server will have approximately 4 6 times the performance of the same server in 2008 • Continued improvements in architecture along with density • − Niche architectures will have freedom to embed other systems elements on chip – comm, crypto, etc.
Server Performance Server performance will continue to increase • By 2010, a 2 socket server will have approximately 4 6 times the performance of the same server in 2008 • Continued improvements in architecture along with density • − Niche architectures will have freedom to embed other systems elements on chip – comm, crypto, etc.
 Processors trends Silicon compaction continues (65 nm, 45 nm, 32 nm) • Higher levels of functional blocks integration Large gate count • − Caches, Memory controller(s), I/O, TPM • All server processors going to NUMA using processor links (no more FSB) − More efficient coherency protocols (Intel: Home Snooping; AMD: HT Assist) • Higher number of and faster interfaces Large pin-count pkg − One or more processor links More flexible designs • Intel QPI • AMD HT − Multiple memory links Flexible memory configurations − Integrated I/O links (PCIe 3, USB 3) I/O closer to processor & memory Core count increase continues (4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 16) • Core clock frequencies increase slow down (topping around 3 GHz) • More physical memory address bits (Intel: 46; AMD: 48) • Wide range of power (TDP) bins (Intel: 37… 150 W; AMD: 45… 140 W) • − Depends on core count, cache size, coherent link count 12 8 June, 2009
Processors trends Silicon compaction continues (65 nm, 45 nm, 32 nm) • Higher levels of functional blocks integration Large gate count • − Caches, Memory controller(s), I/O, TPM • All server processors going to NUMA using processor links (no more FSB) − More efficient coherency protocols (Intel: Home Snooping; AMD: HT Assist) • Higher number of and faster interfaces Large pin-count pkg − One or more processor links More flexible designs • Intel QPI • AMD HT − Multiple memory links Flexible memory configurations − Integrated I/O links (PCIe 3, USB 3) I/O closer to processor & memory Core count increase continues (4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 16) • Core clock frequencies increase slow down (topping around 3 GHz) • More physical memory address bits (Intel: 46; AMD: 48) • Wide range of power (TDP) bins (Intel: 37… 150 W; AMD: 45… 140 W) • − Depends on core count, cache size, coherent link count 12 8 June, 2009
 Memory trends • Increase DDR 3 speeds with tradeoffs on # DIMMs per channel (DPC) • DRAM chip capacity increase • DIMM capacity increase • 8 GB DIMM will be linearly priced in 2010 • Reduced DIMM power rail and consumption • DIMM interfaces (DDR, SMI/VMSE) changing to address DDR bus limitations • Non-volatile components will add memory/storage hierarchy 13 8 June, 2009
Memory trends • Increase DDR 3 speeds with tradeoffs on # DIMMs per channel (DPC) • DRAM chip capacity increase • DIMM capacity increase • 8 GB DIMM will be linearly priced in 2010 • Reduced DIMM power rail and consumption • DIMM interfaces (DDR, SMI/VMSE) changing to address DDR bus limitations • Non-volatile components will add memory/storage hierarchy 13 8 June, 2009
 Server Futures • Continued escalation of core count and memory − Expect differentiation in choice of on-board peripherals and accelerators at both chip and board level − Continual pressure toward denser, higher layer count boards − “Communications radius” effects, SI and connector limits • Changing options for design − Link-based connections for more flexible design − More options for local and near storage • Design differentiation as requirements bi/trifurcate − GP, scale out, virtualization designs • Value increasingly in packaging, rack-scale and larger integration
Server Futures • Continued escalation of core count and memory − Expect differentiation in choice of on-board peripherals and accelerators at both chip and board level − Continual pressure toward denser, higher layer count boards − “Communications radius” effects, SI and connector limits • Changing options for design − Link-based connections for more flexible design − More options for local and near storage • Design differentiation as requirements bi/trifurcate − GP, scale out, virtualization designs • Value increasingly in packaging, rack-scale and larger integration
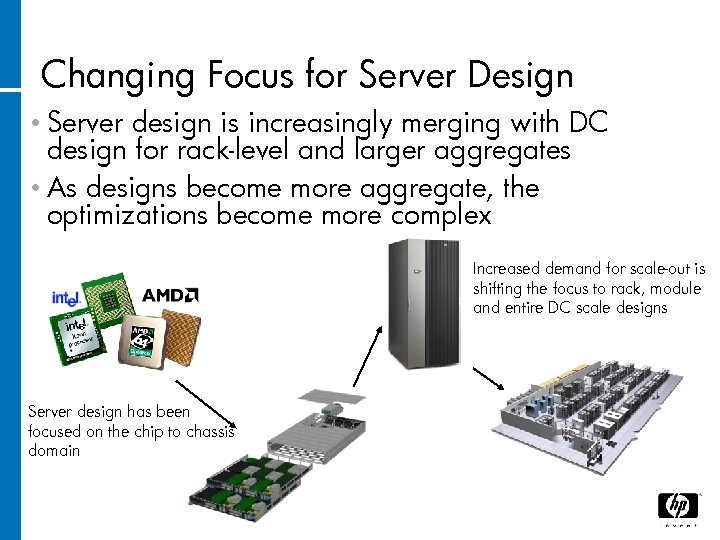 Changing Focus for Server Design • Server design is increasingly merging with DC design for rack-level and larger aggregates • As designs become more aggregate, the optimizations become more complex Increased demand for scale-out is shifting the focus to rack, module and entire DC scale designs Server design has been focused on the chip to chassis domain
Changing Focus for Server Design • Server design is increasingly merging with DC design for rack-level and larger aggregates • As designs become more aggregate, the optimizations become more complex Increased demand for scale-out is shifting the focus to rack, module and entire DC scale designs Server design has been focused on the chip to chassis domain
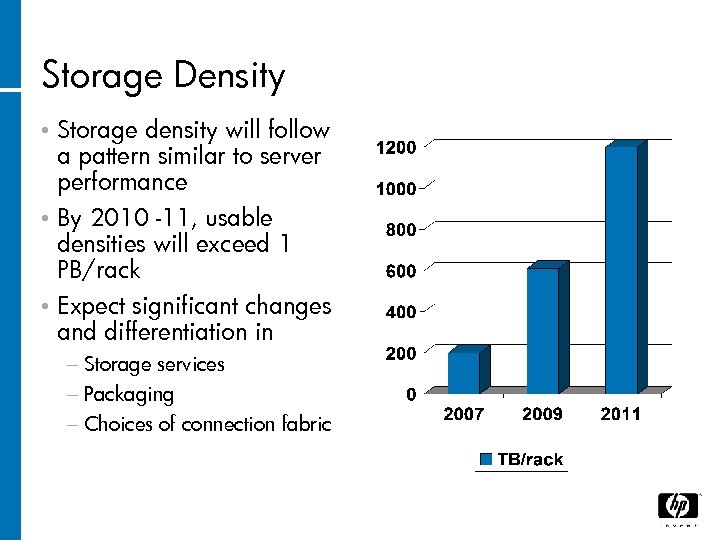 Storage Density Storage density will follow a pattern similar to server performance • By 2010 -11, usable densities will exceed 1 PB/rack • Expect significant changes and differentiation in • − Storage services − Packaging − Choices of connection fabric
Storage Density Storage density will follow a pattern similar to server performance • By 2010 -11, usable densities will exceed 1 PB/rack • Expect significant changes and differentiation in • − Storage services − Packaging − Choices of connection fabric
 Block storage device trends • Cost competiveness drove HDD industry consolidation • HDD interfaces going fast serial links: SAS/SATA − SAS growing to be the interface of choice in enterprise − FC HDD growth is flat or shrinking • Switched SAS also enables storage fabric for shared block storage − But, lots of things need to be developed for complete solutions • HDD capacity continue to increase, while rpm tops at 15 K − HDD areal density ~30 -40% AGR [SFF 0. 5 TB in ’ 10, TB in ’ 11] • SFF dominates in enterprise − Enterprise SFF 10 K adoption growing (largest segment) while LFF 15 K vol. shrinking • Flash storage is disruptive − SSD $/GB cross-over with SFF SAS 15 K rpm in ’ 11 -’ 12 • 256 G/512 G in ’ 10, TB in ‘ 11 − PCIe-based Flash storage significantly improves storage I/O − New storage hierarchies and models, including memory cache, disc cache, i/o accelerators 17 8 June, 2009 17
Block storage device trends • Cost competiveness drove HDD industry consolidation • HDD interfaces going fast serial links: SAS/SATA − SAS growing to be the interface of choice in enterprise − FC HDD growth is flat or shrinking • Switched SAS also enables storage fabric for shared block storage − But, lots of things need to be developed for complete solutions • HDD capacity continue to increase, while rpm tops at 15 K − HDD areal density ~30 -40% AGR [SFF 0. 5 TB in ’ 10, TB in ’ 11] • SFF dominates in enterprise − Enterprise SFF 10 K adoption growing (largest segment) while LFF 15 K vol. shrinking • Flash storage is disruptive − SSD $/GB cross-over with SFF SAS 15 K rpm in ’ 11 -’ 12 • 256 G/512 G in ’ 10, TB in ‘ 11 − PCIe-based Flash storage significantly improves storage I/O − New storage hierarchies and models, including memory cache, disc cache, i/o accelerators 17 8 June, 2009 17
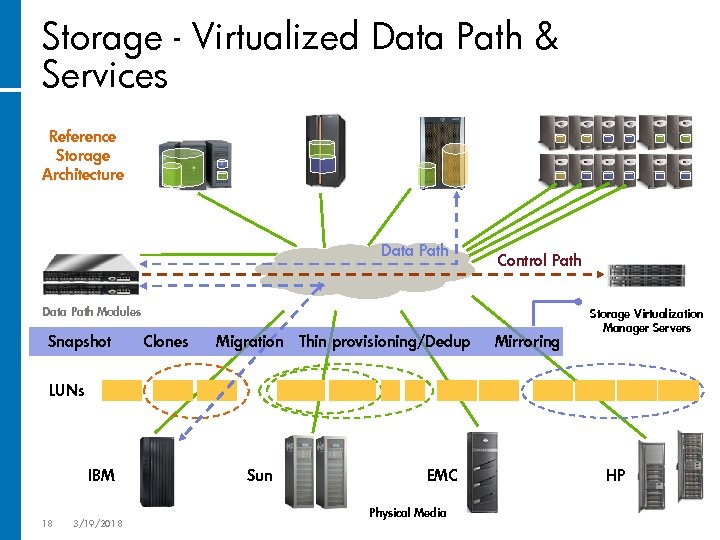 Storage - Virtualized Data Path & Services Reference Storage Architecture Data Path Control Path Data Path Modules Snapshot Clones Migration Thin provisioning/Dedup Mirroring Storage Virtualization Manager Servers LUNs IBM 18 3/19/2018 Sun EMC Physical Media HP
Storage - Virtualized Data Path & Services Reference Storage Architecture Data Path Control Path Data Path Modules Snapshot Clones Migration Thin provisioning/Dedup Mirroring Storage Virtualization Manager Servers LUNs IBM 18 3/19/2018 Sun EMC Physical Media HP
 Data Center Logical Architecture – Changing Resource Distribution Strategies WAN & Campus Core Data Center Core Fabric storage SLB Distribution/ Aggregation Firewall Access (Server Edge) Rack-mount Server farms Blade server Chassis SAN storage 19 3/19/2018 SAN Virtual Machines • Changes in density and fabric are changing the approach to modularity of storage and servers • Converged fabrics allow more flexibility in location and reduce interconnect costs • Local “mini-SANs” such as switched SAS allow refactoring storage to bring it near consumers and producers – and away from the SAN team • Increasingly flexible storage services models
Data Center Logical Architecture – Changing Resource Distribution Strategies WAN & Campus Core Data Center Core Fabric storage SLB Distribution/ Aggregation Firewall Access (Server Edge) Rack-mount Server farms Blade server Chassis SAN storage 19 3/19/2018 SAN Virtual Machines • Changes in density and fabric are changing the approach to modularity of storage and servers • Converged fabrics allow more flexibility in location and reduce interconnect costs • Local “mini-SANs” such as switched SAS allow refactoring storage to bring it near consumers and producers – and away from the SAN team • Increasingly flexible storage services models
 Physical Architecture – Is There a Podular DC in Your Future? • Lower TCO • • • − Higher PUE and power/cooling efficiency vs traditional DC Geographic flexibility − Can deploy closer to customers, and in locales not suitable for brick & mortar − Controlled/hybrid co-lo environments Faster time to Revenue for customers − Brick & Mortar 18+ months design/build vs Container in <6 months Improved return on capital − “Pay as you go” vs. $millions up-front investment for brick & mortar More efficient procurement chunk size − Rack too small, datacenter takes too long Scalable with enterprise architecture − Core/Regional Gateway/Point-of-Purchase
Physical Architecture – Is There a Podular DC in Your Future? • Lower TCO • • • − Higher PUE and power/cooling efficiency vs traditional DC Geographic flexibility − Can deploy closer to customers, and in locales not suitable for brick & mortar − Controlled/hybrid co-lo environments Faster time to Revenue for customers − Brick & Mortar 18+ months design/build vs Container in <6 months Improved return on capital − “Pay as you go” vs. $millions up-front investment for brick & mortar More efficient procurement chunk size − Rack too small, datacenter takes too long Scalable with enterprise architecture − Core/Regional Gateway/Point-of-Purchase
 HP Blade. System c-Class Server Blade Virtualization, Enclosure Orchestration, Automation and Infrastructure Agility
HP Blade. System c-Class Server Blade Virtualization, Enclosure Orchestration, Automation and Infrastructure Agility
 Virtualization – A Blessing & a Curse • Virtualization – of servers, storage, networks and I/O hardware – brings major benefits … − Capital resource efficiency (the initial sell) − Standardization and ease of migration − A gateway to adaptive architectures • … as well as significant burdens – management, management − Are you substituting one vendor lock-in for another? − How many more tools do you want to add to your environment? − How do you integrate the physical and virtual management layer? • Be prepared for major innovation and vendor conflict in this arena for the next five years − You need to have a strategy, metrics and a roadmap
Virtualization – A Blessing & a Curse • Virtualization – of servers, storage, networks and I/O hardware – brings major benefits … − Capital resource efficiency (the initial sell) − Standardization and ease of migration − A gateway to adaptive architectures • … as well as significant burdens – management, management − Are you substituting one vendor lock-in for another? − How many more tools do you want to add to your environment? − How do you integrate the physical and virtual management layer? • Be prepared for major innovation and vendor conflict in this arena for the next five years − You need to have a strategy, metrics and a roadmap
 Enterprise Customers continue to be challenged managing infrastructure • Server admin and management costs grow with the installed base of servers 1 − Basic operations such as installing a server typically take weeks requiring manual coordination across multiple customer organizations • Power, cooling and facilities limitations continue to loom as limits - the “$10 Million server” − This will drive multiple deployment options such as cloud in an attempt to tap economies of scale • Virtualization helps some things, but potentially complicates the management environment − Expect continued experimentation in virtualization management models, expanded virtualization options
Enterprise Customers continue to be challenged managing infrastructure • Server admin and management costs grow with the installed base of servers 1 − Basic operations such as installing a server typically take weeks requiring manual coordination across multiple customer organizations • Power, cooling and facilities limitations continue to loom as limits - the “$10 Million server” − This will drive multiple deployment options such as cloud in an attempt to tap economies of scale • Virtualization helps some things, but potentially complicates the management environment − Expect continued experimentation in virtualization management models, expanded virtualization options
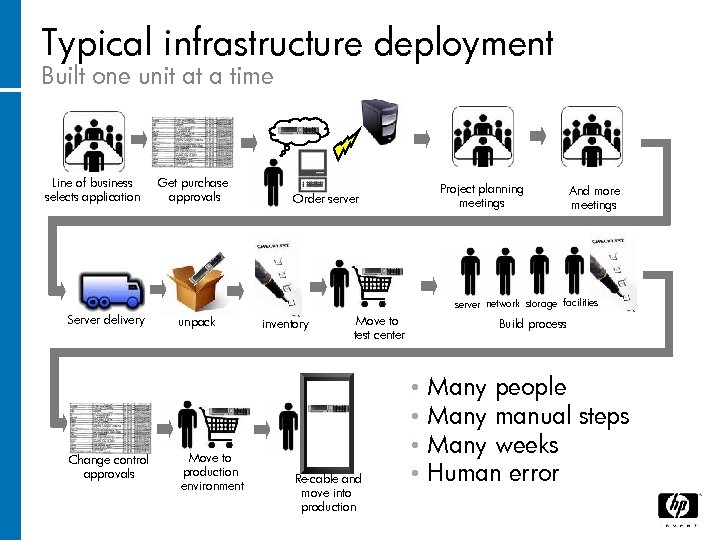 Typical infrastructure deployment Built one unit at a time Line of business selects application Get purchase approvals Project planning meetings Order server And more meetings server network storage facilities Server delivery Change control approvals unpack Move to production environment inventory Move to test center Re-cable and move into production Build process • • Many people Many manual steps Many weeks Human error
Typical infrastructure deployment Built one unit at a time Line of business selects application Get purchase approvals Project planning meetings Order server And more meetings server network storage facilities Server delivery Change control approvals unpack Move to production environment inventory Move to test center Re-cable and move into production Build process • • Many people Many manual steps Many weeks Human error
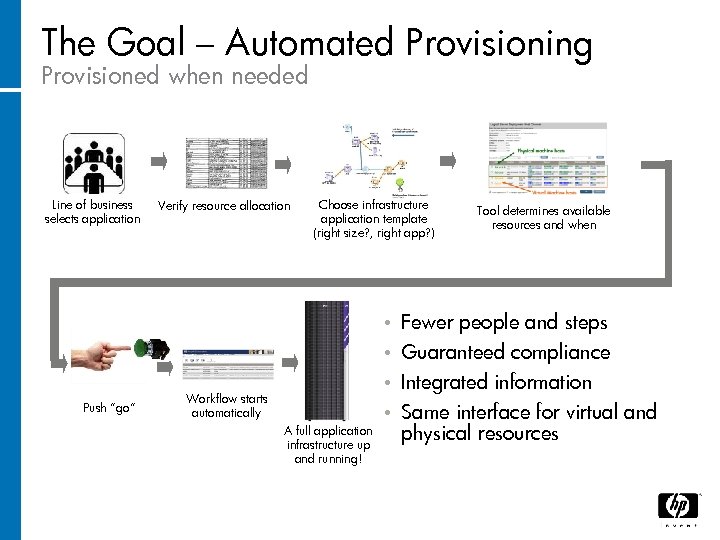 The Goal – Automated Provisioning Provisioned when needed Line of business selects application Verify resource allocation Choose infrastructure application template (right size? , right app? ) Tool determines available resources and when • • Push “go” Fewer people and steps Guaranteed compliance Integrated information • Same interface for virtual and physical resources • Workflow starts automatically A full application infrastructure up and running!
The Goal – Automated Provisioning Provisioned when needed Line of business selects application Verify resource allocation Choose infrastructure application template (right size? , right app? ) Tool determines available resources and when • • Push “go” Fewer people and steps Guaranteed compliance Integrated information • Same interface for virtual and physical resources • Workflow starts automatically A full application infrastructure up and running!
 What You Need to Add • Comprehensive VM management CONVERGED with physical management − Power-aware load placement and movement − Physical/logical discovery & visualization − Multi-tier provisioning of VMs, networks and applications − Lifecycle management of VMs − Resilience, changing how we do HA • And the good news is that you have at least 100 niche/startup vendors to choose from • As well as the feuding major vendors − We ALL want to be your management console of record
What You Need to Add • Comprehensive VM management CONVERGED with physical management − Power-aware load placement and movement − Physical/logical discovery & visualization − Multi-tier provisioning of VMs, networks and applications − Lifecycle management of VMs − Resilience, changing how we do HA • And the good news is that you have at least 100 niche/startup vendors to choose from • As well as the feuding major vendors − We ALL want to be your management console of record
 HP Blade. System c-Class Server Blade Infrastructure Enclosure Transformation – How to Get There From Here
HP Blade. System c-Class Server Blade Infrastructure Enclosure Transformation – How to Get There From Here
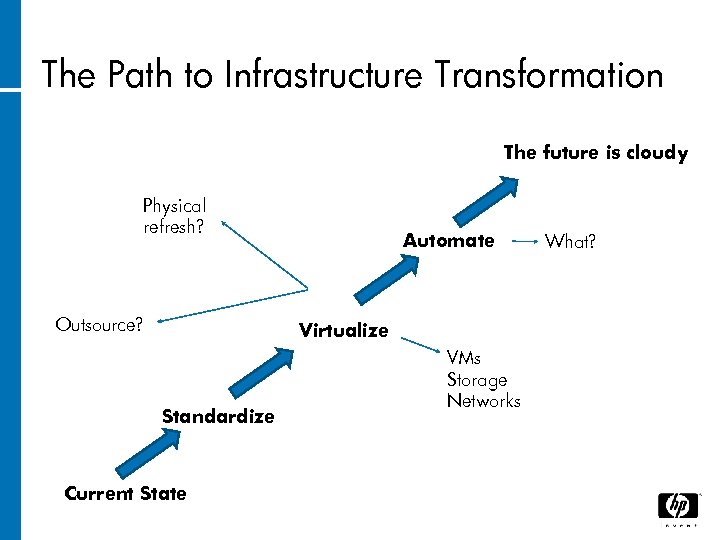 The Path to Infrastructure Transformation The future is cloudy Physical refresh? Outsource? Automate Virtualize Standardize Current State VMs Storage Networks What?
The Path to Infrastructure Transformation The future is cloudy Physical refresh? Outsource? Automate Virtualize Standardize Current State VMs Storage Networks What?
 Some Essential Principles • Draconian standardization − It’s really amazing how simple you can make an enterprise environment if you just don’t let anyone complain (or at least stop listening to them) • Vendor simplification − Software is particularly important − You may want to maintain very coarse-grained hardware heterogeneity for vendor management • Almost always, fewer is better − Locations, software titles, options − Once standardization has been in place for a full dev cycle, requests for variations become few and far between
Some Essential Principles • Draconian standardization − It’s really amazing how simple you can make an enterprise environment if you just don’t let anyone complain (or at least stop listening to them) • Vendor simplification − Software is particularly important − You may want to maintain very coarse-grained hardware heterogeneity for vendor management • Almost always, fewer is better − Locations, software titles, options − Once standardization has been in place for a full dev cycle, requests for variations become few and far between
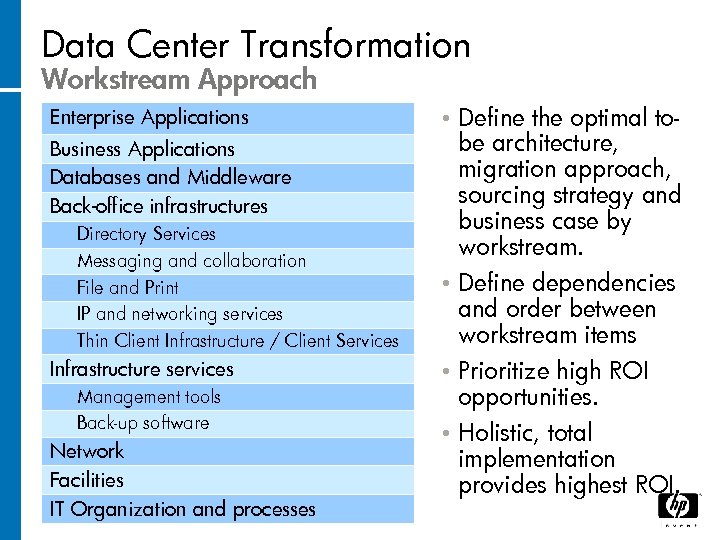 Data Center Transformation Workstream Approach Enterprise Applications Business Applications Databases and Middleware Back-office infrastructures Directory Services Messaging and collaboration File and Print IP and networking services Thin Client Infrastructure / Client Services Infrastructure services Management tools Back-up software Network Facilities IT Organization and processes Define the optimal tobe architecture, migration approach, sourcing strategy and business case by workstream. • Define dependencies and order between workstream items • Prioritize high ROI opportunities. • Holistic, total implementation provides highest ROI. •
Data Center Transformation Workstream Approach Enterprise Applications Business Applications Databases and Middleware Back-office infrastructures Directory Services Messaging and collaboration File and Print IP and networking services Thin Client Infrastructure / Client Services Infrastructure services Management tools Back-up software Network Facilities IT Organization and processes Define the optimal tobe architecture, migration approach, sourcing strategy and business case by workstream. • Define dependencies and order between workstream items • Prioritize high ROI opportunities. • Holistic, total implementation provides highest ROI. •
 Data Center & IT Transformation What Can You Achieve? Reduce Cost • Overall lower total IT costs – your mileage will vary • Up to 50% savings from IT consolidation, apps rationalization • Up to 60% energy savings from modern facilities • Up to 25% real estate, location savings Mitigate Risk • Centralize & standardize IT and data center processes • Establish compliance with industry best practices • Protect company revenue, brand & reputation from outage or disaster Grow Business • Timely response to new business initiatives (that old alignment thing) • Spend more time focusing on business value instead of fighting fires and managing MAC addresses
Data Center & IT Transformation What Can You Achieve? Reduce Cost • Overall lower total IT costs – your mileage will vary • Up to 50% savings from IT consolidation, apps rationalization • Up to 60% energy savings from modern facilities • Up to 25% real estate, location savings Mitigate Risk • Centralize & standardize IT and data center processes • Establish compliance with industry best practices • Protect company revenue, brand & reputation from outage or disaster Grow Business • Timely response to new business initiatives (that old alignment thing) • Spend more time focusing on business value instead of fighting fires and managing MAC addresses
 Best Practices to Achieve the Vision • Simplify through standardization : Standard & consistent data center architecture and design; standard hardware, tools, and infrastructure • Establish PMO for governance: Provides framework for how effort will be structured, who will make decisions Go modular : Allows for fast build, flexibility, scalability, and efficiencies; isolates and separates risk Break plan into bite-size chunks: Divide into workstreams , engage proper expertise, identify clear goals & deliverables by quarter Synchronize—timing everything: Facilities must be ready to receive is servers; servers must be ready to receive applications Define one set of processes: A properly documented single set of processes aligned to ITIL V 3 model ensures desired outcomes, allows for automation Actively manage and communicate change: Change management and well-executed communication strategy critical for success • • •
Best Practices to Achieve the Vision • Simplify through standardization : Standard & consistent data center architecture and design; standard hardware, tools, and infrastructure • Establish PMO for governance: Provides framework for how effort will be structured, who will make decisions Go modular : Allows for fast build, flexibility, scalability, and efficiencies; isolates and separates risk Break plan into bite-size chunks: Divide into workstreams , engage proper expertise, identify clear goals & deliverables by quarter Synchronize—timing everything: Facilities must be ready to receive is servers; servers must be ready to receive applications Define one set of processes: A properly documented single set of processes aligned to ITIL V 3 model ensures desired outcomes, allows for automation Actively manage and communicate change: Change management and well-executed communication strategy critical for success • • •
 What Lies Beyond: Cloud Computing A pool of abstracted, highly scalable, and managed compute infrastructure capable of hosting end customer applications and billed by consumption. Cloud computing's ecosystem in the future will include Google-like public clouds as a platform for applications, and virtual private clouds, which are third-party clouds, or segments of the public cloud with additional features for security, compliance, etc. The data centre of the future also will include private (internal) clouds, which will be an extension of virtualization and used primarily because of their capital or operational efficiencies. For some applications, data just won't leave the enterprise. “If managing a massive data center isn’t a core competency of your business, maybe you should get out of this business and pass the responsibility to someone who has “ Amazon CTO Werner Vogels, 2007 Next Generation Data Center Conference
What Lies Beyond: Cloud Computing A pool of abstracted, highly scalable, and managed compute infrastructure capable of hosting end customer applications and billed by consumption. Cloud computing's ecosystem in the future will include Google-like public clouds as a platform for applications, and virtual private clouds, which are third-party clouds, or segments of the public cloud with additional features for security, compliance, etc. The data centre of the future also will include private (internal) clouds, which will be an extension of virtualization and used primarily because of their capital or operational efficiencies. For some applications, data just won't leave the enterprise. “If managing a massive data center isn’t a core competency of your business, maybe you should get out of this business and pass the responsibility to someone who has “ Amazon CTO Werner Vogels, 2007 Next Generation Data Center Conference
 Clouds – A Long Haul • Good • Hey, concept, great marketing buzz. where are the applications? • Welcome to the world of almost consistent data. • Where did you say my data is? • Did someone say standards? • Hi, I’m Coke. Am I sharing my cloud with Pepsi? • What’s the difference between a well designed shared services platform and an internal cloud? • But it does have a future …
Clouds – A Long Haul • Good • Hey, concept, great marketing buzz. where are the applications? • Welcome to the world of almost consistent data. • Where did you say my data is? • Did someone say standards? • Hi, I’m Coke. Am I sharing my cloud with Pepsi? • What’s the difference between a well designed shared services platform and an internal cloud? • But it does have a future …
 Thank You Richard Fichera Director, Blade. Systems Strategy Blade. System & Infrastructure Software richard. fichera@hp. com
Thank You Richard Fichera Director, Blade. Systems Strategy Blade. System & Infrastructure Software richard. fichera@hp. com
 Expanding on the Themes at NGDC Beyond Power and Cooling: Improving Data Center Productivity Speaker, John Pflueger, Technology Strategist, Dell • How the Sustainable Data Center Will Reduce Costs and Improve IT, Doug Washburn, Forrester Research • Creating the Most Efficient, Resilient and Sustainable Data Centers, Patrick Leonard, Senior Manager, Strategic Initiatives , • Equinix, Inc. • Working With our Utilities: Getting What You Need When You Want It, Mark Bramfitt, Principal Program Manager, PG&E Corporation • From Monitoring to Management: Gaining Comprehensive Visibility into Data Center Operations, Traci Yarbrough, Product Marketing Manager, Aperture Technologies
Expanding on the Themes at NGDC Beyond Power and Cooling: Improving Data Center Productivity Speaker, John Pflueger, Technology Strategist, Dell • How the Sustainable Data Center Will Reduce Costs and Improve IT, Doug Washburn, Forrester Research • Creating the Most Efficient, Resilient and Sustainable Data Centers, Patrick Leonard, Senior Manager, Strategic Initiatives , • Equinix, Inc. • Working With our Utilities: Getting What You Need When You Want It, Mark Bramfitt, Principal Program Manager, PG&E Corporation • From Monitoring to Management: Gaining Comprehensive Visibility into Data Center Operations, Traci Yarbrough, Product Marketing Manager, Aperture Technologies


