b6a9f6de40716c4b5adfb9e048c15756.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 33
 Emerging Information Technologies Dr. Charles C. Tappert Department of CSIS Pace University
Emerging Information Technologies Dr. Charles C. Tappert Department of CSIS Pace University
 Emerging Information Technologies w. What are Emerging Info Technologies? w. Moore’s Law and what might follow w. Wearable/Handheld Computers w. Virtual Reality w. Artificial Intelligence we-Commerce w. Speech and Handwriting Interfaces
Emerging Information Technologies w. What are Emerging Info Technologies? w. Moore’s Law and what might follow w. Wearable/Handheld Computers w. Virtual Reality w. Artificial Intelligence we-Commerce w. Speech and Handwriting Interfaces
 Technology Life Cycle w w w Precursor - dream or contemplation Invention Emergence (development) Acceptance (established) Surplus or Obsolescence
Technology Life Cycle w w w Precursor - dream or contemplation Invention Emergence (development) Acceptance (established) Surplus or Obsolescence
 Moore’s Law w Every 18 months we put twice as many transistors on an integrated circuit doubling computing power w Been in effect about 40 years w Projected to continue another 20 years w This will end when the size of a transistor approaches the size of a few atoms and conventional shrinking methods won’t work w What will happen then?
Moore’s Law w Every 18 months we put twice as many transistors on an integrated circuit doubling computing power w Been in effect about 40 years w Projected to continue another 20 years w This will end when the size of a transistor approaches the size of a few atoms and conventional shrinking methods won’t work w What will happen then?
 After Moore’s Law New Technologies Will Emerge w Nanotechnology w Quantum Computing w Chaos Computing w Optical Computing
After Moore’s Law New Technologies Will Emerge w Nanotechnology w Quantum Computing w Chaos Computing w Optical Computing
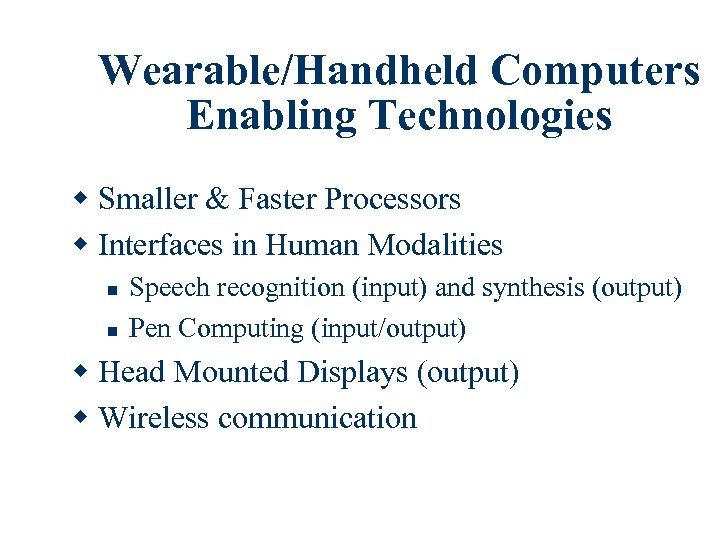 Wearable/Handheld Computers Enabling Technologies w Smaller & Faster Processors w Interfaces in Human Modalities n n Speech recognition (input) and synthesis (output) Pen Computing (input/output) w Head Mounted Displays (output) w Wireless communication
Wearable/Handheld Computers Enabling Technologies w Smaller & Faster Processors w Interfaces in Human Modalities n n Speech recognition (input) and synthesis (output) Pen Computing (input/output) w Head Mounted Displays (output) w Wireless communication
 Photos of Wearable Computers
Photos of Wearable Computers
 Virtual Reality w Head Mounted Displays n n Block view of outside world Completely immerse user in virtual world w Applications n n n Flight simulators Equipment operators Game playing
Virtual Reality w Head Mounted Displays n n Block view of outside world Completely immerse user in virtual world w Applications n n n Flight simulators Equipment operators Game playing
 Photos of VR HMDs
Photos of VR HMDs
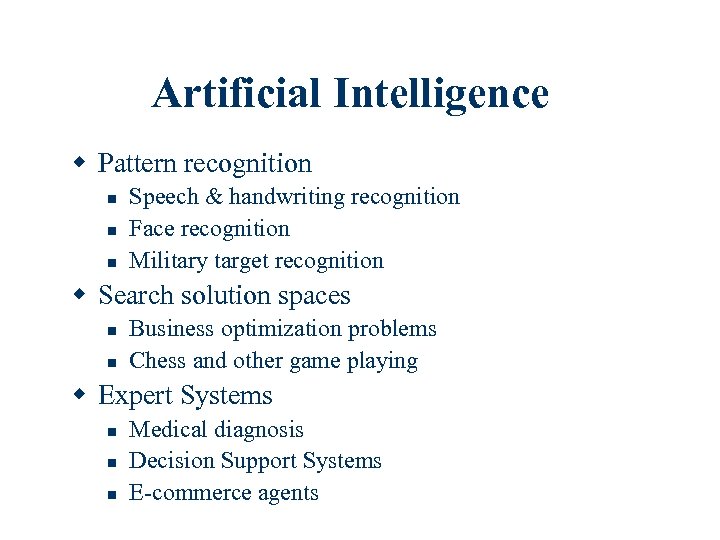 Artificial Intelligence w Pattern recognition n Speech & handwriting recognition Face recognition Military target recognition w Search solution spaces n n Business optimization problems Chess and other game playing w Expert Systems n n n Medical diagnosis Decision Support Systems E-commerce agents
Artificial Intelligence w Pattern recognition n Speech & handwriting recognition Face recognition Military target recognition w Search solution spaces n n Business optimization problems Chess and other game playing w Expert Systems n n n Medical diagnosis Decision Support Systems E-commerce agents
 e-Commerce Web Metamorphosis w from digital library n n static web pages focus on retrieval w to an electronic marketplace n n dynamic web pages focus on transactions w requires new perspective & control mechanisms
e-Commerce Web Metamorphosis w from digital library n n static web pages focus on retrieval w to an electronic marketplace n n dynamic web pages focus on transactions w requires new perspective & control mechanisms
 e-Commerce Web Pull/Push Technologies w Web pull technologies n n Surfing the Net Using a search engine Personal search engines Using an evolutionary agent w Web push technologies n n Broadcasting/Webcasting Selective channeling & filtering Push what the user wants (cookies) Evolutionary push provides exact user needs
e-Commerce Web Pull/Push Technologies w Web pull technologies n n Surfing the Net Using a search engine Personal search engines Using an evolutionary agent w Web push technologies n n Broadcasting/Webcasting Selective channeling & filtering Push what the user wants (cookies) Evolutionary push provides exact user needs
 e-Commerce Agents w w w w Web Representation - marketplace goods & services Promotion - interactive ads Payment & settlement - secure funds transfer Valuation - online auctions and bargaining Customer info - track customer preferences and habits Quality - ratings, reviews, recommendations Risk Management - product guarantees, loss insurance Negotiation - automated systems for negotiation
e-Commerce Agents w w w w Web Representation - marketplace goods & services Promotion - interactive ads Payment & settlement - secure funds transfer Valuation - online auctions and bargaining Customer info - track customer preferences and habits Quality - ratings, reviews, recommendations Risk Management - product guarantees, loss insurance Negotiation - automated systems for negotiation
 Speech Recognition w Isolated words n Navigation and control systems w Continuous speech recognition n Dictation w Speech understanding systems n General speech input
Speech Recognition w Isolated words n Navigation and control systems w Continuous speech recognition n Dictation w Speech understanding systems n General speech input
 Speech Recognition Problems w Dialects w Telephone/cell phone limitations w Noisy environments w Similar sounding words
Speech Recognition Problems w Dialects w Telephone/cell phone limitations w Noisy environments w Similar sounding words
 Speech Recognition Problems w Similar sounding words n n Recognize speech Wreck a nice beach w Identically sounding words - homophones n n The sun’s rays meet The sons raise meat
Speech Recognition Problems w Similar sounding words n n Recognize speech Wreck a nice beach w Identically sounding words - homophones n n The sun’s rays meet The sons raise meat
 Speech Understanding Problems Natural Language Understanding w The spirit is willing but the flesh is weak
Speech Understanding Problems Natural Language Understanding w The spirit is willing but the flesh is weak
 Speech Understanding Problems Natural Language Understanding w The spirit is willing but the flesh is weak w The vodka is strong but the meat is rotten
Speech Understanding Problems Natural Language Understanding w The spirit is willing but the flesh is weak w The vodka is strong but the meat is rotten
 Handwriting Recognition w Offline n n Scanned Images Static Information w Online n n Electronic Tablet or Digitizer Real-Time, Dynamic Information
Handwriting Recognition w Offline n n Scanned Images Static Information w Online n n Electronic Tablet or Digitizer Real-Time, Dynamic Information
 Online Handwriting Recognition w Invention of electronic tablets -- late 1950 s n Tablet and display were separate w Pen Computing -- 1980 s n n Combined tablets and dislpay Brought input and output into the same surface Immediate feedback via electronic ink Created the paper-like interface
Online Handwriting Recognition w Invention of electronic tablets -- late 1950 s n Tablet and display were separate w Pen Computing -- 1980 s n n Combined tablets and dislpay Brought input and output into the same surface Immediate feedback via electronic ink Created the paper-like interface
 Dynamic Handwriting Information w Number of strokes a stroke is the ink trace from pen down to pen up w Order of strokes w Stroke direction w Stroke velocity, acceleration
Dynamic Handwriting Information w Number of strokes a stroke is the ink trace from pen down to pen up w Order of strokes w Stroke direction w Stroke velocity, acceleration
 Written Language and Handwriting Properties w Alphabet n Letters, digits, punctuation, special symbols w Writing is a time sequence of strokes n Complete one character before beginning next except for delayed strokes n Spatial order -- for example, left to right
Written Language and Handwriting Properties w Alphabet n Letters, digits, punctuation, special symbols w Writing is a time sequence of strokes n Complete one character before beginning next except for delayed strokes n Spatial order -- for example, left to right
 Written English Writing Styles w Handprint n n Uppercase -- about 2 strokes per letter Lowercase -- about 1 stroke per letter w Cursive Script n n Less than a stroke per letter Delayed crossing and dotting strokes
Written English Writing Styles w Handprint n n Uppercase -- about 2 strokes per letter Lowercase -- about 1 stroke per letter w Cursive Script n n Less than a stroke per letter Delayed crossing and dotting strokes
 Computer Problems in English w Constrained Handprint n n Printing on lines -- symbols can touch or overlap Printing one symbol per box -- form filling w Unconstrained Handprint n No lines and symbols can touch or overlap w Cursive Script w Mixed Printing and Cursive
Computer Problems in English w Constrained Handprint n n Printing on lines -- symbols can touch or overlap Printing one symbol per box -- form filling w Unconstrained Handprint n No lines and symbols can touch or overlap w Cursive Script w Mixed Printing and Cursive
 Handprint Recognition Difficulties w Digitizer problems w Writing variation not handled by system w Uppercase versus lowercase versus digits w Segmentation -- character within character problem
Handprint Recognition Difficulties w Digitizer problems w Writing variation not handled by system w Uppercase versus lowercase versus digits w Segmentation -- character within character problem
 Design of Graffiti for Palm Pilot w Small Alphabet n uppercase, digits, special symbols w One stroke per symbol to avoid segmentation difficulty w Separate writing areas to avoid letter and digit confusion
Design of Graffiti for Palm Pilot w Small Alphabet n uppercase, digits, special symbols w One stroke per symbol to avoid segmentation difficulty w Separate writing areas to avoid letter and digit confusion
 Graffiti Alphabet
Graffiti Alphabet
 Early Shorthand Alphabets w Ancient Greeks -- 400 BC w Tironian -- 63 BC w Stenographie -- 1602 w Gabelsberger -- 1834 w Moon -- 1894 w Goldberg’s Unistrokes (Xerox) -- 1993
Early Shorthand Alphabets w Ancient Greeks -- 400 BC w Tironian -- 63 BC w Stenographie -- 1602 w Gabelsberger -- 1834 w Moon -- 1894 w Goldberg’s Unistrokes (Xerox) -- 1993
 Stenographie Alphabet 1602
Stenographie Alphabet 1602
 Moon Alphabet 1894
Moon Alphabet 1894
 Pen Computing Future Work w Graffiti recognizer greatly simplified the recognition problem w Handprint problem not completely solved n Even with IBM’s Think. Write, CIC’s Jot, and Microsoft products w Cursive script not solved
Pen Computing Future Work w Graffiti recognizer greatly simplified the recognition problem w Handprint problem not completely solved n Even with IBM’s Think. Write, CIC’s Jot, and Microsoft products w Cursive script not solved
 Example of the Difficulty of Recognizing Cursive Script
Example of the Difficulty of Recognizing Cursive Script
 Summary w. What are Emerging Info Technologies? w. Moore’s Law and what might follow w. Wearable/Handheld Computers w. Virtual Reality w. Artificial Intelligence we-Commerce w. Speech and Handwriting Interfaces
Summary w. What are Emerging Info Technologies? w. Moore’s Law and what might follow w. Wearable/Handheld Computers w. Virtual Reality w. Artificial Intelligence we-Commerce w. Speech and Handwriting Interfaces


