44cfa96ed96fefbd74f4593dd8a66bfc.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 54
 Emergency Risk Communication Principles and Applied Practices Melinda Frost, MA, MPH Health Communications Officer US Embassy, Beijing 1 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
Emergency Risk Communication Principles and Applied Practices Melinda Frost, MA, MPH Health Communications Officer US Embassy, Beijing 1 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
 Presentation Outline • Emergency and Risk Communication Definitions • Emergency Risk Communication Principles • Emergency Risk Communication in China • Developing an Emergency Risk Communication Plan 2 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
Presentation Outline • Emergency and Risk Communication Definitions • Emergency Risk Communication Principles • Emergency Risk Communication in China • Developing an Emergency Risk Communication Plan 2 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
 Definitions • Risk Communication: communication about potential (uncertain) health risks to support informed decisions • Emergency: a health threat in which urgent response is required 3 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
Definitions • Risk Communication: communication about potential (uncertain) health risks to support informed decisions • Emergency: a health threat in which urgent response is required 3 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
 Why? Emergency Risk Communication • To provide accurate and timely information as well as essential coordination during an emergency 4 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
Why? Emergency Risk Communication • To provide accurate and timely information as well as essential coordination during an emergency 4 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
 Why? Emergency Risk Communication • To inform the public of potential risks and steps being taken during an emergency 5 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
Why? Emergency Risk Communication • To inform the public of potential risks and steps being taken during an emergency 5 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
 Why? Emergency Risk Communication • To aid individuals, stakeholders, or communities to accept the imperfect nature of choices and to make best possible decisions during an emergency 6 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
Why? Emergency Risk Communication • To aid individuals, stakeholders, or communities to accept the imperfect nature of choices and to make best possible decisions during an emergency 6 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
 Emergency Communication Challenges • Uncertainty • High potential for altered or conflicting recommendations • People are looking at multiple channels to check on rumors 7 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
Emergency Communication Challenges • Uncertainty • High potential for altered or conflicting recommendations • People are looking at multiple channels to check on rumors 7 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
 THE CERTAINTIES OF COMMUNICATING UNCERTAINTY • You will be tempted to suppress your uncertainty and sound confident – it’s human nature • Things will turn out better if you resist that temptation 8 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
THE CERTAINTIES OF COMMUNICATING UNCERTAINTY • You will be tempted to suppress your uncertainty and sound confident – it’s human nature • Things will turn out better if you resist that temptation 8 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
 THE CERTAINTIES OF COMMUNICATING UNCERTAINTY • Over-confidence rings false, undermining everyone else’s confidence even if you turn out right • Over-confidence provokes acrimony, especially among your critics • Over-confidence devastates your credibility and your ability to lead if you turn out wrong 9 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
THE CERTAINTIES OF COMMUNICATING UNCERTAINTY • Over-confidence rings false, undermining everyone else’s confidence even if you turn out right • Over-confidence provokes acrimony, especially among your critics • Over-confidence devastates your credibility and your ability to lead if you turn out wrong 9 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
 Emergency Risk Communication Principles 10 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
Emergency Risk Communication Principles 10 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
 WHO Outbreak Communication (Emergency Risk) Principles • Trust • Announce early • Transparency • Listen to and involve the public • Planning 11 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
WHO Outbreak Communication (Emergency Risk) Principles • Trust • Announce early • Transparency • Listen to and involve the public • Planning 11 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
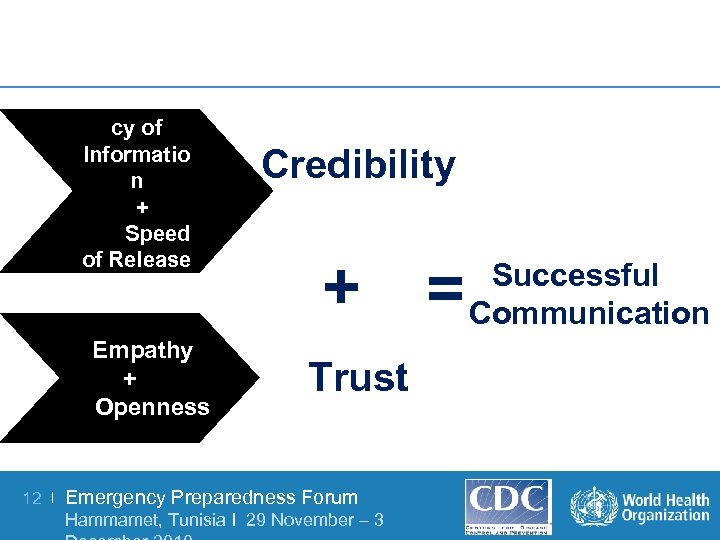 Accura cy of Informatio n + Speed of Release Empathy + Openness 12 | Credibility + = Trust Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3 Successful Communication
Accura cy of Informatio n + Speed of Release Empathy + Openness 12 | Credibility + = Trust Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3 Successful Communication
 Components of Trust The public perception of: Motives: Are responders acting to protect my health and the health of my family? Honesty: Are the responders holding back information? Competence: Are the responders capable of controlling the outbreak? Trust must come before the crisis 13 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
Components of Trust The public perception of: Motives: Are responders acting to protect my health and the health of my family? Honesty: Are the responders holding back information? Competence: Are the responders capable of controlling the outbreak? Trust must come before the crisis 13 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
 Announce Early First Announcement • The most critical of all outbreak communication messages • Must be early • Likely to be wrong 14 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
Announce Early First Announcement • The most critical of all outbreak communication messages • Must be early • Likely to be wrong 14 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
 Transparency Barriers to Transparency: • Real or perceived competing interest (economic vs. public health) • Spokespersons uncomfortable with delivering bad news 15 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
Transparency Barriers to Transparency: • Real or perceived competing interest (economic vs. public health) • Spokespersons uncomfortable with delivering bad news 15 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
 Transparency Barriers to Transparency: • Fear the media will misrepresent bad or uncertain news • Concern the public can‘t tolerate uncertainty or will “panic” • Official belief that if you say nothing, nothing will happen 16 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
Transparency Barriers to Transparency: • Fear the media will misrepresent bad or uncertain news • Concern the public can‘t tolerate uncertainty or will “panic” • Official belief that if you say nothing, nothing will happen 16 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
 Listen to and involve the public • State continued concern before stating updates • Acknowledge uncertainty • Emphasize a process in place • Tell people what to expect • Give people things to do • Let people choose their own actions • Ask more of people 17 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
Listen to and involve the public • State continued concern before stating updates • Acknowledge uncertainty • Emphasize a process in place • Tell people what to expect • Give people things to do • Let people choose their own actions • Ask more of people 17 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
 Listen to and involve the public • Don’t try to allay panic • Acknowledge people’s fears • In every message, try to use – Empathy – Action – Respect 18 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
Listen to and involve the public • Don’t try to allay panic • Acknowledge people’s fears • In every message, try to use – Empathy – Action – Respect 18 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
 Influenza A H 1 N 1 Communication Response Announce Early, Transparency & Trust • First cases laboratory confirmed 4/15 - 17 • 4/22 Activation of Emergency Operations Center (http: //www. cdc. gov/h 1 n 1 flu/) • 4/23 Daily press briefings (http: //www. cdc. gov/h 1 n 1 flu/press/) 19 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
Influenza A H 1 N 1 Communication Response Announce Early, Transparency & Trust • First cases laboratory confirmed 4/15 - 17 • 4/22 Activation of Emergency Operations Center (http: //www. cdc. gov/h 1 n 1 flu/) • 4/23 Daily press briefings (http: //www. cdc. gov/h 1 n 1 flu/press/) 19 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
 Risk Communication Principles Project Background Public Health Emergency Risk Communication Draft Guidelines and Handbook 20 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
Risk Communication Principles Project Background Public Health Emergency Risk Communication Draft Guidelines and Handbook 20 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
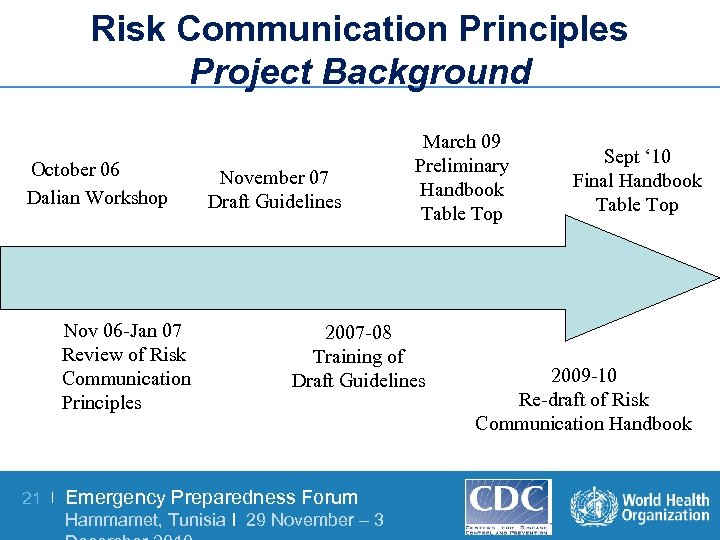 Risk Communication Principles Project Background October 06 Dalian Workshop Nov 06 -Jan 07 Review of Risk Communication Principles 21 | November 07 Draft Guidelines March 09 Preliminary Handbook Table Top 2007 -08 Training of Draft Guidelines Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3 Sept ‘ 10 Final Handbook Table Top 2009 -10 Re-draft of Risk Communication Handbook
Risk Communication Principles Project Background October 06 Dalian Workshop Nov 06 -Jan 07 Review of Risk Communication Principles 21 | November 07 Draft Guidelines March 09 Preliminary Handbook Table Top 2007 -08 Training of Draft Guidelines Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3 Sept ‘ 10 Final Handbook Table Top 2009 -10 Re-draft of Risk Communication Handbook
 Risk Communication Principles Pilot Training and Testing Fujian Province Guizhou Province Jiangsu Province 22 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3 January 07 March 08
Risk Communication Principles Pilot Training and Testing Fujian Province Guizhou Province Jiangsu Province 22 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3 January 07 March 08
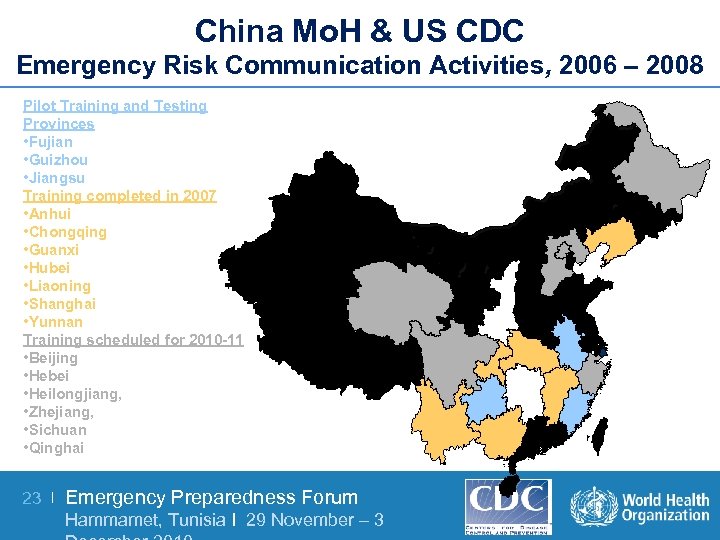 China Mo. H & US CDC Emergency Risk Communication Activities, 2006 – 2008 Pilot Training and Testing Provinces • Fujian • Guizhou • Jiangsu Training completed in 2007 • Anhui • Chongqing • Guanxi • Hubei • Liaoning • Shanghai • Yunnan Training scheduled for 2010 -11 • Beijing • Hebei • Heilongjiang, • Zhejiang, • Sichuan • Qinghai 23 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
China Mo. H & US CDC Emergency Risk Communication Activities, 2006 – 2008 Pilot Training and Testing Provinces • Fujian • Guizhou • Jiangsu Training completed in 2007 • Anhui • Chongqing • Guanxi • Hubei • Liaoning • Shanghai • Yunnan Training scheduled for 2010 -11 • Beijing • Hebei • Heilongjiang, • Zhejiang, • Sichuan • Qinghai 23 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
 Testing and Training of Effective Risk Communication Principles In Fujian Province (Jan 2007), Guizhou and Jiangsu (Mar 2008) activities in to test Was training on the risk communication principles effective? Are risk communication principles effective for Chinese public? 24 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
Testing and Training of Effective Risk Communication Principles In Fujian Province (Jan 2007), Guizhou and Jiangsu (Mar 2008) activities in to test Was training on the risk communication principles effective? Are risk communication principles effective for Chinese public? 24 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
 Risk Communication Principles Project Protocol Step 1: Health officials wrote public health messages based on a hypothetical case study involving a 3 stage H 5 N 1 scenario. Step 2: Trained on Risk Communication Principles and Practice Step 3: Message revision based on principles and training Step 4: Message testing with citizen groups 25 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
Risk Communication Principles Project Protocol Step 1: Health officials wrote public health messages based on a hypothetical case study involving a 3 stage H 5 N 1 scenario. Step 2: Trained on Risk Communication Principles and Practice Step 3: Message revision based on principles and training Step 4: Message testing with citizen groups 25 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
 The risk communication training was effective Post-training messages – More risk communication principles – More types of principles to address psychological functions of risk communication: • • 26 | Decrease feelings of uncertainty and fear Increase feelings of control Increased trust in health authority Address public’s cognitive needs Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
The risk communication training was effective Post-training messages – More risk communication principles – More types of principles to address psychological functions of risk communication: • • 26 | Decrease feelings of uncertainty and fear Increase feelings of control Increased trust in health authority Address public’s cognitive needs Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
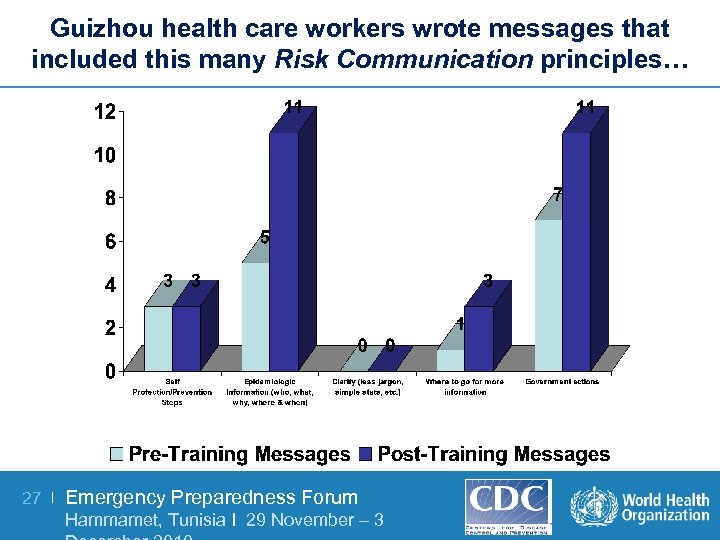 Guizhou health care workers wrote messages that included this many Risk Communication principles… 27 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
Guizhou health care workers wrote messages that included this many Risk Communication principles… 27 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
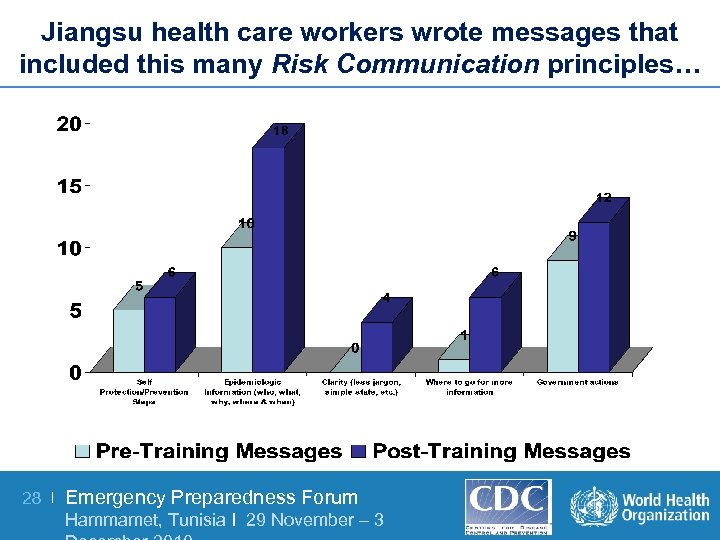 Jiangsu health care workers wrote messages that included this many Risk Communication principles… 28 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
Jiangsu health care workers wrote messages that included this many Risk Communication principles… 28 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
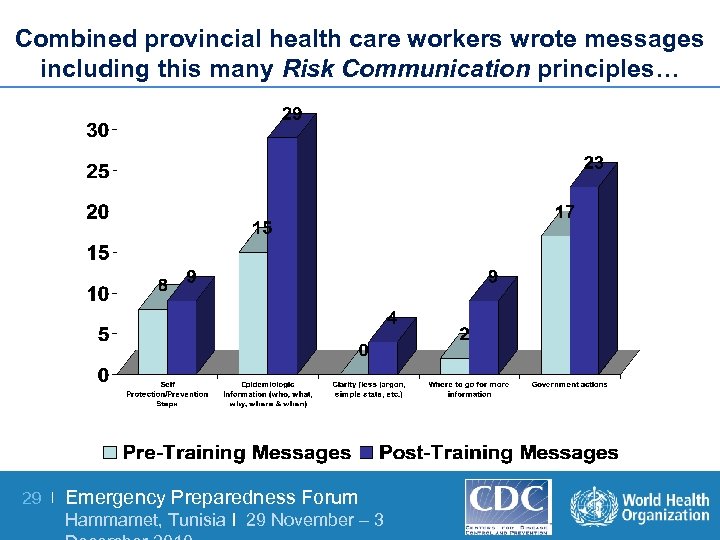 Combined provincial health care workers wrote messages including this many Risk Communication principles… 29 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
Combined provincial health care workers wrote messages including this many Risk Communication principles… 29 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
 Risk Communication Principles Message Testing Results 184 Citizens 30 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
Risk Communication Principles Message Testing Results 184 Citizens 30 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
 Risk Communication Principles Message Testing Results 31 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
Risk Communication Principles Message Testing Results 31 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
 What the Public Wants to Know Topics from US Audiences • What is the health threat? • How does it harm people? • How will I know if I’ve been exposed? • Signs and symptoms (long/short term) • How can I protect myself/my family • How is it treated? • Where can I get more information? 32 | Feedback from Fujian Province Audiences • How can I prevent getting the disease? * • How is the disease transmitted? • Is what I’m hearing about the disease true? • What is the disease? And how serious? • What is the government doing to prevent the spread of disease? • Where can we go for more information? • Is there a vaccine available? Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
What the Public Wants to Know Topics from US Audiences • What is the health threat? • How does it harm people? • How will I know if I’ve been exposed? • Signs and symptoms (long/short term) • How can I protect myself/my family • How is it treated? • Where can I get more information? 32 | Feedback from Fujian Province Audiences • How can I prevent getting the disease? * • How is the disease transmitted? • Is what I’m hearing about the disease true? • What is the disease? And how serious? • What is the government doing to prevent the spread of disease? • Where can we go for more information? • Is there a vaccine available? Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
 Where are People Going for Information? • Television news – CCTV • Newspapers • Website – Health bureau, News Website, Sina. com, Xinhua. com, MSNBC. com, Baidu search engine • Local health bureau • Community residents’ committee • Telephone line for public inquiries (hotline) – Local health department, national hotline • • 33 CDC Local hospital Emergency Center Neighbors | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
Where are People Going for Information? • Television news – CCTV • Newspapers • Website – Health bureau, News Website, Sina. com, Xinhua. com, MSNBC. com, Baidu search engine • Local health bureau • Community residents’ committee • Telephone line for public inquiries (hotline) – Local health department, national hotline • • 33 CDC Local hospital Emergency Center Neighbors | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
 Channels Used by The Public to Seek Emergency Information • Distant threat: passive channels – TV news, newspaper • Threat is close by, but not in our community: more active information seeking, but impersonal channels – Internet, Website, Search engines • Threat is here: pro-active search through interpersonal channels – – – 34 | Hotlines Visit local health bureau Call hospital Visit or call local community residents center and committee Call CDC Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
Channels Used by The Public to Seek Emergency Information • Distant threat: passive channels – TV news, newspaper • Threat is close by, but not in our community: more active information seeking, but impersonal channels – Internet, Website, Search engines • Threat is here: pro-active search through interpersonal channels – – – 34 | Hotlines Visit local health bureau Call hospital Visit or call local community residents center and committee Call CDC Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
 Emergency Risk Communication Lifecycle Pre-crisis Initial Maintenance Resolution Evaluation • To facilitate and anticipate the needs of the public, the media, and partners at different stages • Each stage has unique communications and information requirements 35 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
Emergency Risk Communication Lifecycle Pre-crisis Initial Maintenance Resolution Evaluation • To facilitate and anticipate the needs of the public, the media, and partners at different stages • Each stage has unique communications and information requirements 35 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
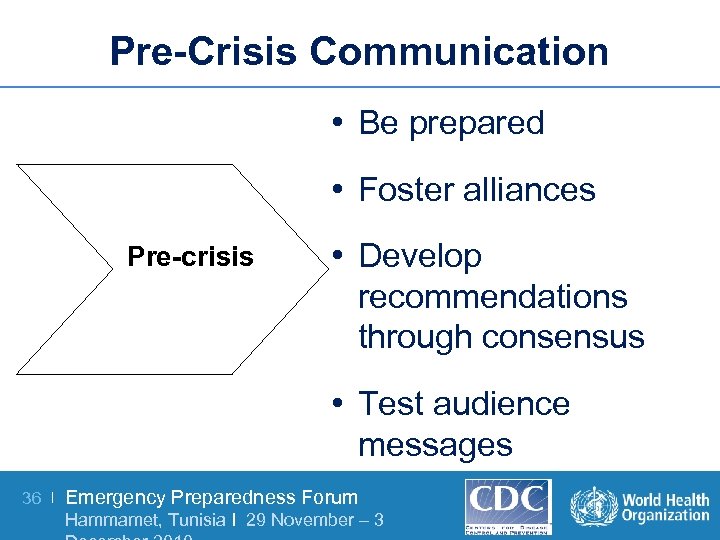 Pre-Crisis Communication • Be prepared • Foster alliances Pre-crisis • Develop recommendations through consensus • Test audience messages 36 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
Pre-Crisis Communication • Be prepared • Foster alliances Pre-crisis • Develop recommendations through consensus • Test audience messages 36 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
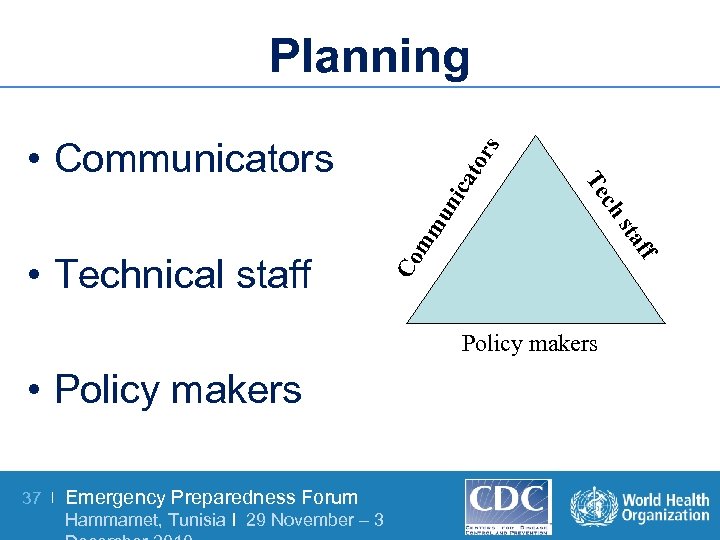 Planning ato mm un ic Co Policy makers • Policy makers 37 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3 aff st ch Te • Technical staff rs • Communicators
Planning ato mm un ic Co Policy makers • Policy makers 37 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3 aff st ch Te • Technical staff rs • Communicators
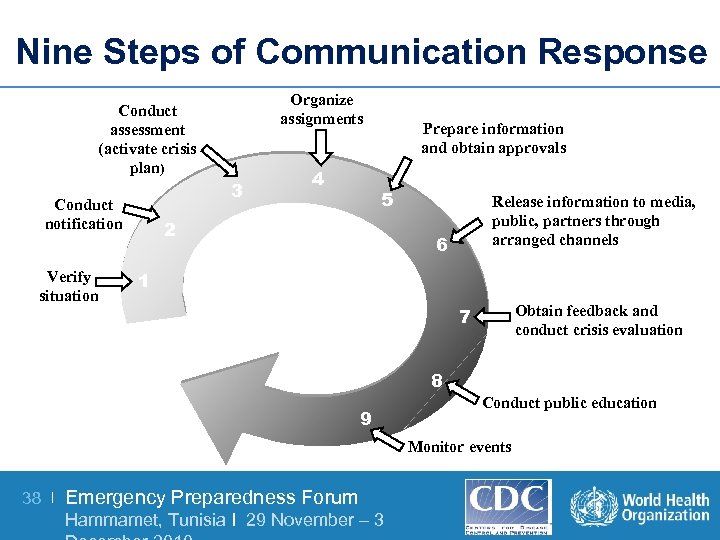 Nine Steps of Communication Response Organize assignments Conduct assessment (activate crisis plan) 3 Conduct notification Verify situation 4 Prepare information and obtain approvals 5 2 Release information to media, public, partners through arranged channels 6 1 Obtain feedback and conduct crisis evaluation 7 8 9 Conduct public education Monitor events 38 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
Nine Steps of Communication Response Organize assignments Conduct assessment (activate crisis plan) 3 Conduct notification Verify situation 4 Prepare information and obtain approvals 5 2 Release information to media, public, partners through arranged channels 6 1 Obtain feedback and conduct crisis evaluation 7 8 9 Conduct public education Monitor events 38 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
 Public Information Release Select the appropriate channels of communication and apply them: Simply Timely Accurately Repeatedly Credibly Consistently 39 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
Public Information Release Select the appropriate channels of communication and apply them: Simply Timely Accurately Repeatedly Credibly Consistently 39 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
 Trust Case Study Measles, Mumps Rubella Vaccine (MMR) United Kingdom, 2008 40 Raithatha N, Holland R, Gerrard S, Harvey I, A qualitative investigation of vaccine risk perception amongst parents who immunize their children: | Emergency Preparedness Forum Health Medicine. 25 (2) 2003 a matter of public health concern. J. of Public Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
Trust Case Study Measles, Mumps Rubella Vaccine (MMR) United Kingdom, 2008 40 Raithatha N, Holland R, Gerrard S, Harvey I, A qualitative investigation of vaccine risk perception amongst parents who immunize their children: | Emergency Preparedness Forum Health Medicine. 25 (2) 2003 a matter of public health concern. J. of Public Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
 MMR Vaccination in the UK: What happened? • In 1998, a researcher suggested that the MMR vaccine may cause autism • In 2001, the same researcher developed another paper questioning the safety of MMR 41 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
MMR Vaccination in the UK: What happened? • In 1998, a researcher suggested that the MMR vaccine may cause autism • In 2001, the same researcher developed another paper questioning the safety of MMR 41 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
 MMR Vaccination in the UK: What happened? • The media reported the paper out of proportion • Subsequent papers and studies have disproved the link between MMR and autism 42 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
MMR Vaccination in the UK: What happened? • The media reported the paper out of proportion • Subsequent papers and studies have disproved the link between MMR and autism 42 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
 Context in the United Kingdom in early 2000 s • Parents understood true benefits of vaccination but still felt “dread” at thoughts of long-term disability • Lack of trust in recent government reaction to BSE crisis • Slight lack of trust in motives, and knowledge base of doctors 43 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
Context in the United Kingdom in early 2000 s • Parents understood true benefits of vaccination but still felt “dread” at thoughts of long-term disability • Lack of trust in recent government reaction to BSE crisis • Slight lack of trust in motives, and knowledge base of doctors 43 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
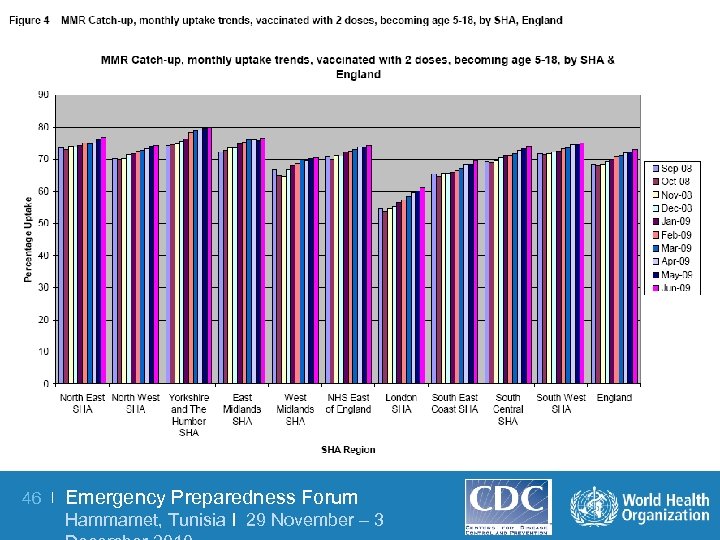
 MMR Vaccination in the UK The Results • MMR Vaccination rates dropped from 91% to 80% between 1998 and 2004 • 1, 049 cases of measles between Jan – Oct, 2008 (the worst year since 1995) • 55, 000 cases of mumps between 2004 -06 44 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
MMR Vaccination in the UK The Results • MMR Vaccination rates dropped from 91% to 80% between 1998 and 2004 • 1, 049 cases of measles between Jan – Oct, 2008 (the worst year since 1995) • 55, 000 cases of mumps between 2004 -06 44 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
 45 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
45 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
 46 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
46 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
 Audience Perceptions and Rumors A rumor is a specific (or topical) proposition for belief, passed along from person to person, without secure standards or evidence being present. 47 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
Audience Perceptions and Rumors A rumor is a specific (or topical) proposition for belief, passed along from person to person, without secure standards or evidence being present. 47 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
 Rumor sources • Blogosphere • SMS text messaging • Internet • Word of mouth • Where else? 48 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
Rumor sources • Blogosphere • SMS text messaging • Internet • Word of mouth • Where else? 48 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
 Audience Perceptions – Sources of Insight • Monitoring for rumors (listening to your audience) – Social media – websites, blogospheres – Hotlines (12320, hospitals, etc. ) – Print/broadcast media 49 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
Audience Perceptions – Sources of Insight • Monitoring for rumors (listening to your audience) – Social media – websites, blogospheres – Hotlines (12320, hospitals, etc. ) – Print/broadcast media 49 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
 Audience Perceptions – Sources of Insight • Listening to your audience – Focus groups – Intercept interviews – What else? 50 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
Audience Perceptions – Sources of Insight • Listening to your audience – Focus groups – Intercept interviews – What else? 50 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
 Rumor found – to react or ignore? The two factors that influence a rumor are its importance to the listener and its ambiguity. Rumors travel when events have importance in the lives of individuals, and when the news received about them is either lacking or subjectivity ambiguous. The ambiguity may arise from the fact that the news is not clearly reported, or from the fact the conflicting versions of the news have reached the individual, or from his incapacity to comprehend the news he receives. 51 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
Rumor found – to react or ignore? The two factors that influence a rumor are its importance to the listener and its ambiguity. Rumors travel when events have importance in the lives of individuals, and when the news received about them is either lacking or subjectivity ambiguous. The ambiguity may arise from the fact that the news is not clearly reported, or from the fact the conflicting versions of the news have reached the individual, or from his incapacity to comprehend the news he receives. 51 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
 How do we address misinformation? Risk Communication Principles Rumors fly in the absence of news. Therefore, we must give the people the most accurate possible news, promptly and completely. • Announce early • Be transparent • Listen to the public • Show empathy 52 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
How do we address misinformation? Risk Communication Principles Rumors fly in the absence of news. Therefore, we must give the people the most accurate possible news, promptly and completely. • Announce early • Be transparent • Listen to the public • Show empathy 52 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
 How do we address a rumor? Messaging • Simply denying a rumor does not eliminate ambiguity; it may even increase it. • “No comment” increases ambiguity. • Silence REALLY increases ambiguity. 53 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
How do we address a rumor? Messaging • Simply denying a rumor does not eliminate ambiguity; it may even increase it. • “No comment” increases ambiguity. • Silence REALLY increases ambiguity. 53 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
 Thank you! Questions? 54 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3
Thank you! Questions? 54 | Emergency Preparedness Forum Hammamet, Tunisia I 29 November – 3


