ef818984bd69ac431fb3af744457b8ae.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 53
Embryonic and tissue stem cells - therapeutic use. . ? Arne Sunde Head Fertility Clinic St. Olav’s University Hospital Professor II, NTNU

Stem cells ? • I’m a fertility specialist running a Fertility clinic, teaching reproductive biology for medical students - I’m not doing any active research on stem cells • The In vitro Fertilisation community has been intimately connected to the emerging stem cell field because IVF started with research on (pre)embryos - In fact, In vitro fertilisation was developed primarily to obtain human embryonic stem cells, not as a method for the treatment of infertile couples. That came as an unintended side-effect

Stem cells… ? - 1) Presentation of the little buggers - 2) Potential clinical applications - 3) Ethical considerations (short)
Stem cells • Adults - Traditionally: - Cells that maintain a certain differentiated tissue (unipotency) –Epithelia in the guts –Skin –Haemapoetic cells • In embryos: - Cells that may give rise to several cells and tissue types (pluripotency)

Tissue stem cells in the small intestine
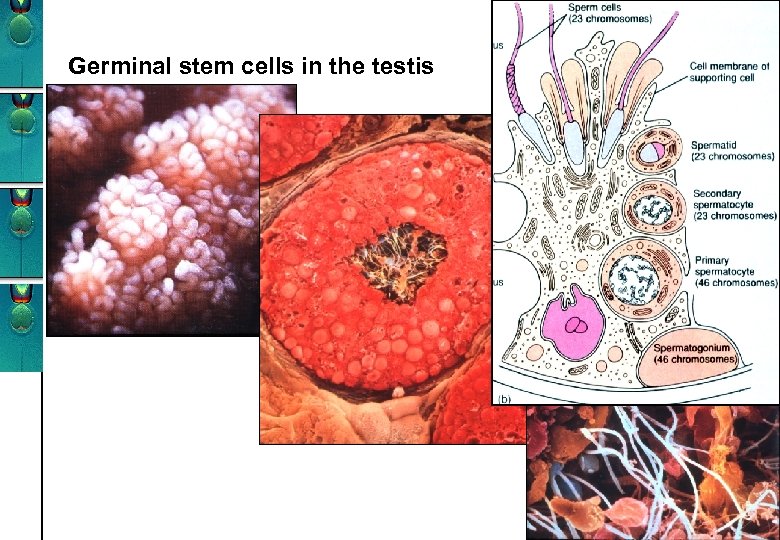
Germinal stem cells in the testis

Different sources of stem cells st tocy Blas b Em

Stem cells - potential for growth and differentiation

Different types of stem cells • Embryonic stem cells - Pluripotent stem cells derived from (pre) embryos - Can differentiate to ALL stem cell types in the body (still not to placenta and membranes) - Still only a research tool - Basic science - At best experimental medicine

Different types of stem cells • Foetal stem cells - Stem cells extracted from aborted foetuses - Has been used clinically – mixed success –Parkinson’s disease –Diabetes –Metabolic diseases

Different types of stem cells • Umbilical cord blood contains hematopoietic stem cells that functionally is close to bone marrow stem cells. - Is used clinically in many countries. - Not utilised in Norway

Different types of stem cells - Umbilical cord blood stem cells – useful? - Considerations: - For yourself ? – Cost benefit. . ? (ISO 9001 vs Science Fiction) - For donation (”bone marrow”) – Large part of the Australian bone marrow bank is in reality a cord blood bank - Saviour siblings – 20 years since the first successful trial (Faconi anemia) – The Mehmet case in Norway
Tissue stem cells (”adult stem cells”) - Transplantation of tissue stem cells is clinical routine - I. e. Bone marrow to replace bone marrow – Huge international effort – More than a million bone marrow donors – Bone barrow from Australia to Norwegians and vice versa
Tissue stem cells (”adult stem cells”) • Trans-differentiation of tissue stem cells? - Liver from bone marrow -heart muscle from liver. . ? - IPS: Induced pluripotent stem cells – Basic research, but moving closer to the clinic – Experimental medicine

The totipotent stem cell • The cloning of Dolly the sheep led to a new understanding of cell differentiation • A revolution. .
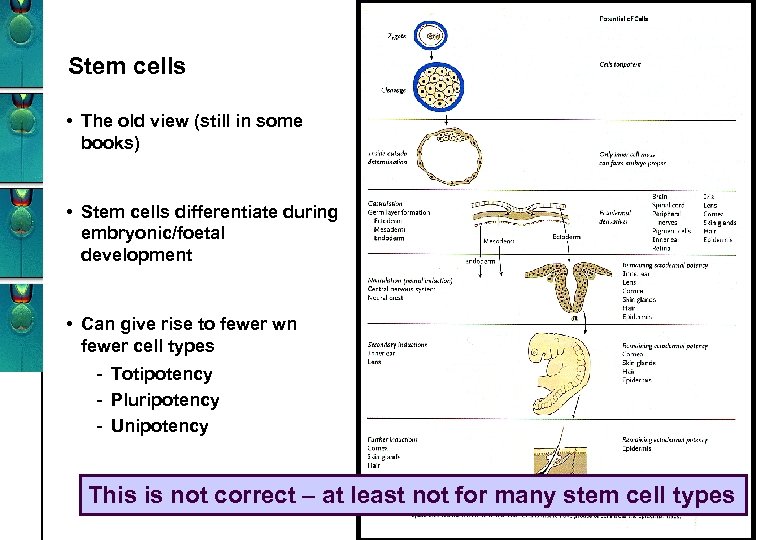
Stem cells • The old view (still in some books) • Stem cells differentiate during embryonic/foetal development • Can give rise to fewer wn fewer cell types - Totipotency - Pluripotency - Unipotency This is not correct – at least not for many stem cell types
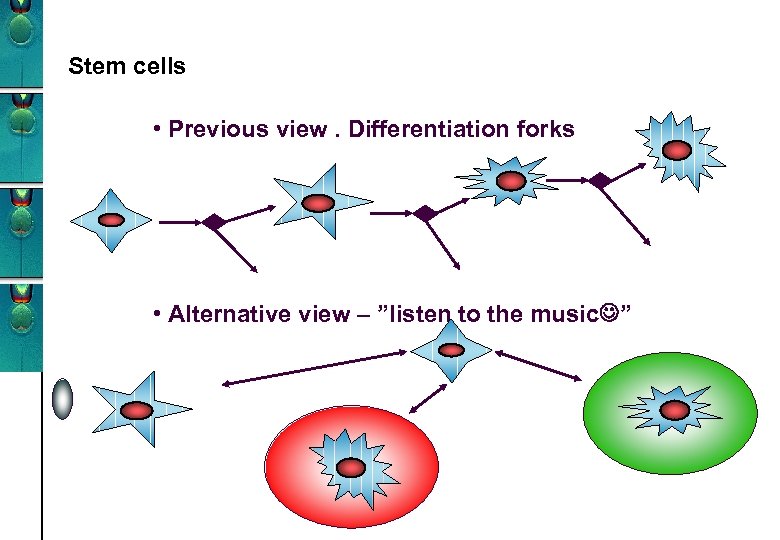
Stem cells • Previous view. Differentiation forks • Alternative view – ”listen to the music ”

• Embryonic stem cells ?
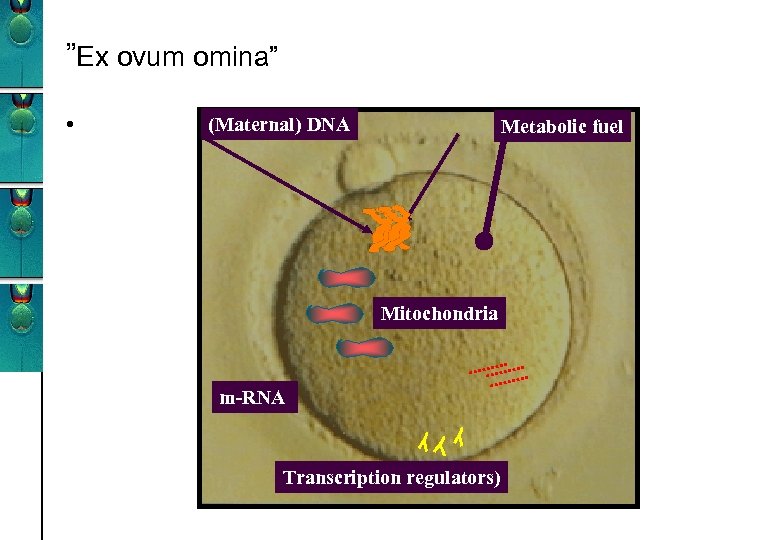
”Ex ovum omina” • (Maternal) DNA Metabolic fuel Mitochondria m-RNA Transcription regulators)
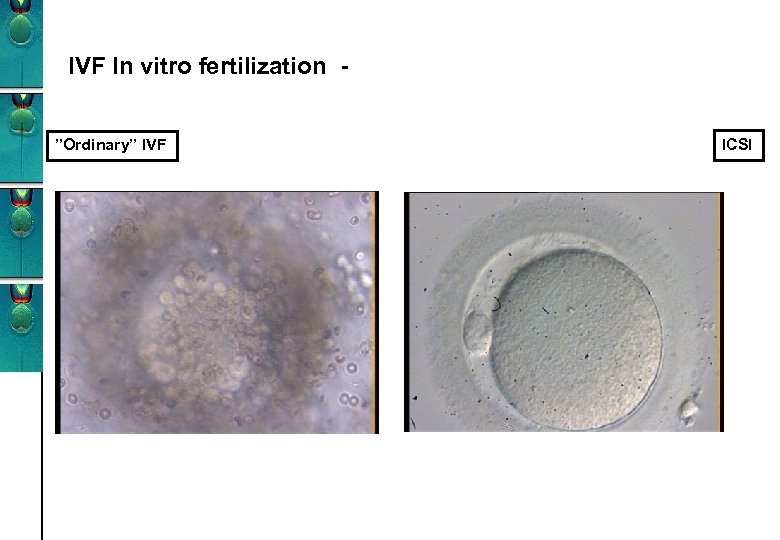
IVF In vitro fertilization ”Ordinary” IVF ICSI
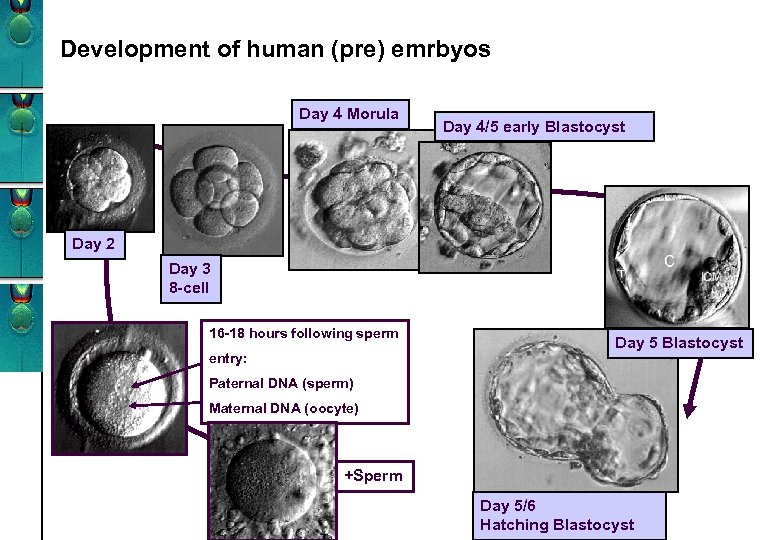
Development of human (pre) emrbyos Day 4 Morula Day 4/5 early Blastocyst Day 2 Day 3 8 -cell 16 -18 hours following sperm entry: Day 5 Blastocyst Paternal DNA (sperm) Maternal DNA (oocyte) +Sperm Day 5/6 Hatching Blastocyst
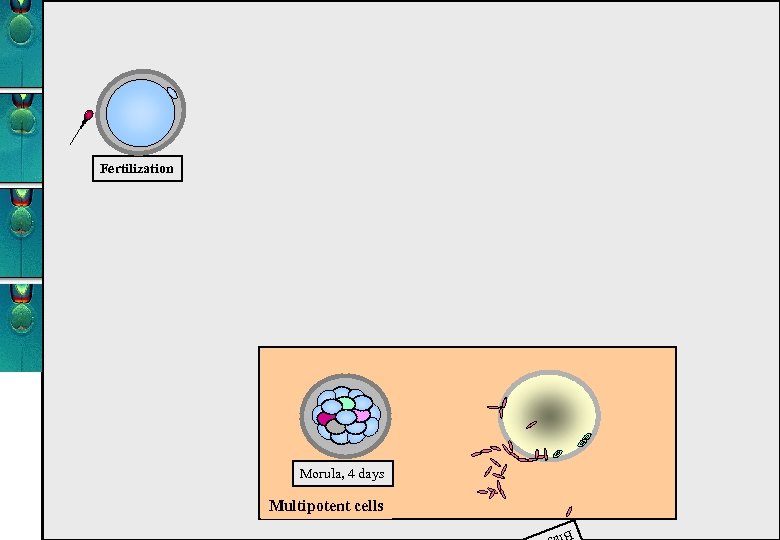
Fertilization Morula, 4 days Multipotent cells Blas t

Humans are strange - aneuploidies are very frequent 30 -5 0% Blas 100 tocy %? st 5 /6 d ays
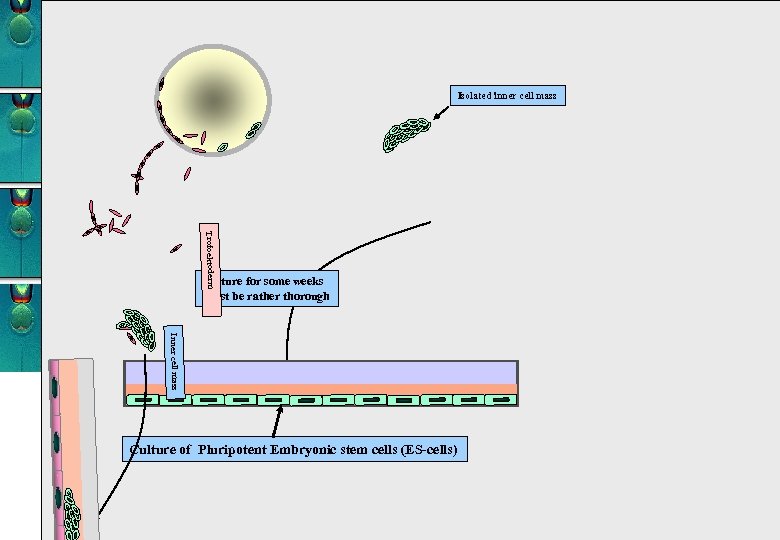
Isolated inner cell mass Trofoektoderm Culture for some weeks Must be rather thorough Inner cell mass Culture of Pluripotent Embryonic stem cells (ES-cells)

Example of potential use of embryonic stem cells • This is by no means an exhaustive list • Just to stir your imagination - And to show some of the data generating a stem cell hype
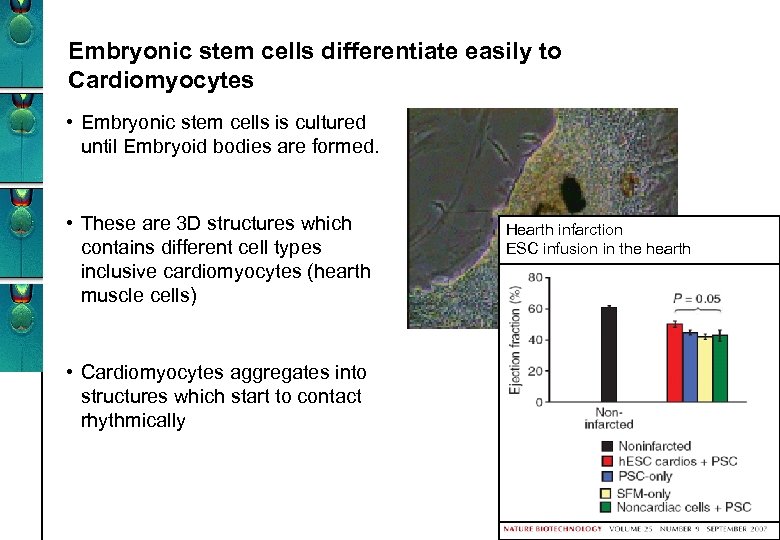
Embryonic stem cells differentiate easily to Cardiomyocytes • Embryonic stem cells is cultured until Embryoid bodies are formed. • These are 3 D structures which contains different cell types inclusive cardiomyocytes (hearth muscle cells) • Cardiomyocytes aggregates into structures which start to contact rhythmically Hearth infarction ESC infusion in the hearth
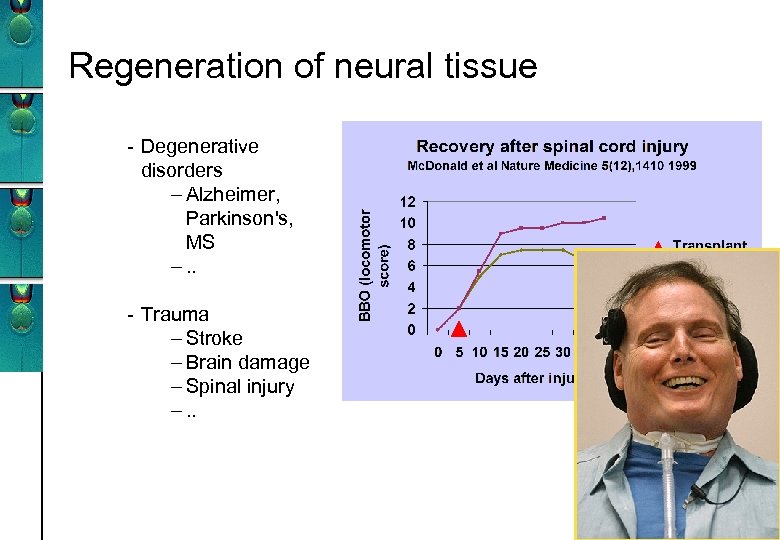
Regeneration of neural tissue - Degenerative disorders – Alzheimer, Parkinson's, MS –. . - Trauma – Stroke – Brain damage – Spinal injury –. .
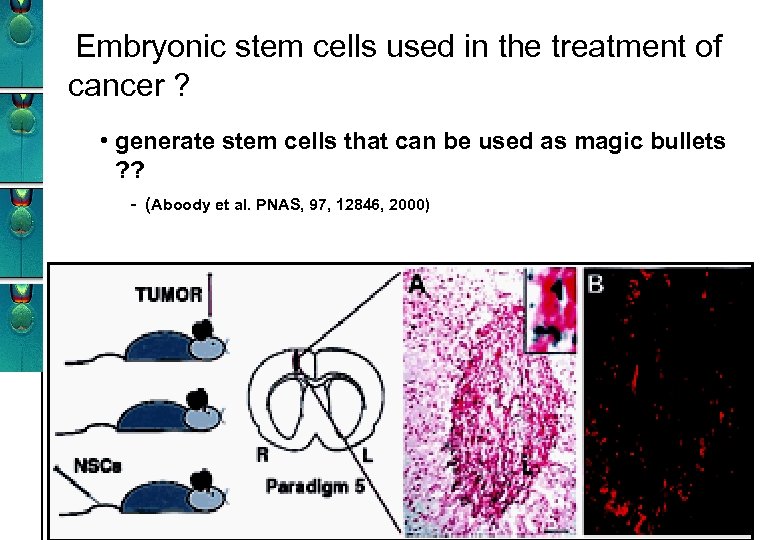
Embryonic stem cells used in the treatment of cancer ? • generate stem cells that can be used as magic bullets ? ? - (Aboody et al. PNAS, 97, 12846, 2000) Glioma-cells Fibroblasts Glioma-cells Neronal stem cells

Cloning • ”Therapeutic” cloning in order to generate your ”own” stem cells. . ?
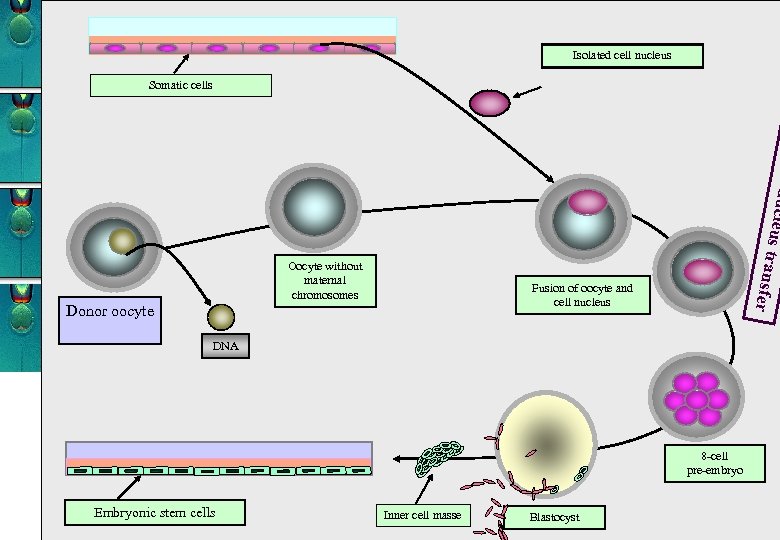
Isolated cell nucleus Somatic cells nu cleus t ran Oocyte without maternal chromosomes Donor oocyte sfer Fusion of oocyte and cell nucleus DNA 8 -cell pre-embryo Embryonic stem cells Inner cell masse Blastocyst
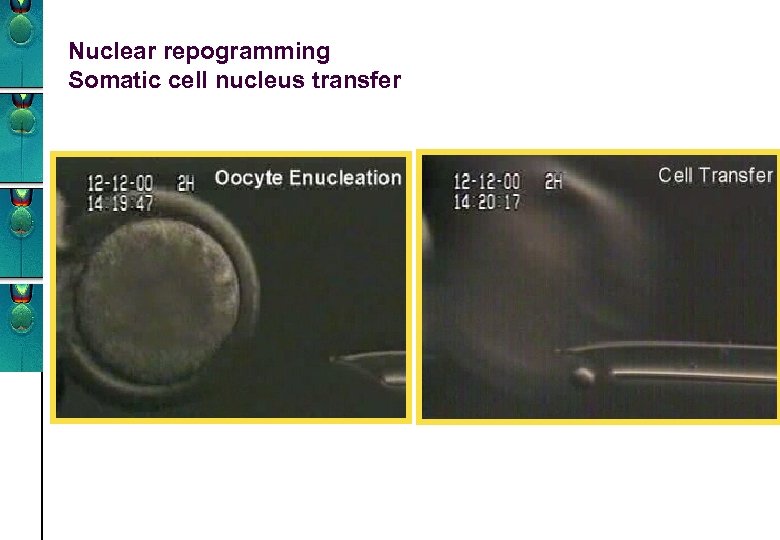
Nuclear repogramming Somatic cell nucleus transfer
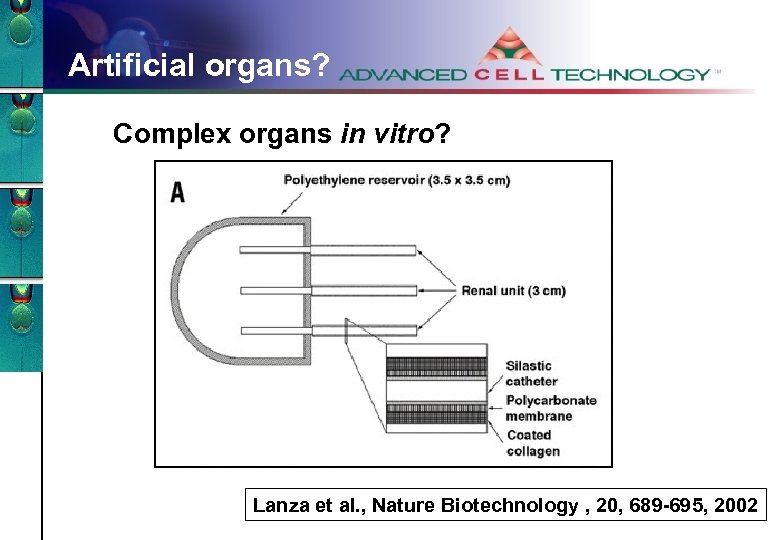
Artificial organs? Complex organs in vitro? Lanza et al. , Nature Biotechnology , 20, 689 -695, 2002
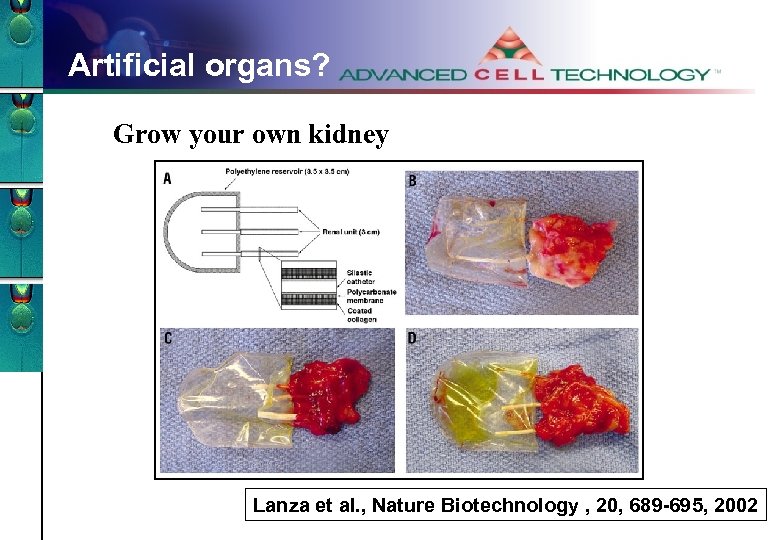
Artificial organs? Grow your own kidney Lanza et al. , Nature Biotechnology , 20, 689 -695, 2002

Therapeutic cloning • Seemed to be fairly easy in many animals - Ruminants and rodents as models - Lower primates more difficult - Higher primates proved to be very difficult - No one has yet convincible been able to produce a developing human embryo by cloning - Somatic nucleus cell transfer - SCNT
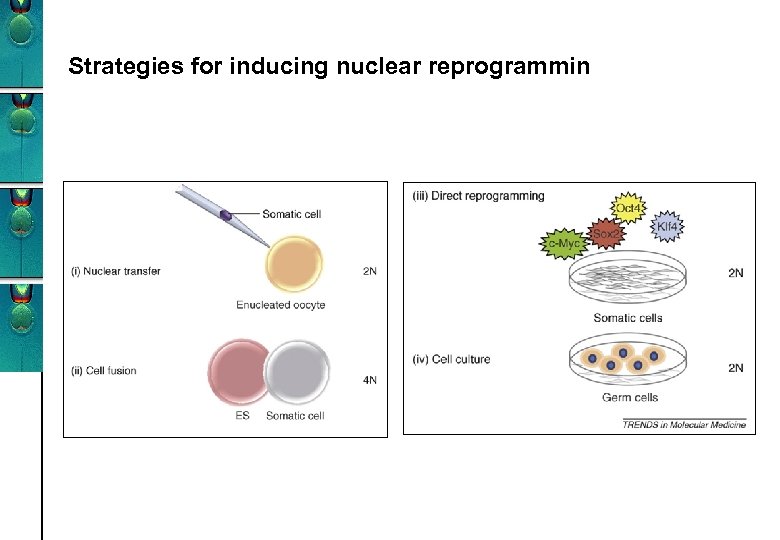
Strategies for inducing nuclear reprogrammin
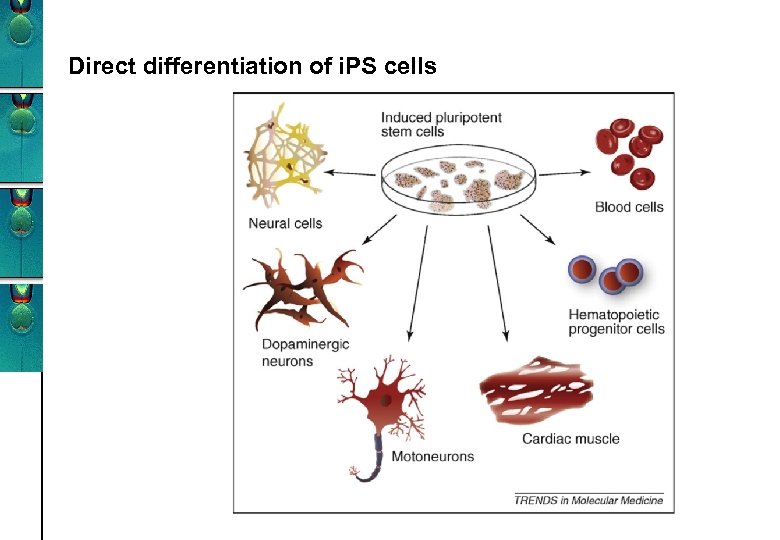
Direct differentiation of i. PS cells

Induced pluripotent stem cells: IPS-cells • Nuclei from different somatic cell types can be induced • May be useful clinically in the future - Liver and heart from skin and fat

Tissue stem cells • To be clinically useful: - Potential for growth (mitotic potential) - ” 1 cell is enough” - It must be a real stem cell – not an imposter. - ”Ikke får i ulveklær”

Tissue stem cells – induced somatic cells • Transdifferentiated tissue stem cells or IPS cells • Example: - Bone marrow heart muscle • Not large enough mitotic potential - Get 1000 cells. Needs 1011 to 1012 • Unclear to what degree they are imposters - Do they really do the job—or just pretending to do do. . ? - Blood vessels and nor heart muscle • Still experimental. Many scientists originally working with tissue stem cells abandoned this approach an started to work with embryonic stem cells in order to better understand stem cell differentiation

Safety issues • Embryonic stem cells: - Teratoma formation - Formation of tumours (benign) in the body after transplantation - It is a serious problem • IPS cells: - Viral vectors used for transformation? - Other vector constructs that may be harmful - Stability of differentiation?

International efforts • Asians want to be in the forefront - Taiwan, Singapore, China - Korea? • Australia - National research centre - The leader headhunted to California by Swarzenegger • Middle East - Israel has very competent research groups - Egypt, Jordan, Saudi and Iran are all in it

International efforts • Europe: - EU has difficulties (The Pope) - UK. . wants to be in there - Sweden (Lund and Karolinska) - Spain, Belgium, Netherlands, Germany(!) • USA - Was in a difficult position (Bush) - Federal funds could not be used - The state of California allocated 3 billion USD - US Industry can do whatever they want - US experienced a “brain drain” - Obama have reversed most of Bush’s action in this context

Ethical considerations • Safety - Primum non nocere. “do no harm” basic principle in medical ethics. - All new interventions and drugs will have to undergo an evaluation of safety • Moral judgement - Is it right do perform an intervention even if it is harmless? - This evaluation will be strongly dependent on religion and culture

The debate about clinical use of stem cells clash of cultures: • Ethics and moral philosophy - The moral status of the human embryo, divergent views: - To be considered a person in a moral sense - The Vatican and some conservative protestants - The moral status higher than any other aggregation of cells, but not a person - Liberal protestants the Anglican Church , The Orthodox Churches - Jews, Muslims, Buddhists - Atheists. . • Rough debate tactics from both sides concerning research and potential clinical use of embryonic stem cells

The Nordic countries are remarkably different Regarding moral and legal issues in research on human embryos and embryonic stem cells Pragmatic and Midway Something different The Christian Tribe The Scandobaltic Central Europeans The Liberals

Norway has always had a more strict regulation concerning embryo research then the other Nordic countries. • Why so in Norway? • The Church and independent conservative Christian religious groups have significant political influence • Rural dominance culturally - Anti - elite - Anti – academia - “The pureness of ignorance” • Thank you Danes !!
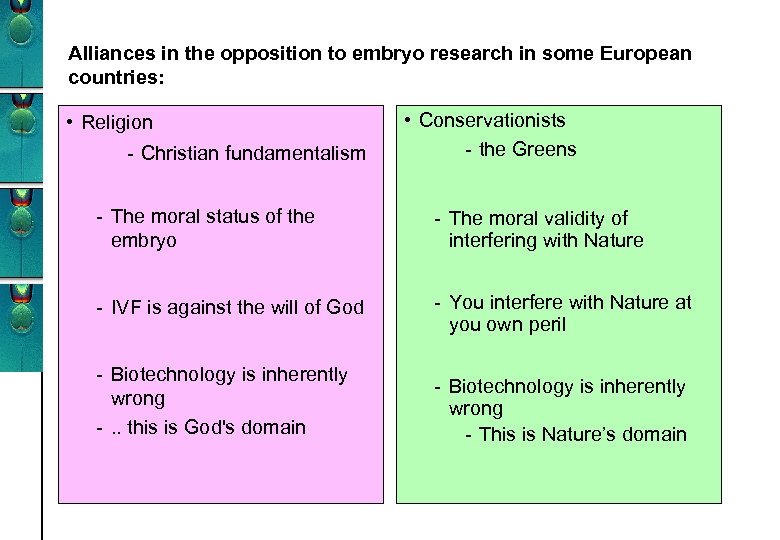
Alliances in the opposition to embryo research in some European countries: • Religion - Christian fundamentalism • Conservationists - the Greens - The moral status of the embryo - The moral validity of interfering with Nature - IVF is against the will of God - You interfere with Nature at you own peril - Biotechnology is inherently wrong -. . this is God's domain - Biotechnology is inherently wrong - This is Nature’s domain

Part of theological basis for banning embryo research Psalm 130, verse 13 -17 16. your eyes saw my unformed body. All the days ordained for me were written in your book before one of them came to be. ” - Source: Jan Helge Solbakk (Cand theol, MD) This and other part of the bible and religious thinking are interpreted differently by different Christian Churches

The current Pope’s crusade • The current Pope - Pope Benedict XVI, Joseph Alois Ratzinger, is very conservative • Have spent a lot of energy since he became into office on: - Banning all aspects of assisted conception - A very strict law in Italy – “The Christmas gift to the Pope in 2004” - Intervened in the EU and the EU parliament - Stop funding of research - Confronts Catholic Universities - Remove their right to be called “Catholic” and to ordain Catholic priests if they are doing “illicit” research
The Vatican’s doctrine • Life begins at procreation - When is does procreation start in practical term? - Not defined • The German Law has defined this in legal terms as the time of pronuclear fusion (syngamy) • The former Norwegian law did not contain such a definition - In Norway we defined it in practical terms as soon a a sperm cell was in the vicinity of an oocyte, the oocyte was fertilized

When did I begin? • Aristotle: - …. into a living being with a vegetative soul after 7 days, and subsequently into one with a sensitive soul at 40 days. At least this was for boys. It was 90 days for girls… • Jews and Muslims - Life begins not before 40 days after fertilisation • Liberal protestants and the orthodox churches have adopted a view that the (pre) embryo gradually attains a full moral status • Catholic Church, conservative protestants and Anglicans - Life begins at fertilization

Summary • Stem cells will become an integral part of a new discipline in medicine: - Regenerative medicine - Embryonic stem cells necessary as a research tool, but my guess is that they will not be extensively used clinically in the future - The goal is to be able to use IPS cells – genetically your own - Can truly be a revolution - Safety is a concern - Stability of differentiation ? - Limited clinical experience so far

• slutt
ef818984bd69ac431fb3af744457b8ae.ppt