9d179c03c0ac39e231c66e78df02c834.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 71

Embedded system design issues
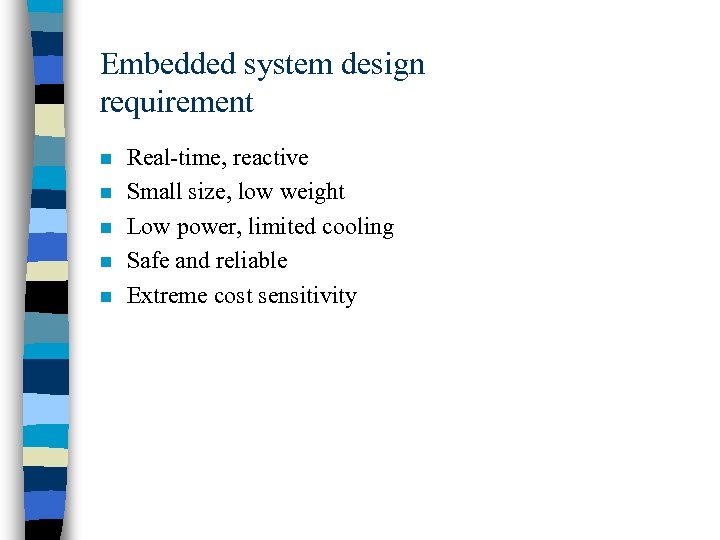
Embedded system design requirement n n n Real-time, reactive Small size, low weight Low power, limited cooling Safe and reliable Extreme cost sensitivity

Real-time operation n Real-time: correctness of result is a function of time it is delivered – Not necessarily ‘real fast’: predictability is the issue – Worst case performance often limits design n Reactive: computation rate is in response to external events – Periodic events can be scheduled statically – Aperioidc events must be statistically predicted, and dynamically scheduled when possible n Design challenges – Least pessimism in worst case analysis – Accurate performance prediction
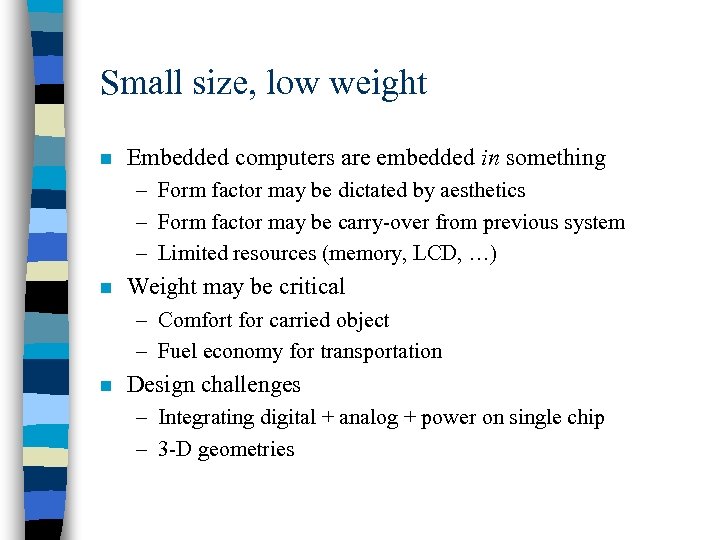
Small size, low weight n Embedded computers are embedded in something – Form factor may be dictated by aesthetics – Form factor may be carry-over from previous system – Limited resources (memory, LCD, …) n Weight may be critical – Comfort for carried object – Fuel economy for transportation n Design challenges – Integrating digital + analog + power on single chip – 3 -D geometries

Safe and reliable n Systems must be safe to protect people & property – Mission critical systems – Regulations n Reliability – Critical to customer (e. g. phone call hand-over) – Traditional fault-tolerant method is expensive – High availability may come at the cost of reliability n Design challenges – Realistic reliability prediction – Low-cost reliability

Harsh environment n Many embedded systems do not have controlled environment – – – – Heat from combustion / limited cooling Vibration / shock Water / corrosion Fire Shipping damage Physical abuse (drop test) Dirty power supply Lightning / electro-magnetic interference

Cost sensitivity n Component cost is visible to engineer – Sometimes wrong thing to optimize for – Cost vs. robustness – Life-cycle optimization

System level design issues

System-level requirements n n End-product utility is the goal System safety & reliability Analog & I/O Power management
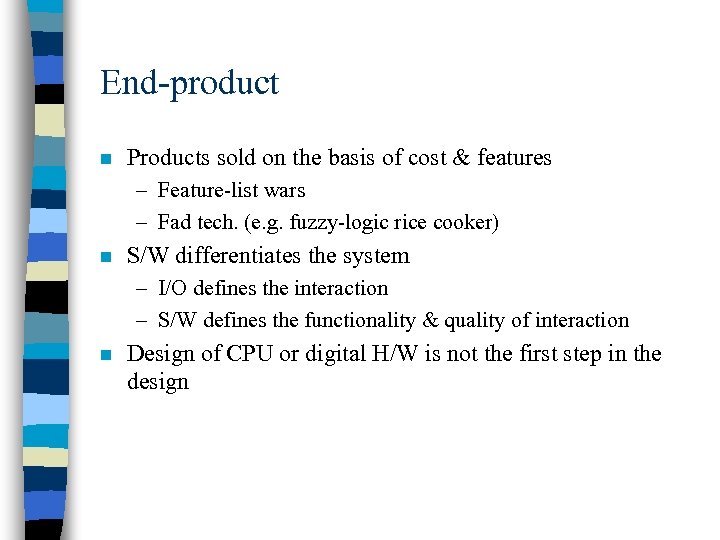
End-product n Products sold on the basis of cost & features – Feature-list wars – Fad tech. (e. g. fuzzy-logic rice cooker) n S/W differentiates the system – I/O defines the interaction – S/W defines the functionality & quality of interaction n Design of CPU or digital H/W is not the first step in the design

System safety & reliability n S/W can invite complexity – Complexity invites problems – Traditional fix: use H/W instead of S/W, but it does not work for dynamic environment n Reliability is cost – A single fault may cause mass recall – Wrong design induces large maintenance cost
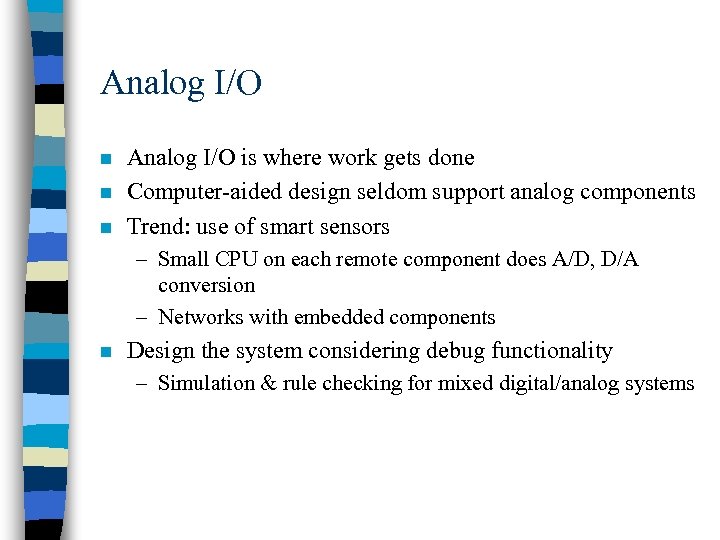
Analog I/O n n n Analog I/O is where work gets done Computer-aided design seldom support analog components Trend: use of smart sensors – Small CPU on each remote component does A/D, D/A conversion – Networks with embedded components n Design the system considering debug functionality – Simulation & rule checking for mixed digital/analog systems
Power management n n Power is limited due to heat or power storage capacity Low power desktop CPUs are not really suitable for embedded systems – Low power Pentium: 3 ~ 7 W – PDA: less than 1 W – Less than 1 m. W for many systems (e. g. Casio data watch) n Design issues – Low-power operation – Fast wake-up – Low-cost power generation

Choosing an OS n License fee – Critical for embedded systems • e. g. Suppose 1$ for 1 piece. • If we sell 1 M pieces, it costs 1 M$ n H/W support – Is there an efficient tool for debug? – How about the device drivers? n Developer support – How expensive is the development tools? n n Reliability Upgrade

Choosing an OS n Networking support – usually the programmer should do it n File system support – Flash file system – NFS – XIP n Software size – Often critical to cost – Sometimes you should abandon some features

Real-time multitasking executives 1. 2. 개관 커널의 구성

1. 개관 RTOS 실행체제 멀티태스킹 기법 태스크
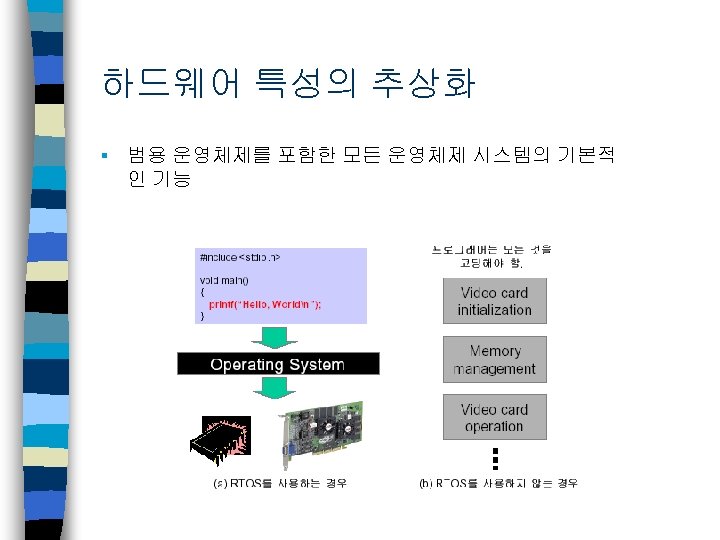
하드웨어 특성의 추상화 § 범용 운영체제를 포함한 모든 운영체제 시스템의 기본적 인 기능

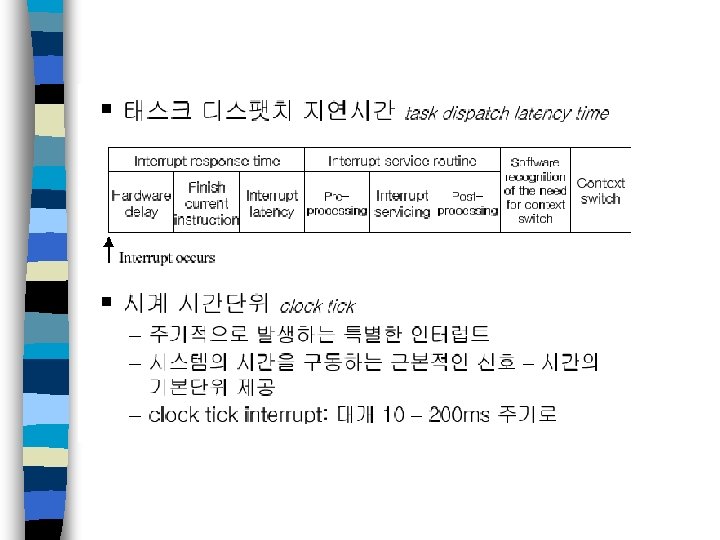
예측 가능한 문맥 전환 n 실시간 시스템 “시간에 맞게” 올바른 결과를 전달하는 시스템 n 시스템 사용 전에 시스템 분석 가능 여부가 매우 중요 n 다양한 정적 분석에 대하여 기능적, 시간적 행동 양식이 충분히 결정적이고 예측 가능해야 함. 실시간 운영체제들은 실시간 태스크를 처리함에 있어서 제한되지 않는 문맥 교환 지연을 발생시키지 않아야 함.

RTOS의 네 가지 필요 조건 1) (완전) 선점형 커널을 제공 2) 우선 순위 기반의 스케줄링 제공 3) 인터럽트 지연시간이 일정 범위 이내여야 함 4) 스케줄링 지연시간이 일정 범위 이내여야 함
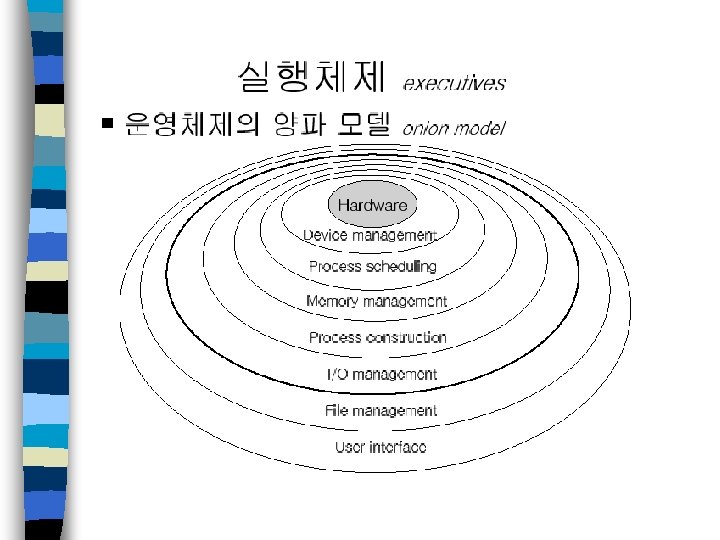



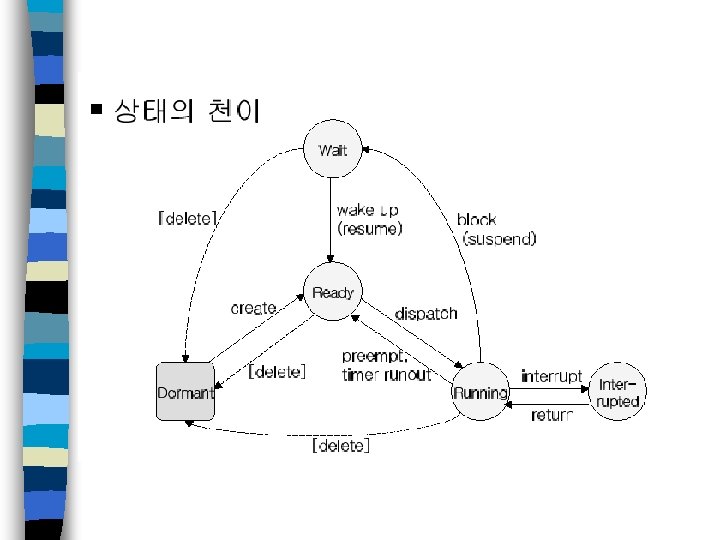
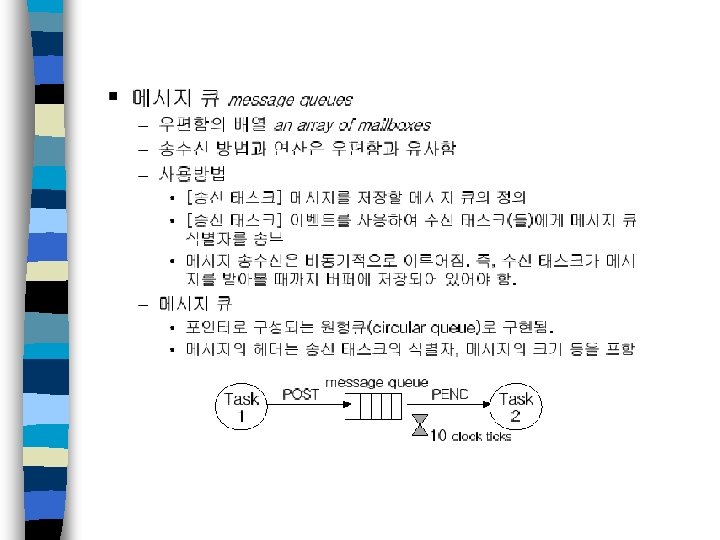
멀티태스킹 n 태스크 - 응용 프로그램의 실행가능 한 기본단위, 설계 단위 - 수행 중단 뒤 재시작 가능하도록 런타임 문맥을 가짐 - 상태 천이 가능 - DART 등을 이용하여 시스템 설계 단계에서 추출가능 n 멀티태스킹 - 태스크들을 CPU 상에서 스케줄링하고 전환하는 과정 - 응용 프로그램의 동시성 증가로 인해 CPU 이용율 증가


멀티태스킹 n 무한 폴링 – 장점 • 간단한 내장형 응용프로그램의 경우 효과적 • RTOS의 멀티태스킹 능력에 의존하지 않으므로 효과적 – 단점 • 많은 CPU 이용율이 폴링 루프에서 불필요하게 낭비 • 한 이벤트의 최대 응답시간은 폴링 루프의 총 수행시간으로 결정
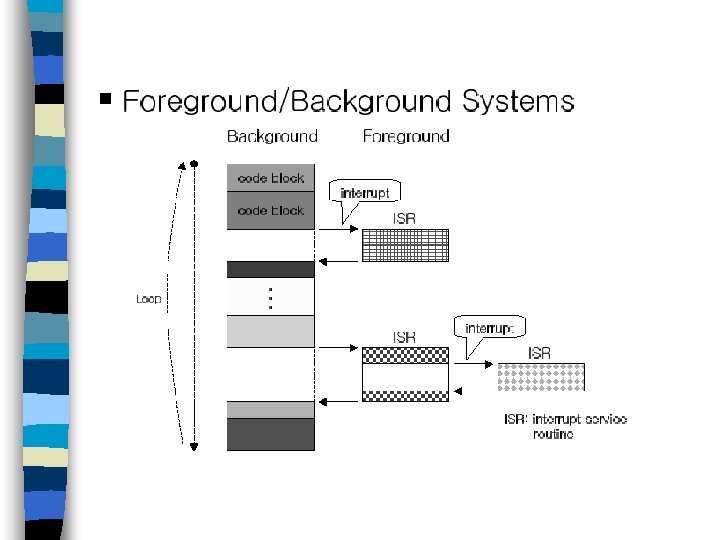

멀티태스킹 n 인터럽트 대응 – 폴링 루프로부터 실시간 이벤트들을 분리함으로써 부분적 문제점 해결가능 ex) 하드웨어 인터럽트 대응 – 이벤트 처리가 과도할 경우, 인터럽트 없는 폴링 루프와 마찬가지임. 태스크 기반 설계 방법 및 멀티태스킹 실시간 커널 필요

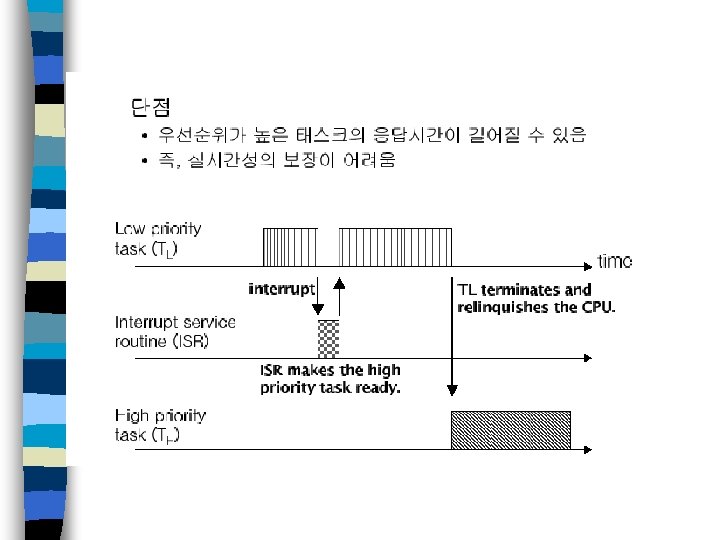
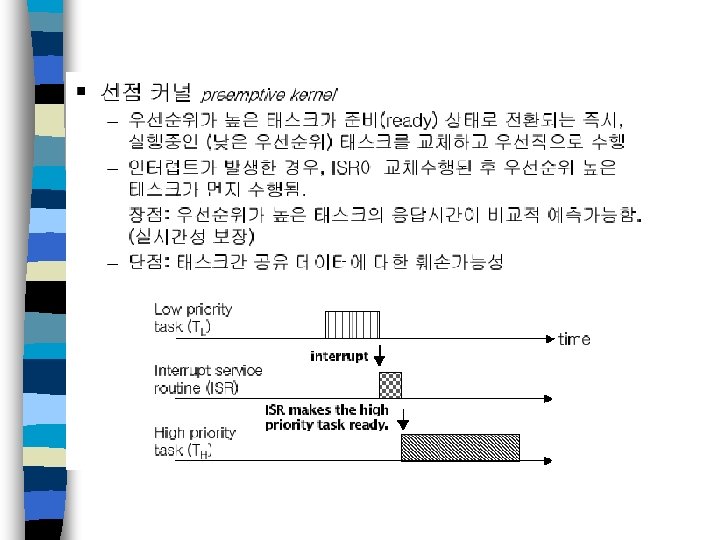
멀티태스킹 n 멀티태스킹 실시간 커널 – 수행 중 태스크의 문맥을 저장하고 복구하는 기능 필요 – 태스크 문맥을 스택에 저장하고 새 태스크의 문맥을 스택으로부터 복 구함으로써 태스크 문맥 전환 수행 시스템 응답 시간 – 태스크는 중요도에 따라 우선순위를 가짐 이 중요한 경우 – 선점형 커널과 비선점형 커널로 구분 선점형 커널 사용


2. 커널의 구성 커널, 상호배제, 동기화, 태스크간 통신, 인터럽트 처리









세마포어



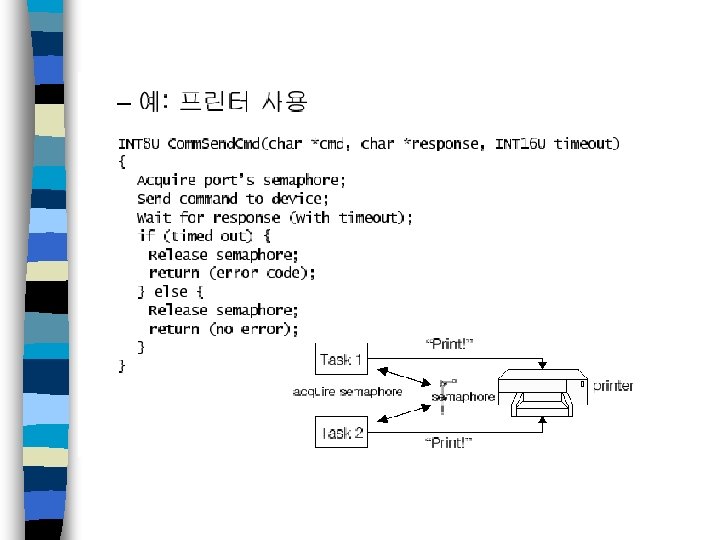

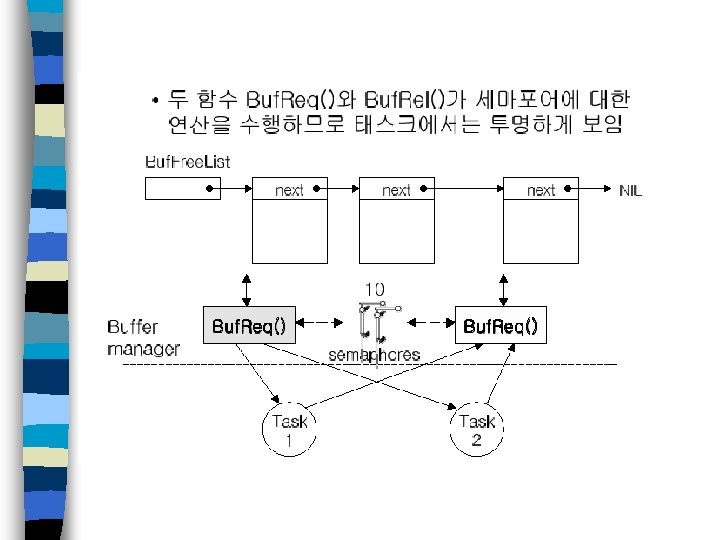

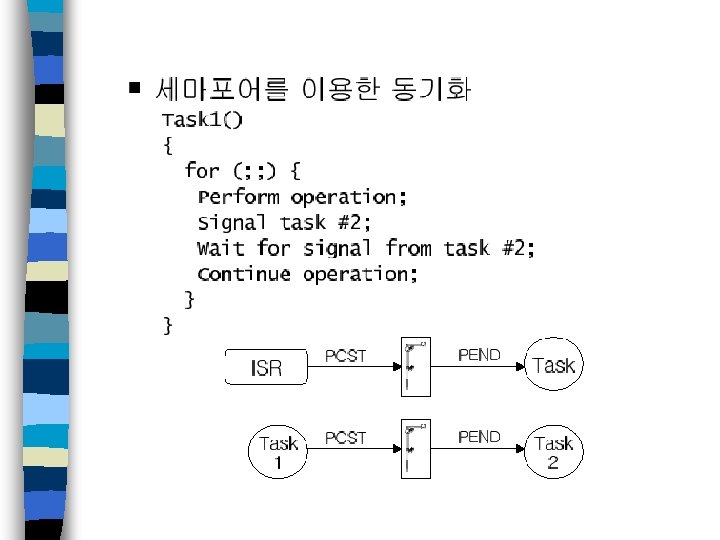
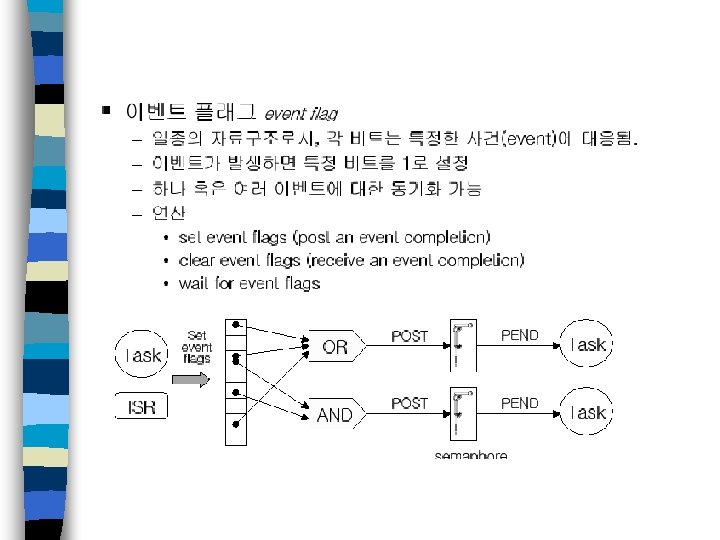



S/W configuration
Selecting a compiler n Build or buy? – Depends on the system • If you have a DSP, you may have to use the compiler provided by the vendor • You can build a cross-compiler by yourself – Open source? • If you have source codes of compiler, you can do many things n Usual tools – GNU tools – ARM Developer Suite (ADS) – Third party tools

Building a cross-compiler n GNU tools – You can find information: • www. armlinux. org/docs/toolchain for arm • penguippc. org/usr/embedded/howto/Power. PC-Embedded. HOWTO. html for Power. PC – toolchain • • gcc glibc gdb binutils – Some targets may not be supported • Especially when the target has DSPs • You should modify the source codes

Example: porting GCC n Writing back-end for the “machine” – Target description macro (machine. h) • Endian, bits per word, pointer size, etc. – Machine description (machine. md) • Description of machine codes in RTL n Configure – Tools (as, ld, ar, ranlib) for the cross-compiler – Libraries: crt 0. o, libgcc 1. a, etc. n Make gcc
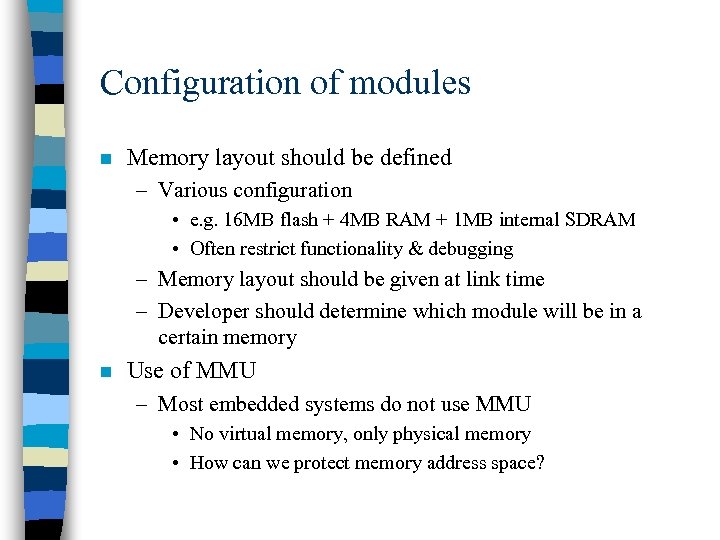
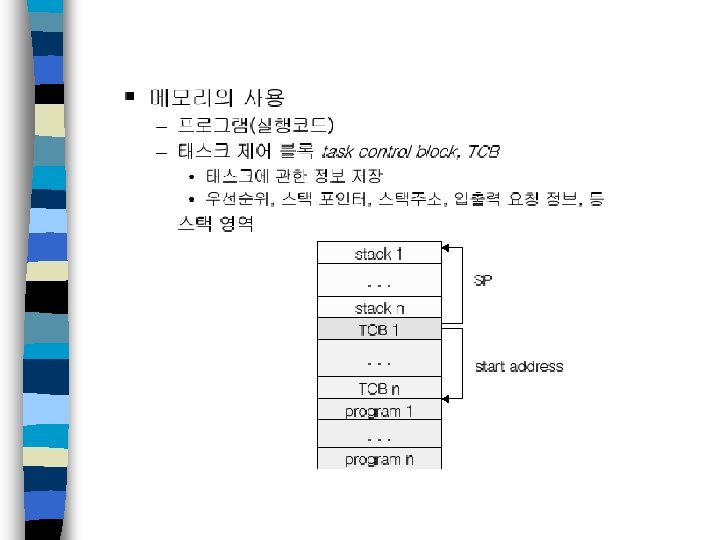
Configuration of modules n Memory layout should be defined – Various configuration • e. g. 16 MB flash + 4 MB RAM + 1 MB internal SDRAM • Often restrict functionality & debugging – Memory layout should be given at link time – Developer should determine which module will be in a certain memory n Use of MMU – Most embedded systems do not use MMU • No virtual memory, only physical memory • How can we protect memory address space?
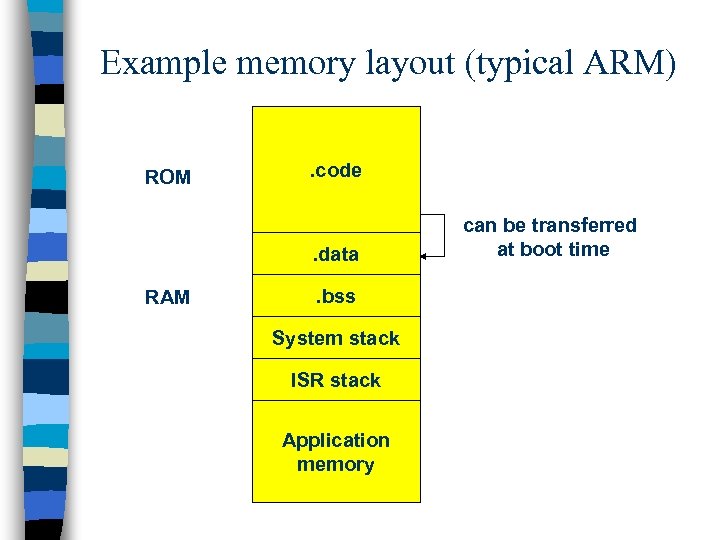
Example memory layout (typical ARM) ROM . code . data RAM . bss System stack ISR stack Application memory can be transferred at boot time

Testing and debugging

Test on host computer as much as possible n Access to debugging tools – Usually we have better debugging tools on host computer than the target n Simpler debugging cycle – Save downloading time – Easy to look the problems n Different environment – It is important to have effective simulation tools – It may take time & cost to develop simulation environment
Debugging tools n ARMulator – Software emulator of the ARM processor – Components • • Processor core model Memory interface Co-processor interface OS interface – Symbolic debugger: ARMsd – It is possible to build a complete, clock-cycle accurate software model – Initial evaluation of design – You must check you can use an emulator • depends on the chip vendor

Debugging tools n OS-level simulator – Independent of H/W – Used to check the behavior of applications on OS – You may need to port all the assembly codes & drivers
Debugging tools n JTAG boundary scan test Architecture – Standard interface (5 -pin serial protocol) • IEEE 1149 – Access and control the signal levels on the pins of a digital circuit – Principal goal – PCB, VSLI testing n Embedded-ICE – Standard solution for ARM debug architecture – Based on the JTAG test port – Can set breakpoints & watchpoints
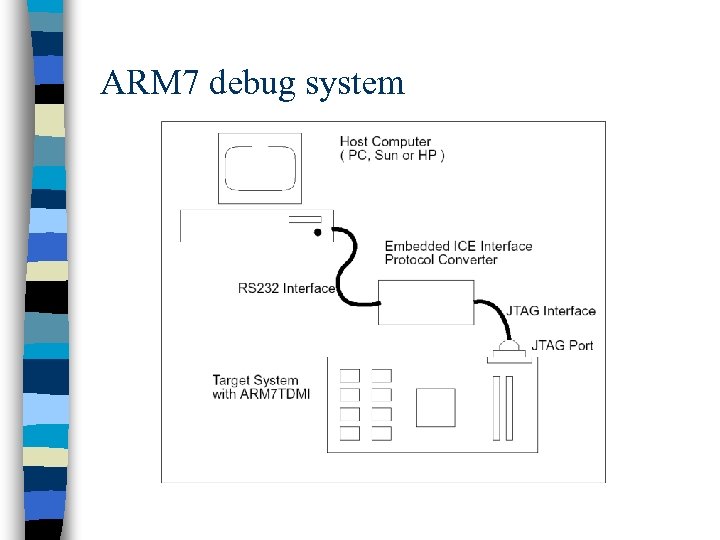
ARM 7 debug system
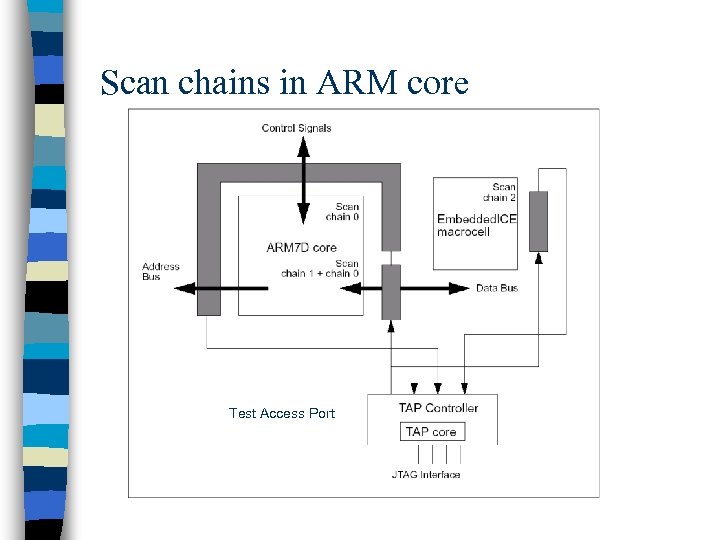
Scan chains in ARM core Test Access Port

Debugging tools n Embedded trace – Basically, printf • See what happens in the S/W modules – Real-Time Trace? • Limited bandwidth between the target & the host • Trace should not interfere the running of the target • It is hard to get “real” real-time trace
9d179c03c0ac39e231c66e78df02c834.ppt