 elementary Particles
elementary Particles
 1897. - Dzh. Tomson discovered the electron 1919 - E. Rutherford opened proton 1932 - J. Chadwick opens neutron
1897. - Dzh. Tomson discovered the electron 1919 - E. Rutherford opened proton 1932 - J. Chadwick opens neutron
 Starting from 1932. Opened more than 400 elementary particles Elementary particle - is the micro-object, which can not be split into its component parts, and which interacts with other micro -objects as a whole.
Starting from 1932. Opened more than 400 elementary particles Elementary particle - is the micro-object, which can not be split into its component parts, and which interacts with other micro -objects as a whole.
 The quantities characterizing the elementary particles n weight n electric charge n lifetime n Spin (angular momentum of its own)
The quantities characterizing the elementary particles n weight n electric charge n lifetime n Spin (angular momentum of its own)
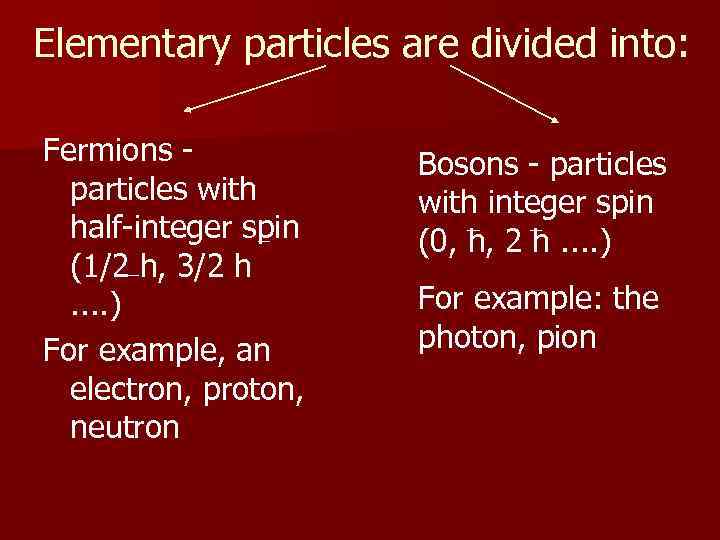 Elementary particles are divided into: Fermions particles with half-integer spin (1/2 h, 3/2 h. . ) For example, an electron, proton, neutron Bosons - particles with integer spin (0, h, 2 h. . ) For example: the photon, pion
Elementary particles are divided into: Fermions particles with half-integer spin (1/2 h, 3/2 h. . ) For example, an electron, proton, neutron Bosons - particles with integer spin (0, h, 2 h. . ) For example: the photon, pion
 Fermions obey the Pauli principle In the same energy state can be located not more than two fermions with opposite spins. Wolfgang Pauli Austrian physicist
Fermions obey the Pauli principle In the same energy state can be located not more than two fermions with opposite spins. Wolfgang Pauli Austrian physicist
 In 1931, English physicist P. Dirac theoretically predicted the existence of the positron - electron antiparticles.
In 1931, English physicist P. Dirac theoretically predicted the existence of the positron - electron antiparticles.
 In 1932, the positron was discovered experimentally by the American physicist Carl Anderson. In 1947. antipion was discovered. In 1955 - the antiproton, and in 1956 antineu.
In 1932, the positron was discovered experimentally by the American physicist Carl Anderson. In 1947. antipion was discovered. In 1955 - the antiproton, and in 1956 antineu.
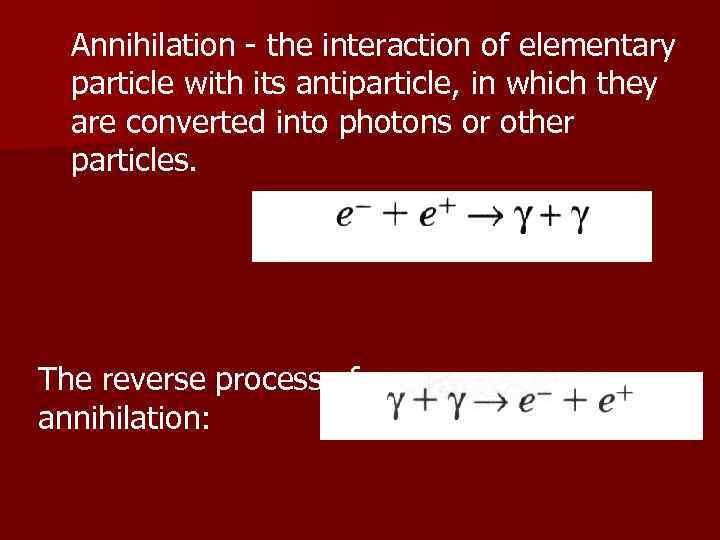 Annihilation - the interaction of elementary particle with its antiparticle, in which they are converted into photons or other particles. The reverse process of annihilation:
Annihilation - the interaction of elementary particle with its antiparticle, in which they are converted into photons or other particles. The reverse process of annihilation:
 n In 1963, American theoretical physicist J. Zweig and M. Gell. Mann hypothesized that hadrons consist of quarks. n In 1969, the experimental confirmation of the quark structure of hadrons came from Stanford.
n In 1963, American theoretical physicist J. Zweig and M. Gell. Mann hypothesized that hadrons consist of quarks. n In 1969, the experimental confirmation of the quark structure of hadrons came from Stanford.
 n. U nd n. S nt n. В n. С up quark down quark strange quark truth quark beauty quark charmed quark
n. U nd n. S nt n. В n. С up quark down quark strange quark truth quark beauty quark charmed quark
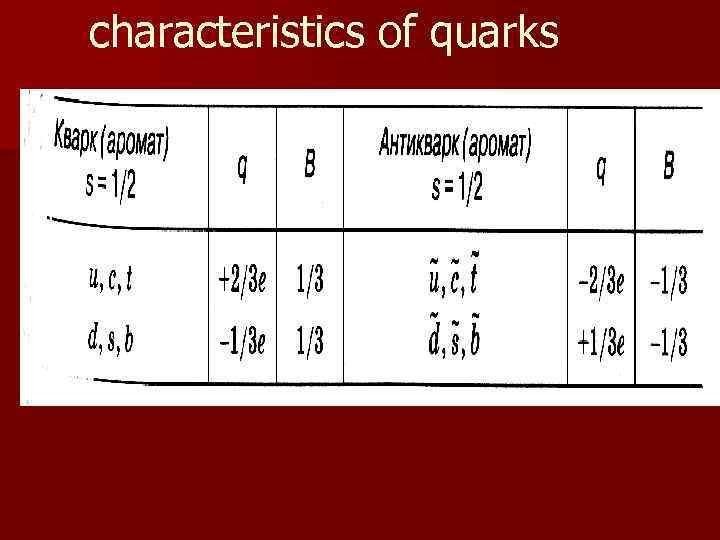 characteristics of quarks
characteristics of quarks
 Quark structure of hadrons n Baryons consist of three quarks: p = (u; u; d), n = (u; d; d) n Mesons consist of a quark and an antiquark: P + = (u; d)
Quark structure of hadrons n Baryons consist of three quarks: p = (u; u; d), n = (u; d; d) n Mesons consist of a quark and an antiquark: P + = (u; d)
 Each type quarks can have three color charge: red, blue and green. All hadrons not color. Since there are 6 and 6 antiquarks quark, each of which may have three colors, then the total number of quark is 36.
Each type quarks can have three color charge: red, blue and green. All hadrons not color. Since there are 6 and 6 antiquarks quark, each of which may have three colors, then the total number of quark is 36.
 Fundamental particles are leptons and quarks. All fundamental particles fermions. Thus, the universe around us is composed of 48 fundamental particles.
Fundamental particles are leptons and quarks. All fundamental particles fermions. Thus, the universe around us is composed of 48 fundamental particles.