f12a06e37e994978cd8633fbaf654a94.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 28
 Electronic Payment Systems 20 -763 Lecture 6 Digital Certificates
Electronic Payment Systems 20 -763 Lecture 6 Digital Certificates
 Outline • • Trust infrastructures Identity documents Digital certificates Certificate hierarchy Certification chains Remote authentication Public key infrastructure (PKI) 20 -763 ELECTRONIC PAYMENT SYSTEMS FALL 2002 COPYRIGHT © 2002 MICHAEL I. SHAMOS
Outline • • Trust infrastructures Identity documents Digital certificates Certificate hierarchy Certification chains Remote authentication Public key infrastructure (PKI) 20 -763 ELECTRONIC PAYMENT SYSTEMS FALL 2002 COPYRIGHT © 2002 MICHAEL I. SHAMOS
 Trust Infrastructures • • • OS (Windows, Linux, BSD…) Device (BIOS, CPU, Video/Audio, Storage) User (Biometrics, smart cards, digital signatures) Applications (Virus checkers, code authentication) Server (Secure Email, SSL) Content (Copy/tamper protection, document authentication) • Network (VPNs, firewalls, proxy servers, intrusion detectors) • Enterprise (Central management procedures) • External organization (Gov’t agency, CA) 20 -763 ELECTRONIC PAYMENT SYSTEMS FALL 2002 COPYRIGHT © 2002 MICHAEL I. SHAMOS
Trust Infrastructures • • • OS (Windows, Linux, BSD…) Device (BIOS, CPU, Video/Audio, Storage) User (Biometrics, smart cards, digital signatures) Applications (Virus checkers, code authentication) Server (Secure Email, SSL) Content (Copy/tamper protection, document authentication) • Network (VPNs, firewalls, proxy servers, intrusion detectors) • Enterprise (Central management procedures) • External organization (Gov’t agency, CA) 20 -763 ELECTRONIC PAYMENT SYSTEMS FALL 2002 COPYRIGHT © 2002 MICHAEL I. SHAMOS
 Identity Documents • What is an identity document? (Passport, birth certificate, driver’s license) – A piece of paper – Issued by a trusted third party – With information verifying the identity of the holder • An identity document is useless unless the holder can be CHALLENGED to demonstrate that he is the person named in the document – Photograph – Signature – Fingerprint 20 -763 ELECTRONIC PAYMENT SYSTEMS FALL 2002 COPYRIGHT © 2002 MICHAEL I. SHAMOS
Identity Documents • What is an identity document? (Passport, birth certificate, driver’s license) – A piece of paper – Issued by a trusted third party – With information verifying the identity of the holder • An identity document is useless unless the holder can be CHALLENGED to demonstrate that he is the person named in the document – Photograph – Signature – Fingerprint 20 -763 ELECTRONIC PAYMENT SYSTEMS FALL 2002 COPYRIGHT © 2002 MICHAEL I. SHAMOS
 Digital Certificate • A digital identity document binding a public-private key pair to a specific person or organization • Verifying a digital signature only proves that the signer had the private key corresponding to the public key used to decrypt the signature • Does not prove that the public-private key pair belonged to the claimed individual • We need an independent third party to verify the person’s identity (through non-electronic means) and issue a digital certificate 20 -763 ELECTRONIC PAYMENT SYSTEMS FALL 2002 COPYRIGHT © 2002 MICHAEL I. SHAMOS
Digital Certificate • A digital identity document binding a public-private key pair to a specific person or organization • Verifying a digital signature only proves that the signer had the private key corresponding to the public key used to decrypt the signature • Does not prove that the public-private key pair belonged to the claimed individual • We need an independent third party to verify the person’s identity (through non-electronic means) and issue a digital certificate 20 -763 ELECTRONIC PAYMENT SYSTEMS FALL 2002 COPYRIGHT © 2002 MICHAEL I. SHAMOS
 Digital Certificate Contents • • Name of holder Public key of holder Name of trusted third party (certificate authority) DIGITAL SIGNATURE OF CERTIFICATE AUTHORITY • Data on which hash and public-key algorithms have been used • Other business or personal information 20 -763 ELECTRONIC PAYMENT SYSTEMS FALL 2002 COPYRIGHT © 2002 MICHAEL I. SHAMOS
Digital Certificate Contents • • Name of holder Public key of holder Name of trusted third party (certificate authority) DIGITAL SIGNATURE OF CERTIFICATE AUTHORITY • Data on which hash and public-key algorithms have been used • Other business or personal information 20 -763 ELECTRONIC PAYMENT SYSTEMS FALL 2002 COPYRIGHT © 2002 MICHAEL I. SHAMOS
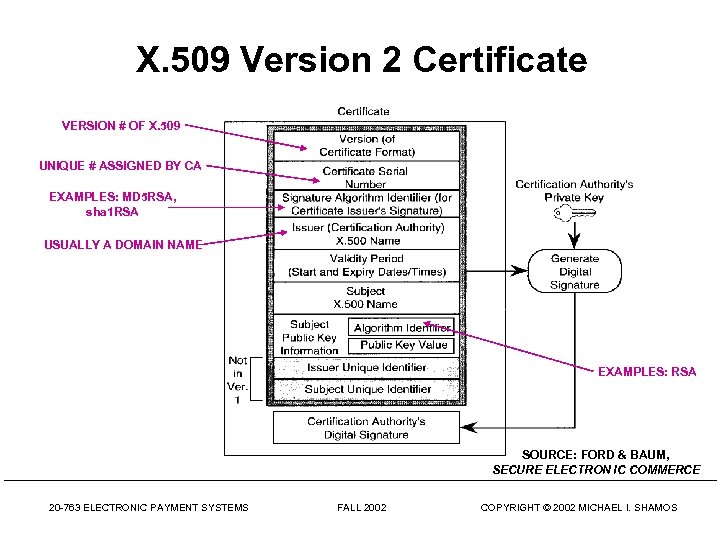 X. 509 Version 2 Certificate VERSION # OF X. 509 UNIQUE # ASSIGNED BY CA EXAMPLES: MD 5 RSA, sha 1 RSA USUALLY A DOMAIN NAME EXAMPLES: RSA SOURCE: FORD & BAUM, SECURE ELECTRON IC COMMERCE 20 -763 ELECTRONIC PAYMENT SYSTEMS FALL 2002 COPYRIGHT © 2002 MICHAEL I. SHAMOS
X. 509 Version 2 Certificate VERSION # OF X. 509 UNIQUE # ASSIGNED BY CA EXAMPLES: MD 5 RSA, sha 1 RSA USUALLY A DOMAIN NAME EXAMPLES: RSA SOURCE: FORD & BAUM, SECURE ELECTRON IC COMMERCE 20 -763 ELECTRONIC PAYMENT SYSTEMS FALL 2002 COPYRIGHT © 2002 MICHAEL I. SHAMOS
 Digital Certificate Verification • Do I trust the CA? (Is it in my list of trust root certification authorities? ) • Is the certificate genuine? – Look up the CA’s public key; use it to decrypt the signature – Compute the certificate’s hash; compare with decrypted sig • Is the holder genuine? This requires a challenge • If the holder is genuine, he must know the private key corresponding to the pubic key in the certificate • Having the certificate is not enough. (They are exchanged over the Internet all the time) • Send him a nonce (random 128 -bit number) 20 -763 ELECTRONIC PAYMENT SYSTEMS FALL 2002 COPYRIGHT © 2002 MICHAEL I. SHAMOS
Digital Certificate Verification • Do I trust the CA? (Is it in my list of trust root certification authorities? ) • Is the certificate genuine? – Look up the CA’s public key; use it to decrypt the signature – Compute the certificate’s hash; compare with decrypted sig • Is the holder genuine? This requires a challenge • If the holder is genuine, he must know the private key corresponding to the pubic key in the certificate • Having the certificate is not enough. (They are exchanged over the Internet all the time) • Send him a nonce (random 128 -bit number) 20 -763 ELECTRONIC PAYMENT SYSTEMS FALL 2002 COPYRIGHT © 2002 MICHAEL I. SHAMOS
 Challenge by Nonce • If you’re really Shamos, you must know his private key • So please encrypt this nonce: “A 87 B 1003 9 F 60 EA 46 71 A 837 BC 1 E 07 B 371” • When the answer comes back, decrypt it using the public key in the certificate • If the result matches, the remote user knew the correct private key • Never use the same nonce twice 20 -763 ELECTRONIC PAYMENT SYSTEMS FALL 2002 COPYRIGHT © 2002 MICHAEL I. SHAMOS
Challenge by Nonce • If you’re really Shamos, you must know his private key • So please encrypt this nonce: “A 87 B 1003 9 F 60 EA 46 71 A 837 BC 1 E 07 B 371” • When the answer comes back, decrypt it using the public key in the certificate • If the result matches, the remote user knew the correct private key • Never use the same nonce twice 20 -763 ELECTRONIC PAYMENT SYSTEMS FALL 2002 COPYRIGHT © 2002 MICHAEL I. SHAMOS
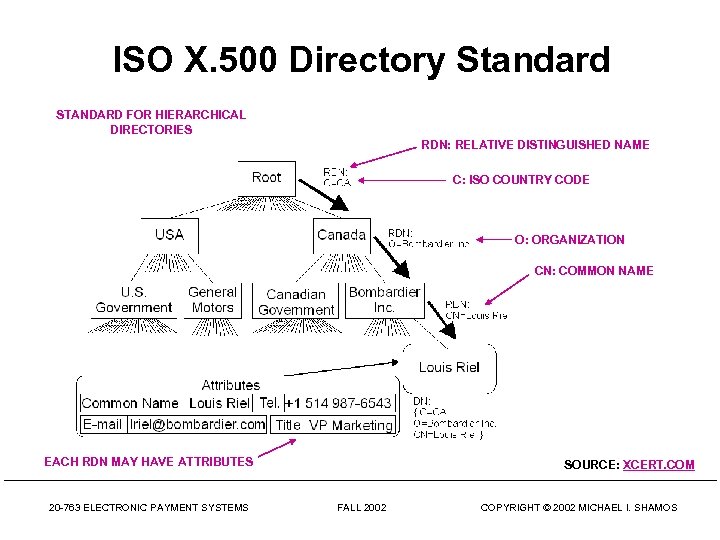 ISO X. 500 Directory Standard STANDARD FOR HIERARCHICAL DIRECTORIES RDN: RELATIVE DISTINGUISHED NAME C: ISO COUNTRY CODE O: ORGANIZATION CN: COMMON NAME EACH RDN MAY HAVE ATTRIBUTES 20 -763 ELECTRONIC PAYMENT SYSTEMS SOURCE: XCERT. COM FALL 2002 COPYRIGHT © 2002 MICHAEL I. SHAMOS
ISO X. 500 Directory Standard STANDARD FOR HIERARCHICAL DIRECTORIES RDN: RELATIVE DISTINGUISHED NAME C: ISO COUNTRY CODE O: ORGANIZATION CN: COMMON NAME EACH RDN MAY HAVE ATTRIBUTES 20 -763 ELECTRONIC PAYMENT SYSTEMS SOURCE: XCERT. COM FALL 2002 COPYRIGHT © 2002 MICHAEL I. SHAMOS
 Certification Hierarchy • What happens if you don’t recognize the CA in a certificate or it is not a trusted CA? • Suppose CA 1 has a certificate issued by trusted CA 2? • You may choose to trust CA 1 20 -763 ELECTRONIC PAYMENT SYSTEMS FALL 2002 COPYRIGHT © 2002 MICHAEL I. SHAMOS
Certification Hierarchy • What happens if you don’t recognize the CA in a certificate or it is not a trusted CA? • Suppose CA 1 has a certificate issued by trusted CA 2? • You may choose to trust CA 1 20 -763 ELECTRONIC PAYMENT SYSTEMS FALL 2002 COPYRIGHT © 2002 MICHAEL I. SHAMOS
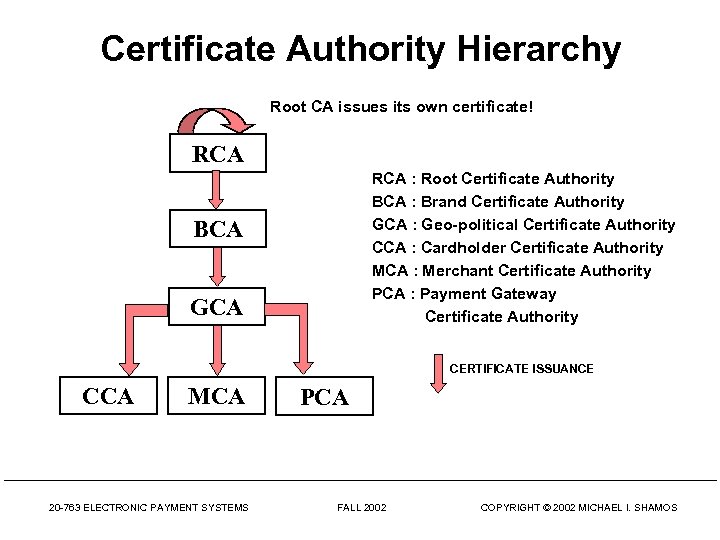 Certificate Authority Hierarchy Root CA issues its own certificate! RCA : Root Certificate Authority BCA : Brand Certificate Authority GCA : Geo-political Certificate Authority CCA : Cardholder Certificate Authority MCA : Merchant Certificate Authority PCA : Payment Gateway Certificate Authority BCA GCA CERTIFICATE ISSUANCE CCA MCA 20 -763 ELECTRONIC PAYMENT SYSTEMS PCA FALL 2002 COPYRIGHT © 2002 MICHAEL I. SHAMOS
Certificate Authority Hierarchy Root CA issues its own certificate! RCA : Root Certificate Authority BCA : Brand Certificate Authority GCA : Geo-political Certificate Authority CCA : Cardholder Certificate Authority MCA : Merchant Certificate Authority PCA : Payment Gateway Certificate Authority BCA GCA CERTIFICATE ISSUANCE CCA MCA 20 -763 ELECTRONIC PAYMENT SYSTEMS PCA FALL 2002 COPYRIGHT © 2002 MICHAEL I. SHAMOS
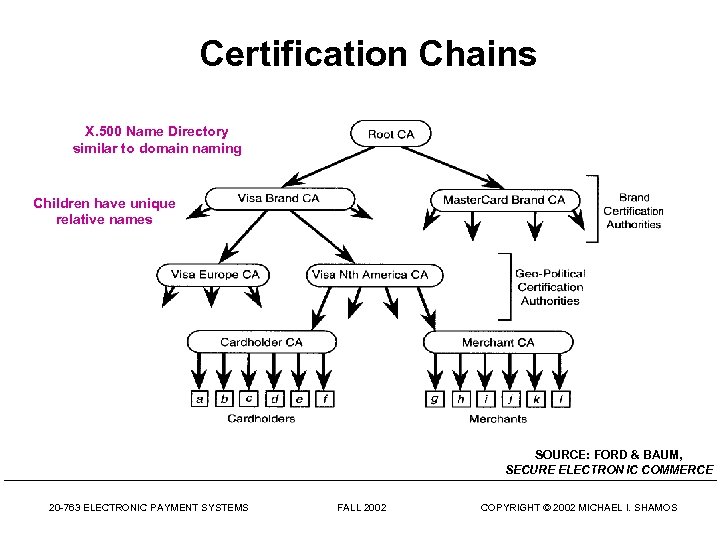 Certification Chains X. 500 Name Directory similar to domain naming Children have unique relative names SOURCE: FORD & BAUM, SECURE ELECTRON IC COMMERCE 20 -763 ELECTRONIC PAYMENT SYSTEMS FALL 2002 COPYRIGHT © 2002 MICHAEL I. SHAMOS
Certification Chains X. 500 Name Directory similar to domain naming Children have unique relative names SOURCE: FORD & BAUM, SECURE ELECTRON IC COMMERCE 20 -763 ELECTRONIC PAYMENT SYSTEMS FALL 2002 COPYRIGHT © 2002 MICHAEL I. SHAMOS
 Certification Paths • Alice has a certificate issued by authority D • To verify Alice’s certificate, Bob needs the public key of authority D (to decrypt D’s signature on the certificate) • How does Bob get it so he is sure it is really the public key of D? This is another verification problem. • Solution: Alice sends Bob a certification path, a sequence of certificates leading from her authority D to Bob. The public key of D is in D’s certificate • (D’s certificate is not enough for verification since Bob may not know D’s certification authority G) 20 -763 ELECTRONIC PAYMENT SYSTEMS FALL 2002 COPYRIGHT © 2002 MICHAEL I. SHAMOS
Certification Paths • Alice has a certificate issued by authority D • To verify Alice’s certificate, Bob needs the public key of authority D (to decrypt D’s signature on the certificate) • How does Bob get it so he is sure it is really the public key of D? This is another verification problem. • Solution: Alice sends Bob a certification path, a sequence of certificates leading from her authority D to Bob. The public key of D is in D’s certificate • (D’s certificate is not enough for verification since Bob may not know D’s certification authority G) 20 -763 ELECTRONIC PAYMENT SYSTEMS FALL 2002 COPYRIGHT © 2002 MICHAEL I. SHAMOS
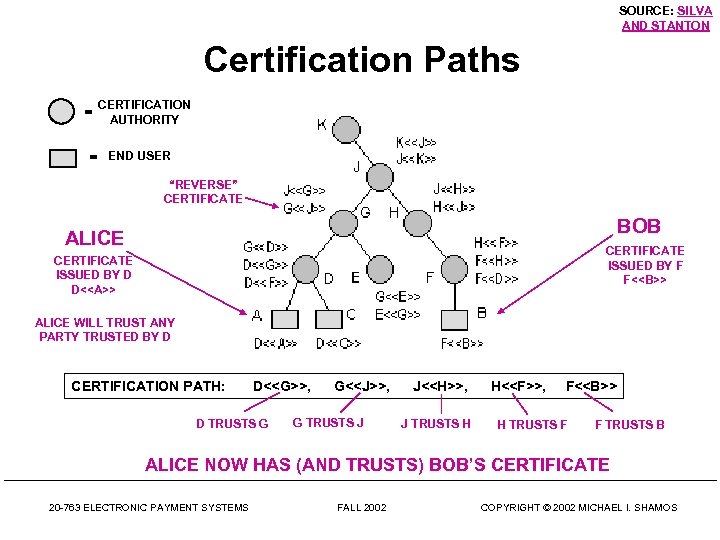 SOURCE: SILVA AND STANTON Certification Paths = CERTIFICATION AUTHORITY = END USER “REVERSE” CERTIFICATE BOB ALICE CERTIFICATE ISSUED BY F F<> CERTIFICATE ISSUED BY D D<> ALICE WILL TRUST ANY PARTY TRUSTED BY D CERTIFICATION PATH: D<
SOURCE: SILVA AND STANTON Certification Paths = CERTIFICATION AUTHORITY = END USER “REVERSE” CERTIFICATE BOB ALICE CERTIFICATE ISSUED BY F F<> CERTIFICATE ISSUED BY D D<> ALICE WILL TRUST ANY PARTY TRUSTED BY D CERTIFICATION PATH: D<
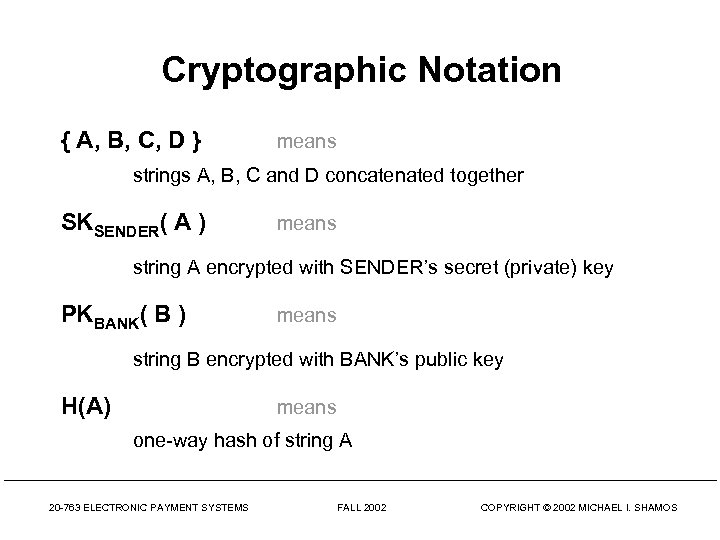 Cryptographic Notation { A, B, C, D } means strings A, B, C and D concatenated together SKSENDER( A ) means string A encrypted with SENDER’s secret (private) key PKBANK( B ) means string B encrypted with BANK’s public key H(A) means one-way hash of string A 20 -763 ELECTRONIC PAYMENT SYSTEMS FALL 2002 COPYRIGHT © 2002 MICHAEL I. SHAMOS
Cryptographic Notation { A, B, C, D } means strings A, B, C and D concatenated together SKSENDER( A ) means string A encrypted with SENDER’s secret (private) key PKBANK( B ) means string B encrypted with BANK’s public key H(A) means one-way hash of string A 20 -763 ELECTRONIC PAYMENT SYSTEMS FALL 2002 COPYRIGHT © 2002 MICHAEL I. SHAMOS
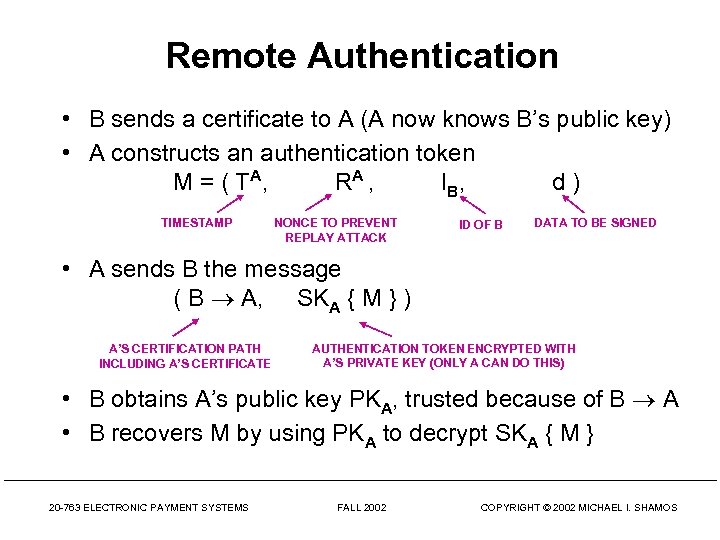 Remote Authentication • B sends a certificate to A (A now knows B’s public key) • A constructs an authentication token M = ( T A, RA , I B, d) TIMESTAMP NONCE TO PREVENT REPLAY ATTACK ID OF B DATA TO BE SIGNED • A sends B the message ( B A, SKA { M } ) A’S CERTIFICATION PATH INCLUDING A’S CERTIFICATE AUTHENTICATION TOKEN ENCRYPTED WITH A’S PRIVATE KEY (ONLY A CAN DO THIS) • B obtains A’s public key PKA, trusted because of B A • B recovers M by using PKA to decrypt SKA { M } 20 -763 ELECTRONIC PAYMENT SYSTEMS FALL 2002 COPYRIGHT © 2002 MICHAEL I. SHAMOS
Remote Authentication • B sends a certificate to A (A now knows B’s public key) • A constructs an authentication token M = ( T A, RA , I B, d) TIMESTAMP NONCE TO PREVENT REPLAY ATTACK ID OF B DATA TO BE SIGNED • A sends B the message ( B A, SKA { M } ) A’S CERTIFICATION PATH INCLUDING A’S CERTIFICATE AUTHENTICATION TOKEN ENCRYPTED WITH A’S PRIVATE KEY (ONLY A CAN DO THIS) • B obtains A’s public key PKA, trusted because of B A • B recovers M by using PKA to decrypt SKA { M } 20 -763 ELECTRONIC PAYMENT SYSTEMS FALL 2002 COPYRIGHT © 2002 MICHAEL I. SHAMOS
 Authentication • • B checks IB to make sure he is the intended recipient B verifies that the timestamp Ta is current B verifies that RA has not been used before (no replay) B knows A’s certificate really belongs to A since only A could have encrypted M with SKA AT THIS POINT, B HAS AUTHENTICATED A. THIS IS “ONE-WAY AUTHENTICATION” • B can send A an authentication token so A will know that B is authentic IF A AND B AUTHENTICATE EACH OTHER, WE HAVE “TWO-WAY AUTHENTICATION” 20 -763 ELECTRONIC PAYMENT SYSTEMS FALL 2002 COPYRIGHT © 2002 MICHAEL I. SHAMOS
Authentication • • B checks IB to make sure he is the intended recipient B verifies that the timestamp Ta is current B verifies that RA has not been used before (no replay) B knows A’s certificate really belongs to A since only A could have encrypted M with SKA AT THIS POINT, B HAS AUTHENTICATED A. THIS IS “ONE-WAY AUTHENTICATION” • B can send A an authentication token so A will know that B is authentic IF A AND B AUTHENTICATE EACH OTHER, WE HAVE “TWO-WAY AUTHENTICATION” 20 -763 ELECTRONIC PAYMENT SYSTEMS FALL 2002 COPYRIGHT © 2002 MICHAEL I. SHAMOS
 Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) • Digital certificates alone are not enough to establish security – Need control over certificate issuance and management • • • Certification authorities issue certificates Who verifies the identify of certification authorities? Naming of entities Certification Practice Statement Certificate Revocation List The metafunctions of certificate issuance form the Public Key Infrastructure 20 -763 ELECTRONIC PAYMENT SYSTEMS FALL 2002 COPYRIGHT © 2002 MICHAEL I. SHAMOS
Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) • Digital certificates alone are not enough to establish security – Need control over certificate issuance and management • • • Certification authorities issue certificates Who verifies the identify of certification authorities? Naming of entities Certification Practice Statement Certificate Revocation List The metafunctions of certificate issuance form the Public Key Infrastructure 20 -763 ELECTRONIC PAYMENT SYSTEMS FALL 2002 COPYRIGHT © 2002 MICHAEL I. SHAMOS
 Certification Practice Statement • Satement by a CA of the policies and procedures it uses to issue certificates • CA private keys are on hardware cryptomodules • View Verisign Certification Practice Statement • INFN (Istituto Nazionale di Fisica Nucleare) CPS CHRYSALIS LUNA CA 3 TRUSTED ROOT KEY SYSTEM 20 -763 ELECTRONIC PAYMENT SYSTEMS IBM S/390 SECURE CRYPTOGRAPHIC MODULE FALL 2002 LITRONIC 440 CIPHERACCELERATOR COPYRIGHT © 2002 MICHAEL I. SHAMOS
Certification Practice Statement • Satement by a CA of the policies and procedures it uses to issue certificates • CA private keys are on hardware cryptomodules • View Verisign Certification Practice Statement • INFN (Istituto Nazionale di Fisica Nucleare) CPS CHRYSALIS LUNA CA 3 TRUSTED ROOT KEY SYSTEM 20 -763 ELECTRONIC PAYMENT SYSTEMS IBM S/390 SECURE CRYPTOGRAPHIC MODULE FALL 2002 LITRONIC 440 CIPHERACCELERATOR COPYRIGHT © 2002 MICHAEL I. SHAMOS
 Certificate Revocation List • Online list of revoked certificates • View Verisign CRL • Verisign CRL usage agreement 20 -763 ELECTRONIC PAYMENT SYSTEMS FALL 2002 COPYRIGHT © 2002 MICHAEL I. SHAMOS
Certificate Revocation List • Online list of revoked certificates • View Verisign CRL • Verisign CRL usage agreement 20 -763 ELECTRONIC PAYMENT SYSTEMS FALL 2002 COPYRIGHT © 2002 MICHAEL I. SHAMOS
 Functions of a Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) • Generate public/private key pairs • Identify and authenticate key subscribers • Bind public keys to subscriber by digital certificate • Issue, maintain, administer, revoke, suspend, reinstate, and renew digital certificates • Create and manage a public key repository 20 -763 ELECTRONIC PAYMENT SYSTEMS FALL 2002 COPYRIGHT © 2002 MICHAEL I. SHAMOS
Functions of a Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) • Generate public/private key pairs • Identify and authenticate key subscribers • Bind public keys to subscriber by digital certificate • Issue, maintain, administer, revoke, suspend, reinstate, and renew digital certificates • Create and manage a public key repository 20 -763 ELECTRONIC PAYMENT SYSTEMS FALL 2002 COPYRIGHT © 2002 MICHAEL I. SHAMOS
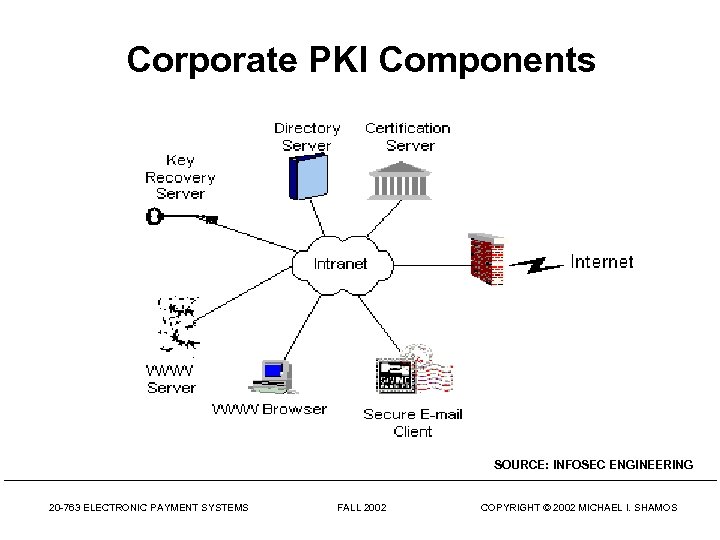 Corporate PKI Components SOURCE: INFOSEC ENGINEERING 20 -763 ELECTRONIC PAYMENT SYSTEMS FALL 2002 COPYRIGHT © 2002 MICHAEL I. SHAMOS
Corporate PKI Components SOURCE: INFOSEC ENGINEERING 20 -763 ELECTRONIC PAYMENT SYSTEMS FALL 2002 COPYRIGHT © 2002 MICHAEL I. SHAMOS
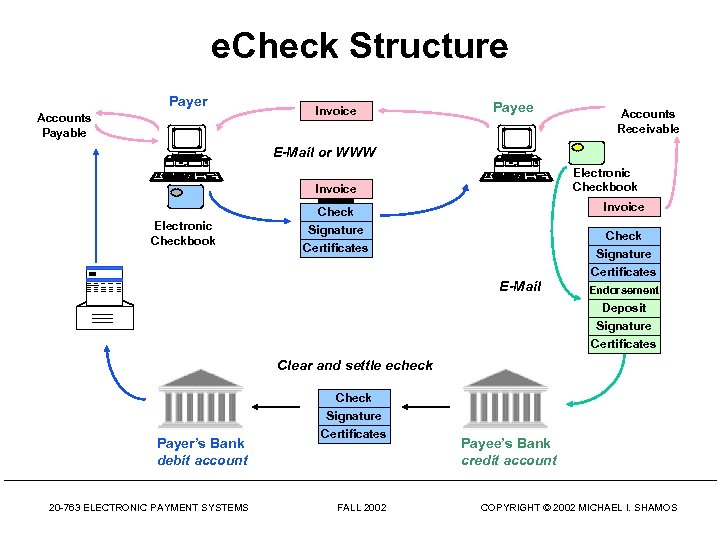 e. Check Structure Payer Accounts Payable Invoice Payee Accounts Receivable E-Mail or WWW Electronic Checkbook Invoice Check Signature Certificates Check Signature E-Mail Certificates Endorsement Deposit Signature Certificates Clear and settle echeck Payer’s Bank debit account 20 -763 ELECTRONIC PAYMENT SYSTEMS Check Signature Certificates FALL 2002 Payee’s Bank credit account COPYRIGHT © 2002 MICHAEL I. SHAMOS
e. Check Structure Payer Accounts Payable Invoice Payee Accounts Receivable E-Mail or WWW Electronic Checkbook Invoice Check Signature Certificates Check Signature E-Mail Certificates Endorsement Deposit Signature Certificates Clear and settle echeck Payer’s Bank debit account 20 -763 ELECTRONIC PAYMENT SYSTEMS Check Signature Certificates FALL 2002 Payee’s Bank credit account COPYRIGHT © 2002 MICHAEL I. SHAMOS
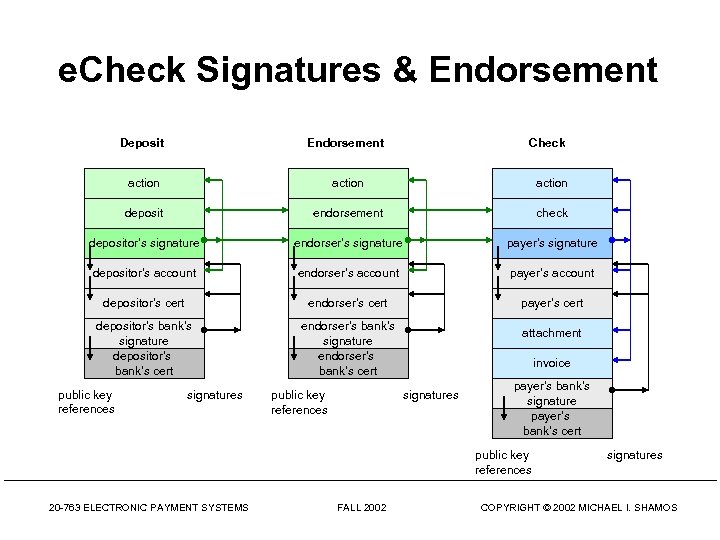 e. Check Signatures & Endorsement Deposit Endorsement action deposit endorsement check depositor’s signature endorser’s signature payer’s signature depositor’s account endorser’s account payer’s account depositor’s cert endorser’s cert payer’s cert depositor’s bank’s signature depositor’s bank’s cert endorser’s bank’s signature endorser’s bank’s cert public key references signatures public key references Check attachment invoice signatures payer’s bank’s signature payer’s bank’s cert public key references 20 -763 ELECTRONIC PAYMENT SYSTEMS FALL 2002 signatures COPYRIGHT © 2002 MICHAEL I. SHAMOS
e. Check Signatures & Endorsement Deposit Endorsement action deposit endorsement check depositor’s signature endorser’s signature payer’s signature depositor’s account endorser’s account payer’s account depositor’s cert endorser’s cert payer’s cert depositor’s bank’s signature depositor’s bank’s cert endorser’s bank’s signature endorser’s bank’s cert public key references signatures public key references Check attachment invoice signatures payer’s bank’s signature payer’s bank’s cert public key references 20 -763 ELECTRONIC PAYMENT SYSTEMS FALL 2002 signatures COPYRIGHT © 2002 MICHAEL I. SHAMOS
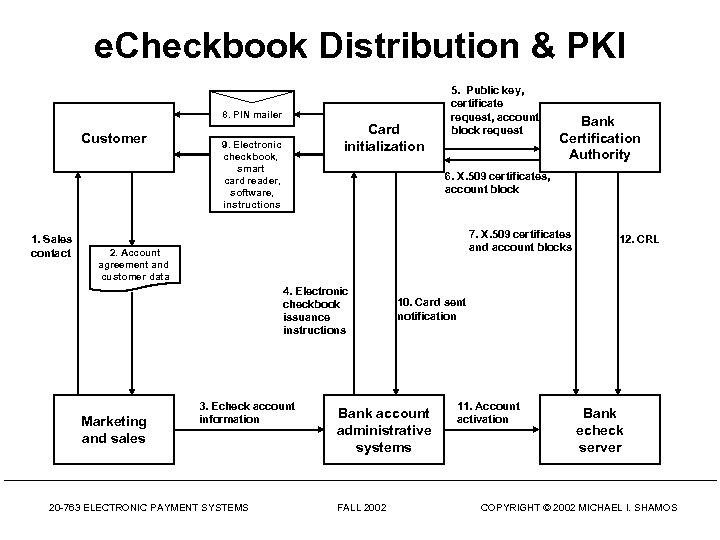 e. Checkbook Distribution & PKI 8. PIN mailer Customer 1. Sales contact Card initialization 9. Electronic checkbook, smart card reader, software, instructions 5. Public key, certificate request, account block request 6. X. 509 certificates, account block 7. X. 509 certificates and account blocks 2. Account agreement and customer data 4. Electronic checkbook issuance instructions Marketing and sales Bank Certification Authority 3. Echeck account information 20 -763 ELECTRONIC PAYMENT SYSTEMS 10. Card sent notification Bank account administrative systems FALL 2002 12. CRL 11. Account activation Bank echeck server COPYRIGHT © 2002 MICHAEL I. SHAMOS
e. Checkbook Distribution & PKI 8. PIN mailer Customer 1. Sales contact Card initialization 9. Electronic checkbook, smart card reader, software, instructions 5. Public key, certificate request, account block request 6. X. 509 certificates, account block 7. X. 509 certificates and account blocks 2. Account agreement and customer data 4. Electronic checkbook issuance instructions Marketing and sales Bank Certification Authority 3. Echeck account information 20 -763 ELECTRONIC PAYMENT SYSTEMS 10. Card sent notification Bank account administrative systems FALL 2002 12. CRL 11. Account activation Bank echeck server COPYRIGHT © 2002 MICHAEL I. SHAMOS
 Major Ideas • Digital certificate is a digital identity document issued by a trusted third party • Digital signatures alone do not prove identity • The holder of a certificate must be challenged to prove he knows the correct private key • Certificate authorities form trust hierarchies • Certification paths lead from sender to recipient, allowing verification of the trust relationship • How crucial are certificates to secure e. Commerce? 20 -763 ELECTRONIC PAYMENT SYSTEMS FALL 2002 COPYRIGHT © 2002 MICHAEL I. SHAMOS
Major Ideas • Digital certificate is a digital identity document issued by a trusted third party • Digital signatures alone do not prove identity • The holder of a certificate must be challenged to prove he knows the correct private key • Certificate authorities form trust hierarchies • Certification paths lead from sender to recipient, allowing verification of the trust relationship • How crucial are certificates to secure e. Commerce? 20 -763 ELECTRONIC PAYMENT SYSTEMS FALL 2002 COPYRIGHT © 2002 MICHAEL I. SHAMOS
 Q&A 20 -763 ELECTRONIC PAYMENT SYSTEMS FALL 2002 COPYRIGHT © 2002 MICHAEL I. SHAMOS
Q&A 20 -763 ELECTRONIC PAYMENT SYSTEMS FALL 2002 COPYRIGHT © 2002 MICHAEL I. SHAMOS


