0df768c9a5002a7bdc75d596b39a7d7e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 22
 Electronic Health Management Information System (e. HMIS) to build Strategic Information in the Ethiopian Health Sector (WEAE 0704) Dr. Wuleta Lemma 1, Assistant Professor, Director of Center for Global Health Equity, Tulane University USA Hiwot Tesfaye 1 , Head of Health Informatics Systems Deployment. Tulane University Ethiopia Program Abigail Belete 2 , Head of Software Development Informatics. Tulane University Ethiopia Program
Electronic Health Management Information System (e. HMIS) to build Strategic Information in the Ethiopian Health Sector (WEAE 0704) Dr. Wuleta Lemma 1, Assistant Professor, Director of Center for Global Health Equity, Tulane University USA Hiwot Tesfaye 1 , Head of Health Informatics Systems Deployment. Tulane University Ethiopia Program Abigail Belete 2 , Head of Software Development Informatics. Tulane University Ethiopia Program
 Outline q Brief Introduction q Objective q Major Features
Outline q Brief Introduction q Objective q Major Features
 Brief Introduction: About Ethiopia health infrastructure Federal level (Federal Ministry of Health) Specialized/ referral Hospital = 15 Regional Level (Regional Health Bureau)=11 Zonal Level (Zonal Health Dept. )=72 Woreda Level (Woreda Health Office)=811 Kebele ~ 15, 000 Regional /Zonal Hospital=34 District Hospital= 56 Primary Health Care Unit (HC + 5 HP) Health Centers = 2, 142 Health Post = 14, 192 *Health and Health Related Indicators 2001 and 2002 Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia Ministry of Health 5 Million Pop 1 Million Pop 250, 000 Pop 25, 000 Pop
Brief Introduction: About Ethiopia health infrastructure Federal level (Federal Ministry of Health) Specialized/ referral Hospital = 15 Regional Level (Regional Health Bureau)=11 Zonal Level (Zonal Health Dept. )=72 Woreda Level (Woreda Health Office)=811 Kebele ~ 15, 000 Regional /Zonal Hospital=34 District Hospital= 56 Primary Health Care Unit (HC + 5 HP) Health Centers = 2, 142 Health Post = 14, 192 *Health and Health Related Indicators 2001 and 2002 Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia Ministry of Health 5 Million Pop 1 Million Pop 250, 000 Pop 25, 000 Pop
 Brief Introduction : About the HMIS q q q Standardize § Indicators & definitions § Disease list for reporting & case definitions § Client / patient flow & data elements § Recording & Reporting forms § Procedure manual § Information use guidelines: Simplify § Reduce data burden § Streamline data management procedures Integrate § Data channel § Client / patient information at facility * HMIS/M&E Technical Documentation , Manual January 2008 Federal Ministry of Health
Brief Introduction : About the HMIS q q q Standardize § Indicators & definitions § Disease list for reporting & case definitions § Client / patient flow & data elements § Recording & Reporting forms § Procedure manual § Information use guidelines: Simplify § Reduce data burden § Streamline data management procedures Integrate § Data channel § Client / patient information at facility * HMIS/M&E Technical Documentation , Manual January 2008 Federal Ministry of Health
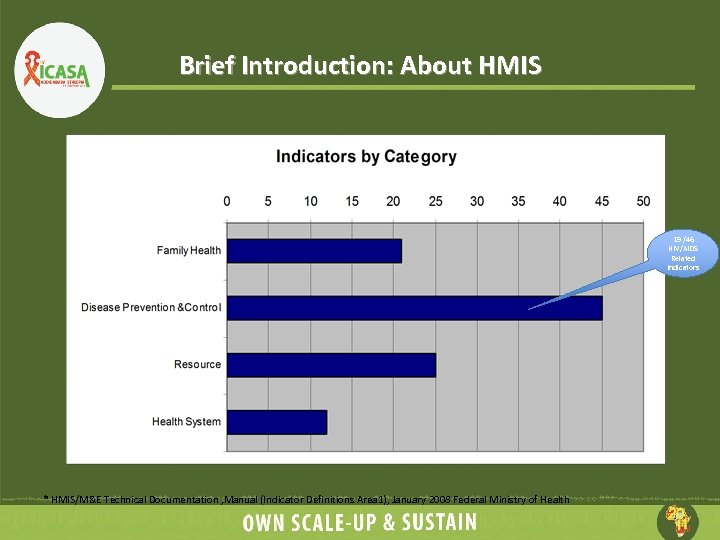 Brief Introduction: About HMIS 19 /46 HIV/AIDS Related Indicators * HMIS/M&E Technical Documentation , Manual (Indicator Definitions Area 1), January 2008 Federal Ministry of Health
Brief Introduction: About HMIS 19 /46 HIV/AIDS Related Indicators * HMIS/M&E Technical Documentation , Manual (Indicator Definitions Area 1), January 2008 Federal Ministry of Health
 Brief Introduction: About HMIS q HMIS captures much of its service and disease surveillance data from client/patient records that health professionals maintain for care and follow up. q HMIS reports contain the data required to calculate the indicators used for monitoring and evaluation of the health system
Brief Introduction: About HMIS q HMIS captures much of its service and disease surveillance data from client/patient records that health professionals maintain for care and follow up. q HMIS reports contain the data required to calculate the indicators used for monitoring and evaluation of the health system
 Objective of Electronic Health Information System q q q The Initiation to Implement EHR system at facility and higher levels by FMOH in collaboration with Tulane and CDC has created good opportunity to establish automated electronic report distributions within the different levels of the health system using e-HMIS module e-HMIS insures data completeness, validity, timeliness, ease of data/report compilation and promotes information use at all levels. e-HMIS system architecture employs Health Data Warehouse concept.
Objective of Electronic Health Information System q q q The Initiation to Implement EHR system at facility and higher levels by FMOH in collaboration with Tulane and CDC has created good opportunity to establish automated electronic report distributions within the different levels of the health system using e-HMIS module e-HMIS insures data completeness, validity, timeliness, ease of data/report compilation and promotes information use at all levels. e-HMIS system architecture employs Health Data Warehouse concept.
 e-HMIS Module Major Features q q Produce all types of HMIS reports at health facility, Woreda Health office, zonal health Department, Regional health Bureau and Federal Ministry of Health on monthly , quarterly and annual bases. Sending and receiving HMIS reports electronically through secure e-mail (by means of any available communication infrastructures including CDMA, GPRS, PSTN-Dialup, Broadband, etc) and other removable media (such as USB flash disk, CD/DVD). Provides data validation, completeness and timeliness. Provide data analysis tools such as indicators computation tools and charts
e-HMIS Module Major Features q q Produce all types of HMIS reports at health facility, Woreda Health office, zonal health Department, Regional health Bureau and Federal Ministry of Health on monthly , quarterly and annual bases. Sending and receiving HMIS reports electronically through secure e-mail (by means of any available communication infrastructures including CDMA, GPRS, PSTN-Dialup, Broadband, etc) and other removable media (such as USB flash disk, CD/DVD). Provides data validation, completeness and timeliness. Provide data analysis tools such as indicators computation tools and charts
 … e-HMIS Module Major Features q q q Provides easy and instant performance monitoring reports and chart. Supports automated data abstraction from site that has fully implemented Smartcare –EMR. Supports multi-point data encoding.
… e-HMIS Module Major Features q q q Provides easy and instant performance monitoring reports and chart. Supports automated data abstraction from site that has fully implemented Smartcare –EMR. Supports multi-point data encoding.
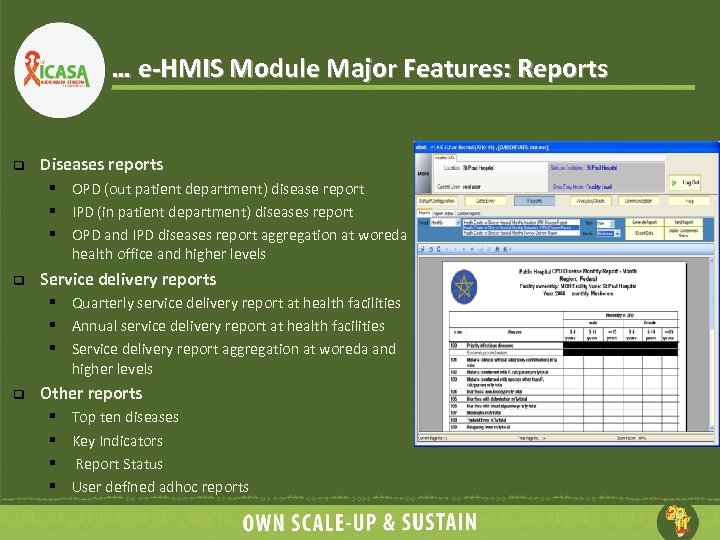 … e-HMIS Module Major Features: Reports q Diseases reports § OPD (out patient department) disease report § IPD (in patient department) diseases report § OPD and IPD diseases report aggregation at woreda health office and higher levels q Service delivery reports § Quarterly service delivery report at health facilities § Annual service delivery report at health facilities § Service delivery report aggregation at woreda and higher levels q Other reports § Top ten diseases § Key Indicators § Report Status § User defined adhoc reports
… e-HMIS Module Major Features: Reports q Diseases reports § OPD (out patient department) disease report § IPD (in patient department) diseases report § OPD and IPD diseases report aggregation at woreda health office and higher levels q Service delivery reports § Quarterly service delivery report at health facilities § Annual service delivery report at health facilities § Service delivery report aggregation at woreda and higher levels q Other reports § Top ten diseases § Key Indicators § Report Status § User defined adhoc reports
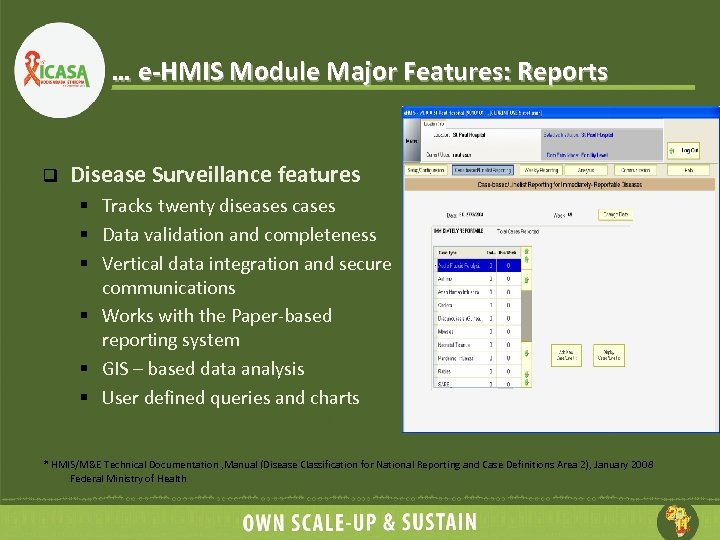 … e-HMIS Module Major Features: Reports q Disease Surveillance features § Tracks twenty diseases cases § Data validation and completeness § Vertical data integration and secure communications § Works with the Paper-based reporting system § GIS – based data analysis § User defined queries and charts * HMIS/M&E Technical Documentation , Manual (Disease Classification for National Reporting and Case Definitions Area 2), January 2008 Federal Ministry of Health
… e-HMIS Module Major Features: Reports q Disease Surveillance features § Tracks twenty diseases cases § Data validation and completeness § Vertical data integration and secure communications § Works with the Paper-based reporting system § GIS – based data analysis § User defined queries and charts * HMIS/M&E Technical Documentation , Manual (Disease Classification for National Reporting and Case Definitions Area 2), January 2008 Federal Ministry of Health
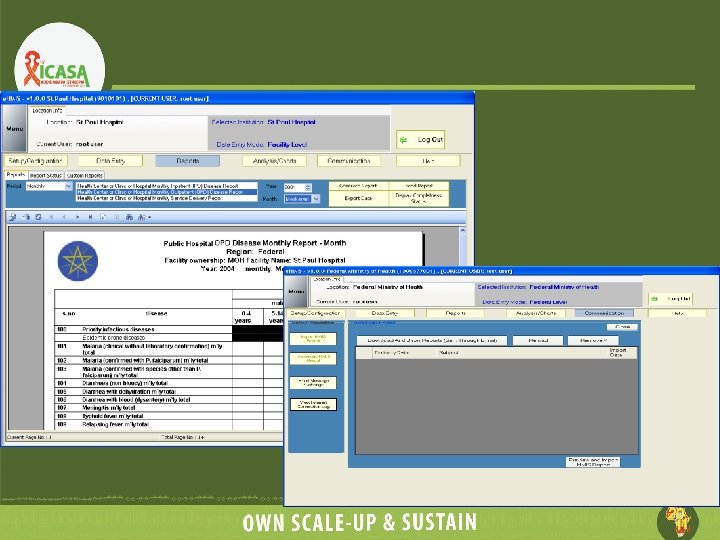
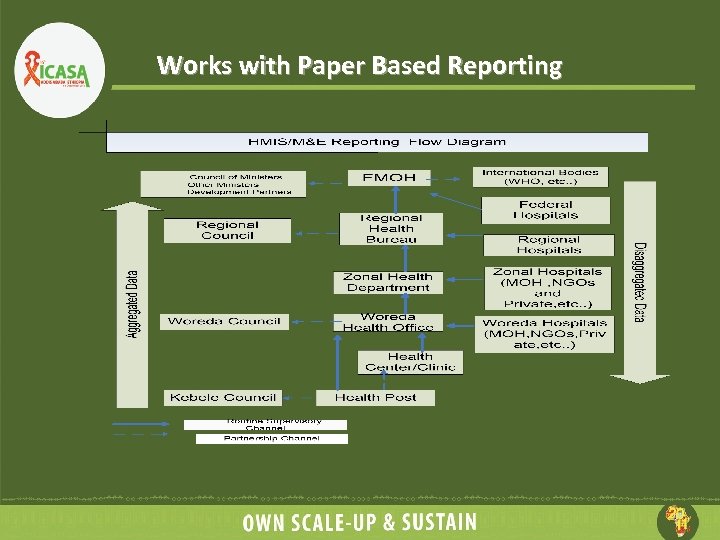 Works with Paper Based Reporting
Works with Paper Based Reporting
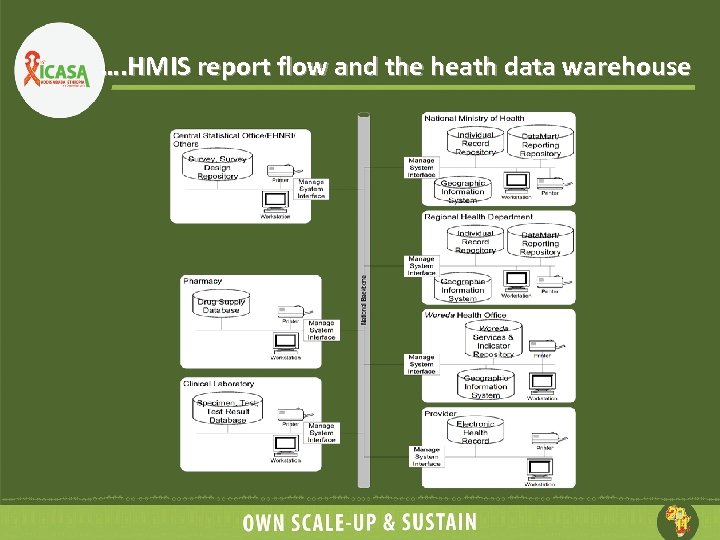 …. HMIS report flow and the heath data warehouse
…. HMIS report flow and the heath data warehouse
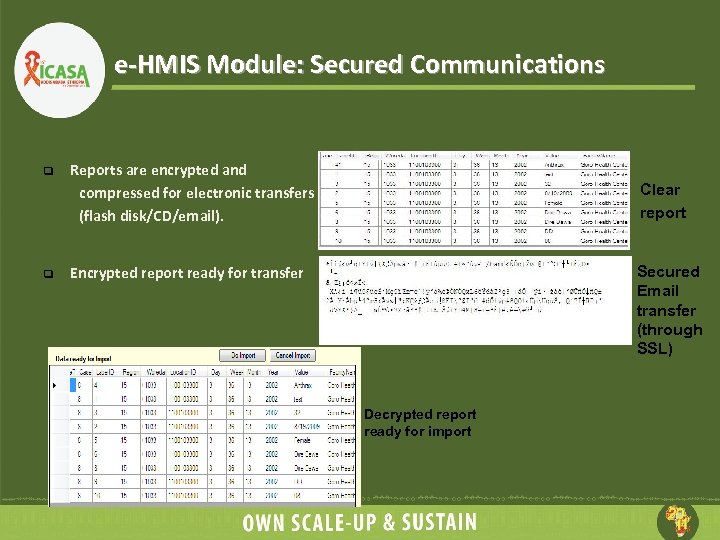 e-HMIS Module: Secured Communications q q Reports are encrypted and compressed for electronic transfers (flash disk/CD/email). Clear report Secured Email transfer (through SSL) Encrypted report ready for transfer Decrypted report ready for import
e-HMIS Module: Secured Communications q q Reports are encrypted and compressed for electronic transfers (flash disk/CD/email). Clear report Secured Email transfer (through SSL) Encrypted report ready for transfer Decrypted report ready for import
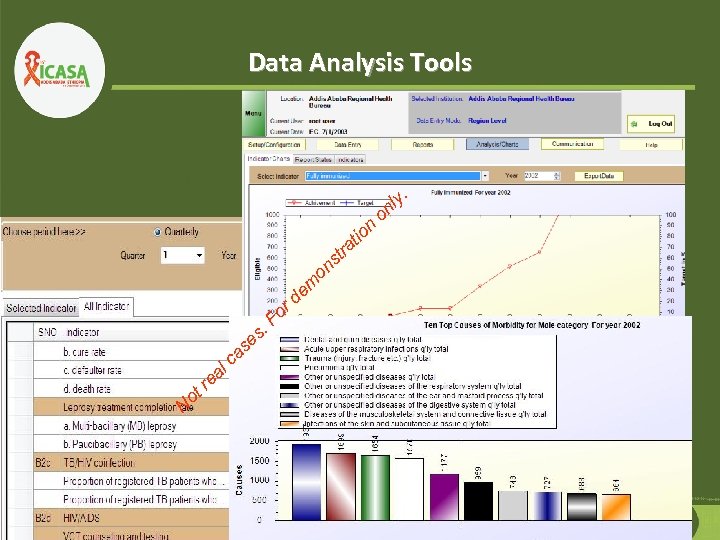 Data Analysis Tools . i t ra t ns o r Fo. a es s c al N e tr o em d on o y nl
Data Analysis Tools . i t ra t ns o r Fo. a es s c al N e tr o em d on o y nl
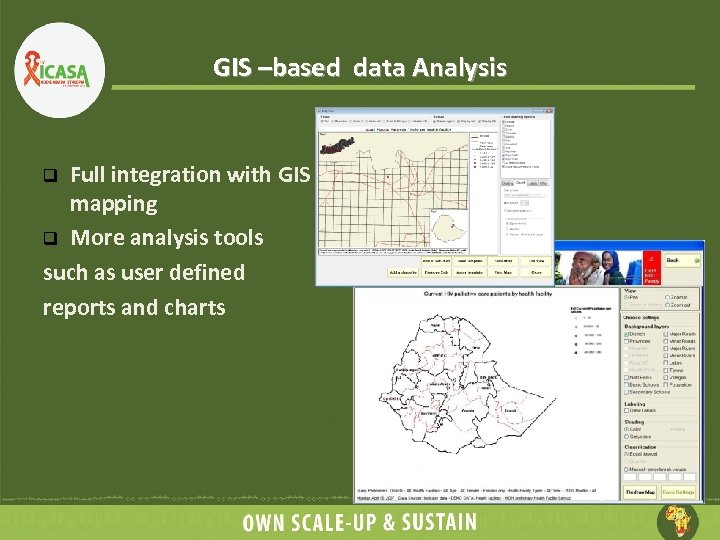 GIS –based data Analysis Full integration with GIS mapping q More analysis tools such as user defined reports and charts q
GIS –based data Analysis Full integration with GIS mapping q More analysis tools such as user defined reports and charts q
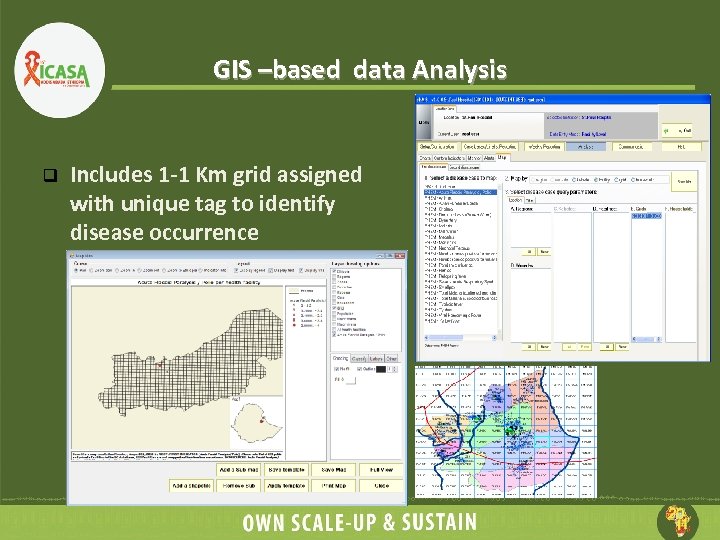 GIS –based data Analysis q Includes 1 -1 Km grid assigned with unique tag to identify disease occurrence
GIS –based data Analysis q Includes 1 -1 Km grid assigned with unique tag to identify disease occurrence
 Next steps • Additional Features – SDMX and Indicator repositories • Scale up to cover more than 800 Woreda’s in Ethiopia by the end of 2012
Next steps • Additional Features – SDMX and Indicator repositories • Scale up to cover more than 800 Woreda’s in Ethiopia by the end of 2012
 Thank You
Thank You


