91d652961b4e69703e845209e8d6ae8d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 32

Electronic Commerce BBA (Hons) (B 2 B Business to Business EC) By: Farhan Mir © Farhan Mir 2016 IMS
Trading Process Network (TPN) Post in General Electric (GE) – Its purchasing was inefficient, involved too many administrative transactions Factories at GE Lighting division used to send hundreds of Requisitions For Quotations (RFQs) to the corporate sourcing department each day for low-value machine parts. For each requisition, the accompanying blueprints had to be requested from storage, retrieved from the vault, transported to the processing site, photocopied, folded, attached to paper requisition forms with quote sheets, stuffed into envelopes and mailed out. This process took at least 7 days and was so complex and timeconsuming that the sourcing department normally sent out bid packages only to two or three suppliers at a time. – Using TPN GE is conducting electronic bids, no paperwork © Farhan Mir 2016 IMS
Trading Process Network (TPN) Post in General Electric (cont. ) • Benefits of using TPN 60%of the staff involved in – It used to take 18 -23 days to identify procurement have been suppliers, prepare a request for bid, redeployed. The sourcing negotiate a price and award the department has at least 6 -8 free contract to a supplier. It now takes days a month to concentrate on 9 -11 days. strategic activities rather than on – With the transaction handled paperwork, photocopying and electronically from beginning to end, envelope stuffing it had to do when the process was manual. invoices are automatically reconciled with purchase orders, Labor involved in procurement reflecting any modifications that declined by 30%. At the same time, materials costs declined 5% happen along the way. -20% due to the ability to reach a – GE Procurement departments wider base of suppliers online. across the world now share information about their best suppliers. © Farhan Mir 2016 IMS

Concepts, Characteristics, and Models of B 2 B EC The Basic Types of B 2 B Transactions and Activities Sell-side Buy-side Exchanges Supply chain improvements and collaborative commerce © Farhan Mir 2016 IMS
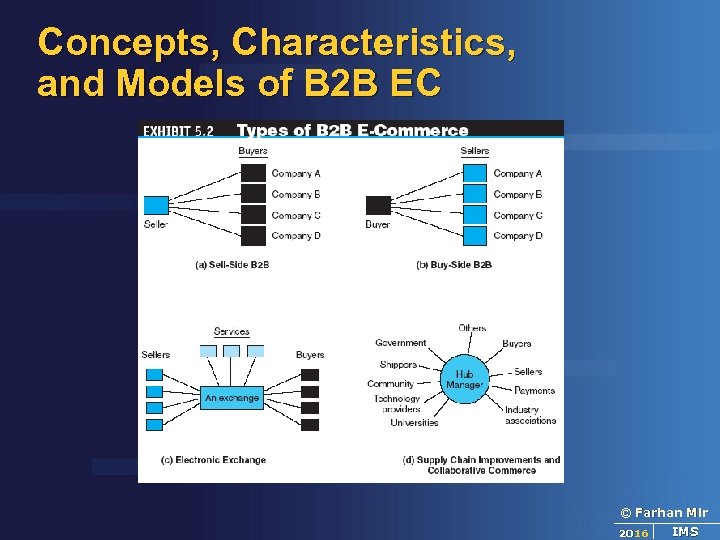
Concepts, Characteristics, and Models of B 2 B EC © Farhan Mir 2016 IMS

Characteristics of B 2 B EC Key Entities of B 2 B EC – – – Buying company with procurement management perspective Selling company with marketing management perspective Electronic Intermediary, an optional third party directory service provider (the scope of service may be extended to order fulfillment) – – – Deliverer who can fulfill a just-in-time delivery Network platform such as the Internet, VAN, intranet and extranet Protocol of communication such as EDI and comparison shopping possibly using software agents – Back-end information system possibly implemented using the intranet and Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems © Farhan Mir 2016 IMS

Characteristics of B 2 B EC Majorly Supplier-oriented marketing Used to sell the company’s products and services to business customers on the Internet Electronic catalogs are basically the same as that for B 2 C EC, but they may be customized © Farhan Mir 2016 IMS

Concepts, Characteristics, and Models of B 2 B EC Types of transactions spot buying The purchase of goods and services as they are needed, usually at prevailing market prices strategic (systematic) sourcing Purchases involving long-term contracts that usually are based on private negotiations between sellers and buyers © Farhan Mir 2016 IMS

Concepts, Characteristics, and Models of B 2 B EC Types of materials traded direct materials Materials used in the production of a product (e. g. , steel in a car or paper in a book) indirect materials Materials used to support production (e. g. , office supplies or light bulbs) MRO (maintenance, repair, and operation) Indirect materials used in activities that support production © Farhan Mir 2016 IMS

Concepts, Characteristics, and Models of B 2 B EC Virtual Service Industries in B 2 B Travel and hospitality services Real estate Financial services Online stock trading Online financing Other online services © Farhan Mir 2016 IMS
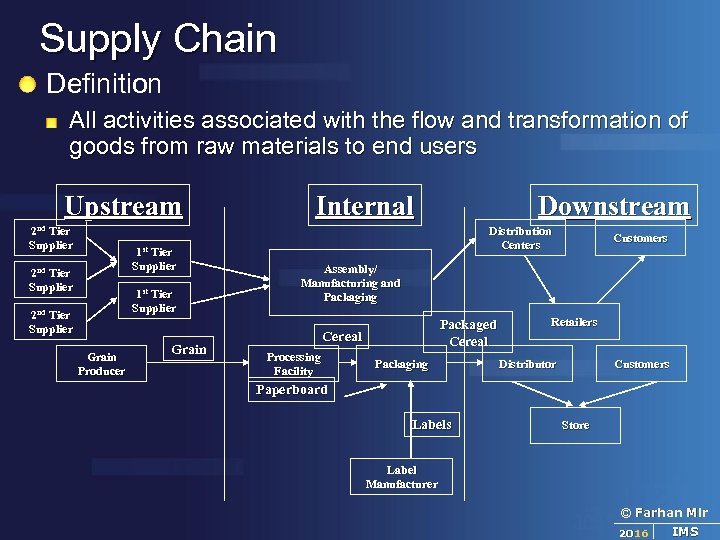
Supply Chain Definition All activities associated with the flow and transformation of goods from raw materials to end users Upstream 2 nd Tier Supplier Internal Downstream Distribution Centers 1 st 2 nd Tier Supplier 1 st Tier Supplier 2 nd Tier Supplier Grain Producer Grain Customers Assembly/ Manufacturing and Packaging Packaged Cereal Processing Facility Packaging Retailers Distributor Customers Paperboard Labels Store Label Manufacturer © Farhan Mir 2016 IMS
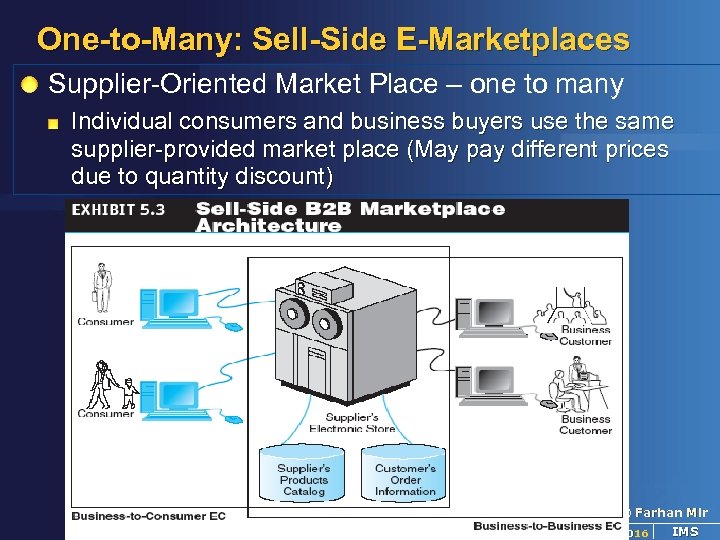
One-to-Many: Sell-Side E-Marketplaces Supplier-Oriented Market Place – one to many Individual consumers and business buyers use the same supplier-provided market place (May pay different prices due to quantity discount) © Farhan Mir 2016 IMS

Case Study of Supplier-Oriented Market Place: CISCO Connection Online Customer Service— Cisco Connection online Ordering— Internet Product Center builds virtually all its products to order Finding Order Status— gives the customers tools to find answers to order status inquiries by themselves Benefits— save the company $363 million per year from technical support, human resources, software distribution and marketing material © Farhan Mir 2016 IMS
© Farhan Mir 2016 IMS
© Farhan Mir 2016 IMS

Selling via Auctions Auctioning from the Company’s Own Site Why should a company pay a commission to an intermediary if the intermediary cannot provide the company with added value If a company decides to auction from its own site, it will have to pay for infrastructure and operate and maintain the auction site © Farhan Mir 2016 IMS

Selling via Auctions Using Intermediaries in Auctions Benefits No additional resources are required No hiring costs or opportunity costs associated with the redeployment of corporate resources Offer fast time-to-market Billing and collection efforts, are handled by the intermediary rather than the company © Farhan Mir 2016 IMS
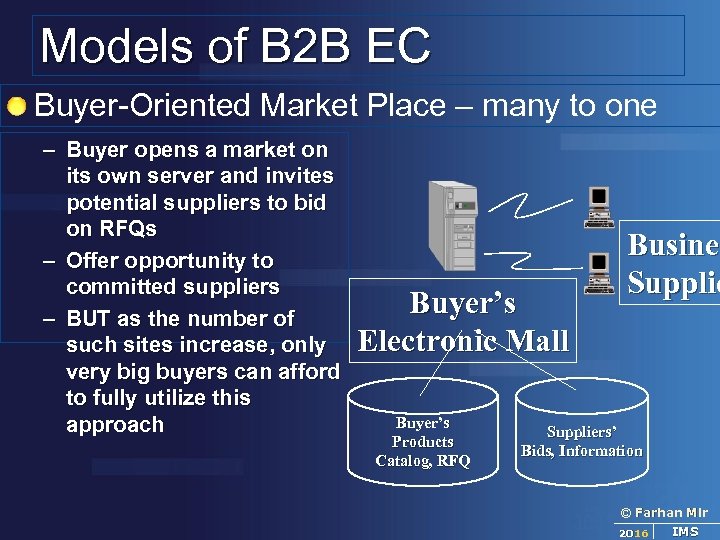
Models of B 2 B EC Buyer-Oriented Market Place – many to one – Buyer opens a market on its own server and invites potential suppliers to bid on RFQs – Offer opportunity to committed suppliers – BUT as the number of such sites increase, only very big buyers can afford to fully utilize this approach Buyer’s Electronic Mall Buyer’s Products Catalog, RFQ Busines Busine Suppliers’ Bids, Information © Farhan Mir 2016 IMS
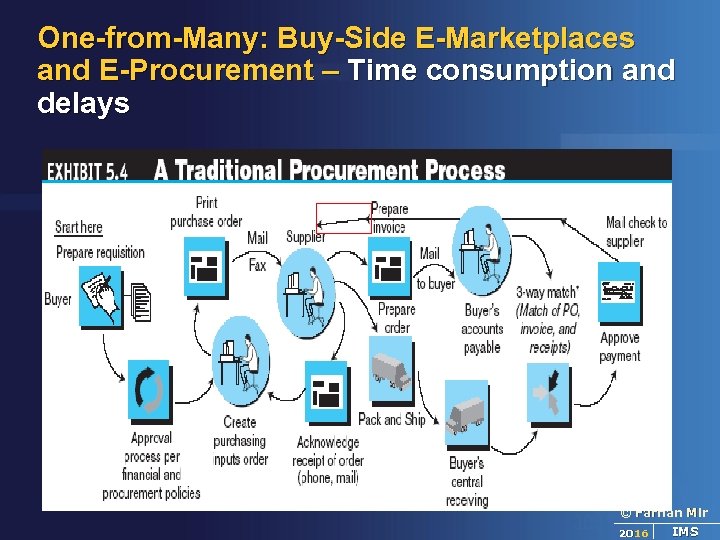
One-from-Many: Buy-Side E-Marketplaces and E-Procurement – Time consumption and delays © Farhan Mir 2016 IMS

Case Study of Customer-Oriented Market Place: GE’s TPN Post Provides a chance for sellers to participate in the bidding process of GE using the following procedure: Buyers prepare bidding project information Buyers post the bidding projects on the Internet Buyers identify potential suppliers Buyers invite suppliers to bid on projects Suppliers download the project information from the Internet Suppliers electronically submit bids for projects Buyers evaluate the suppliers’ bids and negotiate online to achieve the ‘best deal’ Buyers accept the bid that best meets their requirements © Farhan Mir 2016 IMS

One-from-Many: Buy-Side E-Marketplaces and E-Procurement Six Main Types of E-Procurement e-sourcing e-tendering e-reverse auctioning e-informing Web-based ERP (electronic resource planning) e-MRO (maintenance, repair and operating) © Farhan Mir 2016 IMS
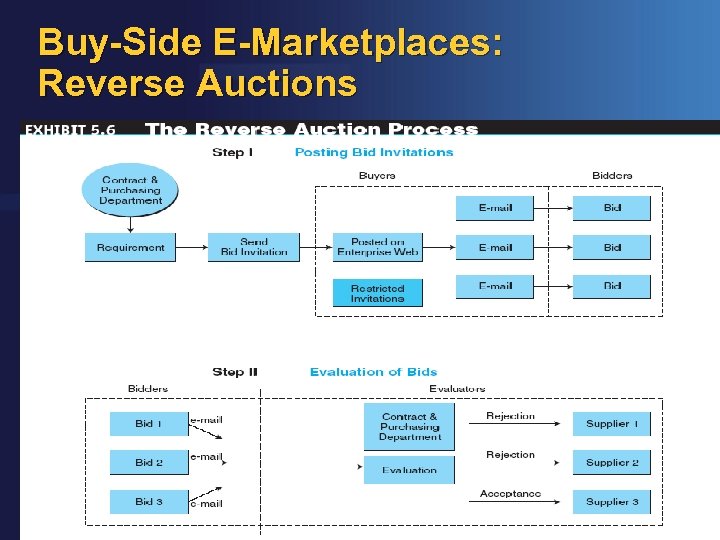
Buy-Side E-Marketplaces: Reverse Auctions © Farhan Mir 2016 IMS
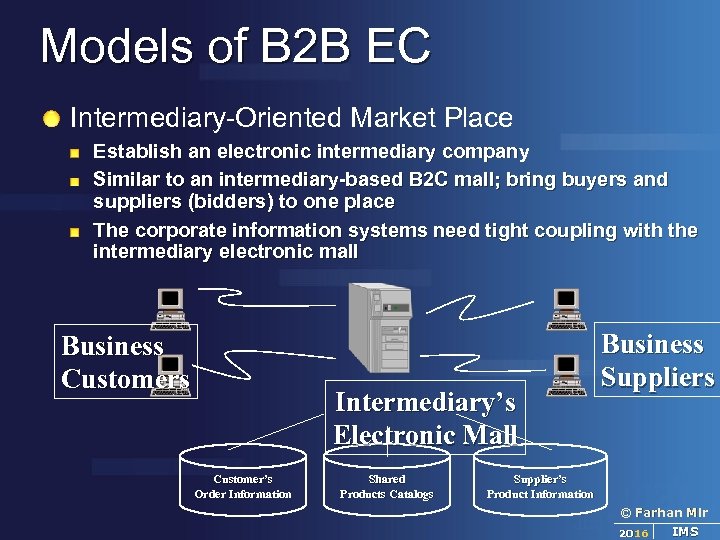
Models of B 2 B EC Intermediary-Oriented Market Place Establish an electronic intermediary company Similar to an intermediary-based B 2 C mall; bring buyers and suppliers (bidders) to one place The corporate information systems need tight coupling with the intermediary electronic mall Business Customers Intermediary’s Electronic Mall Customer’s Order Information Shared Products Catalogs Business Supplier’s Product Information © Farhan Mir 2016 IMS

Case Study of Intermediary-Oriented Market Place: Boeing’s PART Case Acts as an intermediary between the airlines and parts’ suppliers Provides a single point of online access through which airlines and parts providers can access the data needed Goal: provide its customers with one-stop shopping with online parts and maintenance information and ordering capability © Farhan Mir 2016 IMS
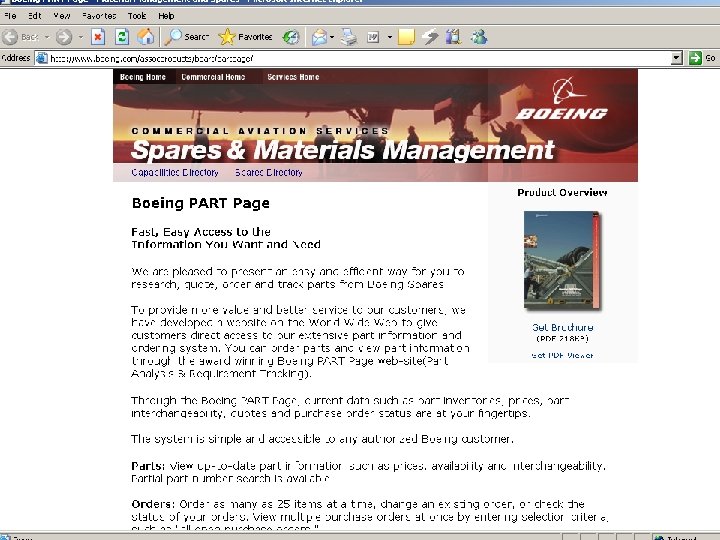
© Farhan Mir 2016 IMS

Case Study of Intermediary-Oriented Market Place: Boeing’s PART (cont. ) Boeing On Line Data (BOLD) Incorporating not only engineering drawings but manuals, catalogs and other technical information that used to be available only in paper or in microfiche format Portable Maintenance Aid (PMA) Solves maintenance problems © Farhan Mir 2016 IMS

Case Study of Intermediary-Oriented Market Place: Boeing’s PART (cont. ) Benefits to Boeing’s Customers Increased productivity spending less time searching for information; frees up engineers and maintenance technicians to focus on more productive activities Reduced costs with information available online at the airports’ gates, through PMA, rather than back in the office, delays at the gate due to missing information are reduced Increased revenue opportunity through BOLD and PMA, a European airline estimates it will save 1 -2 days/year of down time for each aircraft © Farhan Mir 2016 IMS

B 2 B: the many-many exchanges Many-to-many: exchanges (trading communities or trading exchanges) Many-to-many e-marketplaces, usually owned and run by a third party or a consortium, in which many buyers and many sellers meet electronically to trade with each other public e-marketplaces Third-party exchanges that are open to all interested parties (sellers and buyers © Farhan Mir 2016 IMS

Procurement Management Using B 2 B EC Platform Purchasing is now a strategic function, to increase profit margins By automating and streamlining the laborious routine of the purchasing function, purchasing professionals can focus on more strategic purchases, achieving the following goals: Reducing purchasing cycle time and cost Enhancing budgetary control Eliminating administrative errors Lowering prices through product standardization and consolidation of purchases Better information management; e. g. supplier’s information and pricing information Improving the payment process © Farhan Mir 2016 IMS
Infrastructure, Integration, and Software Agents In B 2 B EC Infrastructure for B 2 B electronic data interchange (EDI) The electronic transfer of specially formatted standard business documents, such as bills, orders, and confirmations, sent between business partners value-added networks (VANs) Private, third-party managed networks that add communications services and security to existing common carriers; used to implement traditional EDI systems Internet-based (Web) EDI that runs on the Internet and is widely accessible to most companies, including SMEs © Farhan Mir 2016 IMS

B 2 B in the Web 2. 0 Environment Opportunities Brand awareness, generate traffic, create social communities Use of Web 2 tools in B 2 B Blogs, Wikis and RSS Feeds Social Networks in the B 2 B Marketplace Examples of Other activities American Express-sponsored Business Social network Corporate Profiles on social networks © Farhan Mir 2016 IMS

Managerial Issues 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Can we justify the cost of B 2 B? Which vendor(s) should we select? Which B 2 B model(s) should we use? Should we restructure our procurement system? What are the ethical issues in B 2 B? Will there be massive disintermediation? How can trust and loyalty be cultivated in B 2 B? How is mobile B 2 B done? © Farhan Mir 2016 IMS
91d652961b4e69703e845209e8d6ae8d.ppt