 ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION Laws of Electromagnetic Induction
ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION Laws of Electromagnetic Induction
 Electromagnetic Induction Faraday’s Discovery Faraday’s Law of Electromagnetic Induction Direction of EMF. Lenz’s Law Law of Electromagnetic Induction. Flux Linkage Electromagnetic Induction and Law of Conservation of Energy EMF Induced in a Moving Rod Production of Electric Field from Variable Magnetic Field
Electromagnetic Induction Faraday’s Discovery Faraday’s Law of Electromagnetic Induction Direction of EMF. Lenz’s Law Law of Electromagnetic Induction. Flux Linkage Electromagnetic Induction and Law of Conservation of Energy EMF Induced in a Moving Rod Production of Electric Field from Variable Magnetic Field
 Electromagnetic Induction (cont.) Electromotive Force in a Rotating Coil Self-Induction Energy Stored Inside a Coil. Energy Density of Magnetic Field
Electromagnetic Induction (cont.) Electromotive Force in a Rotating Coil Self-Induction Energy Stored Inside a Coil. Energy Density of Magnetic Field
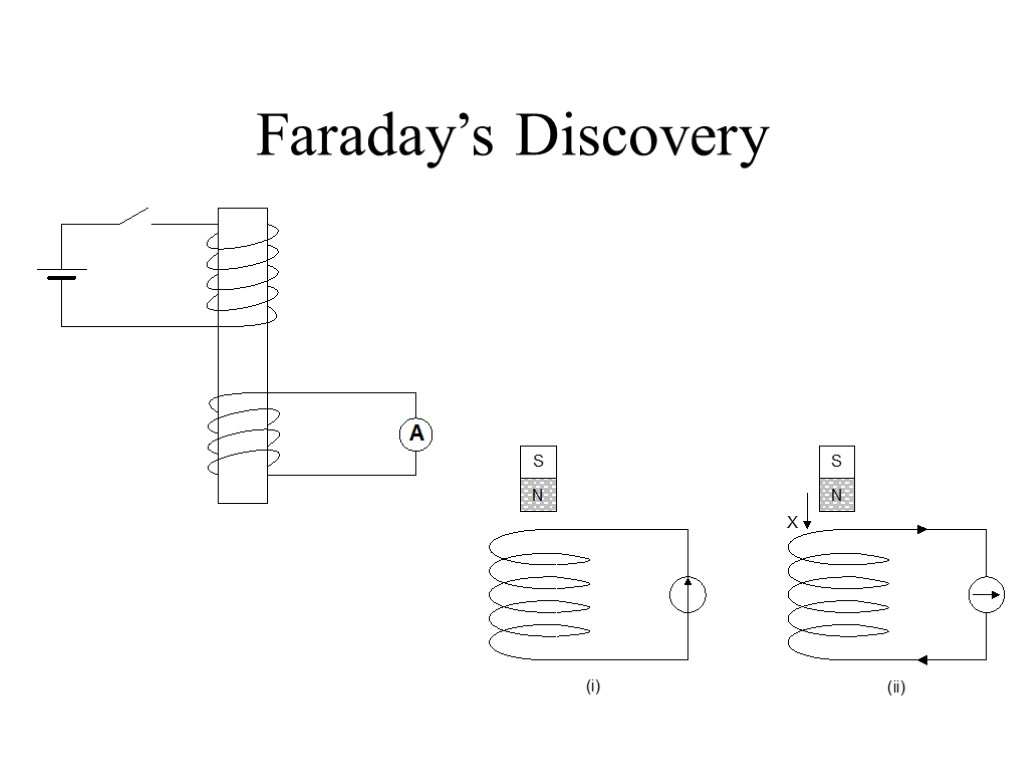 Faraday’s Discovery
Faraday’s Discovery
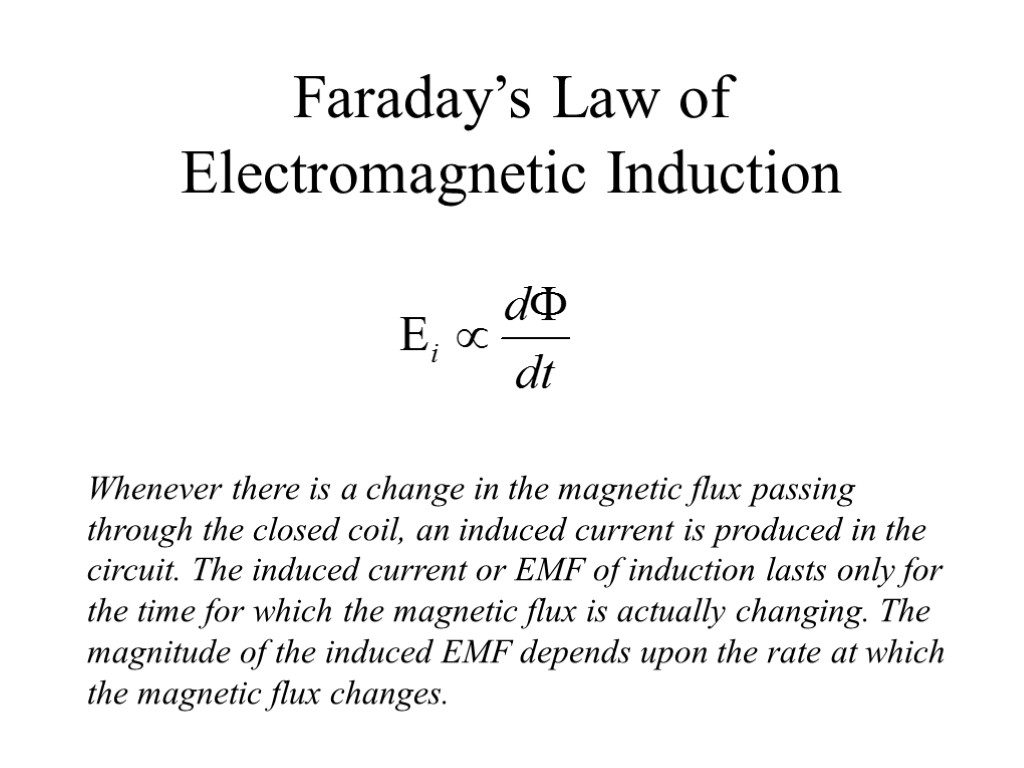 Faraday’s Law of Electromagnetic Induction Whenever there is a change in the magnetic flux passing through the closed coil, an induced current is produced in the circuit. The induced current or EMF of induction lasts only for the time for which the magnetic flux is actually changing. The magnitude of the induced EMF depends upon the rate at which the magnetic flux changes.
Faraday’s Law of Electromagnetic Induction Whenever there is a change in the magnetic flux passing through the closed coil, an induced current is produced in the circuit. The induced current or EMF of induction lasts only for the time for which the magnetic flux is actually changing. The magnitude of the induced EMF depends upon the rate at which the magnetic flux changes.
 Direction of EMF. Lenz’s Law The induced current flows always in such a direction as to oppose the change which is giving rise to it.
Direction of EMF. Lenz’s Law The induced current flows always in such a direction as to oppose the change which is giving rise to it.
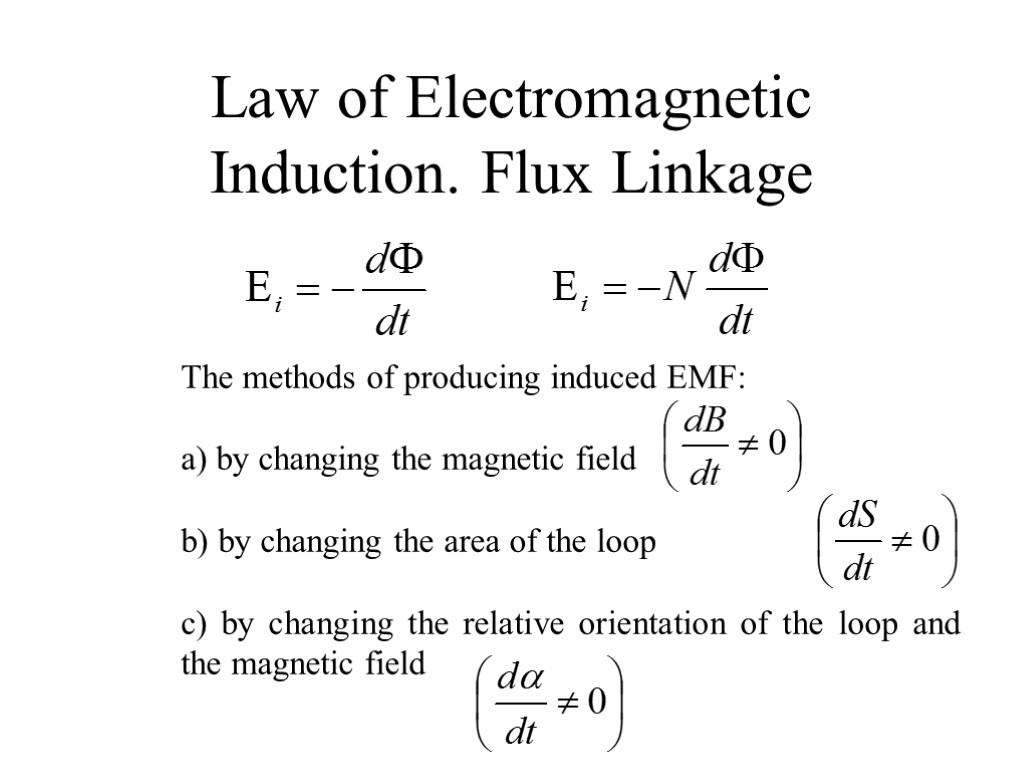 Law of Electromagnetic Induction. Flux Linkage The methods of producing induced EMF: a) by changing the magnetic field b) by changing the area of the loop c) by changing the relative orientation of the loop and the magnetic field
Law of Electromagnetic Induction. Flux Linkage The methods of producing induced EMF: a) by changing the magnetic field b) by changing the area of the loop c) by changing the relative orientation of the loop and the magnetic field
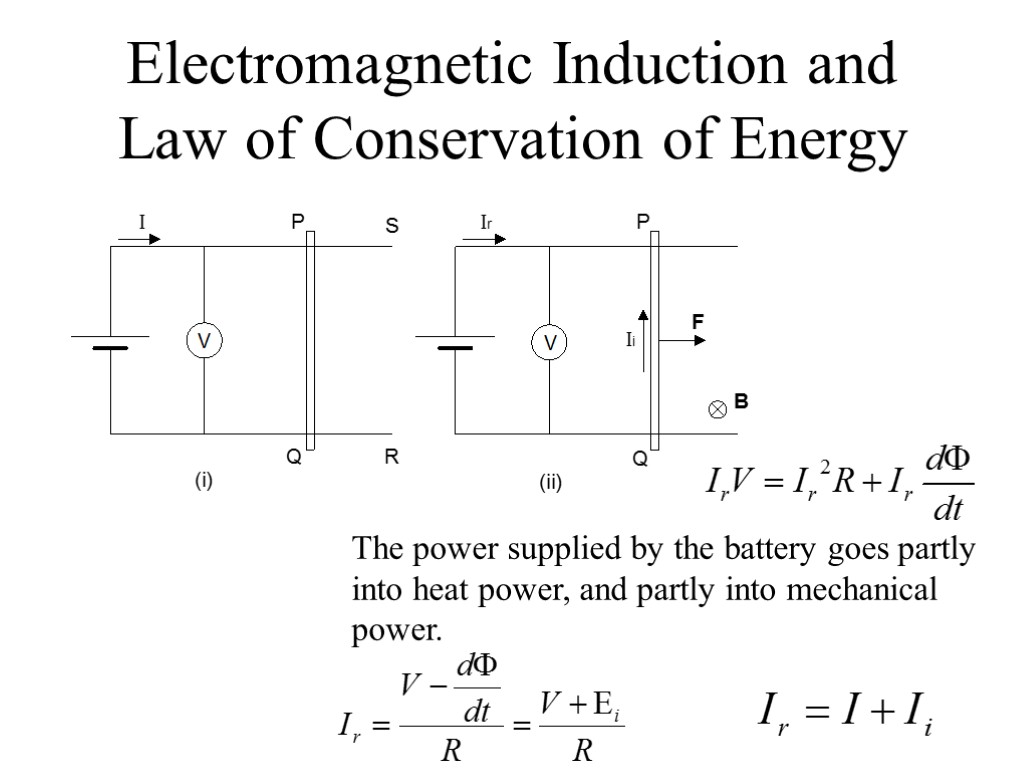 Electromagnetic Induction and Law of Conservation of Energy The power supplied by the battery goes partly into heat power, and partly into mechanical power.
Electromagnetic Induction and Law of Conservation of Energy The power supplied by the battery goes partly into heat power, and partly into mechanical power.
 Fleming’s right-hand law Fleming’s right-hand law: stretch the thumb, the forefinger and the middle finger of the right hand mutually perpendicular to one another. If the thumb represents the direction of the motion of the conductor, the forefinger the direction of the magnetic field, then the middle finger points in the direction in which the current is induced in the circuit.
Fleming’s right-hand law Fleming’s right-hand law: stretch the thumb, the forefinger and the middle finger of the right hand mutually perpendicular to one another. If the thumb represents the direction of the motion of the conductor, the forefinger the direction of the magnetic field, then the middle finger points in the direction in which the current is induced in the circuit.
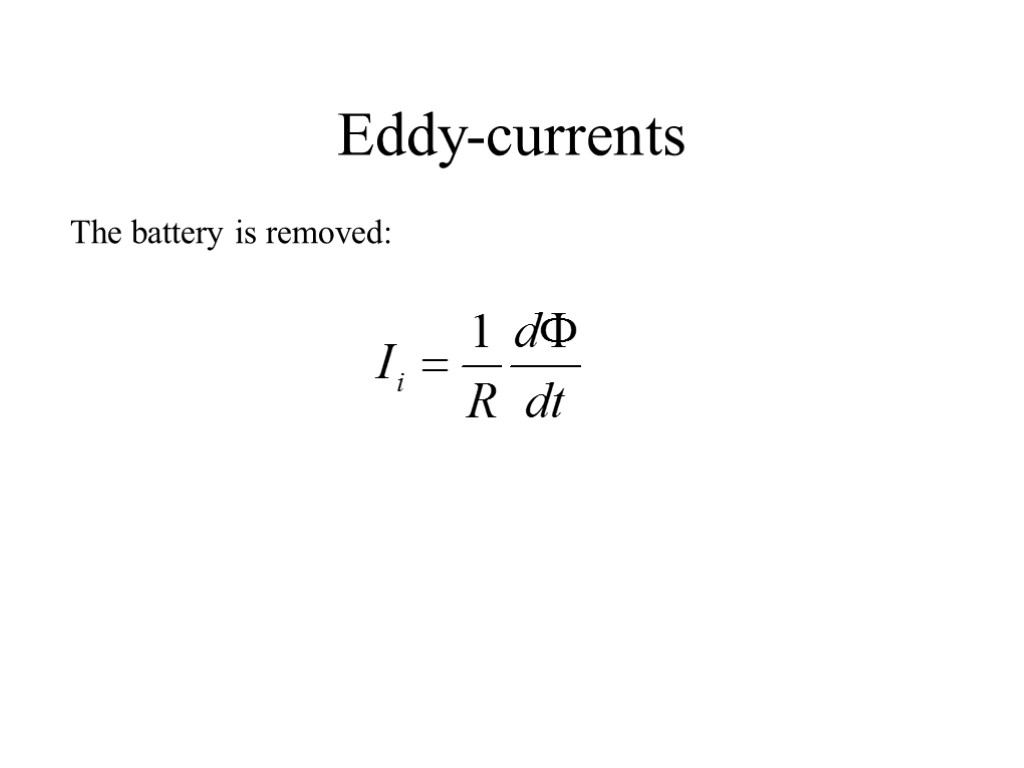 Eddy-currents The battery is removed:
Eddy-currents The battery is removed:
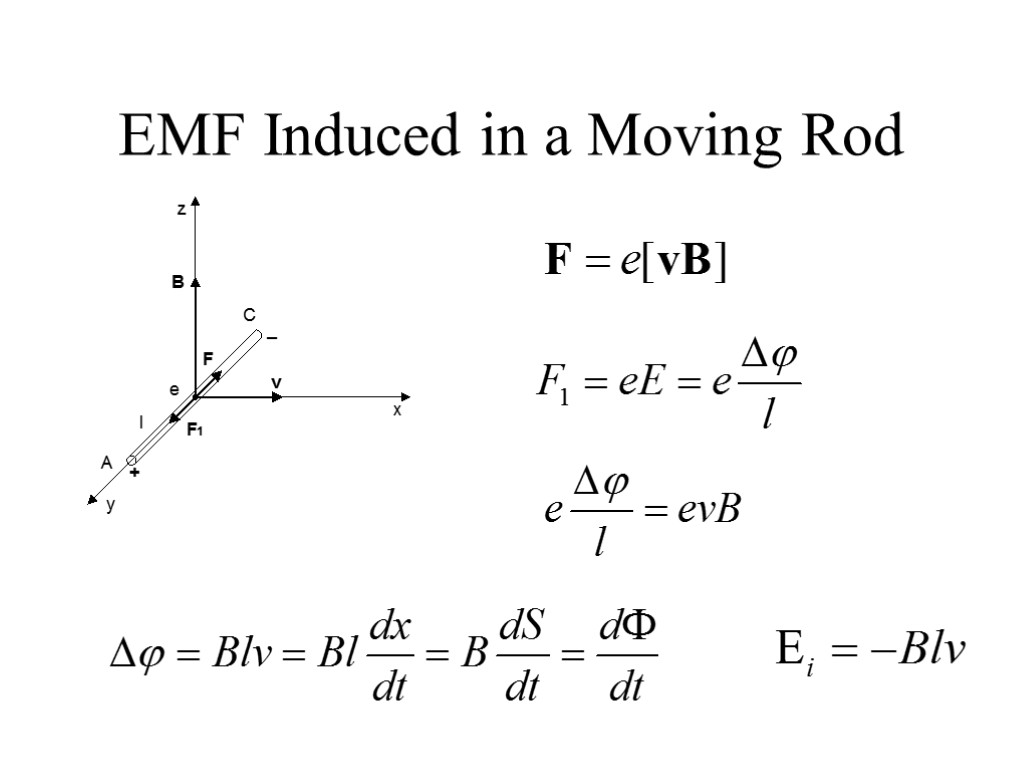 EMF Induced in a Moving Rod
EMF Induced in a Moving Rod
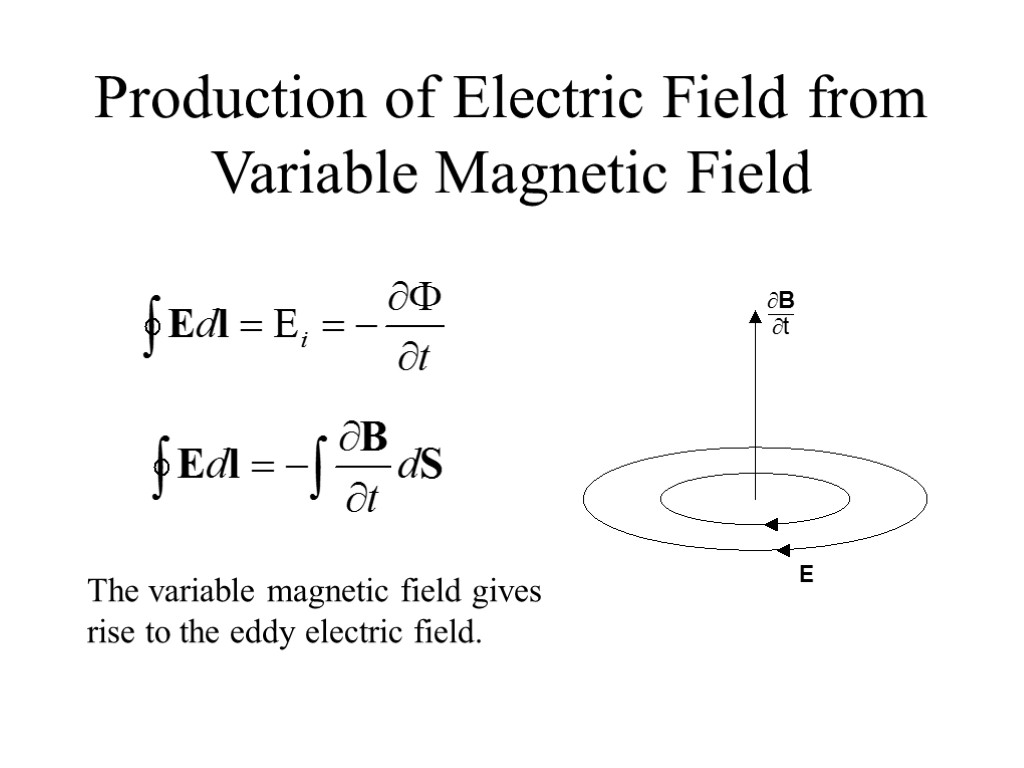 Production of Electric Field from Variable Magnetic Field The variable magnetic field gives rise to the eddy electric field.
Production of Electric Field from Variable Magnetic Field The variable magnetic field gives rise to the eddy electric field.
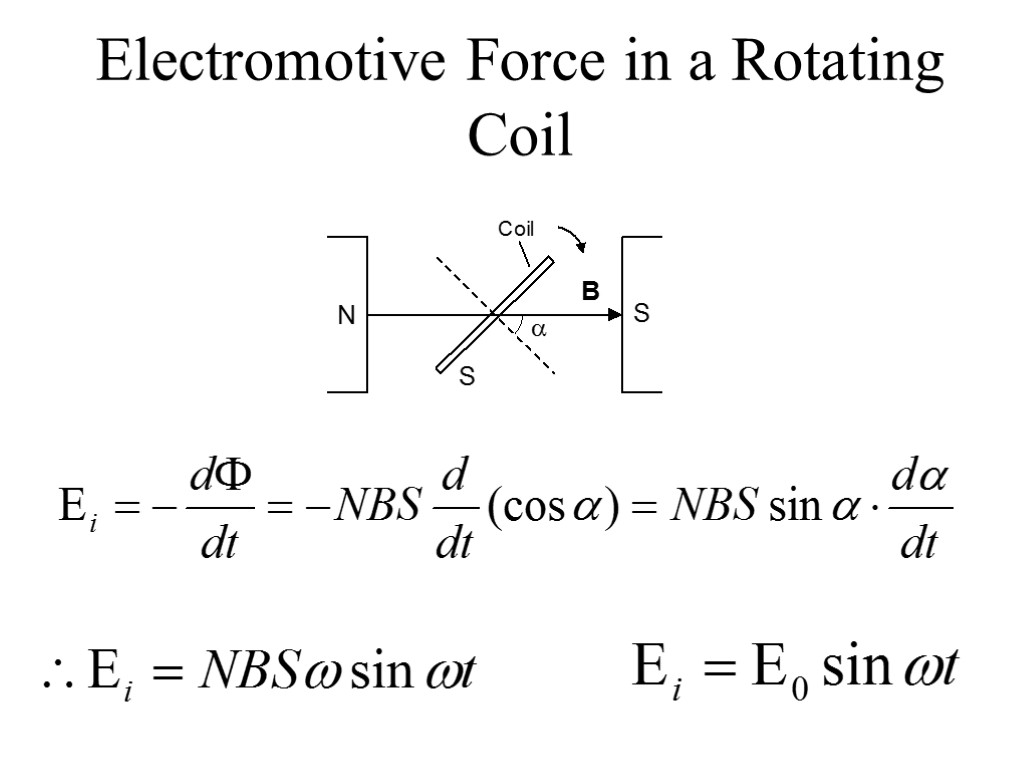 Electromotive Force in a Rotating Coil
Electromotive Force in a Rotating Coil
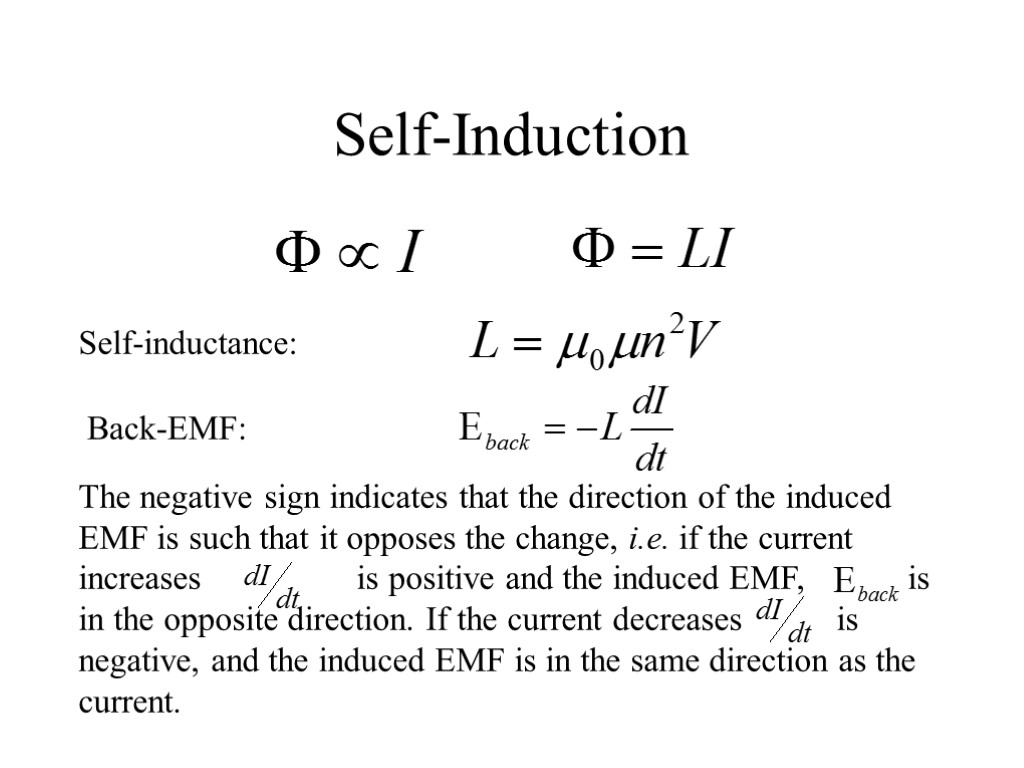 Self-Induction Self-inductance: Back-EMF: The negative sign indicates that the direction of the induced EMF is such that it opposes the change, i.e. if the current increases is positive and the induced EMF, is in the opposite direction. If the current decreases is negative, and the induced EMF is in the same direction as the current.
Self-Induction Self-inductance: Back-EMF: The negative sign indicates that the direction of the induced EMF is such that it opposes the change, i.e. if the current increases is positive and the induced EMF, is in the opposite direction. If the current decreases is negative, and the induced EMF is in the same direction as the current.
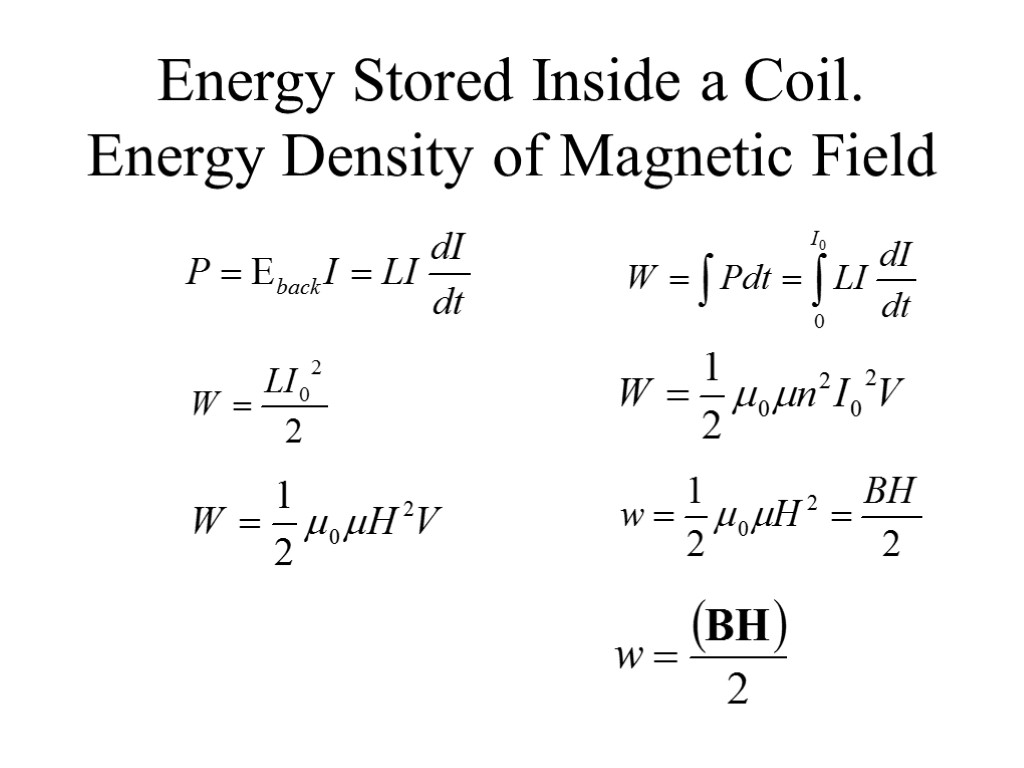 Energy Stored Inside a Coil. Energy Density of Magnetic Field
Energy Stored Inside a Coil. Energy Density of Magnetic Field































