Electrochemistry 1.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 23

Electrochemistry Oxidation-reduction equilibrium in water solutions.
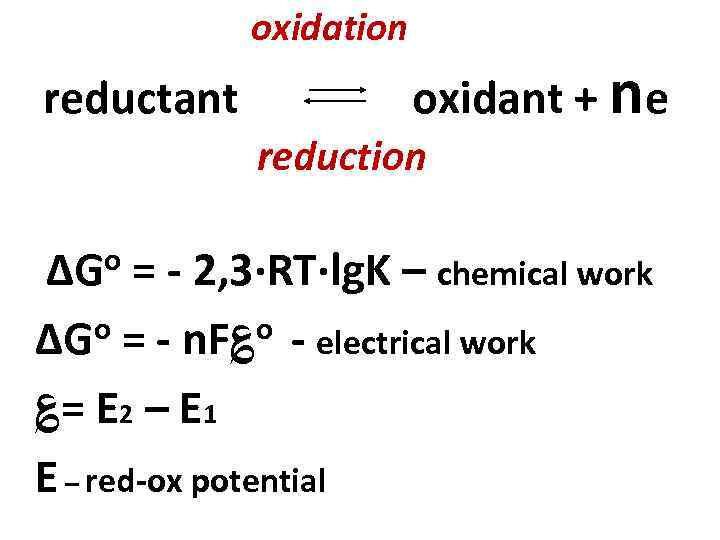
oxidation reductant oxidant + ne reduction o ΔG = - 2, 3·RT·lg. K – chemical work o = - n. F؏o - electrical work ΔG ؏= E 2 – E 1 E – red-ox potential
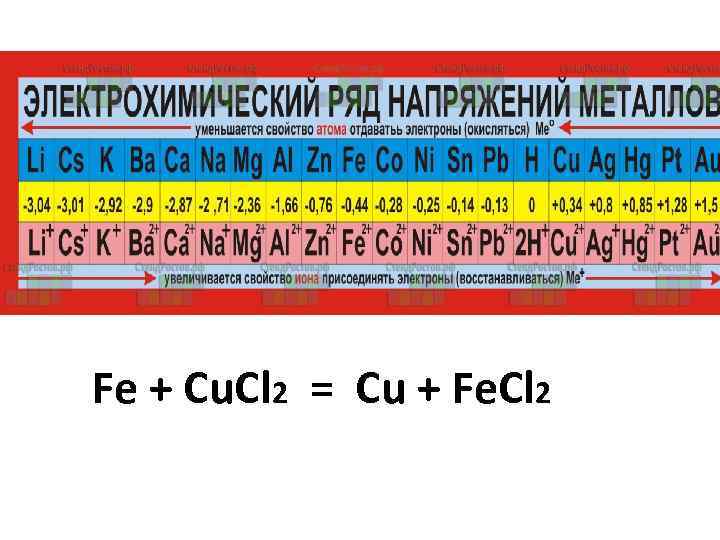
Fe + Cu. Cl 2 = Cu + Fe. Cl 2
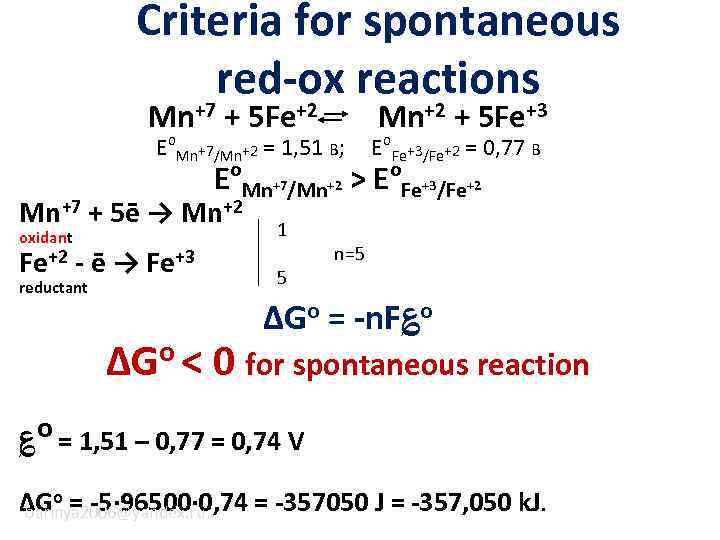
Criteria for spontaneous red-ox reactions Mn+7 + 5 Fe+2 Eo. Mn+7/Mn+2 = 1, 51 В; E o Mn+7/Mn+2 Mn+7 + 5ē → Mn+2 oxidant 1 reductant 5 Fe+2 - ē → Fe+3 Mn+2 + 5 Fe+3 Eo. Fe+3/Fe+2 = 0, 77 В >E o Fe+3/Fe+2 n=5 ΔGo = -n. F؏o ΔGo < 0 for spontaneous reaction ؏o = 1, 51 – 0, 77 = 0, 74 V ΔGo = -5· 96500· 0, 74 = -357050 J = -357, 050 k. J. barinya 2006@yandex. ru
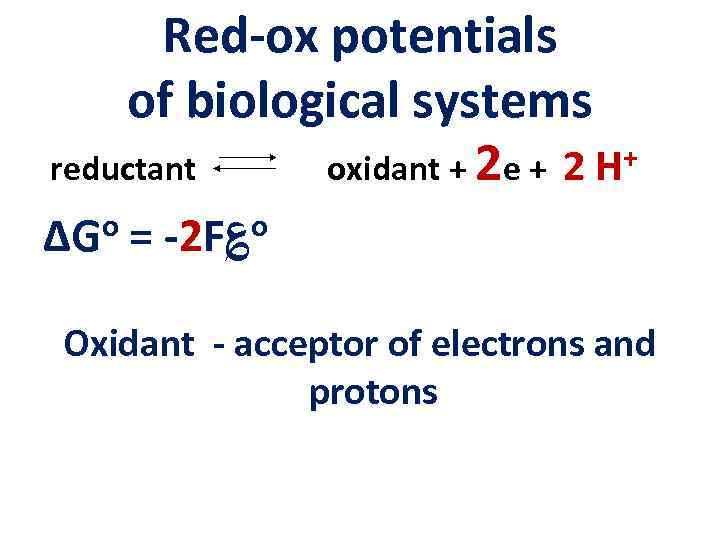
Red-ox potentials of biological systems + reductant oxidant + 2 e + 2 H ΔGo = -2 F؏o Oxidant - acceptor of electrons and protons
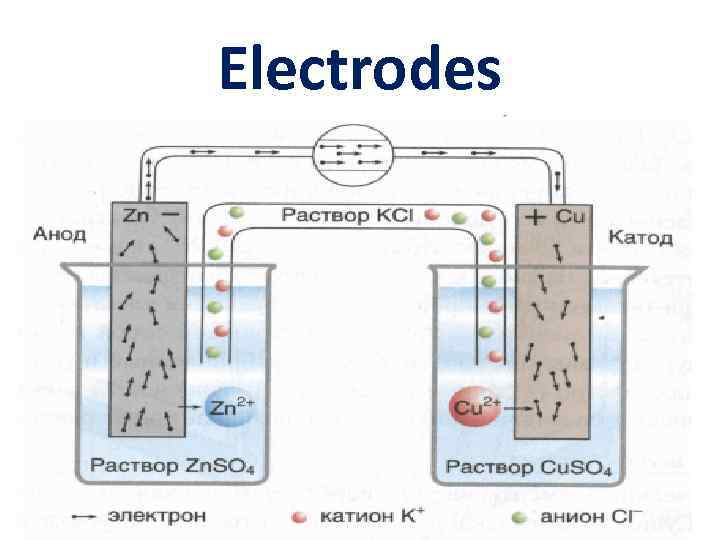
Electrodes
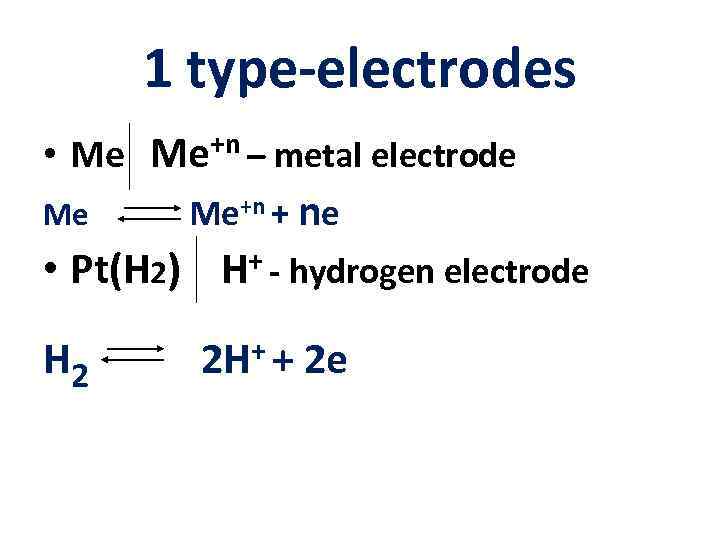
1 type-electrodes • Me Me+n – metal electrode Me Me+n + ne • Pt(H 2) H+ - hydrogen electrode H 2 ++ 2 H 2 e
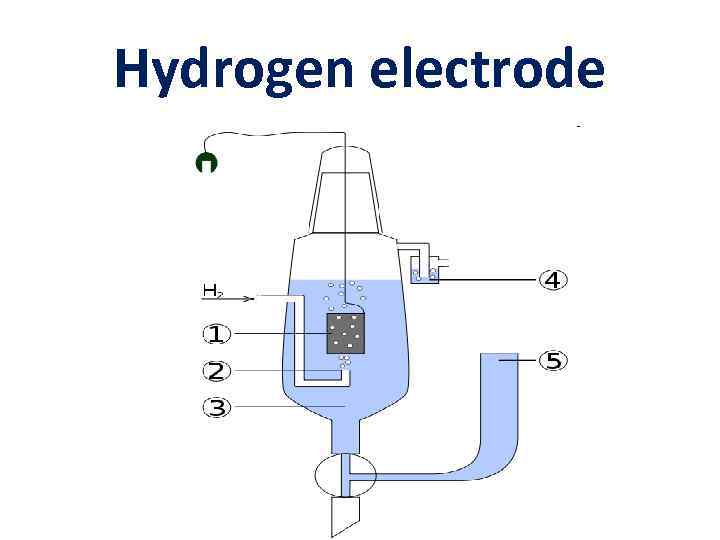
Hydrogen electrode
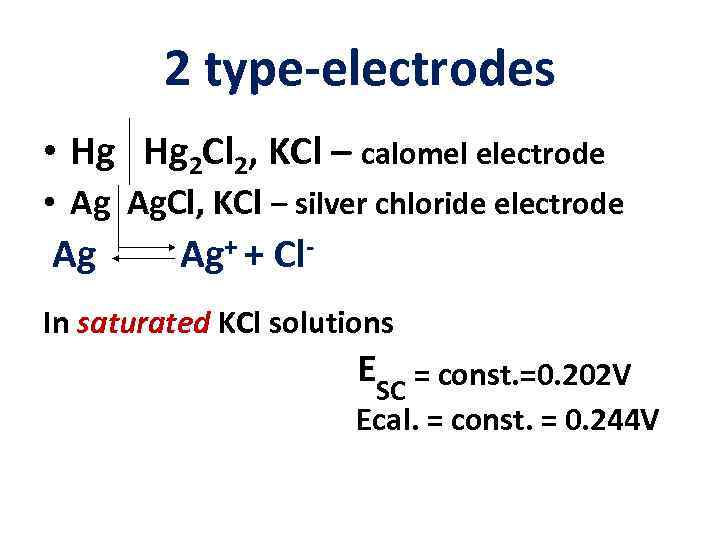
2 type-electrodes • Hg Hg 2 Cl 2, KCl – calomel electrode • Ag Ag. Cl, KCl – silver chloride electrode Ag Ag+ + Cl- In saturated KCl solutions ESC = const. =0. 202 V Ecal. = const. = 0. 244 V
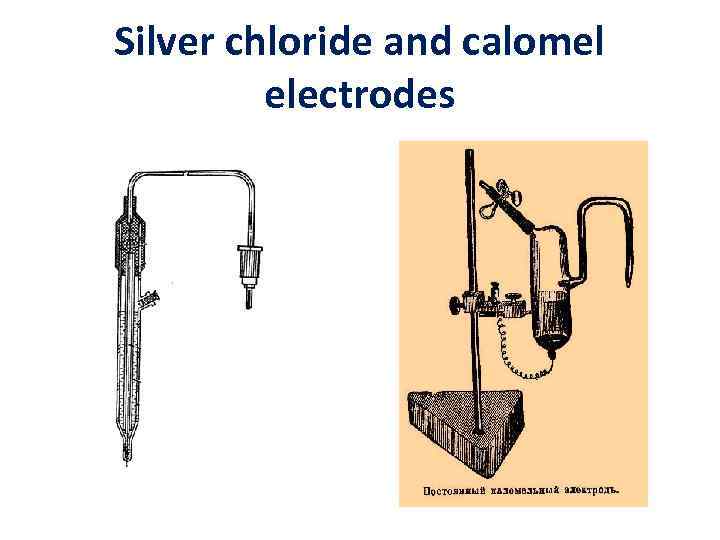
Silver chloride and calomel electrodes
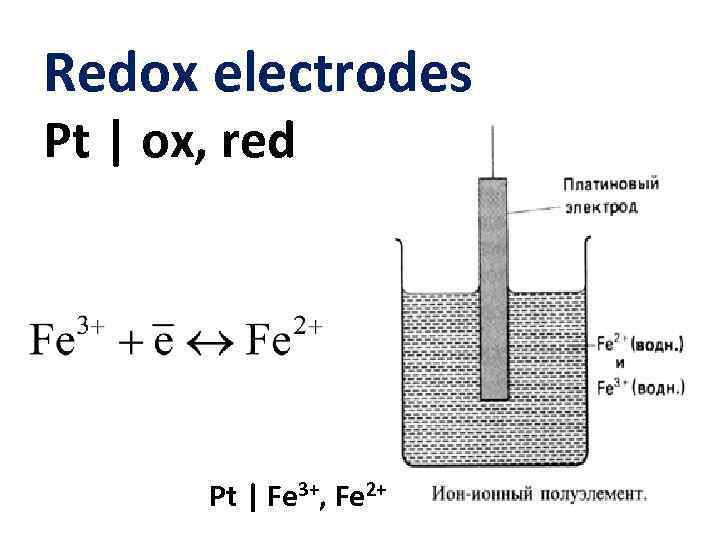
Redox electrodes Pt | ox, red Pt | Fe 3+, Fe 2+
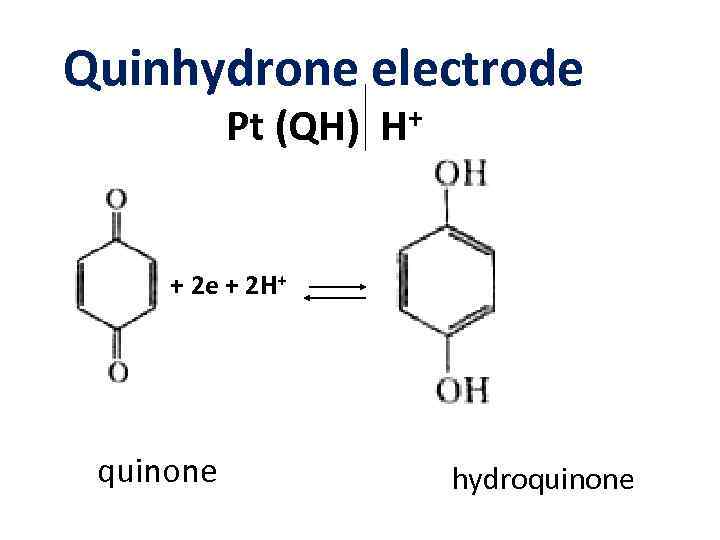
Quinhydrone electrode Pt (QH) + H + 2 e + 2 H+ quinone hydroquinone
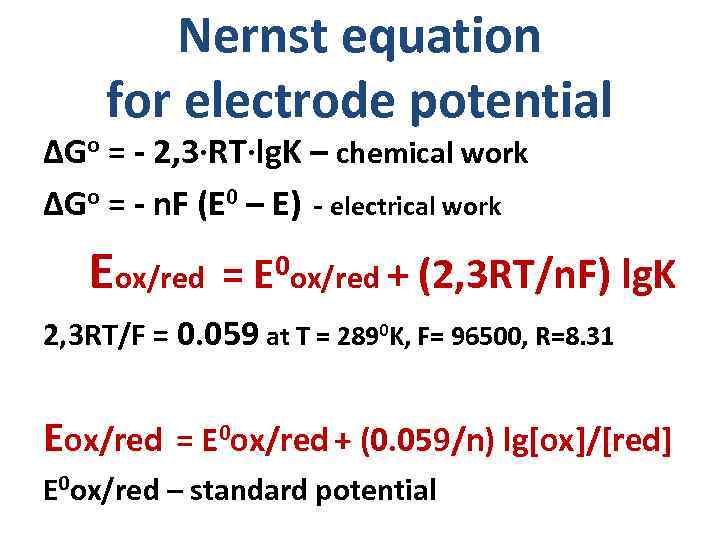
Nernst equation for electrode potential ΔGo = - 2, 3·RT·lg. K – chemical work ΔGo = - n. F (E 0 – E) - electrical work Eox/red = 0 ox/red + E (2, 3 RT/n. F) lg. K 2, 3 RT/F = 0. 059 at T = 2890 K, F= 96500, R=8. 31 Eox/red = E 0 ox/red + (0. 059/n) lg[ox]/[red] E 0 ox/red – standard potential

Hydrogen electrode Pt (H 2) | H+ ½ Н 2 Н+ + ē Eox/red = E 0 ox/red + (0. 059/n) lg. K EН 2 = E 0 Н 2 + (0. 059/1) lg[H+] E 0 Н 2 = 0 Standard potential of hydrogen electrode EН 2 = - 0. 059 p. H
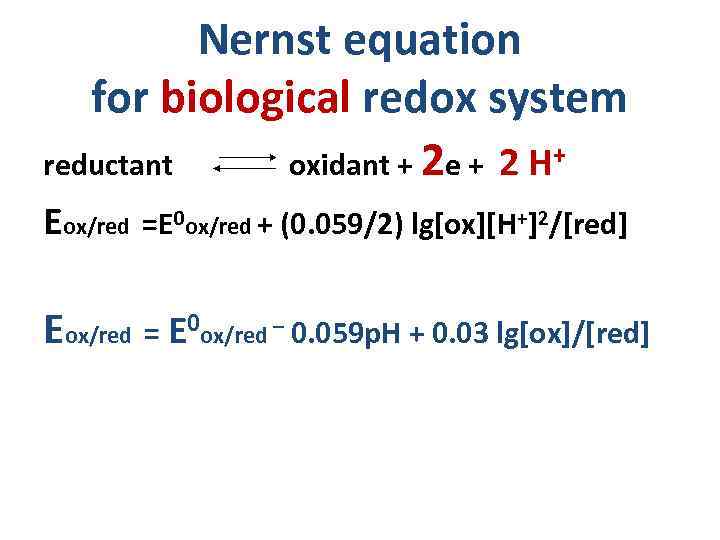
Nernst equation for biological redox system reductant oxidant + 2 e + 2 H+ Eox/red =E 0 ox/red + (0. 059/2) lg[ox][H+]2/[red] Eox/red = E 0 ox/red – 0. 059 p. H + 0. 03 lg[ox]/[red]
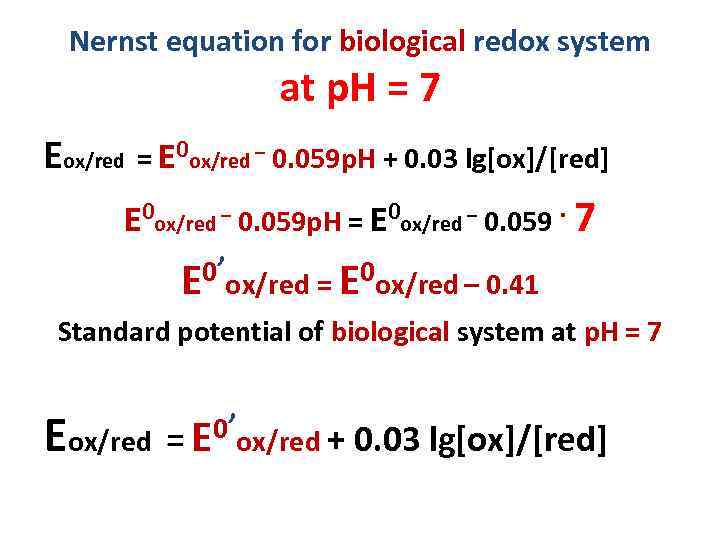
Nernst equation for biological redox system at p. H = 7 Eox/red = E 0 ox/red – 0. 059 p. H + 0. 03 lg[ox]/[red] E 0 ox/red – 0. 059 p. H = E 0 ox/red – 0. 059. 7 0’ox/red = E 0 ox/red – 0. 41 E Standard potential of biological system at p. H = 7 E 0’ox/red + 0. 03 lg[ox]/[red] ox/red = E

Quinhydrone electrode Pt (QH) H+ Eox/red = E 0 ox/red – 0. 059 p. H + 0. 03 lg[ox]/[red] EQH = E 0 – 0. 059 p. H + 0. 03 lg[quinone]/[hydroquinone] QH Quinhydrone = 1 M quinone + 1 Mhydroquinone E 0 – 0. 059 p. H QH = E QH
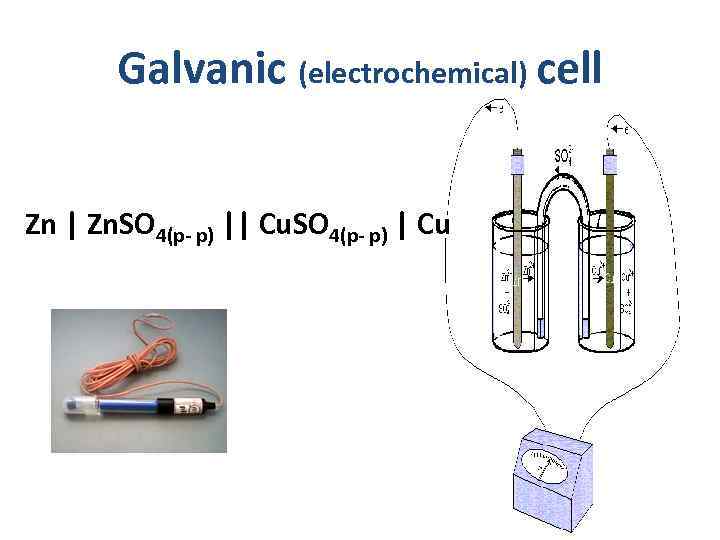
Galvanic (electrochemical) cell - Zn | Zn. SO 4(р- р) || Cu. SO 4(р- р) | Cu

electromotive force (EMF) ؏= E 2 – E 1 ؏о = Еo. Cu – Еo. Zn = 0, 34 – ( - 0, 76) = 1, 1 B Cu. SO 4 + Zn → Zn. SO 4 + Cu reductant Zno - 2ē → Zn 2+ oxidation oxidant Cu 2+ + 2ē → Cuo reduction barinya 2006@yandex. ru
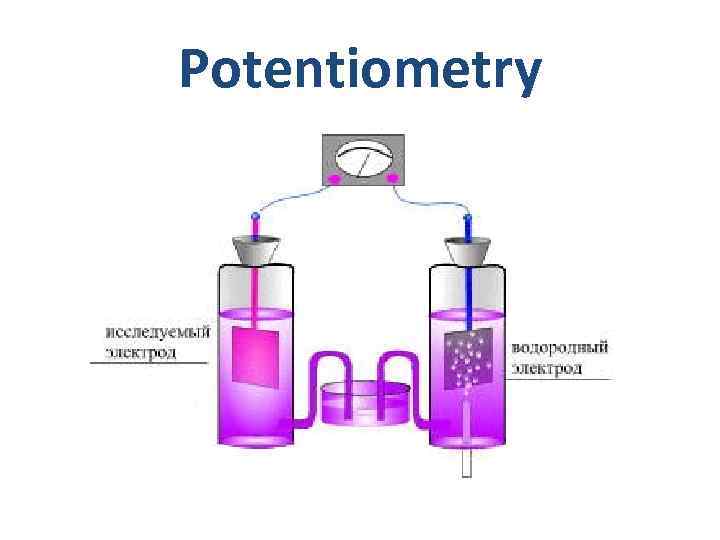
Potentiometry
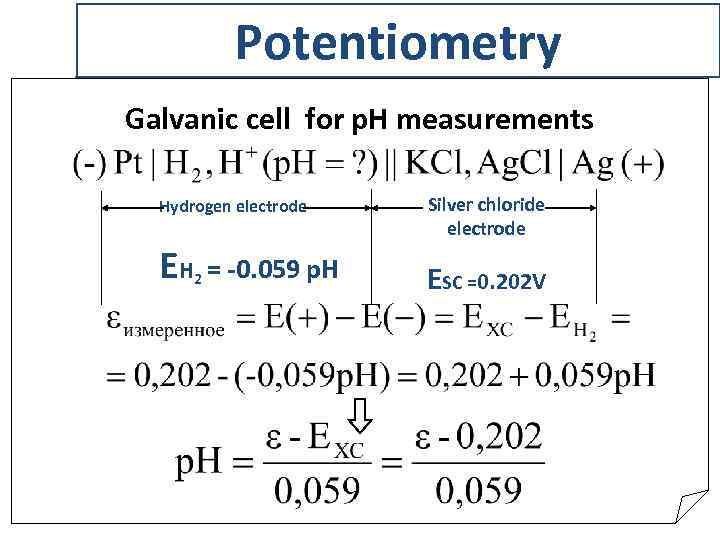
Potentiometry Galvanic cell for p. H measurements Hydrogen electrode EH 2 = -0. 059 p. H Silver chloride electrode ESC =0. 202 V
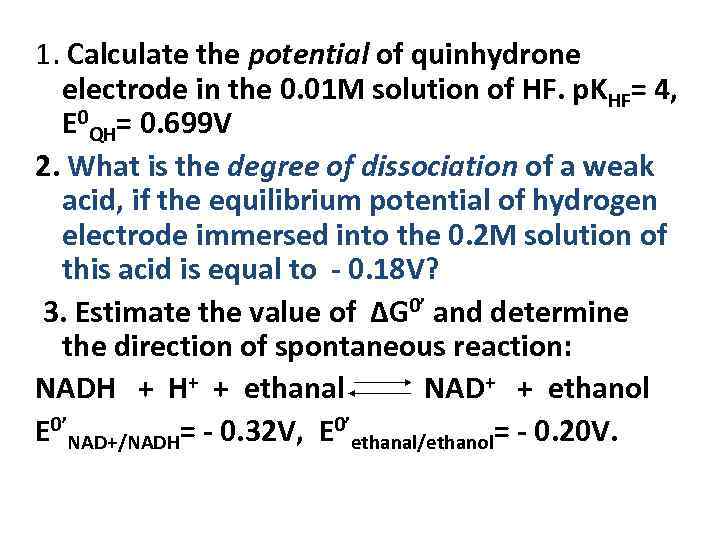
1. Calculate the potential of quinhydronе electrode in the 0. 01 M solution of HF. p. KHF= 4, E 0 QH= 0. 699 V 2. What is the degree of dissociation of a weak acid, if the equilibrium potential of hydrogen electrode immersed into the 0. 2 M solution of this acid is equal to - 0. 18 V? 3. Estimate the value of ΔG 0’ and determine the direction of spontaneous reaction: NADH + H+ + ethanal NAD+ + ethanol E 0’NAD+/NADH= - 0. 32 V, E 0’ethanal/ethanol= - 0. 20 V.

4. Estimate the value of the equilibrium potential of platinum electrode in the solution of two salts: Fe. Cl 2 (0. 25 M) and Fe. Cl 3 (0. 25 M), E 0 Fe 3+/Fe 2+= 0. 77 V, t= 250 C. 5. Determine the ratio of concentrations [fumarate]/[succinate] if the potential of platinum electrode in this solution is equal to 0. 04 V, t= 250 C, E 0’fum/suc= - 0. 031 V, p. H = 7. 6. Diagram the cell consisting of the silver chloride electrode in saturated KCl solution and hydrogen electrode in the 0. 01 M solution of acetic acid. What is the electromotive force (EMF) of this cell? p. KCH COOH = 4. 75, ESC=0. 202 V
Electrochemistry 1.pptx