dd36b97169aeb7f35e5817e0324c1051.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 46
 Electrochemistry Lesson 8 Electrochemical Cells
Electrochemistry Lesson 8 Electrochemical Cells
 Electrochemical cells are Batteries
Electrochemical cells are Batteries
 Alkaline Batteries KOH
Alkaline Batteries KOH
 Car Batteries Pb-Acid H 2 SO 4
Car Batteries Pb-Acid H 2 SO 4
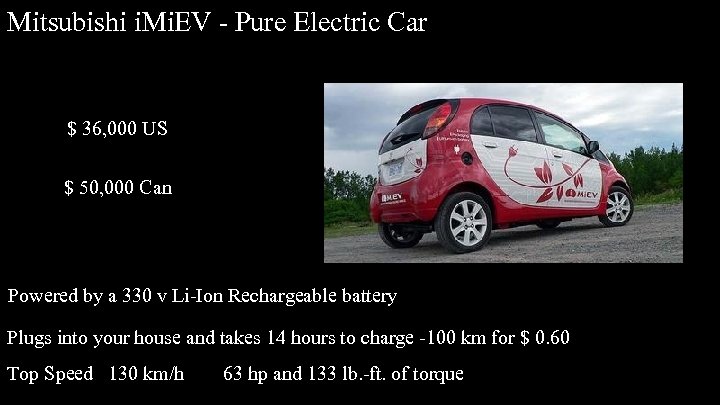 Mitsubishi i. Mi. EV - Pure Electric Car $ 36, 000 US $ 50, 000 Can Powered by a 330 v Li-Ion Rechargeable battery Plugs into your house and takes 14 hours to charge -100 km for $ 0. 60 Top Speed 130 km/h 63 hp and 133 lb. -ft. of torque
Mitsubishi i. Mi. EV - Pure Electric Car $ 36, 000 US $ 50, 000 Can Powered by a 330 v Li-Ion Rechargeable battery Plugs into your house and takes 14 hours to charge -100 km for $ 0. 60 Top Speed 130 km/h 63 hp and 133 lb. -ft. of torque
 Cell Phone batteries Lithium Ion Rechargeable battery
Cell Phone batteries Lithium Ion Rechargeable battery
 Lithium Coin Cell
Lithium Coin Cell
 Space Ship Batteries Powered by Radioisotopes
Space Ship Batteries Powered by Radioisotopes
 Ni-Metal Hydride
Ni-Metal Hydride
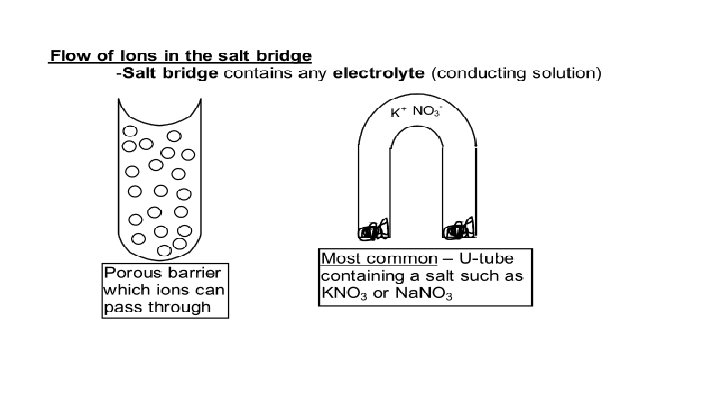
 Notes on Electrochemical Cells An electrochemical cell – a system of electrodes, electrolytes, and salt bridge that allow oxidation and reduction reactions to occur and electrons to flow through an external circuit. 1. 2. 3. Spontaneous redox reaction Produces electricity from chemicals Is commonly called a battery The salt bridge allows ions to migrate from one half-cell to the other without allowing the solutions to mix.
Notes on Electrochemical Cells An electrochemical cell – a system of electrodes, electrolytes, and salt bridge that allow oxidation and reduction reactions to occur and electrons to flow through an external circuit. 1. 2. 3. Spontaneous redox reaction Produces electricity from chemicals Is commonly called a battery The salt bridge allows ions to migrate from one half-cell to the other without allowing the solutions to mix.
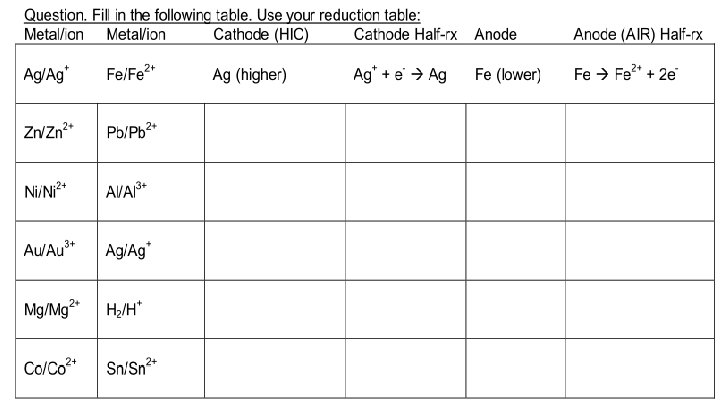
 Analyzing Electrochemical Cells The reaction that is higher on the reduction chart is the reduction and the lower is oxidation and is written in reverse.
Analyzing Electrochemical Cells The reaction that is higher on the reduction chart is the reduction and the lower is oxidation and is written in reverse.
 For any cell Oxidation always occurs at the anode and reduction at the cathode Electrons flow through the wire and go from anode to cathode Anions (- ions) migrate to the anode and cations (+ions) migrate towards the cathode usually through the salt bridge
For any cell Oxidation always occurs at the anode and reduction at the cathode Electrons flow through the wire and go from anode to cathode Anions (- ions) migrate to the anode and cations (+ions) migrate towards the cathode usually through the salt bridge
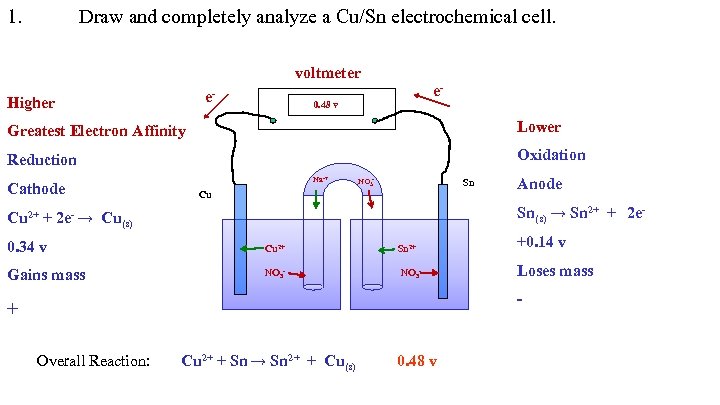 1. Draw and completely analyze a Cu/Sn electrochemical cell. voltmeter e- Higher e- 0. 48 v Greatest Electron Affinity Lower Reduction Oxidation Cathode Na-+ NO 3 - Sn Cu Anode Sn(s) → Sn 2+ + 2 e- Cu 2+ + 2 e- → Cu(s) 0. 34 v Cu 2+ Sn 2+ +0. 14 v Gains mass NO 3 - Loses mass - + Overall Reaction: Cu 2+ + Sn → Sn 2+ + Cu(s) 0. 48 v
1. Draw and completely analyze a Cu/Sn electrochemical cell. voltmeter e- Higher e- 0. 48 v Greatest Electron Affinity Lower Reduction Oxidation Cathode Na-+ NO 3 - Sn Cu Anode Sn(s) → Sn 2+ + 2 e- Cu 2+ + 2 e- → Cu(s) 0. 34 v Cu 2+ Sn 2+ +0. 14 v Gains mass NO 3 - Loses mass - + Overall Reaction: Cu 2+ + Sn → Sn 2+ + Cu(s) 0. 48 v
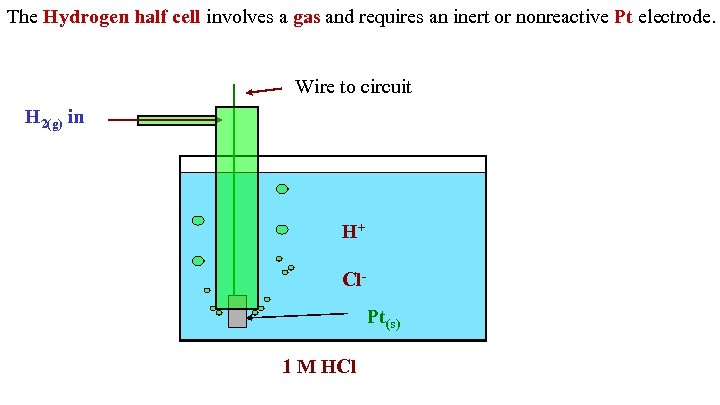 The Hydrogen half cell involves a gas and requires an inert or nonreactive Pt electrode. Wire to circuit H 2(g) in H+ Cl. Pt(s) 1 M HCl
The Hydrogen half cell involves a gas and requires an inert or nonreactive Pt electrode. Wire to circuit H 2(g) in H+ Cl. Pt(s) 1 M HCl
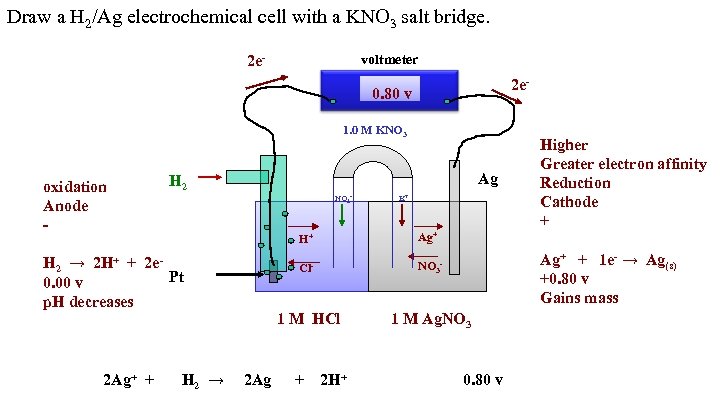 Draw a H 2/Ag electrochemical cell with a KNO 3 salt bridge. voltmeter 2 e 2 e- 0. 80 v 1. 0 M KNO 3 oxidation Anode - H 2 → 2 H+ + 2 e. Pt 0. 00 v p. H decreases Ag NO 3 - K+ H+ Ag+ Cl- NO 3 - Higher Greater electron affinity Reduction Cathode + 1 M HCl 2 Ag+ + H 2 → 2 Ag + 2 H+ Ag+ + 1 e- → Ag(s) +0. 80 v Gains mass 1 M Ag. NO 3 0. 80 v
Draw a H 2/Ag electrochemical cell with a KNO 3 salt bridge. voltmeter 2 e 2 e- 0. 80 v 1. 0 M KNO 3 oxidation Anode - H 2 → 2 H+ + 2 e. Pt 0. 00 v p. H decreases Ag NO 3 - K+ H+ Ag+ Cl- NO 3 - Higher Greater electron affinity Reduction Cathode + 1 M HCl 2 Ag+ + H 2 → 2 Ag + 2 H+ Ag+ + 1 e- → Ag(s) +0. 80 v Gains mass 1 M Ag. NO 3 0. 80 v
 Electrochemical cell Lab Date Your Full Name: Purpose: To draw and completely analyze five electrochemical cells. Procedure: As outlined by the instructor. Data:
Electrochemical cell Lab Date Your Full Name: Purpose: To draw and completely analyze five electrochemical cells. Procedure: As outlined by the instructor. Data:
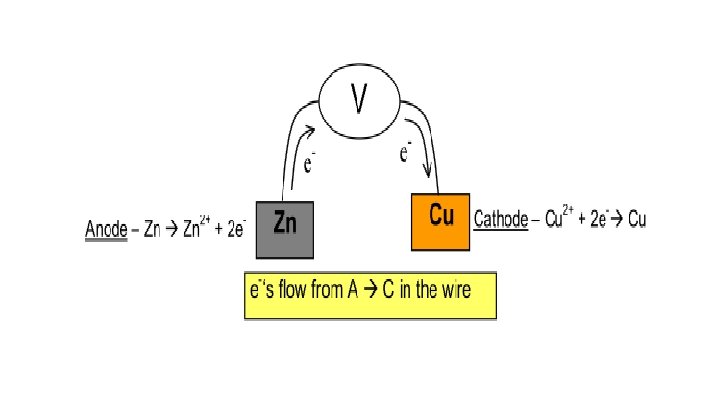
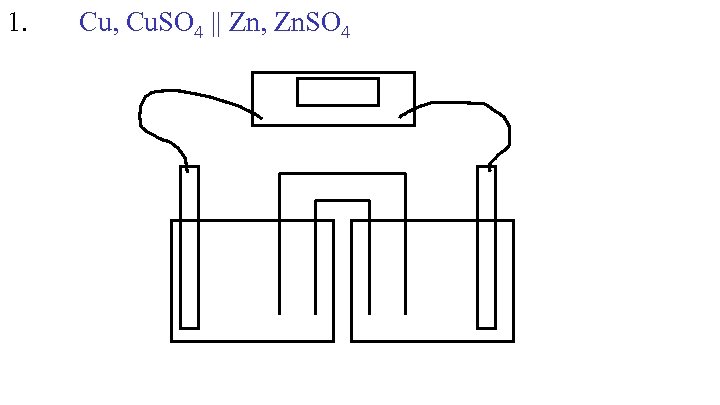 1. Cu, Cu. SO 4 || Zn, Zn. SO 4
1. Cu, Cu. SO 4 || Zn, Zn. SO 4
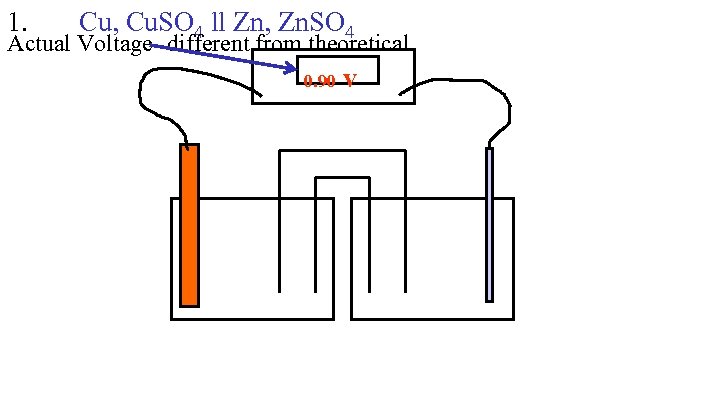 1. Cu, Cu. SO 4 ll Zn, Zn. SO 4 Actual Voltage- different from theoretical 0. 90 v
1. Cu, Cu. SO 4 ll Zn, Zn. SO 4 Actual Voltage- different from theoretical 0. 90 v
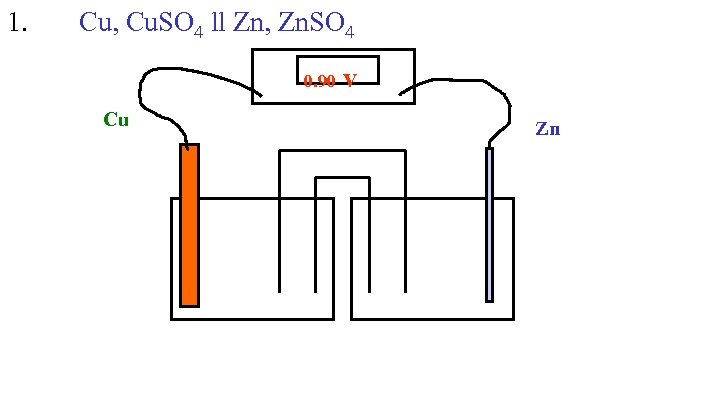 1. Cu, Cu. SO 4 ll Zn, Zn. SO 4 0. 90 v Cu Zn
1. Cu, Cu. SO 4 ll Zn, Zn. SO 4 0. 90 v Cu Zn
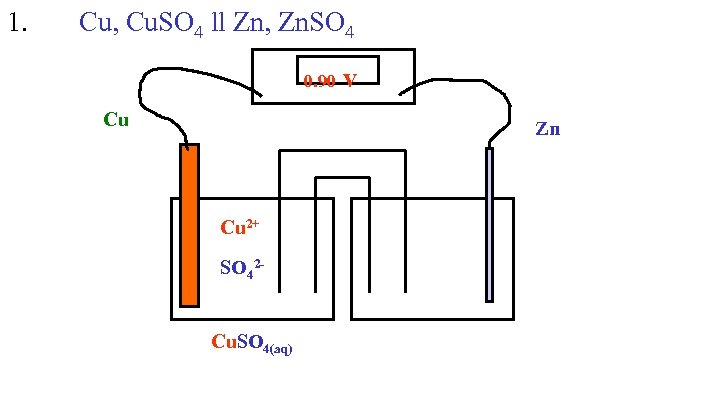 1. Cu, Cu. SO 4 ll Zn, Zn. SO 4 0. 90 v Cu Zn Cu 2+ SO 42 Cu. SO 4(aq)
1. Cu, Cu. SO 4 ll Zn, Zn. SO 4 0. 90 v Cu Zn Cu 2+ SO 42 Cu. SO 4(aq)
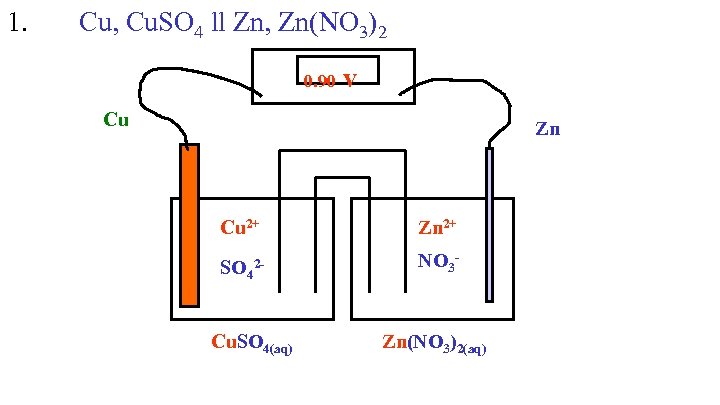 1. Cu, Cu. SO 4 ll Zn, Zn(NO 3)2 0. 90 v Cu Zn Cu 2+ Zn 2+ SO 42 - NO 3 - Cu. SO 4(aq) Zn(NO 3)2(aq)
1. Cu, Cu. SO 4 ll Zn, Zn(NO 3)2 0. 90 v Cu Zn Cu 2+ Zn 2+ SO 42 - NO 3 - Cu. SO 4(aq) Zn(NO 3)2(aq)
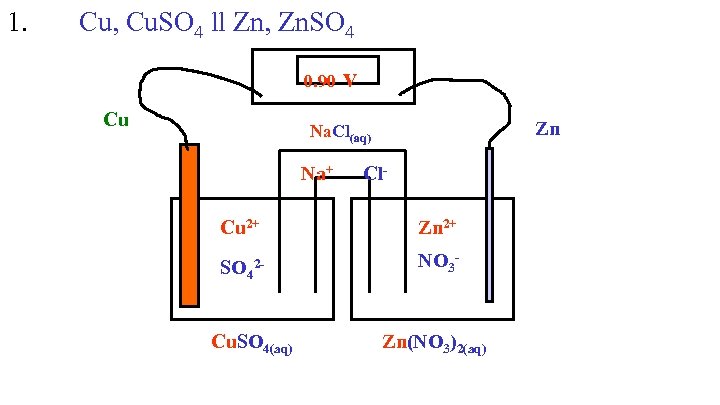 1. Cu, Cu. SO 4 ll Zn, Zn. SO 4 0. 90 v Cu Zn Na. Cl(aq) Na+ Cl. Cu 2+ Zn 2+ SO 42 - NO 3 - Cu. SO 4(aq) Zn(NO 3)2(aq)
1. Cu, Cu. SO 4 ll Zn, Zn. SO 4 0. 90 v Cu Zn Na. Cl(aq) Na+ Cl. Cu 2+ Zn 2+ SO 42 - NO 3 - Cu. SO 4(aq) Zn(NO 3)2(aq)
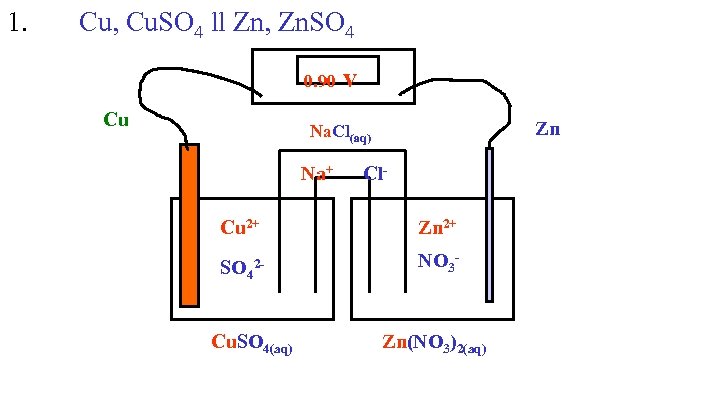 1. Cu, Cu. SO 4 ll Zn, Zn. SO 4 0. 90 v Cu Zn Na. Cl(aq) Na+ Cl. Cu 2+ Zn 2+ SO 42 - NO 3 - Cu. SO 4(aq) Zn(NO 3)2(aq)
1. Cu, Cu. SO 4 ll Zn, Zn. SO 4 0. 90 v Cu Zn Na. Cl(aq) Na+ Cl. Cu 2+ Zn 2+ SO 42 - NO 3 - Cu. SO 4(aq) Zn(NO 3)2(aq)
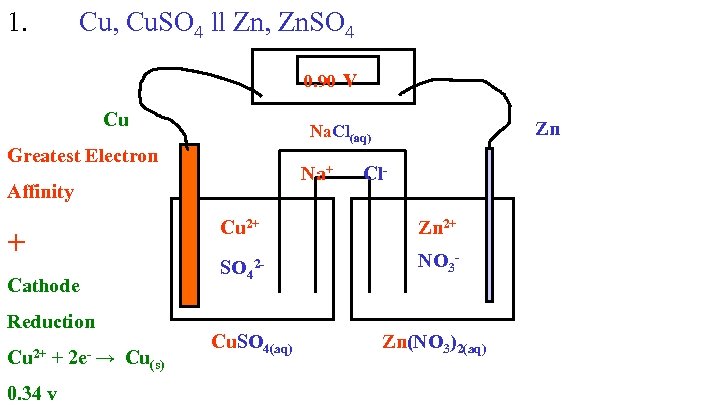 1. Cu, Cu. SO 4 ll Zn, Zn. SO 4 0. 90 v Cu Greatest Electron Na+ Cl- Affinity Cu 2+ Cathode Reduction 0. 34 v Zn 2+ SO 42 - + Cu 2+ + 2 e- → Cu Zn Na. Cl(aq) NO 3 - Cu. SO 4(aq) (s) Zn(NO 3)2(aq)
1. Cu, Cu. SO 4 ll Zn, Zn. SO 4 0. 90 v Cu Greatest Electron Na+ Cl- Affinity Cu 2+ Cathode Reduction 0. 34 v Zn 2+ SO 42 - + Cu 2+ + 2 e- → Cu Zn Na. Cl(aq) NO 3 - Cu. SO 4(aq) (s) Zn(NO 3)2(aq)
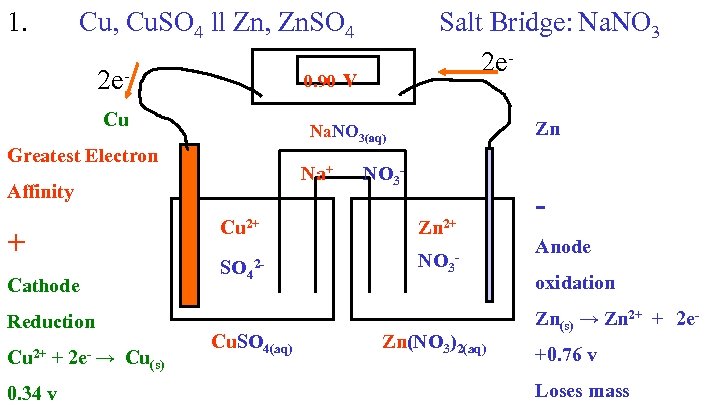 1. Cu, Cu. SO 4 ll Zn, Zn. SO 4 0. 90 v 2 e. Cu Na+ NO 3 - Affinity Cu 2+ Cathode Reduction Zn 2+ SO 42 - + 0. 34 v Zn Na. NO 3(aq) Greatest Electron Cu 2+ + 2 e- → Cu Salt Bridge: Na. NO 3 2 e- NO 3 - Cu. SO 4(aq) (s) Zn(NO 3)2(aq) Anode oxidation Zn(s) → Zn 2+ + 2 e+0. 76 v Loses mass
1. Cu, Cu. SO 4 ll Zn, Zn. SO 4 0. 90 v 2 e. Cu Na+ NO 3 - Affinity Cu 2+ Cathode Reduction Zn 2+ SO 42 - + 0. 34 v Zn Na. NO 3(aq) Greatest Electron Cu 2+ + 2 e- → Cu Salt Bridge: Na. NO 3 2 e- NO 3 - Cu. SO 4(aq) (s) Zn(NO 3)2(aq) Anode oxidation Zn(s) → Zn 2+ + 2 e+0. 76 v Loses mass
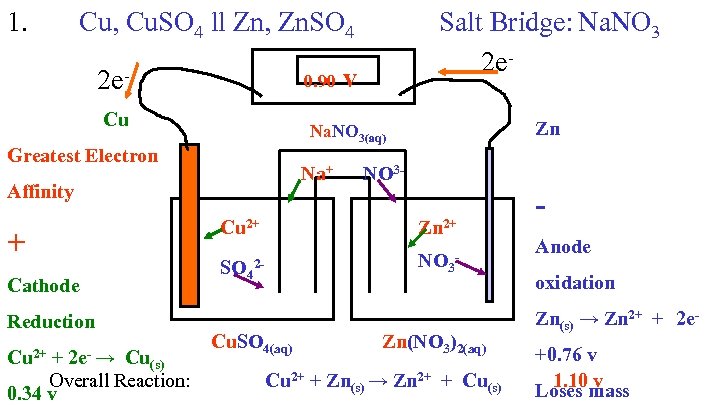 1. Cu, Cu. SO 4 ll Zn, Zn. SO 4 0. 90 v 2 e. Cu Zn Na. NO 3(aq) Greatest Electron Na+ NO 3 - Affinity Cu 2+ Cathode Reduction Zn 2+ SO 42 - + Cu 2+ + 2 e- → Cu Salt Bridge: Na. NO 3 2 e- NO 3 - Cu. SO 4(aq) (s) Overall Reaction: 0. 34 v Zn(NO 3)2(aq) Cu 2+ + Zn(s) → Zn 2+ + Cu(s) Anode oxidation Zn(s) → Zn 2+ + 2 e+0. 76 v 1. 10 v Loses mass
1. Cu, Cu. SO 4 ll Zn, Zn. SO 4 0. 90 v 2 e. Cu Zn Na. NO 3(aq) Greatest Electron Na+ NO 3 - Affinity Cu 2+ Cathode Reduction Zn 2+ SO 42 - + Cu 2+ + 2 e- → Cu Salt Bridge: Na. NO 3 2 e- NO 3 - Cu. SO 4(aq) (s) Overall Reaction: 0. 34 v Zn(NO 3)2(aq) Cu 2+ + Zn(s) → Zn 2+ + Cu(s) Anode oxidation Zn(s) → Zn 2+ + 2 e+0. 76 v 1. 10 v Loses mass
 2. Pb, Pb(NO 3)2 ll Zn, Zn(NO 3)2 Actual Voltage 0. 84 v Salt Bridge: Na. NO 3
2. Pb, Pb(NO 3)2 ll Zn, Zn(NO 3)2 Actual Voltage 0. 84 v Salt Bridge: Na. NO 3
 3. Fe, Fe(NO 3)2 ll Ni, Ni(NO 3)2 Actual Voltage 0. 20 v Salt Bridge: Na. NO 3
3. Fe, Fe(NO 3)2 ll Ni, Ni(NO 3)2 Actual Voltage 0. 20 v Salt Bridge: Na. NO 3
 4. Cu, Cu. SO 4 ll Fe, Fe(NO 3)2 Actual Voltage 0. 74 v Salt Bridge: Na. NO 3
4. Cu, Cu. SO 4 ll Fe, Fe(NO 3)2 Actual Voltage 0. 74 v Salt Bridge: Na. NO 3
 5. Ni, Ni(NO 3)2 ll Zn, Zn(NO 3)2 Actual Voltage 1. 00 v Salt Bridge: Na. NO 3
5. Ni, Ni(NO 3)2 ll Zn, Zn(NO 3)2 Actual Voltage 1. 00 v Salt Bridge: Na. NO 3
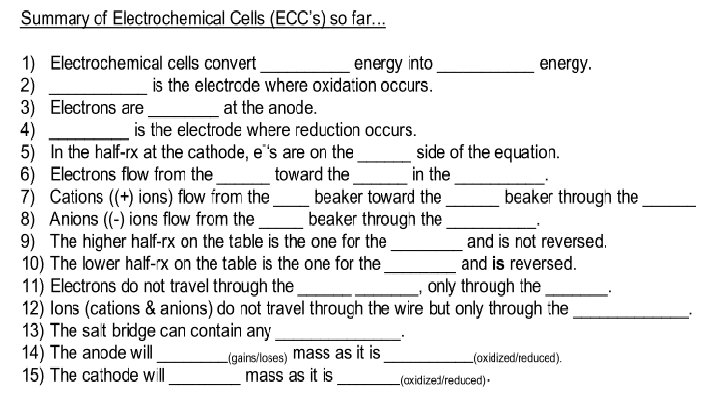
 Discussion describe how you would completely analyze an electrochemical cell- use your notes! Discuss how you determined the anode, cathode, site of oxidation, and site of reduction. Discuss electron flow and ion migration. Explain the function of the salt bridge and what is meant by electron affinity. What are electrochemical cells used for?
Discussion describe how you would completely analyze an electrochemical cell- use your notes! Discuss how you determined the anode, cathode, site of oxidation, and site of reduction. Discuss electron flow and ion migration. Explain the function of the salt bridge and what is meant by electron affinity. What are electrochemical cells used for?