088a807fa38884e3e5881943f55531cb.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 15
 Electrical Engineering Faculty Information Technologies and Computer-Aided Systems Department Basic professional educational programs of higher education the program on the field of training of Magistrates 09. 04. 01 Computer Science and Engineering Education program profile: Automated data processing and management systems Perm 2015
Electrical Engineering Faculty Information Technologies and Computer-Aided Systems Department Basic professional educational programs of higher education the program on the field of training of Magistrates 09. 04. 01 Computer Science and Engineering Education program profile: Automated data processing and management systems Perm 2015
 SOFTWARE ENGINEERING SYLLABUS Workload: 4 CP, 144 academic hours Course aim: The familiarization with modern technologies of programming and acquisition of professional knowledge and skills in the field of software development. In the process of studying this discipline students master the following competencies: • Understanding of existing approaches to software models verification (PK 6); • The ability to design a system with parallel processing and high performance systems and their components (PC 9); • Choose methods and develop algorithms for solving problems of automation objects management and design (PC 11). Course objectives: • Study of software development modern technologies; • The formation of the ability to use engineering design in specific subject areas; • The formation of skills of program documentation development, personal and team software development, independent analysis of new trends and concepts of software development.
SOFTWARE ENGINEERING SYLLABUS Workload: 4 CP, 144 academic hours Course aim: The familiarization with modern technologies of programming and acquisition of professional knowledge and skills in the field of software development. In the process of studying this discipline students master the following competencies: • Understanding of existing approaches to software models verification (PK 6); • The ability to design a system with parallel processing and high performance systems and their components (PC 9); • Choose methods and develop algorithms for solving problems of automation objects management and design (PC 11). Course objectives: • Study of software development modern technologies; • The formation of the ability to use engineering design in specific subject areas; • The formation of skills of program documentation development, personal and team software development, independent analysis of new trends and concepts of software development.
 SOFTWARE ENGINEERING SYLLABUS Workload: 4 CP, 144 academic hours The course place in a structure of professional education As a result of course studying the student should demonstrate the following results: to know: • basics software engineering; • sequence and stages of software development; • methods and standards associated with the processes of software project management; • principles, methods and techniques of writing and debugging programs, • basic design patterns, the Unified Modeling Language (UML); to be able to: • apply methods and standards associated with the processes of software project management; • write software specifications; • develop models of design; • display information processing; • use the class libraries in the development of applications; • use design patterns; • develop programs with modern environments; to possess: • skills in development software documentation; • skills in personal and team software development while planning the software life cycle; • techniques and methods of object oriented analysis and design; • methods of software development using CASE technologies, methods of testing and debugging programs.
SOFTWARE ENGINEERING SYLLABUS Workload: 4 CP, 144 academic hours The course place in a structure of professional education As a result of course studying the student should demonstrate the following results: to know: • basics software engineering; • sequence and stages of software development; • methods and standards associated with the processes of software project management; • principles, methods and techniques of writing and debugging programs, • basic design patterns, the Unified Modeling Language (UML); to be able to: • apply methods and standards associated with the processes of software project management; • write software specifications; • develop models of design; • display information processing; • use the class libraries in the development of applications; • use design patterns; • develop programs with modern environments; to possess: • skills in development software documentation; • skills in personal and team software development while planning the software life cycle; • techniques and methods of object oriented analysis and design; • methods of software development using CASE technologies, methods of testing and debugging programs.
 TRAINING COMPLEX DISCIPLINE «Workshop on CASE-technology» WORK PROGRAMME OF DISCIPLINE The complexity: 5 credit unit 180 hours The purpose of discipline is to acquire complex knowledge and skills in the use of CASE technologies for creation of the automated systems of information processing and management. In the process of studying this discipline a student masters the following competencies: • the ability to draw up reports on the carrying out of research work and to prepare the publication of research results; • possession of the existing methods and algorithms for solving problems of recognition and data processing; • the ability to develop and implement plans for informatization of enterprises and their divisions on the basis of Web and CALS techniques. The tasks of the discipline • Study of the main features, functionality and development prospects of CASE technologies; methodologies for functional modeling of business processes; Unified Modeling Language UML. • Formation of abilities to apply the basic methodology for functional modeling of business processes; to fulfill the development requirements for the information system using diagrams language UML. • Formation of skills of designing the information system using the language of diagrams UML; implementation of software and information systems based on modeling of the information system.
TRAINING COMPLEX DISCIPLINE «Workshop on CASE-technology» WORK PROGRAMME OF DISCIPLINE The complexity: 5 credit unit 180 hours The purpose of discipline is to acquire complex knowledge and skills in the use of CASE technologies for creation of the automated systems of information processing and management. In the process of studying this discipline a student masters the following competencies: • the ability to draw up reports on the carrying out of research work and to prepare the publication of research results; • possession of the existing methods and algorithms for solving problems of recognition and data processing; • the ability to develop and implement plans for informatization of enterprises and their divisions on the basis of Web and CALS techniques. The tasks of the discipline • Study of the main features, functionality and development prospects of CASE technologies; methodologies for functional modeling of business processes; Unified Modeling Language UML. • Formation of abilities to apply the basic methodology for functional modeling of business processes; to fulfill the development requirements for the information system using diagrams language UML. • Formation of skills of designing the information system using the language of diagrams UML; implementation of software and information systems based on modeling of the information system.
 TRAINING COMPLEX DISCIPLINE «Workshop on CASE-technology» WORK PROGRAMME OF DISCIPLINE The complexity: 5 credit unit 180 hours As a result of studying the discipline the student should demonstrate the following results: know: • – concept, main features, functionality and development prospects of CASE technologies; • – functional features of business process modeling using CASE tools; • – the purpose and basic concepts of language UML; • – characteristics of object oriented development requirements using diagrams language UML; • – characteristics of object oriented design using the language of diagrams UML; be able to: • – to carry out the construction of the business process model using the methodology IDEF 0; • – to carry out the construction of the business process model using the methodology IDEF 3; • – to carry out the construction of the business process model using the methodology DFD; • – to carry out the construction of the business process model using the methodology ARIS; • – to carry out the formation of system requirements using diagrams Use Case language UML; • – fulfill the requirements for the formation of an information system with the help of activity diagrams of language UML; • – to carry out the analysis of system requirements using the interaction diagrams of language UML; • – to carry out behavioral modeling using finite automata diagrams language UML; possess: • – the skills of architectural design of information systems with the help of diagrams packages language UML; • – the skills of architectural design of information systems with the aid of diagrams the components of language UML; • – the skills detailed design information system using the language of class diagrams UML; • – the skills charting software deployment systems hardware; • – the skills to generate code based on the language of diagrams UML; • – the skills of transformation of the code in the language diagram UML; • – the skills to build software and information support based on modeling of the information system.
TRAINING COMPLEX DISCIPLINE «Workshop on CASE-technology» WORK PROGRAMME OF DISCIPLINE The complexity: 5 credit unit 180 hours As a result of studying the discipline the student should demonstrate the following results: know: • – concept, main features, functionality and development prospects of CASE technologies; • – functional features of business process modeling using CASE tools; • – the purpose and basic concepts of language UML; • – characteristics of object oriented development requirements using diagrams language UML; • – characteristics of object oriented design using the language of diagrams UML; be able to: • – to carry out the construction of the business process model using the methodology IDEF 0; • – to carry out the construction of the business process model using the methodology IDEF 3; • – to carry out the construction of the business process model using the methodology DFD; • – to carry out the construction of the business process model using the methodology ARIS; • – to carry out the formation of system requirements using diagrams Use Case language UML; • – fulfill the requirements for the formation of an information system with the help of activity diagrams of language UML; • – to carry out the analysis of system requirements using the interaction diagrams of language UML; • – to carry out behavioral modeling using finite automata diagrams language UML; possess: • – the skills of architectural design of information systems with the help of diagrams packages language UML; • – the skills of architectural design of information systems with the aid of diagrams the components of language UML; • – the skills detailed design information system using the language of class diagrams UML; • – the skills charting software deployment systems hardware; • – the skills to generate code based on the language of diagrams UML; • – the skills of transformation of the code in the language diagram UML; • – the skills to build software and information support based on modeling of the information system.
 УЧЕБНО-МЕТОДИЧЕСКИЙ КОМПЛЕКС ДИСЦИПЛИНЫ «Современные методы и инструментальные средства управления проектами и рисками» РАБОЧАЯ ПРОГРАММА ДИСЦИПЛИНЫ Трудоёмкость: 3 ЗЕ 108 ч Цель учебной дисциплины: Приобретение комплекса знаний, умений и навыков управления проектами и рисками, используя современные методы и инструментальные средства. В процессе изучения данной дисциплины студент осваивает следующие компетенции: • использование на практике умения и навыки в организации исследовательских и проектных работ, в управлении коллективом; • способность проявлять инициативу, в том числе в ситуациях риска брать на себя всю полноту ответственности; • владение существующими методами и алгоритмами решения задач цифровой обработки сигналов. Задачи учебной дисциплины: • Изучение методы и инструментальные средства управления проектами и рисками. • Формирование умений формулировать и решать задачи планирования и управления ресурсами проекта. • Формирование навыков построения алгоритмов разработки и создания организационных структур управления проектами.
УЧЕБНО-МЕТОДИЧЕСКИЙ КОМПЛЕКС ДИСЦИПЛИНЫ «Современные методы и инструментальные средства управления проектами и рисками» РАБОЧАЯ ПРОГРАММА ДИСЦИПЛИНЫ Трудоёмкость: 3 ЗЕ 108 ч Цель учебной дисциплины: Приобретение комплекса знаний, умений и навыков управления проектами и рисками, используя современные методы и инструментальные средства. В процессе изучения данной дисциплины студент осваивает следующие компетенции: • использование на практике умения и навыки в организации исследовательских и проектных работ, в управлении коллективом; • способность проявлять инициативу, в том числе в ситуациях риска брать на себя всю полноту ответственности; • владение существующими методами и алгоритмами решения задач цифровой обработки сигналов. Задачи учебной дисциплины: • Изучение методы и инструментальные средства управления проектами и рисками. • Формирование умений формулировать и решать задачи планирования и управления ресурсами проекта. • Формирование навыков построения алгоритмов разработки и создания организационных структур управления проектами.
 УЧЕБНО-МЕТОДИЧЕСКИЙ КОМПЛЕКС ДИСЦИПЛИНЫ «Современные методы и инструментальные средства управления проектами и рисками» РАБОЧАЯ ПРОГРАММА ДИСЦИПЛИНЫ Трудоёмкость: 3 ЗЕ 108 ч В результате изучения дисциплины обучающийся должен демонстрировать следующие результаты: Знать: • базовые понятия и их классификацию управления проектами; • организационные структуры управления проектами; • основные показатели и принципы оценки эффективности инвестиционных проектов; • основные принципы управления стоимостью проекта; • качественный и количественный анализ рисков. Уметь: • выполнять исследования систем планирования и управления проектными решениями; • выполнять описание задач планирования проектами и организации работ по управлению рисками; • разрабатывать и выбирать современные методы и инструментальные средства управления проектами и рисками; • составлять алгоритмы разработки и создания организационных структур управления проектами; • выполнять предварительную проработку целей и задач проекта; • разрабатывать проектно сметную документацию. Владеть навыками: • исследования систем планирования и управления проектными решениями; • описания задач планирования проектами и организации работ по управлению рисками; • разработки и выбора современных методов и инструментальных средств управления проектами и рисками; • составления алгоритмов разработки и создания организационных структур управления проектами; • выполнения предварительной проработки целей и задач проекта; • разработки проектно сметной документации.
УЧЕБНО-МЕТОДИЧЕСКИЙ КОМПЛЕКС ДИСЦИПЛИНЫ «Современные методы и инструментальные средства управления проектами и рисками» РАБОЧАЯ ПРОГРАММА ДИСЦИПЛИНЫ Трудоёмкость: 3 ЗЕ 108 ч В результате изучения дисциплины обучающийся должен демонстрировать следующие результаты: Знать: • базовые понятия и их классификацию управления проектами; • организационные структуры управления проектами; • основные показатели и принципы оценки эффективности инвестиционных проектов; • основные принципы управления стоимостью проекта; • качественный и количественный анализ рисков. Уметь: • выполнять исследования систем планирования и управления проектными решениями; • выполнять описание задач планирования проектами и организации работ по управлению рисками; • разрабатывать и выбирать современные методы и инструментальные средства управления проектами и рисками; • составлять алгоритмы разработки и создания организационных структур управления проектами; • выполнять предварительную проработку целей и задач проекта; • разрабатывать проектно сметную документацию. Владеть навыками: • исследования систем планирования и управления проектными решениями; • описания задач планирования проектами и организации работ по управлению рисками; • разработки и выбора современных методов и инструментальных средств управления проектами и рисками; • составления алгоритмов разработки и создания организационных структур управления проектами; • выполнения предварительной проработки целей и задач проекта; • разработки проектно сметной документации.
 Mathematic models and algorithms of automated control systems for technologic processes Workload: 3 CP, 108 academic hours Course aim: Formation of a complex of knowledge and skills in the field of mathematics and software for automated control systems of technological processes, basics of modeling and analysis of automated control systems, based on open systems conception, studying of basic instrumental tools and systems that are used for describing and analysis of automated control systems, and gaining of practical skills of modeling automated control systems. In the process of studying this discipline, students master the following competencies: • Ability to acquire and apply new knowledge and skills by using information technologies, including fields of knowledge that are not directly connected with the field of activity (OK 7); • Ability to use of modern equipment and tools (OK 8); • Possession of existing methods and algorithms for solving problems of digital signal processing. Course objectives: • Studying of general characteristics of automated control systems; automated control systems development principles; system analysis of technological control objects; mathematic background of automated control systems; types of automated control systems; features of construction, design and implementation of automated control systems; economic efficiency of using automated control systems. • The formation of ability to use modern control tools of automatization for automated control systems. • The formation of skills to use instrumental tools of development and analysis of automated control systems models.
Mathematic models and algorithms of automated control systems for technologic processes Workload: 3 CP, 108 academic hours Course aim: Formation of a complex of knowledge and skills in the field of mathematics and software for automated control systems of technological processes, basics of modeling and analysis of automated control systems, based on open systems conception, studying of basic instrumental tools and systems that are used for describing and analysis of automated control systems, and gaining of practical skills of modeling automated control systems. In the process of studying this discipline, students master the following competencies: • Ability to acquire and apply new knowledge and skills by using information technologies, including fields of knowledge that are not directly connected with the field of activity (OK 7); • Ability to use of modern equipment and tools (OK 8); • Possession of existing methods and algorithms for solving problems of digital signal processing. Course objectives: • Studying of general characteristics of automated control systems; automated control systems development principles; system analysis of technological control objects; mathematic background of automated control systems; types of automated control systems; features of construction, design and implementation of automated control systems; economic efficiency of using automated control systems. • The formation of ability to use modern control tools of automatization for automated control systems. • The formation of skills to use instrumental tools of development and analysis of automated control systems models.
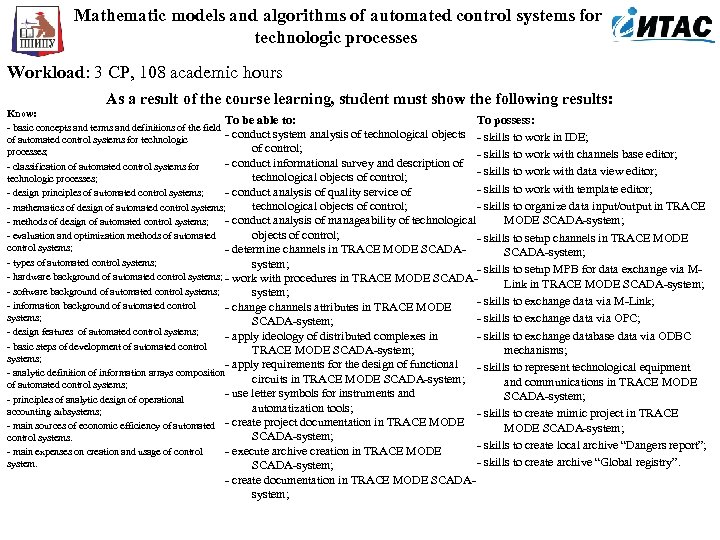 Mathematic models and algorithms of automated control systems for technologic processes Workload: 3 CP, 108 academic hours As a result of the course learning, student must show the following results: Know: To be able to: To possess: basic concepts and terms and definitions of the field conduct system analysis of technological objects skills to work in IDE; of automated control systems for technologic of control; processes; skills to work with channels base editor; conduct informational survey and description of classification of automated control systems for skills to work with data view editor; technological objects of control; technologic processes; skills to work with template editor; conduct analysis of quality service of design principles of automated control systems; technological objects of control; skills to organize data input/output in TRACE mathematics of design of automated control systems; conduct analysis of manageability of technological MODE SCADA system; methods of design of automated control systems; objects of control; evaluation and optimization methods of automated skills to setup channels in TRACE MODE control systems; determine channels in TRACE MODE SCADA system; types of automated control systems; system; skills to setup MPB for data exchange via M hardware background of automated control systems; work with procedures in TRACE MODE SCADA Link in TRACE MODE SCADA system; software background of automated control systems; system; skills to exchange data via M Link; information background of automated control change channels attributes in TRACE MODE systems; skills to exchange data via OPC; SCADA system; design features of automated control systems; apply ideology of distributed complexes in skills to exchange database data via ODBC basic steps of development of automated control TRACE MODE SCADA system; mechanisms; systems; apply requirements for the design of functional skills to represent technological equipment analytic definition of information arrays composition circuits in TRACE MODE SCADA system; and communications in TRACE MODE of automated control systems; use letter symbols for instruments and SCADA system; principles of analytic design of operational automatization tools; accounting subsystems; skills to create mimic project in TRACE main sources of economic efficiency of automated create project documentation in TRACE MODE SCADA system; control systems. skills to create local archive “Dangers report”; execute archive creation in TRACE MODE main expenses on creation and usage of control skills to create archive “Global registry”. system. SCADA system; create documentation in TRACE MODE SCADA system;
Mathematic models and algorithms of automated control systems for technologic processes Workload: 3 CP, 108 academic hours As a result of the course learning, student must show the following results: Know: To be able to: To possess: basic concepts and terms and definitions of the field conduct system analysis of technological objects skills to work in IDE; of automated control systems for technologic of control; processes; skills to work with channels base editor; conduct informational survey and description of classification of automated control systems for skills to work with data view editor; technological objects of control; technologic processes; skills to work with template editor; conduct analysis of quality service of design principles of automated control systems; technological objects of control; skills to organize data input/output in TRACE mathematics of design of automated control systems; conduct analysis of manageability of technological MODE SCADA system; methods of design of automated control systems; objects of control; evaluation and optimization methods of automated skills to setup channels in TRACE MODE control systems; determine channels in TRACE MODE SCADA system; types of automated control systems; system; skills to setup MPB for data exchange via M hardware background of automated control systems; work with procedures in TRACE MODE SCADA Link in TRACE MODE SCADA system; software background of automated control systems; system; skills to exchange data via M Link; information background of automated control change channels attributes in TRACE MODE systems; skills to exchange data via OPC; SCADA system; design features of automated control systems; apply ideology of distributed complexes in skills to exchange database data via ODBC basic steps of development of automated control TRACE MODE SCADA system; mechanisms; systems; apply requirements for the design of functional skills to represent technological equipment analytic definition of information arrays composition circuits in TRACE MODE SCADA system; and communications in TRACE MODE of automated control systems; use letter symbols for instruments and SCADA system; principles of analytic design of operational automatization tools; accounting subsystems; skills to create mimic project in TRACE main sources of economic efficiency of automated create project documentation in TRACE MODE SCADA system; control systems. skills to create local archive “Dangers report”; execute archive creation in TRACE MODE main expenses on creation and usage of control skills to create archive “Global registry”. system. SCADA system; create documentation in TRACE MODE SCADA system;
 КNOWLEDGE BASES AND ONTOLOGY SYLLABUS Workload: 3 CP, 108 academic hours Course aim: The course aim is obtaining complex of knowledge and skills of modeling and algorithmization of knowledge bases, ontologies and expert systems design problems. In the process of studying this discipline students master the following competencies: • The ability to understand the role of science in the development of civilization, the relationship of science and technology, have an understanding of related contemporary social and ethnic problems, understand the value of scientific rationality and its historical types (OK 2); Course objectives: • The study of processes and technologies for the identification, creation, distribution, processing, storing and providing for the use of knowledge; • Formation of abilities to formulate and solve the problem of designing knowledge bases, ontologies and expert systems; • Formation of skills to choose the software tools for the creation of knowledge bases, ontologies and expert systems.
КNOWLEDGE BASES AND ONTOLOGY SYLLABUS Workload: 3 CP, 108 academic hours Course aim: The course aim is obtaining complex of knowledge and skills of modeling and algorithmization of knowledge bases, ontologies and expert systems design problems. In the process of studying this discipline students master the following competencies: • The ability to understand the role of science in the development of civilization, the relationship of science and technology, have an understanding of related contemporary social and ethnic problems, understand the value of scientific rationality and its historical types (OK 2); Course objectives: • The study of processes and technologies for the identification, creation, distribution, processing, storing and providing for the use of knowledge; • Formation of abilities to formulate and solve the problem of designing knowledge bases, ontologies and expert systems; • Formation of skills to choose the software tools for the creation of knowledge bases, ontologies and expert systems.
 КNOWLEDGE BASES AND ONTOLOGY SYLLABUS Workload: 3 CP, 108 academic hours The course place in a structure of professional education As a result of course studying the student should demonstrate the following results: to know: • the basic concepts of the model of knowledge representation; • features of operations research and modeling with fuzzy knowledge; • models and methods of describing the problems of knowledge bases, ontologies and expert systems designing; • mathematical methods and algorithms of knowledge representation for bases, ontologies and expert systems; • designation, possibility, composition, organization and functioning of the features of expert systems (ES); • ways of organizing the solutions search; possibilities of explanations regime; principles of the EC. to be able to: • describe tasks of extraction and structuring of knowledge; • describe tasks of visual design of knowledge bases, ontologies and expert systems; • research latent knowledge structures and learning systems; • develop and select the models and methods of knowledge bases, ontologies and expert systems design; • analyze the architecture of the ES from the standpoint of knowledge engineer and the user; • assess the applicability of a particular ES to meet the problems of a given class; • represent knowledge using tools; • implement a simple ES. to possess: • skills of research of latent structures of knowledge and learning systems; • skills of description of problems of visual design of knowledge bases, ontologies and expert systems; • skills of development and selection of models and design method ofknowledge bases, ontologies and expert systems; • skills of constructing computing algorithms for solving problems of CAM; • skills of use software tools of system development based on knowledge.
КNOWLEDGE BASES AND ONTOLOGY SYLLABUS Workload: 3 CP, 108 academic hours The course place in a structure of professional education As a result of course studying the student should demonstrate the following results: to know: • the basic concepts of the model of knowledge representation; • features of operations research and modeling with fuzzy knowledge; • models and methods of describing the problems of knowledge bases, ontologies and expert systems designing; • mathematical methods and algorithms of knowledge representation for bases, ontologies and expert systems; • designation, possibility, composition, organization and functioning of the features of expert systems (ES); • ways of organizing the solutions search; possibilities of explanations regime; principles of the EC. to be able to: • describe tasks of extraction and structuring of knowledge; • describe tasks of visual design of knowledge bases, ontologies and expert systems; • research latent knowledge structures and learning systems; • develop and select the models and methods of knowledge bases, ontologies and expert systems design; • analyze the architecture of the ES from the standpoint of knowledge engineer and the user; • assess the applicability of a particular ES to meet the problems of a given class; • represent knowledge using tools; • implement a simple ES. to possess: • skills of research of latent structures of knowledge and learning systems; • skills of description of problems of visual design of knowledge bases, ontologies and expert systems; • skills of development and selection of models and design method ofknowledge bases, ontologies and expert systems; • skills of constructing computing algorithms for solving problems of CAM; • skills of use software tools of system development based on knowledge.
 ПРОГРАММА НАУЧНО-ИССЛЕДОВАТЕЛЬСКОЙ РАБОТЫ Трудоёмкость: 8 ЗЕ; 288 ач. Цель научно-исследовательской работы подготовить магистранта как к самостоятельной научно исследовательской работе, основным результатом которой является написание и успешная защита магистерской диссертации, так и к проведению научных исследований в составе творческого коллектива. • • Задачи научно-исследовательской работы: изучение методологии научного исследования в области информатики и вычислительной техники; формирование умения применять математические методы в формализации задач информатизации объектов автоматизации; формирование умения выполнять и публично защищать научные проекты; формирование умения подготовить научные статьи и отчеты; формирование навыков организации и выполнения научно исследовательских и проектных работ, управления коллективом исследователей с использованием современных информационных технологий и методов искусственного интеллекта; формирование навыков приобретения новых знаний и умений в новых областях знаний с использованием современных информационных технологий и методов искусственного интеллекта; формирование навыков разработки технического задания и программных и/или аппаратных комплексов для информатизации объектов исследования и автоматизации.
ПРОГРАММА НАУЧНО-ИССЛЕДОВАТЕЛЬСКОЙ РАБОТЫ Трудоёмкость: 8 ЗЕ; 288 ач. Цель научно-исследовательской работы подготовить магистранта как к самостоятельной научно исследовательской работе, основным результатом которой является написание и успешная защита магистерской диссертации, так и к проведению научных исследований в составе творческого коллектива. • • Задачи научно-исследовательской работы: изучение методологии научного исследования в области информатики и вычислительной техники; формирование умения применять математические методы в формализации задач информатизации объектов автоматизации; формирование умения выполнять и публично защищать научные проекты; формирование умения подготовить научные статьи и отчеты; формирование навыков организации и выполнения научно исследовательских и проектных работ, управления коллективом исследователей с использованием современных информационных технологий и методов искусственного интеллекта; формирование навыков приобретения новых знаний и умений в новых областях знаний с использованием современных информационных технологий и методов искусственного интеллекта; формирование навыков разработки технического задания и программных и/или аппаратных комплексов для информатизации объектов исследования и автоматизации.
 ПРОГРАММА НАУЧНО-ИССЛЕДОВАТЕЛЬСКОЙ РАБОТЫ Трудоёмкость: 8 ЗЕ; 288 ач. Место научно-исследовательской работы в структуре основной профессиональной образовательной программы Научно исследовательская работа (далее НИР) является одной из основных форм организации научно исследовательской работы студентов программы магистратуры и подготовки ими магистерской диссертации. НИР нацелен на усиление исследовательской составляющей в процессе обучения по программе магистратуры в ФГБОУ ВПО «ПНИПУ» и на приобретение студентами исследовательских компетенций и соответствующих практических навыков, что соответствует приоритетам развития ФГБОУ ВПО «ПНИПУ» как национального исследовательского университета. Цель проведения НИР: • вовлечение магистрантов в научно исследовательскую деятельность; • стимулирование к применению на практике знаний, полученных в рамках изучения теоретических дисциплин магистерской программы; • развитие навыков подготовки научных статей и докладов, знакомство с правилами их создания и оформления; • обсуждение выполняемых и готовых исследовательских работ магистрантов; • выработка у магистрантов навыков ведения научной дискуссии и презентации полученных результатов.
ПРОГРАММА НАУЧНО-ИССЛЕДОВАТЕЛЬСКОЙ РАБОТЫ Трудоёмкость: 8 ЗЕ; 288 ач. Место научно-исследовательской работы в структуре основной профессиональной образовательной программы Научно исследовательская работа (далее НИР) является одной из основных форм организации научно исследовательской работы студентов программы магистратуры и подготовки ими магистерской диссертации. НИР нацелен на усиление исследовательской составляющей в процессе обучения по программе магистратуры в ФГБОУ ВПО «ПНИПУ» и на приобретение студентами исследовательских компетенций и соответствующих практических навыков, что соответствует приоритетам развития ФГБОУ ВПО «ПНИПУ» как национального исследовательского университета. Цель проведения НИР: • вовлечение магистрантов в научно исследовательскую деятельность; • стимулирование к применению на практике знаний, полученных в рамках изучения теоретических дисциплин магистерской программы; • развитие навыков подготовки научных статей и докладов, знакомство с правилами их создания и оформления; • обсуждение выполняемых и готовых исследовательских работ магистрантов; • выработка у магистрантов навыков ведения научной дискуссии и презентации полученных результатов.
 ПРОГРАММА УЧЕБНОЙ ПРАКТИКИ (практика по получению первичных профессиональных умений и навыков научноисследовательской работы) Трудоёмкость: 6 ЗЕ; 4 недели; 216 ач. Вид практики: учебная. Форма (тип) практики: практика по получению первичных профессиональных умений и навыков научно исследовательской работы. Цель практики формирование заданных компетенций, обеспечивающих подготовку магистрантов к проведению самостоятельных исследований в рамках научно исследовательской деятельности в области информатики и вычислительной техники. Задачи практики: • выполнение этапов работы, определенных индивидуальным заданием на научно исследовательскую практику, календарным планом, формой представления отчетных материалов и обеспечи вающих выполнение планируемых в компетентностном формате результатов; • оформление отчета, содержащего материалы этапов работы, раскрывающих уровень освоения заданного перечня компетенций; • подготовка и проведение защиты полученных результатов. Место практики в структуре основной профессиональной образовательной программы Научно исследовательская практика входит в блок № 2 «Практики и НИР» (код Б 2. основной образовательной программы по направлению подготовки 09. 04. 01 «Информатика, вычислительная техника» и представляет собой одну из форм организации учебного процесса, заключающуюся в научно исследовательской подготовке студентов на базе кафедры ИТАС (предприятия).
ПРОГРАММА УЧЕБНОЙ ПРАКТИКИ (практика по получению первичных профессиональных умений и навыков научноисследовательской работы) Трудоёмкость: 6 ЗЕ; 4 недели; 216 ач. Вид практики: учебная. Форма (тип) практики: практика по получению первичных профессиональных умений и навыков научно исследовательской работы. Цель практики формирование заданных компетенций, обеспечивающих подготовку магистрантов к проведению самостоятельных исследований в рамках научно исследовательской деятельности в области информатики и вычислительной техники. Задачи практики: • выполнение этапов работы, определенных индивидуальным заданием на научно исследовательскую практику, календарным планом, формой представления отчетных материалов и обеспечи вающих выполнение планируемых в компетентностном формате результатов; • оформление отчета, содержащего материалы этапов работы, раскрывающих уровень освоения заданного перечня компетенций; • подготовка и проведение защиты полученных результатов. Место практики в структуре основной профессиональной образовательной программы Научно исследовательская практика входит в блок № 2 «Практики и НИР» (код Б 2. основной образовательной программы по направлению подготовки 09. 04. 01 «Информатика, вычислительная техника» и представляет собой одну из форм организации учебного процесса, заключающуюся в научно исследовательской подготовке студентов на базе кафедры ИТАС (предприятия).
 ПРОГРАММА УЧЕБНОЙ ПРАКТИКИ (практика по получению первичных профессиональных умений и навыков научноисследовательской работы) Трудоёмкость: 6 ЗЕ; 4 недели; 216 ач. Научно-исследовательская практика расширяет и закрепляет части следующих компетенций (планируемых результатов освоения образовательной программы): 1. способность самостоятельно приобретать с помощью информационных технологий и использовать в практической деятельности новые знания и умения, в том числе в новых областях знаний, непосредственно не связанных со сферой деятельности, уровень освоения средний; • Знание теоретических и практических основ информационных технологий. • Умение самостоятельно приобретать, развивать и применять знания для решения нестандартных задач. • Владение практическими навыками применения новых знаний и умений в разных сферах деятельности и областях знаний. 2. способность анализировать и оценивать уровни своих компетенций в сочетании со способностью и готовностью к саморегулированию дальнейшего образования и профессиональной мобильности, уровень освоения средний. • Знание компетенций, получаемых в процессе обучения. • Умение оценивать текущий уровень своих компетенций. • Владение навыками анализа текущего уровня своих компетенций
ПРОГРАММА УЧЕБНОЙ ПРАКТИКИ (практика по получению первичных профессиональных умений и навыков научноисследовательской работы) Трудоёмкость: 6 ЗЕ; 4 недели; 216 ач. Научно-исследовательская практика расширяет и закрепляет части следующих компетенций (планируемых результатов освоения образовательной программы): 1. способность самостоятельно приобретать с помощью информационных технологий и использовать в практической деятельности новые знания и умения, в том числе в новых областях знаний, непосредственно не связанных со сферой деятельности, уровень освоения средний; • Знание теоретических и практических основ информационных технологий. • Умение самостоятельно приобретать, развивать и применять знания для решения нестандартных задач. • Владение практическими навыками применения новых знаний и умений в разных сферах деятельности и областях знаний. 2. способность анализировать и оценивать уровни своих компетенций в сочетании со способностью и готовностью к саморегулированию дальнейшего образования и профессиональной мобильности, уровень освоения средний. • Знание компетенций, получаемых в процессе обучения. • Умение оценивать текущий уровень своих компетенций. • Владение навыками анализа текущего уровня своих компетенций


