 ELECTRIC FIELD
ELECTRIC FIELD
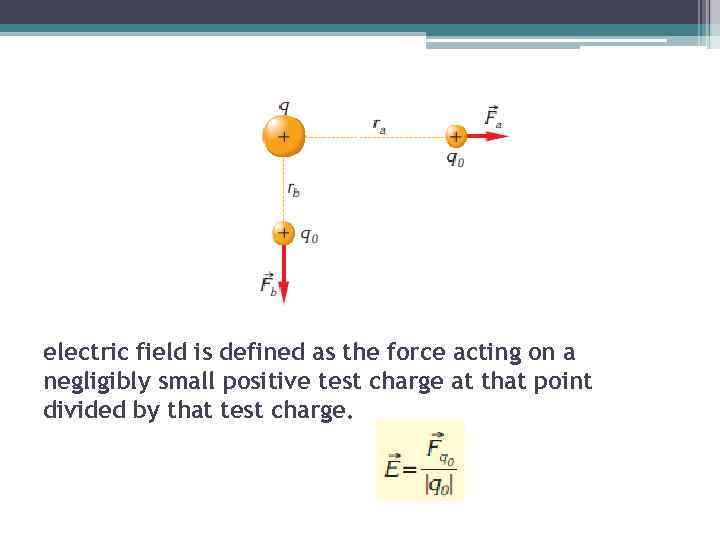 electric field is defined as the force acting on a negligibly small positive test charge at that point divided by that test charge.
electric field is defined as the force acting on a negligibly small positive test charge at that point divided by that test charge.
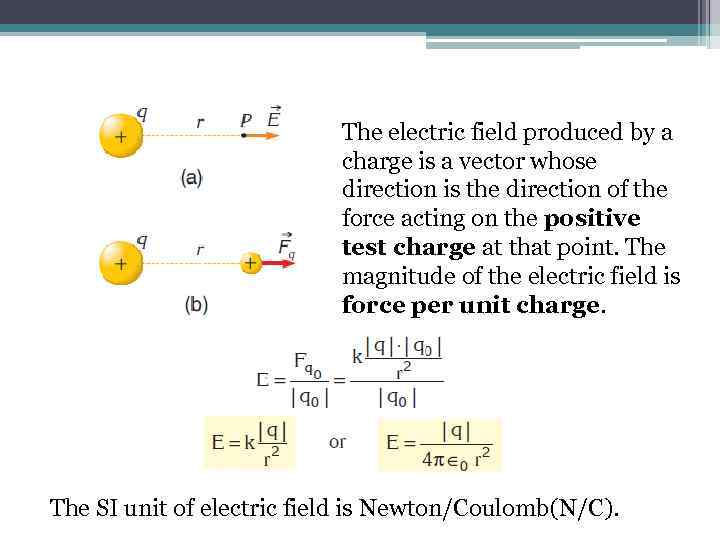 The electric field produced by a charge is a vector whose direction is the direction of the force acting on the positive test charge at that point. The magnitude of the electric field is force per unit charge. The SI unit of electric field is Newton/Coulomb(N/C).
The electric field produced by a charge is a vector whose direction is the direction of the force acting on the positive test charge at that point. The magnitude of the electric field is force per unit charge. The SI unit of electric field is Newton/Coulomb(N/C).
 The Superposition Principle: • If there are more than one charge that produce electric fields, of ÁE 1, ÁE 2, . . . etc. at the same point in the space, the net electric field is the vector sum of all the fields due to each individual charge.
The Superposition Principle: • If there are more than one charge that produce electric fields, of ÁE 1, ÁE 2, . . . etc. at the same point in the space, the net electric field is the vector sum of all the fields due to each individual charge.
 Two charges of q 1 = +10 μC and q 2 = – 20 μC are placed as shown in the figure. What is the magnitude and direction of the electric field at point-P?
Two charges of q 1 = +10 μC and q 2 = – 20 μC are placed as shown in the figure. What is the magnitude and direction of the electric field at point-P?
 Determine the electric field at point-P at a distance 20 cm from the negatively charged particle of q = – 4 μC. What force does a charge of q 1 = +1 μC experience if it is placed at point. P?
Determine the electric field at point-P at a distance 20 cm from the negatively charged particle of q = – 4 μC. What force does a charge of q 1 = +1 μC experience if it is placed at point. P?
 HW 5 1. Find the magnitude of the electric field at a point 10 cm from a point charge of q = – 6 μC. 2. Two point charges of q 1 = 8 n. C and q 2 = – 6 n. C are located along +x-axis, 10 cm apart. Find the magnitude and direction of the net electric field at the midpoint. Where be the electric field is zero? 3. If the electric field at point K, between the charges q 1 and q 2, is zero, what is the ratio of r 1/r 2 ?
HW 5 1. Find the magnitude of the electric field at a point 10 cm from a point charge of q = – 6 μC. 2. Two point charges of q 1 = 8 n. C and q 2 = – 6 n. C are located along +x-axis, 10 cm apart. Find the magnitude and direction of the net electric field at the midpoint. Where be the electric field is zero? 3. If the electric field at point K, between the charges q 1 and q 2, is zero, what is the ratio of r 1/r 2 ?