 Electric Circuits and Resistance M. D. The Professional Development Service for Teachers is funded by the Department of Education and Skills under the National Development Plan
Electric Circuits and Resistance M. D. The Professional Development Service for Teachers is funded by the Department of Education and Skills under the National Development Plan
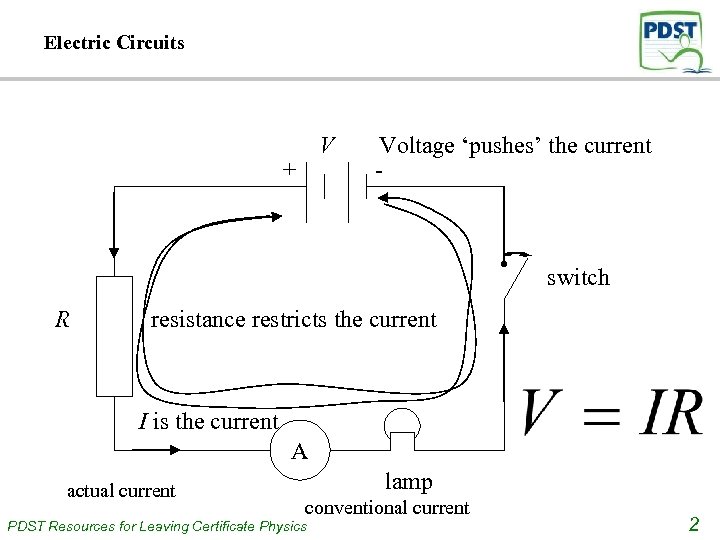 Electric Circuits V + Voltage ‘pushes’ the current - switch R resistance restricts the current I is the current A actual current lamp conventional current PDST Resources for Leaving Certificate Physics 2
Electric Circuits V + Voltage ‘pushes’ the current - switch R resistance restricts the current I is the current A actual current lamp conventional current PDST Resources for Leaving Certificate Physics 2
 Resistance slows down the movement of electrons… …and therefore reduces the current The resistance of an object is the ratio of the voltage applied across its ends to the current which flows through it. PDST Resources for Leaving Certificate Physics 3
Resistance slows down the movement of electrons… …and therefore reduces the current The resistance of an object is the ratio of the voltage applied across its ends to the current which flows through it. PDST Resources for Leaving Certificate Physics 3
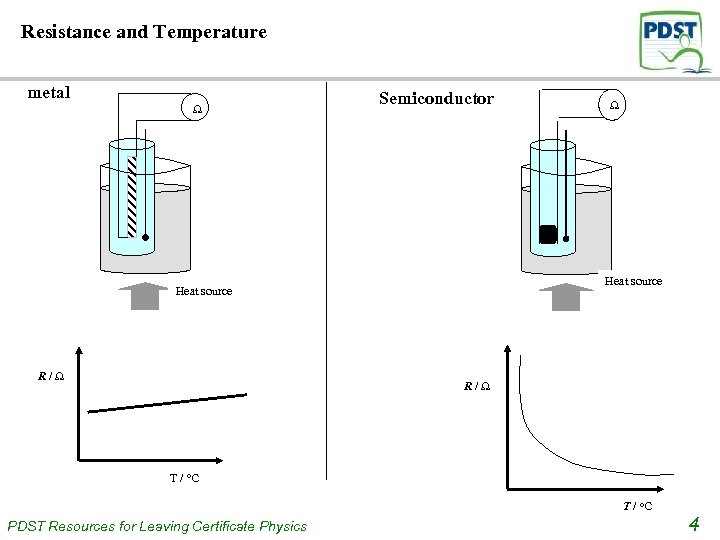 Resistance and Temperature metal Semiconductor Heat source R/ R/ T / o. C PDST Resources for Leaving Certificate Physics 4
Resistance and Temperature metal Semiconductor Heat source R/ R/ T / o. C PDST Resources for Leaving Certificate Physics 4
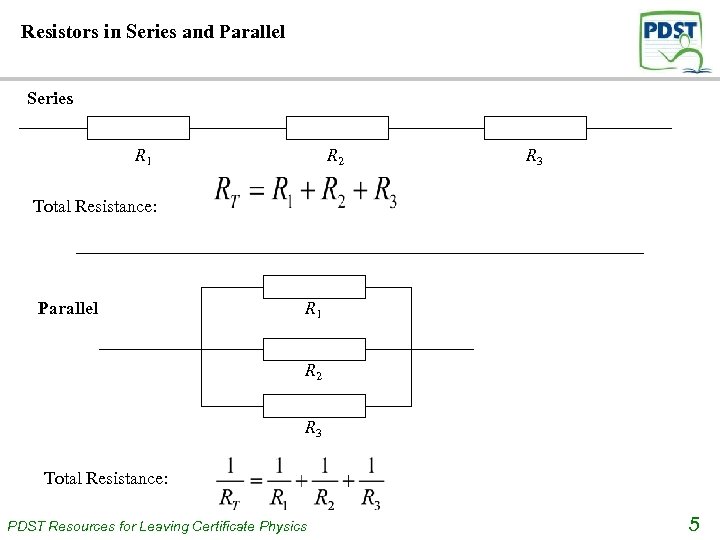 Resistors in Series and Parallel Series R 1 R 2 R 3 Total Resistance: Parallel R 1 R 2 R 3 Total Resistance: PDST Resources for Leaving Certificate Physics 5
Resistors in Series and Parallel Series R 1 R 2 R 3 Total Resistance: Parallel R 1 R 2 R 3 Total Resistance: PDST Resources for Leaving Certificate Physics 5
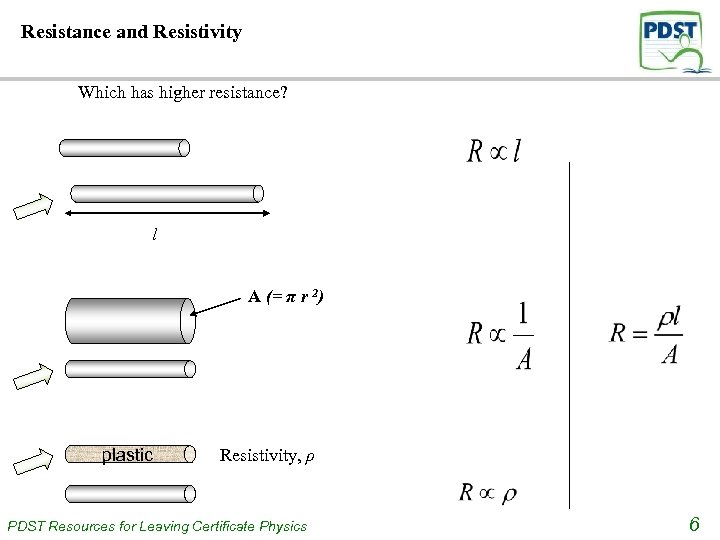 Resistance and Resistivity Which has higher resistance? l A (= π r 2) plastic Resistivity, ρ PDST Resources for Leaving Certificate Physics 6
Resistance and Resistivity Which has higher resistance? l A (= π r 2) plastic Resistivity, ρ PDST Resources for Leaving Certificate Physics 6
 2005, Q. 9 PDST Resources for Leaving Certificate Physics 7
2005, Q. 9 PDST Resources for Leaving Certificate Physics 7
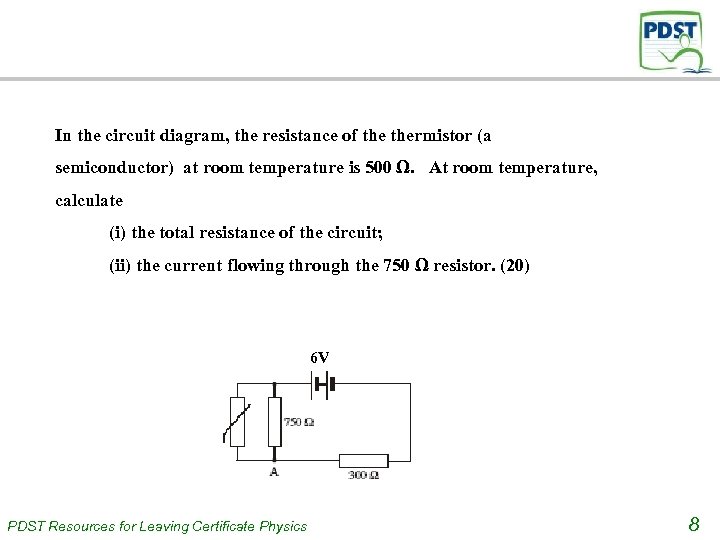 In the circuit diagram, the resistance of thermistor (a semiconductor) at room temperature is 500 Ω. At room temperature, calculate (i) the total resistance of the circuit; (ii) the current flowing through the 750 Ω resistor. (20) 6 V PDST Resources for Leaving Certificate Physics 8
In the circuit diagram, the resistance of thermistor (a semiconductor) at room temperature is 500 Ω. At room temperature, calculate (i) the total resistance of the circuit; (ii) the current flowing through the 750 Ω resistor. (20) 6 V PDST Resources for Leaving Certificate Physics 8
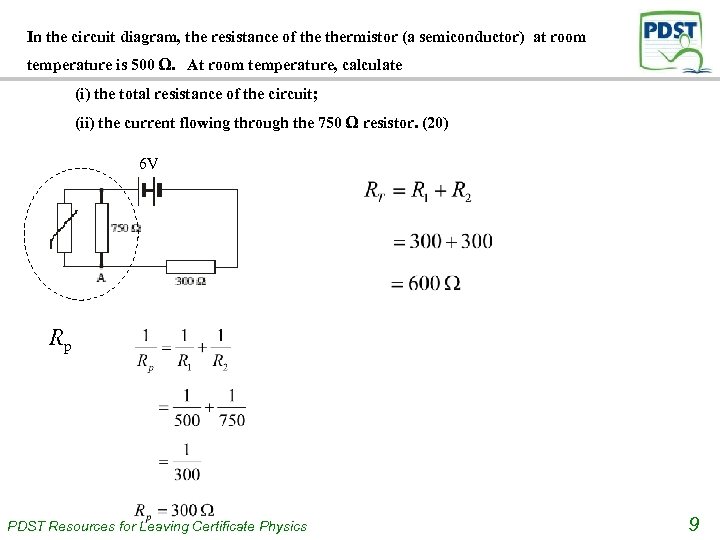 In the circuit diagram, the resistance of thermistor (a semiconductor) at room temperature is 500 Ω. At room temperature, calculate (i) the total resistance of the circuit; (ii) the current flowing through the 750 Ω resistor. (20) 6 V Rp PDST Resources for Leaving Certificate Physics 9
In the circuit diagram, the resistance of thermistor (a semiconductor) at room temperature is 500 Ω. At room temperature, calculate (i) the total resistance of the circuit; (ii) the current flowing through the 750 Ω resistor. (20) 6 V Rp PDST Resources for Leaving Certificate Physics 9
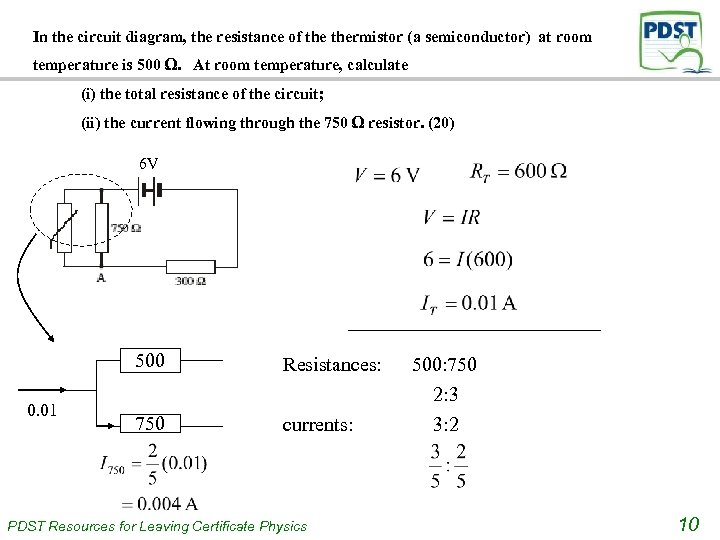 In the circuit diagram, the resistance of thermistor (a semiconductor) at room temperature is 500 Ω. At room temperature, calculate (i) the total resistance of the circuit; (ii) the current flowing through the 750 Ω resistor. (20) 6 V 500 0. 01 Resistances: 750 currents: PDST Resources for Leaving Certificate Physics 500: 750 2: 3 3: 2 10
In the circuit diagram, the resistance of thermistor (a semiconductor) at room temperature is 500 Ω. At room temperature, calculate (i) the total resistance of the circuit; (ii) the current flowing through the 750 Ω resistor. (20) 6 V 500 0. 01 Resistances: 750 currents: PDST Resources for Leaving Certificate Physics 500: 750 2: 3 3: 2 10
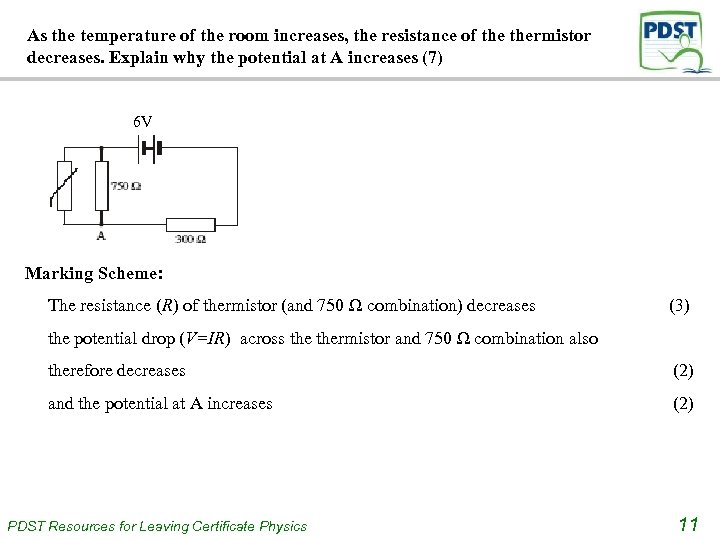 As the temperature of the room increases, the resistance of thermistor decreases. Explain why the potential at A increases (7) 6 V Marking Scheme: The resistance (R) of thermistor (and 750 Ω combination) decreases (3) the potential drop (V=IR) across thermistor and 750 Ω combination also therefore decreases (2) and the potential at A increases (2) PDST Resources for Leaving Certificate Physics 11
As the temperature of the room increases, the resistance of thermistor decreases. Explain why the potential at A increases (7) 6 V Marking Scheme: The resistance (R) of thermistor (and 750 Ω combination) decreases (3) the potential drop (V=IR) across thermistor and 750 Ω combination also therefore decreases (2) and the potential at A increases (2) PDST Resources for Leaving Certificate Physics 11