ec524c83f26849ba111ef25fff8c7b6d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 40
 Election of 1800: The Original “Real Housewives” or “Love and Hip-Hop” • Brutal Election between two former friends turned rivals… • John Adams (Federalist, President) v. Thomas Jefferson (Democratic Republican, VP) • Divisions between the two worsened by the Alien and Sedition Acts • Dirty Campaign: • Jefferson calls Adams a "hideous hermaphroditical character, which has neither the force and firmness of a man, nor the gentleness and sensibility of a woman. " • Adams Administration spreads rumor that Jefferson “had died” • Outcome: • Jefferson wins presidency; defeats John Adams • Election Establishes 2 Party System: Federalists v. Democratic Republicans • Despite Washington’s warning, was the formation of political parties inevitable? • Federalists (Hamilton/Adams) • Favor strong central government; a national bank; protective tariffs • Economic power = National power • Democratic-Republicans (Jefferson) • Limits on Federal Government; protect states rights o Daily Show: Richard Brookhiser Interview
Election of 1800: The Original “Real Housewives” or “Love and Hip-Hop” • Brutal Election between two former friends turned rivals… • John Adams (Federalist, President) v. Thomas Jefferson (Democratic Republican, VP) • Divisions between the two worsened by the Alien and Sedition Acts • Dirty Campaign: • Jefferson calls Adams a "hideous hermaphroditical character, which has neither the force and firmness of a man, nor the gentleness and sensibility of a woman. " • Adams Administration spreads rumor that Jefferson “had died” • Outcome: • Jefferson wins presidency; defeats John Adams • Election Establishes 2 Party System: Federalists v. Democratic Republicans • Despite Washington’s warning, was the formation of political parties inevitable? • Federalists (Hamilton/Adams) • Favor strong central government; a national bank; protective tariffs • Economic power = National power • Democratic-Republicans (Jefferson) • Limits on Federal Government; protect states rights o Daily Show: Richard Brookhiser Interview
 A Young Republic A Growing Nation…With Growing Tensions
A Young Republic A Growing Nation…With Growing Tensions
 Jefferson Administration (1801 -1809) • The Election of 1800 • A Bitter Battle That Changed The Constitution • 12 th Amendment • Creates separate ballots for President and Vice President • Thomas Jefferson: 3 rd President (1801 -1809) • Vision: Reduce Central Government/Preserve States’ Rights • • Naturalization Law of 1802 Reduce size of Army Eliminate internal taxes Seeks to decrease influence of national bank, but keeps it in place
Jefferson Administration (1801 -1809) • The Election of 1800 • A Bitter Battle That Changed The Constitution • 12 th Amendment • Creates separate ballots for President and Vice President • Thomas Jefferson: 3 rd President (1801 -1809) • Vision: Reduce Central Government/Preserve States’ Rights • • Naturalization Law of 1802 Reduce size of Army Eliminate internal taxes Seeks to decrease influence of national bank, but keeps it in place
 LOUISIANA PURCHASE
LOUISIANA PURCHASE
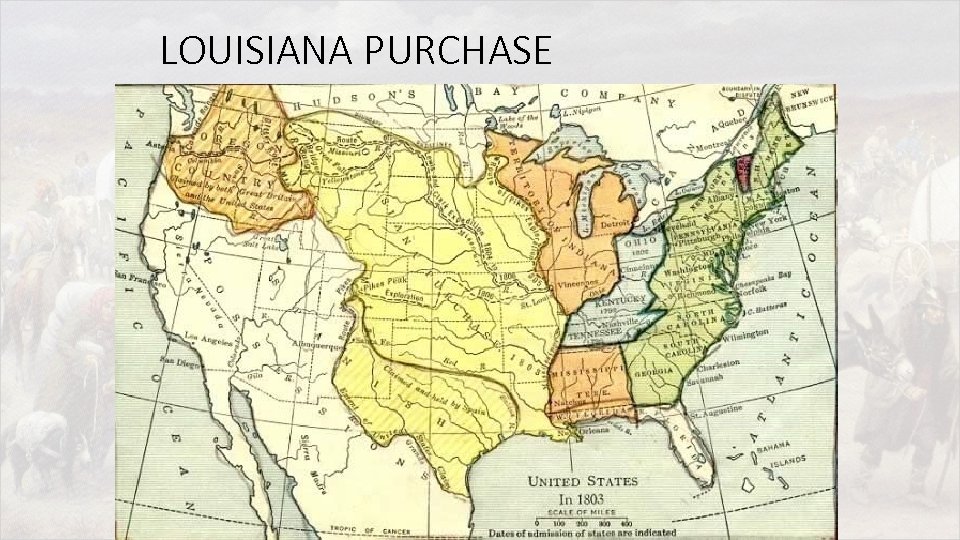
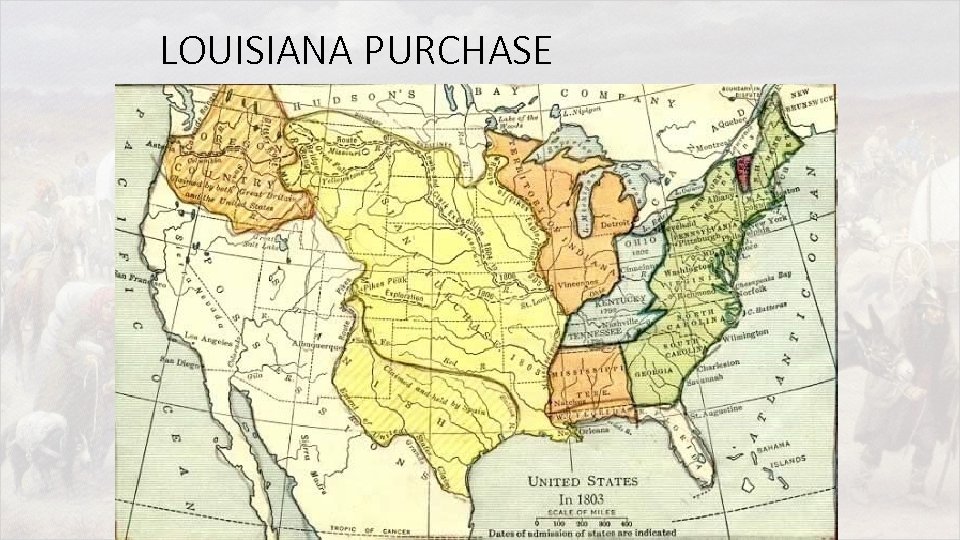
 Jefferson and the Louisiana Purchase • Who: • U. S. (Jefferson) & France (Napoleon) • What: • Acquisition of the Louisiana Territory from the French for $15 million • Why would Napoleon be willing to sell this land? • When: • 1803 • Where: • Louisiana Territory (today all/part of 15 different states west of the Mississippi River) • Why was the Louisiana Purchase significant? • Doubled the size of the US (largest single land acquisition in nation’s history) • Sets precedent for future land acquisitions and incorporation of territories as equal states • Gave the U. S. control of the Mississippi River…one of the richest river valleys in the world! • Ejected any remaining French influence from North America…while avoiding alliance with Brits (Allows US to pursue isolationist policy in future toward Europe)
Jefferson and the Louisiana Purchase • Who: • U. S. (Jefferson) & France (Napoleon) • What: • Acquisition of the Louisiana Territory from the French for $15 million • Why would Napoleon be willing to sell this land? • When: • 1803 • Where: • Louisiana Territory (today all/part of 15 different states west of the Mississippi River) • Why was the Louisiana Purchase significant? • Doubled the size of the US (largest single land acquisition in nation’s history) • Sets precedent for future land acquisitions and incorporation of territories as equal states • Gave the U. S. control of the Mississippi River…one of the richest river valleys in the world! • Ejected any remaining French influence from North America…while avoiding alliance with Brits (Allows US to pursue isolationist policy in future toward Europe)
 LOUISIANA PURCHASE
LOUISIANA PURCHASE
 Supreme Court Strengthens the Federal Govt. • Not only was the nation growing in size, but the federal government was growing in strength…despite Jefferson’s wishes… • Marshall: 34 Years of Federalist Decisions…a man who outlived his party… • Chief Justice John Marshall (Supreme Court)…Federalist Mainstay • Marbury v. Madison (1803) • Who had final authority to determine the meaning of the Constitution…up until 1803, Jefferson proposed in Kentucky Resolutions that it be the states…now new concept emerged, judicial review • Established Judicial Review—power of the court to declare a law unconstitutional • Mc. Culloch v. Maryland • Upheld the Necessary and Proper Clause and the Supremacy Clause of the Constitution • Cohens v. Virginia • Sup. Ct. has right to review decision of state supreme courts in all cases involving powers of fed. government • Gibbons v. Ogden • Upheld Congress’ power to regulate interstate commerce (trade between states)
Supreme Court Strengthens the Federal Govt. • Not only was the nation growing in size, but the federal government was growing in strength…despite Jefferson’s wishes… • Marshall: 34 Years of Federalist Decisions…a man who outlived his party… • Chief Justice John Marshall (Supreme Court)…Federalist Mainstay • Marbury v. Madison (1803) • Who had final authority to determine the meaning of the Constitution…up until 1803, Jefferson proposed in Kentucky Resolutions that it be the states…now new concept emerged, judicial review • Established Judicial Review—power of the court to declare a law unconstitutional • Mc. Culloch v. Maryland • Upheld the Necessary and Proper Clause and the Supremacy Clause of the Constitution • Cohens v. Virginia • Sup. Ct. has right to review decision of state supreme courts in all cases involving powers of fed. government • Gibbons v. Ogden • Upheld Congress’ power to regulate interstate commerce (trade between states)
 Trouble Brewing with England…Again • The War in Europe… • France controls the land, Britain the Sea • British Orders of Council (1806) • Closed European ports under French control to foreign shipping, including US, unless vessels first stop at British port • Napolean orders capture of any ships entering British ports… • Impressment of American Sailors • Chesapeake Affair • Brits fire on American ship, kill 3 Americans, after demanding turnover of 4 sailors • Jefferson Responds w/ Embargo Act…fails badly
Trouble Brewing with England…Again • The War in Europe… • France controls the land, Britain the Sea • British Orders of Council (1806) • Closed European ports under French control to foreign shipping, including US, unless vessels first stop at British port • Napolean orders capture of any ships entering British ports… • Impressment of American Sailors • Chesapeake Affair • Brits fire on American ship, kill 3 Americans, after demanding turnover of 4 sailors • Jefferson Responds w/ Embargo Act…fails badly
 James Madison Administration (1809 -1817) • James Madison: 4 th President • Author of Federalist Papers • “Father of the Constitution” • Macon’s Bill #2 • Reopens trade w/ world, even GB & FR if they repeal their commercial restrictions… • FR sees its chance… • BR refuse…having control of the seas • US reestablishes Embargo on Britain…end of American neutrality
James Madison Administration (1809 -1817) • James Madison: 4 th President • Author of Federalist Papers • “Father of the Constitution” • Macon’s Bill #2 • Reopens trade w/ world, even GB & FR if they repeal their commercial restrictions… • FR sees its chance… • BR refuse…having control of the seas • US reestablishes Embargo on Britain…end of American neutrality
 James Madison & War of 1812 • Inching toward War • Growing Tension w/ Natives over American encroachment…natives side with British…Madison views it essential to take out “Native Base” in Canada • Nation Split • South and West Support & many Republicans • North and most Federalists oppose… • War of 1812: “ 2 nd War for Independence”…or an Imperialist War? • Madison seeks to restore confidence in “Republican Experiment” • Significance of War of 1812 • Showed Weaknesses in U. S. —Had to be addressed • National Roads, Stronger Army • • Increased World Respect Spurs Industrialization…and Efforts to protect American Industry (Tariff of 1816) Led to collapse of the Federalist Party (Hartford Resolutions)…NE threaten secession Increased U. S. Nationalism
James Madison & War of 1812 • Inching toward War • Growing Tension w/ Natives over American encroachment…natives side with British…Madison views it essential to take out “Native Base” in Canada • Nation Split • South and West Support & many Republicans • North and most Federalists oppose… • War of 1812: “ 2 nd War for Independence”…or an Imperialist War? • Madison seeks to restore confidence in “Republican Experiment” • Significance of War of 1812 • Showed Weaknesses in U. S. —Had to be addressed • National Roads, Stronger Army • • Increased World Respect Spurs Industrialization…and Efforts to protect American Industry (Tariff of 1816) Led to collapse of the Federalist Party (Hartford Resolutions)…NE threaten secession Increased U. S. Nationalism
 James Monroe (1817 -1825) • Adams-Onis Treaty • Anglo American Convention • MONROE DOCTRINE (1823) • Stated that further efforts by European nations to colonize land or interfere with states in North or South America would be viewed as acts of aggression, requiring U. S. intervention • US = “New Boss” in Town • Threat more symbolic in nature…why? • Monroe: “Era of Good Feelings”… American Nationalism • One-party rule w/ fall of Feds. • But behind scenes sectional tensions rising
James Monroe (1817 -1825) • Adams-Onis Treaty • Anglo American Convention • MONROE DOCTRINE (1823) • Stated that further efforts by European nations to colonize land or interfere with states in North or South America would be viewed as acts of aggression, requiring U. S. intervention • US = “New Boss” in Town • Threat more symbolic in nature…why? • Monroe: “Era of Good Feelings”… American Nationalism • One-party rule w/ fall of Feds. • But behind scenes sectional tensions rising
 Election of 1824 • Election: • Electoral Vote: • Jackson— 89; JQ Adams--84 ; Will Crawford— 41; Henry Clay— 37 (all claim to be Republicans • Popular vote: • Jackson 41. 3%; Adams 30. 9%; Crawford— 11. 2; Clay— 13% • Election thrown to House of Reps…must choose from top 3 candidates • Who is Speaker of the House? • Henry Clay…Say Whaaaattt… • Throws support behind Adams (didn’t like Jackson) • Corrupt Bargain? Clay chosen as Adams Sec. of State…Jacksonians In uproar • Adams…Great Sec. of State…Bad President • Adams Nationalism flies in face of States’ Rights • Calls on Congress for national roads, canals; proposal for national university • South fears these initiatives require more federal $. . . which could mean more tariffs…
Election of 1824 • Election: • Electoral Vote: • Jackson— 89; JQ Adams--84 ; Will Crawford— 41; Henry Clay— 37 (all claim to be Republicans • Popular vote: • Jackson 41. 3%; Adams 30. 9%; Crawford— 11. 2; Clay— 13% • Election thrown to House of Reps…must choose from top 3 candidates • Who is Speaker of the House? • Henry Clay…Say Whaaaattt… • Throws support behind Adams (didn’t like Jackson) • Corrupt Bargain? Clay chosen as Adams Sec. of State…Jacksonians In uproar • Adams…Great Sec. of State…Bad President • Adams Nationalism flies in face of States’ Rights • Calls on Congress for national roads, canals; proposal for national university • South fears these initiatives require more federal $. . . which could mean more tariffs…
 Election of 1828 • Republican Party Splits • National Republicans side with Adams • Democratic Republicans side with Jackson • Mudslinging • Adams camp calls Jackson’s mother a prostitute, wife an adultress • Jackson camp accuse Adams of procuring servant girl for Russian Tsar • Sectional Election • Jackson wins South and West • Adams wins New England • Jackson wins in landslide…
Election of 1828 • Republican Party Splits • National Republicans side with Adams • Democratic Republicans side with Jackson • Mudslinging • Adams camp calls Jackson’s mother a prostitute, wife an adultress • Jackson camp accuse Adams of procuring servant girl for Russian Tsar • Sectional Election • Jackson wins South and West • Adams wins New England • Jackson wins in landslide…
 Andrew Jackson: Election of 1828 • Election of 1828 • Suffrage Expanded…all white males…Jackson benefits… • Estbl. Democratic Party • Jackson employs “Spoils System” • Andrew Jackson: Indian Removal Act (1830)— Why? • Opens 25 million acres to white settlement/ slavery…discovery of gold in Georgia • Forced Move Natives west of MS River onto reservations • Worcester v. Georgia (1832) • Jackson fails to enforce ct. decision
Andrew Jackson: Election of 1828 • Election of 1828 • Suffrage Expanded…all white males…Jackson benefits… • Estbl. Democratic Party • Jackson employs “Spoils System” • Andrew Jackson: Indian Removal Act (1830)— Why? • Opens 25 million acres to white settlement/ slavery…discovery of gold in Georgia • Forced Move Natives west of MS River onto reservations • Worcester v. Georgia (1832) • Jackson fails to enforce ct. decision
 “To the Cherokee Tribe of Indians” Andrew Jackson--1835 • “I have no motive to deceive you. . . I tell you that you cannot remain where you now are. . . You have but one remedy within your reach. And that is, to remove to the west and join your countrymen, who are already established there. ” • “The choice now is before you. . . As certain as the sun shines to guide you in your path, so certain is it that you cannot drive back the laws of Georgia from among you. Look at the condition of the Creeks. . . their young men are committing depredations upon the property of our citizens, and are shedding their blood. This cannot and will not be allowed. Punishment will follow… Your young men will commit the same acts, and the same consequences must ensue…Look at your condition as it now is, and then consider what it will be if you follow the advice I give you. ”
“To the Cherokee Tribe of Indians” Andrew Jackson--1835 • “I have no motive to deceive you. . . I tell you that you cannot remain where you now are. . . You have but one remedy within your reach. And that is, to remove to the west and join your countrymen, who are already established there. ” • “The choice now is before you. . . As certain as the sun shines to guide you in your path, so certain is it that you cannot drive back the laws of Georgia from among you. Look at the condition of the Creeks. . . their young men are committing depredations upon the property of our citizens, and are shedding their blood. This cannot and will not be allowed. Punishment will follow… Your young men will commit the same acts, and the same consequences must ensue…Look at your condition as it now is, and then consider what it will be if you follow the advice I give you. ”
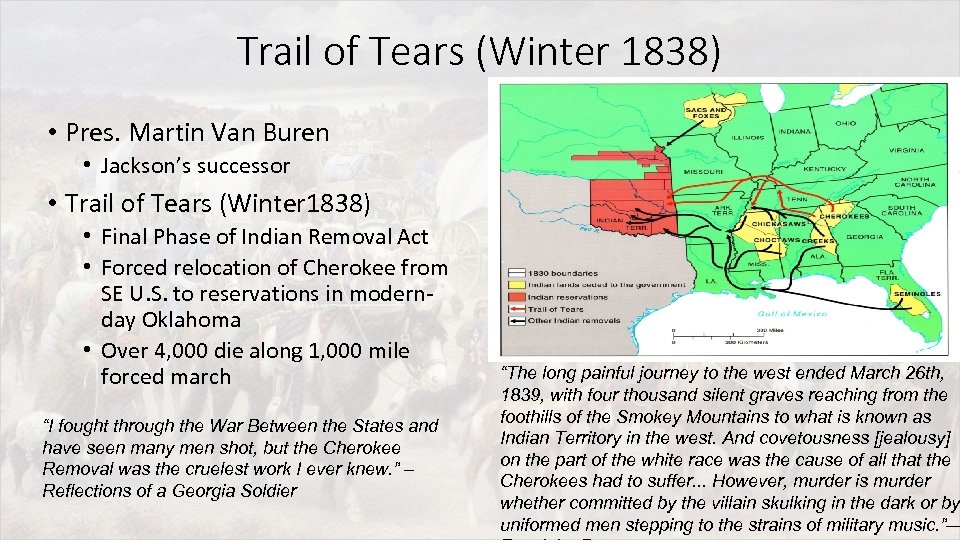 Trail of Tears (Winter 1838) • Pres. Martin Van Buren • Jackson’s successor • Trail of Tears (Winter 1838) • Final Phase of Indian Removal Act • Forced relocation of Cherokee from SE U. S. to reservations in modernday Oklahoma • Over 4, 000 die along 1, 000 mile forced march “I fought through the War Between the States and have seen many men shot, but the Cherokee Removal was the cruelest work I ever knew. ” – Reflections of a Georgia Soldier “The long painful journey to the west ended March 26 th, 1839, with four thousand silent graves reaching from the foothills of the Smokey Mountains to what is known as Indian Territory in the west. And covetousness [jealousy] on the part of the white race was the cause of all that the Cherokees had to suffer. . . However, murder is murder whether committed by the villain skulking in the dark or by uniformed men stepping to the strains of military music. ”—
Trail of Tears (Winter 1838) • Pres. Martin Van Buren • Jackson’s successor • Trail of Tears (Winter 1838) • Final Phase of Indian Removal Act • Forced relocation of Cherokee from SE U. S. to reservations in modernday Oklahoma • Over 4, 000 die along 1, 000 mile forced march “I fought through the War Between the States and have seen many men shot, but the Cherokee Removal was the cruelest work I ever knew. ” – Reflections of a Georgia Soldier “The long painful journey to the west ended March 26 th, 1839, with four thousand silent graves reaching from the foothills of the Smokey Mountains to what is known as Indian Territory in the west. And covetousness [jealousy] on the part of the white race was the cause of all that the Cherokees had to suffer. . . However, murder is murder whether committed by the villain skulking in the dark or by uniformed men stepping to the strains of military music. ”—
 Tariffs: Rising Tension between North and South • Tariff of 1828…Why does Congress Pass? – Protect American Industry…who supports? Who opposes? Why? – Raises cost of importing in South…thus… – ↓in Brit. Exports; Brits ↓ $ to buy Southern cotton • South Carolina Threatens Secession – “Tariff of Abominations” – S. C. blame ↓ economy on tariffs – “Being drowned out by Yankee Industrialists” • Vice Pres. John C. Calhoun – Poses idea of nullification – What was idea of nullification? VP: John C. Calhoun
Tariffs: Rising Tension between North and South • Tariff of 1828…Why does Congress Pass? – Protect American Industry…who supports? Who opposes? Why? – Raises cost of importing in South…thus… – ↓in Brit. Exports; Brits ↓ $ to buy Southern cotton • South Carolina Threatens Secession – “Tariff of Abominations” – S. C. blame ↓ economy on tariffs – “Being drowned out by Yankee Industrialists” • Vice Pres. John C. Calhoun – Poses idea of nullification – What was idea of nullification? VP: John C. Calhoun
 “Nullification Crisis” • 1832 Revised Tariff Passed • S. C. Legislature: Votes to nullify the law • Andrew Jackson’s Response: • Nullification = Act of Treason by SC • Sends Battleship to Charleston, SC • Clay’s Compromise • Gradually ↓ tariffs; SC repeals nullification • Significance? • Symbolized the growing divide between N. & S. • Force Bill: Congress authorizes president to have power to use military force to collect customs duties
“Nullification Crisis” • 1832 Revised Tariff Passed • S. C. Legislature: Votes to nullify the law • Andrew Jackson’s Response: • Nullification = Act of Treason by SC • Sends Battleship to Charleston, SC • Clay’s Compromise • Gradually ↓ tariffs; SC repeals nullification • Significance? • Symbolized the growing divide between N. & S. • Force Bill: Congress authorizes president to have power to use military force to collect customs duties
 Rising Sectionalism North • Economy • More Industry • Industrial Revolution • Labor • Skilled/Unskilled Workers • Blending cultures… • Union takes Priority South • Economy • Agricultural • Eli Whitney: Cotton Gin • Labor • Slave Labor • Antiquated Social Order • States Rights • ↓ Authority/Nullification • Support Tariffs…why? • Oppose Tariffs…why?
Rising Sectionalism North • Economy • More Industry • Industrial Revolution • Labor • Skilled/Unskilled Workers • Blending cultures… • Union takes Priority South • Economy • Agricultural • Eli Whitney: Cotton Gin • Labor • Slave Labor • Antiquated Social Order • States Rights • ↓ Authority/Nullification • Support Tariffs…why? • Oppose Tariffs…why?
 Rise of the Whig Party
Rise of the Whig Party

 Brief Review • What was the significance of the Louisiana Purchase? • What was the significance of the War of 1812? • What was the Monroe Doctrine? Who did the US depend on to enforce the doctrine? • Why might the election of 1824 be considered a disputed election? • Who won the election of 1828? Why was this election significant? • What was Andrew Jackson’s policy toward Native Americans? • What was the Nullification Crisis? What triggered it? Why was it significant? • What were 3 differences between North and South that caused growing tensions between the two halves of the country?
Brief Review • What was the significance of the Louisiana Purchase? • What was the significance of the War of 1812? • What was the Monroe Doctrine? Who did the US depend on to enforce the doctrine? • Why might the election of 1824 be considered a disputed election? • Who won the election of 1828? Why was this election significant? • What was Andrew Jackson’s policy toward Native Americans? • What was the Nullification Crisis? What triggered it? Why was it significant? • What were 3 differences between North and South that caused growing tensions between the two halves of the country?
 Roots of the Civil War Re-emerging Sectionalism
Roots of the Civil War Re-emerging Sectionalism
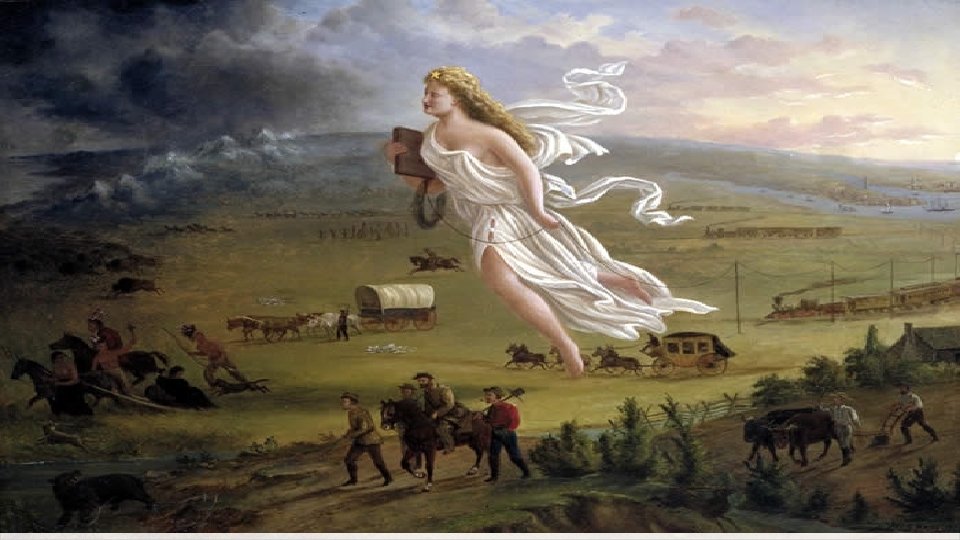
 Painting Analysis Prompts • The painting is titled, Manifest Destiny. What is the definition of Manifest Destiny? • How does the painting demonstrate the concept of Manifest Destiny? (What are some specific images in the painting that illustrate the idea of Manifest Destiny? ) • Who or what (image) dominates the painting? Why? • What info can we gather from the painting?
Painting Analysis Prompts • The painting is titled, Manifest Destiny. What is the definition of Manifest Destiny? • How does the painting demonstrate the concept of Manifest Destiny? (What are some specific images in the painting that illustrate the idea of Manifest Destiny? ) • Who or what (image) dominates the painting? Why? • What info can we gather from the painting?

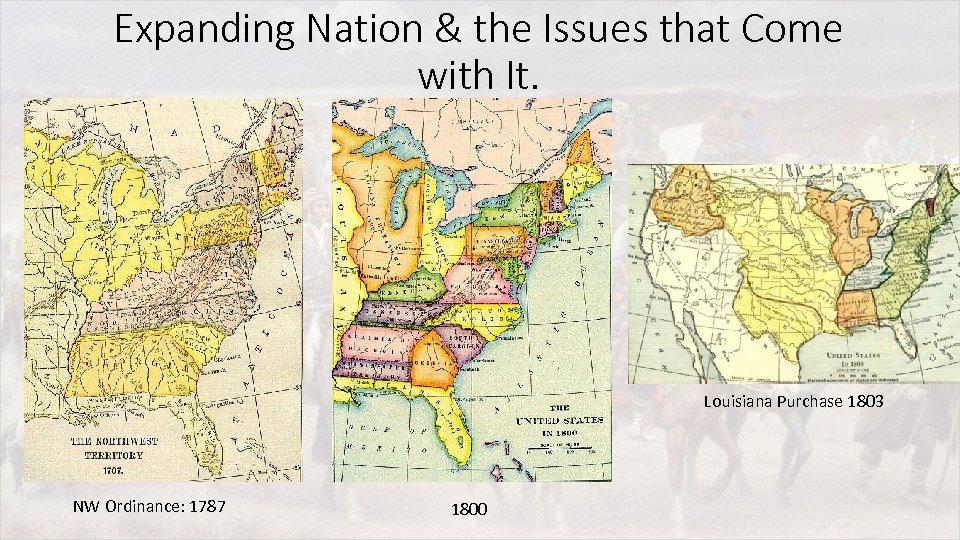 Expanding Nation & the Issues that Come with It. Louisiana Purchase 1803 NW Ordinance: 1787 1800
Expanding Nation & the Issues that Come with It. Louisiana Purchase 1803 NW Ordinance: 1787 1800
 Westward Expansion • What factors contribute to U. S. westward expansion? – Improving transportation (steamboat, Cumberland Road, – Cheap Land – Pacification of Natives by Harrison and Jackson – Resources – Manifest Destiny • As territories grow, they can apply for statehood…what’s the big question? – Should slavery expand into the region?
Westward Expansion • What factors contribute to U. S. westward expansion? – Improving transportation (steamboat, Cumberland Road, – Cheap Land – Pacification of Natives by Harrison and Jackson – Resources – Manifest Destiny • As territories grow, they can apply for statehood…what’s the big question? – Should slavery expand into the region?
 America in 1819 • 11 Free States – New Hampshire – Vermont – Massachusetts – Rhode Island – Connecticut – New York – New Jersey – Pennsylvania – Ohio – Indiana – Illinois • 11 Slave States 1819: Missouri Applies for Statehood as a Slave State…Denied…What’s the issue? – Delaware – Maryland – Virginia – Kentucky – Tennessee – North Carolina – South Carolina – Georgia – Alabama – Mississippi – Louisiana
America in 1819 • 11 Free States – New Hampshire – Vermont – Massachusetts – Rhode Island – Connecticut – New York – New Jersey – Pennsylvania – Ohio – Indiana – Illinois • 11 Slave States 1819: Missouri Applies for Statehood as a Slave State…Denied…What’s the issue? – Delaware – Maryland – Virginia – Kentucky – Tennessee – North Carolina – South Carolina – Georgia – Alabama – Mississippi – Louisiana
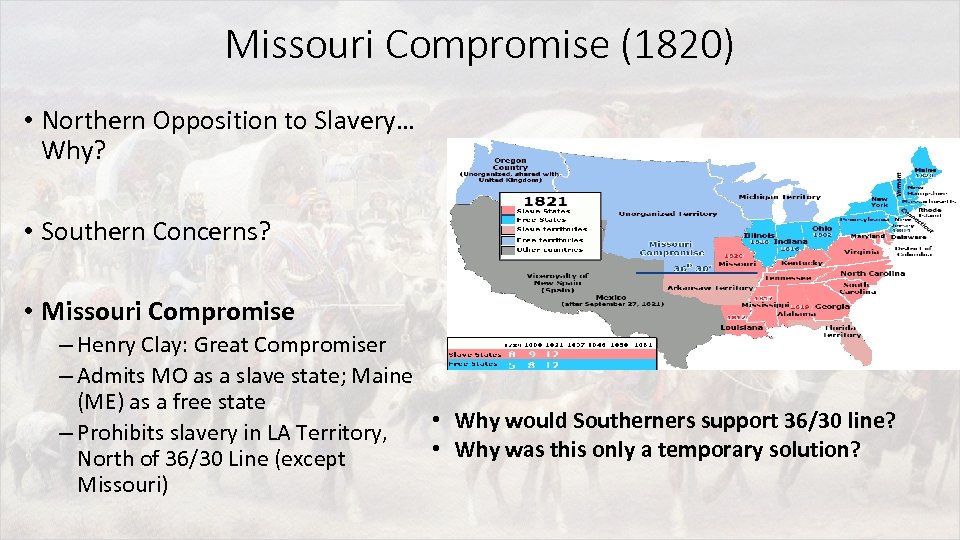 Missouri Compromise (1820) • Northern Opposition to Slavery… Why? • Southern Concerns? • Missouri Compromise – Henry Clay: Great Compromiser – Admits MO as a slave state; Maine (ME) as a free state • Why would Southerners support 36/30 line? – Prohibits slavery in LA Territory, • Why was this only a temporary solution? North of 36/30 Line (except Missouri)
Missouri Compromise (1820) • Northern Opposition to Slavery… Why? • Southern Concerns? • Missouri Compromise – Henry Clay: Great Compromiser – Admits MO as a slave state; Maine (ME) as a free state • Why would Southerners support 36/30 line? – Prohibits slavery in LA Territory, • Why was this only a temporary solution? North of 36/30 Line (except Missouri)
 A Divided Nation Effects Texas War for Independence and Mexican. American War
A Divided Nation Effects Texas War for Independence and Mexican. American War
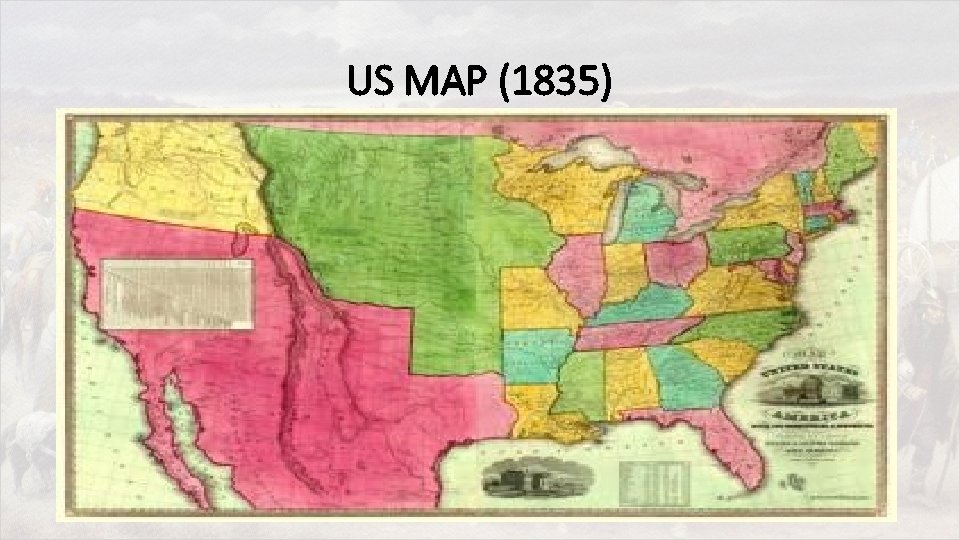 US MAP (1835)
US MAP (1835)
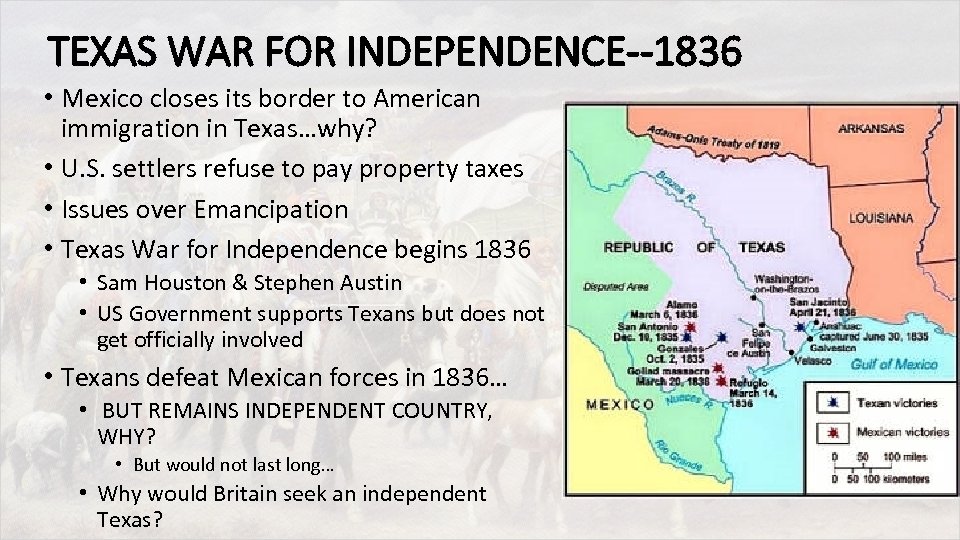 TEXAS WAR FOR INDEPENDENCE--1836 • Mexico closes its border to American immigration in Texas…why? • U. S. settlers refuse to pay property taxes • Issues over Emancipation • Texas War for Independence begins 1836 • Sam Houston & Stephen Austin • US Government supports Texans but does not get officially involved • Texans defeat Mexican forces in 1836… • BUT REMAINS INDEPENDENT COUNTRY, WHY? • But would not last long… • Why would Britain seek an independent Texas?
TEXAS WAR FOR INDEPENDENCE--1836 • Mexico closes its border to American immigration in Texas…why? • U. S. settlers refuse to pay property taxes • Issues over Emancipation • Texas War for Independence begins 1836 • Sam Houston & Stephen Austin • US Government supports Texans but does not get officially involved • Texans defeat Mexican forces in 1836… • BUT REMAINS INDEPENDENT COUNTRY, WHY? • But would not last long… • Why would Britain seek an independent Texas?
 The Mexican-American War
The Mexican-American War
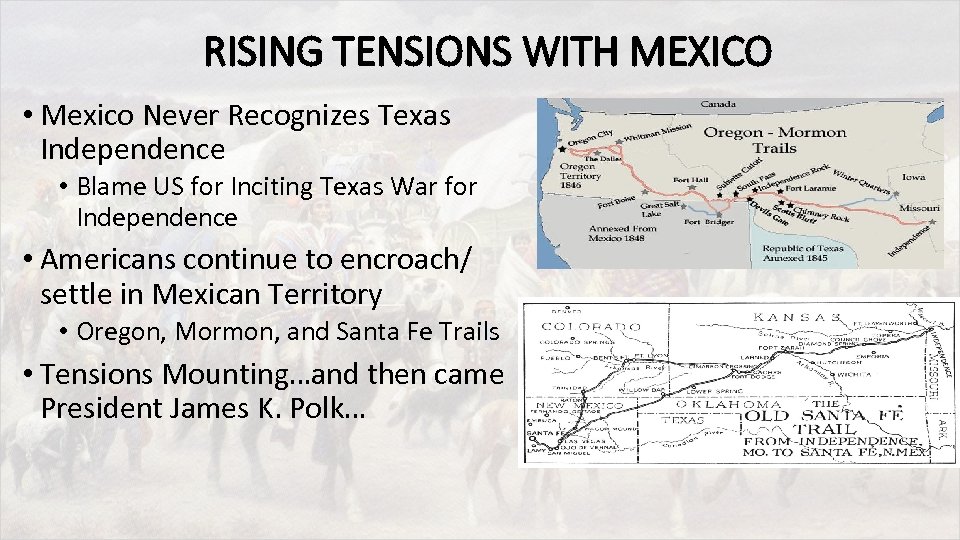 RISING TENSIONS WITH MEXICO • Mexico Never Recognizes Texas Independence • Blame US for Inciting Texas War for Independence • Americans continue to encroach/ settle in Mexican Territory • Oregon, Mormon, and Santa Fe Trails • Tensions Mounting…and then came President James K. Polk…
RISING TENSIONS WITH MEXICO • Mexico Never Recognizes Texas Independence • Blame US for Inciting Texas War for Independence • Americans continue to encroach/ settle in Mexican Territory • Oregon, Mormon, and Santa Fe Trails • Tensions Mounting…and then came President James K. Polk…
 President James K. Polk (1845 -1849) • James K. Polk: Elected in 1844 • Ardent follower of Manifest Destiny • Annexes Texas in 1845…why now? • Wisconsin’s planned admission in 1848 • Coincides with impending acquisition of Oregon in deal with British • Why did this bring tensions with Mexico to a boiling point? • Polk sets his eyes on California next…Why? • Tries to buy; Mexico Declines • Polk Enraged…believes it’s Americas right… • So what does Polk decide to do? • Why is starting a war tricky business? • How do you get people to buy in then?
President James K. Polk (1845 -1849) • James K. Polk: Elected in 1844 • Ardent follower of Manifest Destiny • Annexes Texas in 1845…why now? • Wisconsin’s planned admission in 1848 • Coincides with impending acquisition of Oregon in deal with British • Why did this bring tensions with Mexico to a boiling point? • Polk sets his eyes on California next…Why? • Tries to buy; Mexico Declines • Polk Enraged…believes it’s Americas right… • So what does Polk decide to do? • Why is starting a war tricky business? • How do you get people to buy in then?
 MEXICAN WAR (1846 -1848) • Abraham Lincoln Emerges • Rep. from Illinois • Questions events leading up to war. • Questions the Constitutionality of the war and Polk’s Motivations. • Why did anti-slavery groups oppose the Mexican American War? • How do you pay for a war? • Raising taxes to pay for war in the South seems “fishy” to northerners (THOREAU)
MEXICAN WAR (1846 -1848) • Abraham Lincoln Emerges • Rep. from Illinois • Questions events leading up to war. • Questions the Constitutionality of the war and Polk’s Motivations. • Why did anti-slavery groups oppose the Mexican American War? • How do you pay for a war? • Raising taxes to pay for war in the South seems “fishy” to northerners (THOREAU)
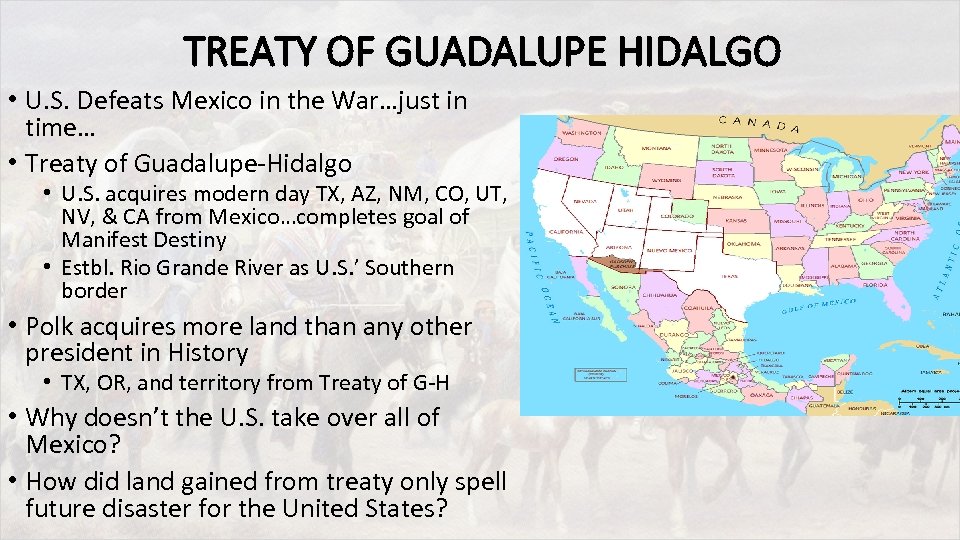 TREATY OF GUADALUPE HIDALGO • U. S. Defeats Mexico in the War…just in time… • Treaty of Guadalupe-Hidalgo • U. S. acquires modern day TX, AZ, NM, CO, UT, NV, & CA from Mexico…completes goal of Manifest Destiny • Estbl. Rio Grande River as U. S. ’ Southern border • Polk acquires more land than any other president in History • TX, OR, and territory from Treaty of G-H • Why doesn’t the U. S. take over all of Mexico? • How did land gained from treaty only spell future disaster for the United States?
TREATY OF GUADALUPE HIDALGO • U. S. Defeats Mexico in the War…just in time… • Treaty of Guadalupe-Hidalgo • U. S. acquires modern day TX, AZ, NM, CO, UT, NV, & CA from Mexico…completes goal of Manifest Destiny • Estbl. Rio Grande River as U. S. ’ Southern border • Polk acquires more land than any other president in History • TX, OR, and territory from Treaty of G-H • Why doesn’t the U. S. take over all of Mexico? • How did land gained from treaty only spell future disaster for the United States?
 Short and Long Term Effects of the Mexican. American War • “Mexico will poison us”—Ralph Waldo Emerson • 13, 000 Americans dead (most from disease) • America’s total territory increased by 1/3 (even larger than LA Territory) • Test run for officers who served in Civil War • Estbl. Of new Naval Academy at Annapolis • Increased respect for US internationally from military standpoint • Marked turn for worse in relationship between US and Latin America…US viewed as greedy bully • Most importantly…fueled tensions over slavery
Short and Long Term Effects of the Mexican. American War • “Mexico will poison us”—Ralph Waldo Emerson • 13, 000 Americans dead (most from disease) • America’s total territory increased by 1/3 (even larger than LA Territory) • Test run for officers who served in Civil War • Estbl. Of new Naval Academy at Annapolis • Increased respect for US internationally from military standpoint • Marked turn for worse in relationship between US and Latin America…US viewed as greedy bully • Most importantly…fueled tensions over slavery
 Wilmot Proviso • Abolitionists perceive war as provoked by southern slave interests • Wilmot Proviso (David Wilmot) • Proposed law in Congress • Calls for banning of slavery in any territory gained from MX • Supported by Lincoln…Remember for later and why Southerners secede with his election… • Southerners Enraged…Rising Tensions • “Congress has NO authority to ban slavery” • Wilmot Proviso…blocked by Senate • Cass Compromise • Citizens should decide issue of slavery in territories thru popular vote by local populations Rep. David Wilmot
Wilmot Proviso • Abolitionists perceive war as provoked by southern slave interests • Wilmot Proviso (David Wilmot) • Proposed law in Congress • Calls for banning of slavery in any territory gained from MX • Supported by Lincoln…Remember for later and why Southerners secede with his election… • Southerners Enraged…Rising Tensions • “Congress has NO authority to ban slavery” • Wilmot Proviso…blocked by Senate • Cass Compromise • Citizens should decide issue of slavery in territories thru popular vote by local populations Rep. David Wilmot
 Abolitionist Movement Jigsaw • For your assigned portion of the reading…complete the following • • Identify your section of the Abolitionist Movement What were the main strategies your group pursued? Who did they target? What barriers did your group face? • Summary Question • To what extent was the rise of the Abolitionist Movement a factor in the outbreak of the Civil War/Southern Secession.
Abolitionist Movement Jigsaw • For your assigned portion of the reading…complete the following • • Identify your section of the Abolitionist Movement What were the main strategies your group pursued? Who did they target? What barriers did your group face? • Summary Question • To what extent was the rise of the Abolitionist Movement a factor in the outbreak of the Civil War/Southern Secession.


