ce2ba6fae980f2ff3c6380be125eeb56.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20
 ELearning Frameworks and e. Admin Hugh Davis Event
ELearning Frameworks and e. Admin Hugh Davis Event
 The Research Questions • What is the ELearning Framework? • How does an Service Oriented Architecture improve the implementation of e. Learning? • What are the design methods being used and will they work? Event
The Research Questions • What is the ELearning Framework? • How does an Service Oriented Architecture improve the implementation of e. Learning? • What are the design methods being used and will they work? Event
 The Primary Focus of VLEs/MLEs/Portals • VLEs – Tools to ease the teachers job in managing web based learning • • • Module Organisation Sequencing of Leaning Content Delivery Intra Class Communication (Synchronous and Asynchronous) Assessment MLEs – Tools to integrate the VLE with the Enterprise systems • Student information systems • Fees systems • Gradebooks • Portals – Provide a customisable “doorway” onto relevant links, services & searches • Library, ISS, etc • Community services (bulletin boards, email, for-sale lists, events) • School websites, Blackboard etc Event 3
The Primary Focus of VLEs/MLEs/Portals • VLEs – Tools to ease the teachers job in managing web based learning • • • Module Organisation Sequencing of Leaning Content Delivery Intra Class Communication (Synchronous and Asynchronous) Assessment MLEs – Tools to integrate the VLE with the Enterprise systems • Student information systems • Fees systems • Gradebooks • Portals – Provide a customisable “doorway” onto relevant links, services & searches • Library, ISS, etc • Community services (bulletin boards, email, for-sale lists, events) • School websites, Blackboard etc Event 3
 The E-Learning Framework • The ELF is an – – international effort to develop a service-orientated approach to the development and integration of computer systems in the sphere of learning, research and education administration. • A kind of Pick and Mix VLE! – Open Source – Community Design Event
The E-Learning Framework • The ELF is an – – international effort to develop a service-orientated approach to the development and integration of computer systems in the sphere of learning, research and education administration. • A kind of Pick and Mix VLE! – Open Source – Community Design Event
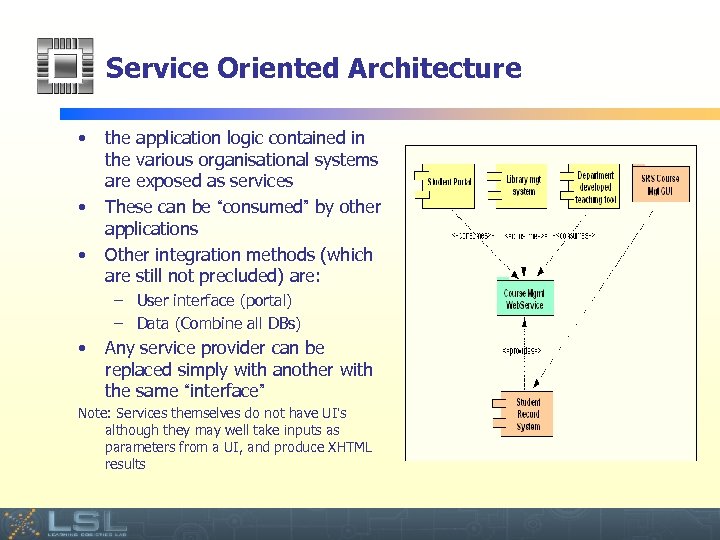 Service Oriented Architecture • • • the application logic contained in the various organisational systems are exposed as services These can be “consumed” by other applications Other integration methods (which are still not precluded) are: – User interface (portal) – Data (Combine all DBs) • Any service provider can be replaced simply with another with the same “interface” Note: Services themselves do not have UI’s although they may well take inputs as parameters from a UI, and produce XHTML results Event
Service Oriented Architecture • • • the application logic contained in the various organisational systems are exposed as services These can be “consumed” by other applications Other integration methods (which are still not precluded) are: – User interface (portal) – Data (Combine all DBs) • Any service provider can be replaced simply with another with the same “interface” Note: Services themselves do not have UI’s although they may well take inputs as parameters from a UI, and produce XHTML results Event
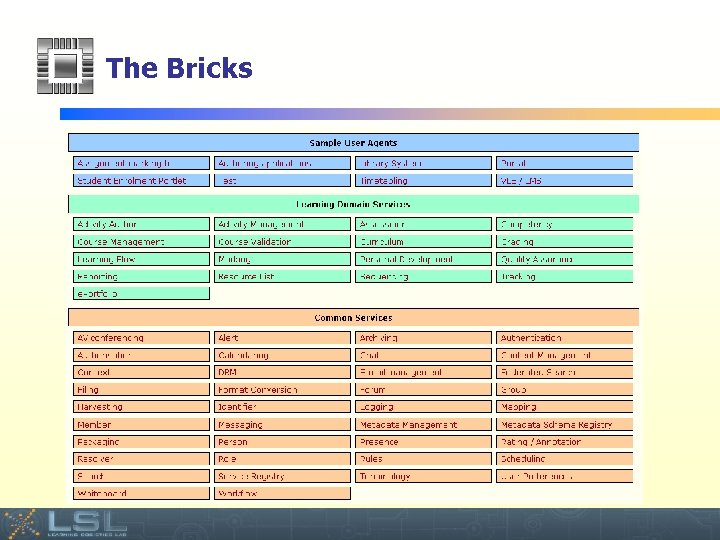 The Bricks Event
The Bricks Event
 Development of the ELF • Open Source • Uses existing specifications/standards • Community Design – But not Community Source like Sakai • Bottom-up – Toolkit Projects • Top Down – Reference Model Projects (to identify common services and workflows) • Evaluation – Demonstrator Projects Event
Development of the ELF • Open Source • Uses existing specifications/standards • Community Design – But not Community Source like Sakai • Bottom-up – Toolkit Projects • Top Down – Reference Model Projects (to identify common services and workflows) • Evaluation – Demonstrator Projects Event
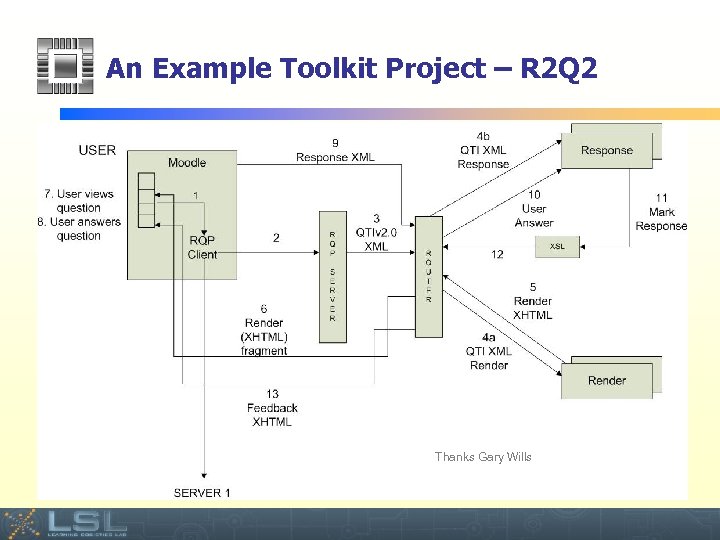 An Example Toolkit Project – R 2 Q 2 Thanks Gary Wills Event
An Example Toolkit Project – R 2 Q 2 Thanks Gary Wills Event
 An Example Reference Model Project FREMA • FREMA is developing a Reference Model for the Assessment domain – Supporting design-time activities – Supporting run-time activities – Virtual organisations and lifelong learning • What is a Reference Model? – A description of how services behave within a particular domain – A community resource Event
An Example Reference Model Project FREMA • FREMA is developing a Reference Model for the Assessment domain – Supporting design-time activities – Supporting run-time activities – Virtual organisations and lifelong learning • What is a Reference Model? – A description of how services behave within a particular domain – A community resource Event
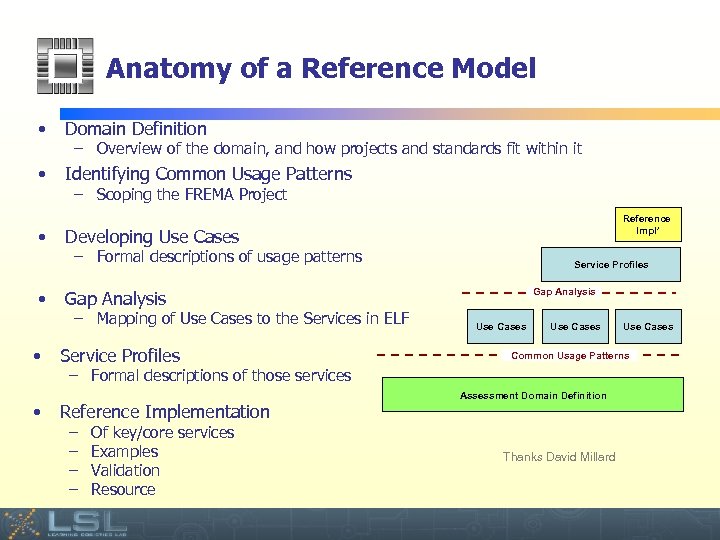 Anatomy of a Reference Model • Domain Definition • Identifying Common Usage Patterns • • – Overview of the domain, and how projects and standards fit within it – Scoping the FREMA Project Reference Impl’ Developing Use Cases – Formal descriptions of usage patterns Service Profiles Gap Analysis – Mapping of Use Cases to the Services in ELF Service Profiles Use Cases Common Usage Patterns – Formal descriptions of those services Assessment Domain Definition Reference Implementation – – Use Cases Of key/core services Examples Validation Resource Thanks David Millard Event
Anatomy of a Reference Model • Domain Definition • Identifying Common Usage Patterns • • – Overview of the domain, and how projects and standards fit within it – Scoping the FREMA Project Reference Impl’ Developing Use Cases – Formal descriptions of usage patterns Service Profiles Gap Analysis – Mapping of Use Cases to the Services in ELF Service Profiles Use Cases Common Usage Patterns – Formal descriptions of those services Assessment Domain Definition Reference Implementation – – Use Cases Of key/core services Examples Validation Resource Thanks David Millard Event
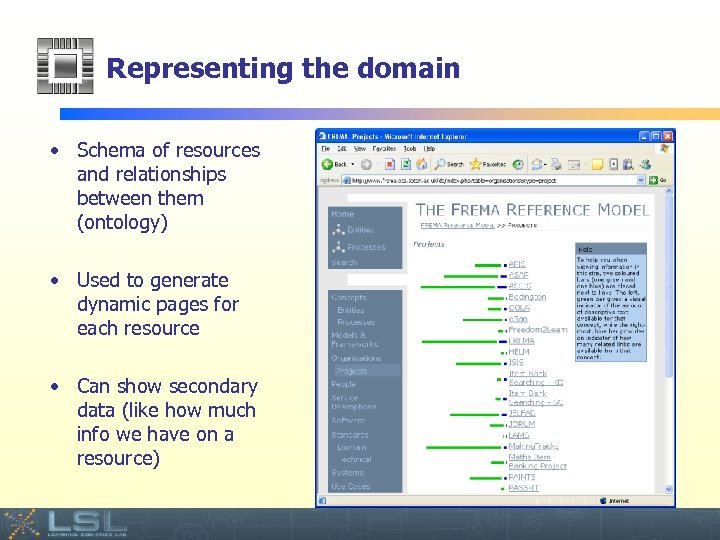 Representing the domain • Schema of resources and relationships between them (ontology) • Used to generate dynamic pages for each resource • Can show secondary data (like how much info we have on a resource) Event
Representing the domain • Schema of resources and relationships between them (ontology) • Used to generate dynamic pages for each resource • Can show secondary data (like how much info we have on a resource) Event
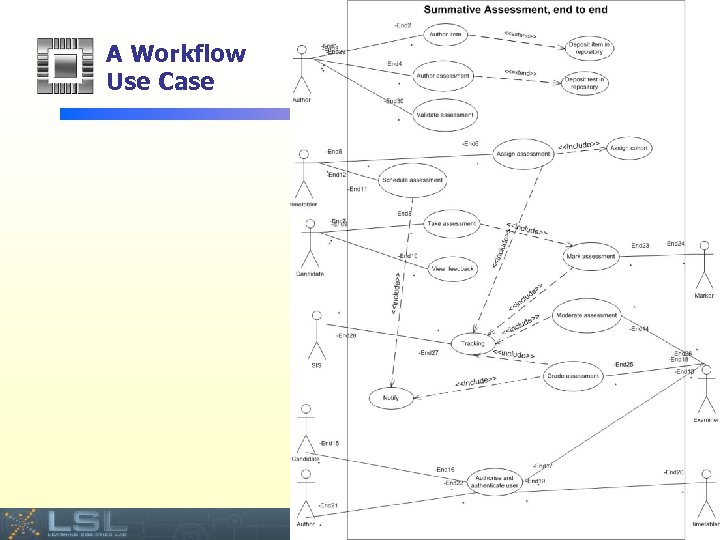 A Workflow Use Case Event
A Workflow Use Case Event
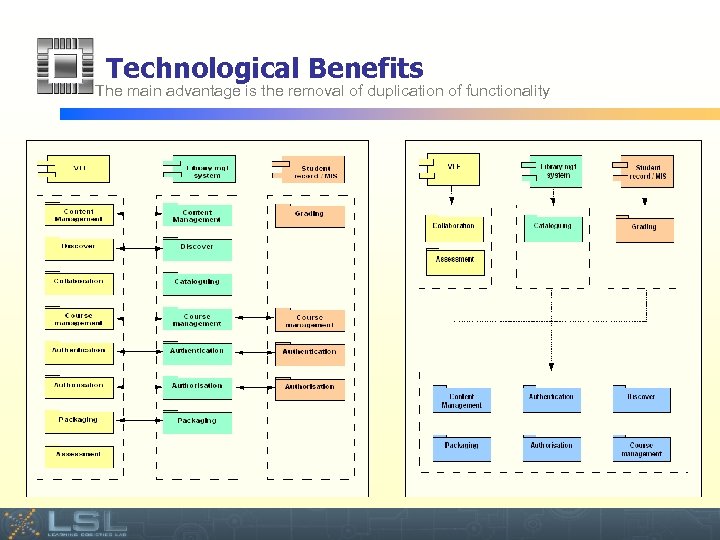 Technological Benefits The main advantage is the removal of duplication of functionality Event
Technological Benefits The main advantage is the removal of duplication of functionality Event
 Benefits to teachers and learners • Supporting pedagogic diversity – It becomes possible to support a very diverse set of learning models as it becomes feasible to configure the low-level elements of the learning architecture to fit a variety of pedagogic and institutional business models • Enabling pedagogy-driven implementations – By exposing modular processes as separate services, which can be configured in multiple ways, the construction of technology solutions can become driven by pedagogical imperatives, rather than the reverse. From “Technical Framework to Support e. Learning” S. Wilson, B. Olivier, S. Jeyes, A. Powell, T Franklin Event
Benefits to teachers and learners • Supporting pedagogic diversity – It becomes possible to support a very diverse set of learning models as it becomes feasible to configure the low-level elements of the learning architecture to fit a variety of pedagogic and institutional business models • Enabling pedagogy-driven implementations – By exposing modular processes as separate services, which can be configured in multiple ways, the construction of technology solutions can become driven by pedagogical imperatives, rather than the reverse. From “Technical Framework to Support e. Learning” S. Wilson, B. Olivier, S. Jeyes, A. Powell, T Franklin Event
 Benefits to Institutions • Providing better returns on technology investment – Applications can be developed or acquired as needed, so reducing both purchasing and implementation costs, particularly in terms of staff development and training. • Enabling faster deployment of technology – As components are independent it will often be easier to deploy new components • Providing a modular and flexible technology base. – where the individual components can be added or replaced more easily than in traditional models • Making collaboration between institutions easier – Through a common framework. It may also make sharing of applications easier, as it will be simpler to define small applications which are needed in common and can be developed to meet the needs of each institution. Event
Benefits to Institutions • Providing better returns on technology investment – Applications can be developed or acquired as needed, so reducing both purchasing and implementation costs, particularly in terms of staff development and training. • Enabling faster deployment of technology – As components are independent it will often be easier to deploy new components • Providing a modular and flexible technology base. – where the individual components can be added or replaced more easily than in traditional models • Making collaboration between institutions easier – Through a common framework. It may also make sharing of applications easier, as it will be simpler to define small applications which are needed in common and can be developed to meet the needs of each institution. Event
 The Risks of the Approach • The design method is not yet proven – without explicit direction will a design emerge? • Not all universities (and very few FE colleges) have the expertise to work with this open software. • Currently many HEIs prefer spend on maintenance contracts • Will the commercial software vendors buy in? • There are those who still doubt that the web service approach will scale Event
The Risks of the Approach • The design method is not yet proven – without explicit direction will a design emerge? • Not all universities (and very few FE colleges) have the expertise to work with this open software. • Currently many HEIs prefer spend on maintenance contracts • Will the commercial software vendors buy in? • There are those who still doubt that the web service approach will scale Event
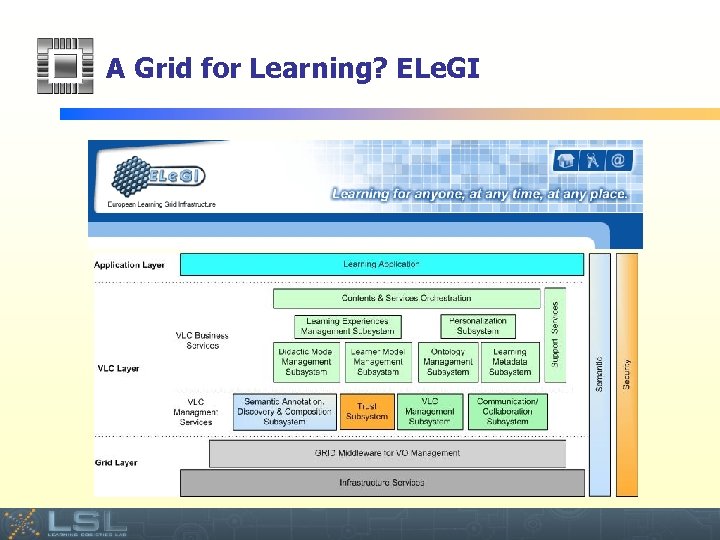 A Grid for Learning? ELe. GI Event
A Grid for Learning? ELe. GI Event
 What is the GRID? • Ian Foster says – 1) coordinates resources that are not subject to centralized control … – (2) … using standard, open, general-purpose protocols and interfaces…. – 3) … to deliver nontrivial qualities of service. • • • Plaszczak/Wellner define grid technology as "the technology that enables resource virtualization, on-demand provisioning, and service (resource) sharing between organizations. " IBM says, "Grid is the ability, using a set of open standards and protocols, to gain access to applications and data, processing power, storage capacity and a cast array or other computing resources over the Internet. A Grid is a type of parallel and distributed system that enables the sharing, selection, and aggregation of resources distributed across multiple administrative domains based on the resources availability, capacity, performance and users' quality-of-service requirements". An important corollary to this is that the GRID provides the environment for Virtual Organisations. Event
What is the GRID? • Ian Foster says – 1) coordinates resources that are not subject to centralized control … – (2) … using standard, open, general-purpose protocols and interfaces…. – 3) … to deliver nontrivial qualities of service. • • • Plaszczak/Wellner define grid technology as "the technology that enables resource virtualization, on-demand provisioning, and service (resource) sharing between organizations. " IBM says, "Grid is the ability, using a set of open standards and protocols, to gain access to applications and data, processing power, storage capacity and a cast array or other computing resources over the Internet. A Grid is a type of parallel and distributed system that enables the sharing, selection, and aggregation of resources distributed across multiple administrative domains based on the resources availability, capacity, performance and users' quality-of-service requirements". An important corollary to this is that the GRID provides the environment for Virtual Organisations. Event
 What does the GRID bring to e. Learning? • The GRID is the architecture for next generation distributed systems • Effective for implementing e-Science infrastructure for sharing data, applications and knowledge • Web service systems that allow resource sharing in a secure and controlled way • Virtualisation and sharing of several kind of resources • Dynamic service discovery and creation will allow the true personalisation • Allows the creation of Virtual Learning Communities • Semantic and Knowledge Grid implementation are fundamental to future learning scenarios Event
What does the GRID bring to e. Learning? • The GRID is the architecture for next generation distributed systems • Effective for implementing e-Science infrastructure for sharing data, applications and knowledge • Web service systems that allow resource sharing in a secure and controlled way • Virtualisation and sharing of several kind of resources • Dynamic service discovery and creation will allow the true personalisation • Allows the creation of Virtual Learning Communities • Semantic and Knowledge Grid implementation are fundamental to future learning scenarios Event
 Design Issues for a Hand-in Machine • What functionality will the hand in machine need? (much more than what the student sees) • What services do you think might be provided outside of the hand-in machine program? • Draw a use case/ workflow diagram Event
Design Issues for a Hand-in Machine • What functionality will the hand in machine need? (much more than what the student sees) • What services do you think might be provided outside of the hand-in machine program? • Draw a use case/ workflow diagram Event


