ff796a9760e10b8bd42d2b85b2e43862.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 65
 ELC 200 Day 26
ELC 200 Day 26
 Agenda l Questions from last Class? l Assignment 6, 7 & 8 all posted ¡ Assignment 6 Corrected l ¡ Assignment 7 due Today l ¡ l 6 A’s, 5 B’s, 1 C, 1 F (late) and 1 MIA Will have them back to you on Thursday Assignment 8 due May 8 @ 8 AM EBiz plan and presentations Send your plans and Power. Points to me in Web. CT by 8 AM on May 8 ¡ More information in assignments section of Web. CT l Today we will the discussing e. Commerce Strategies. ¡
Agenda l Questions from last Class? l Assignment 6, 7 & 8 all posted ¡ Assignment 6 Corrected l ¡ Assignment 7 due Today l ¡ l 6 A’s, 5 B’s, 1 C, 1 F (late) and 1 MIA Will have them back to you on Thursday Assignment 8 due May 8 @ 8 AM EBiz plan and presentations Send your plans and Power. Points to me in Web. CT by 8 AM on May 8 ¡ More information in assignments section of Web. CT l Today we will the discussing e. Commerce Strategies. ¡
 E-Strategy Landscape Strategy initiation: organization prepares information about its vision, mission, purpose, and the contribution that EC could make to the business l Strategy formulation: l Identification of EC applications ¡ Cost-benefit analysis ¡ Risk analysis ¡
E-Strategy Landscape Strategy initiation: organization prepares information about its vision, mission, purpose, and the contribution that EC could make to the business l Strategy formulation: l Identification of EC applications ¡ Cost-benefit analysis ¡ Risk analysis ¡
 E-Strategy Landscape (cont. ) l Strategy implementation: ¡ Organization’s resources are analyzed ¡ A plan is developed for attaining the goals l Strategy assessment: ¡ Organization periodically assesses progress toward the strategic goals ¡ Involves the development of EC metrics
E-Strategy Landscape (cont. ) l Strategy implementation: ¡ Organization’s resources are analyzed ¡ A plan is developed for attaining the goals l Strategy assessment: ¡ Organization periodically assesses progress toward the strategic goals ¡ Involves the development of EC metrics
 Exhibit 11. 1 The Landscape of EC Strategy
Exhibit 11. 1 The Landscape of EC Strategy
 Strategy Initiation l Strategy initiation—the initial phase of estrategy in which an organization prepares information about its vision, mission, purpose, and the contribution that EC could make 1. 2. 3. Review the organization’s business and IT vision and mission Generate vision and mission for EC Begin with industry and competitive analysis
Strategy Initiation l Strategy initiation—the initial phase of estrategy in which an organization prepares information about its vision, mission, purpose, and the contribution that EC could make 1. 2. 3. Review the organization’s business and IT vision and mission Generate vision and mission for EC Begin with industry and competitive analysis
 Industry Assessment l l l What industry is the EC initiative related to? Who are the customers? What are the current practices of selling and buying? Who are the major competitors? (How intense is the competition? ) What e-strategies are used, by whom? How is value added throughout the value chain? l What are the major opportunities and threats? l Are there any metrics or best practices in place? l What are the existing and potential partnerships for EC? l
Industry Assessment l l l What industry is the EC initiative related to? Who are the customers? What are the current practices of selling and buying? Who are the major competitors? (How intense is the competition? ) What e-strategies are used, by whom? How is value added throughout the value chain? l What are the major opportunities and threats? l Are there any metrics or best practices in place? l What are the existing and potential partnerships for EC? l
 Company Assessment l The organization investigates its own: Business strategy ¡ Performance ¡ Customers ¡ Partners ¡ l It looks at everything that has an impact on its operations Processes ¡ People ¡ Information flows ¡ Technology support ¡
Company Assessment l The organization investigates its own: Business strategy ¡ Performance ¡ Customers ¡ Partners ¡ l It looks at everything that has an impact on its operations Processes ¡ People ¡ Information flows ¡ Technology support ¡
 Industry, Company, and Competitive Analysis SWOT analysis—a methodology that surveys the opportunities and threats in the external environment and relates them to the organization’s particular strengths and weaknesses l SWOT Analysis l ¡ ¡ Strengths Opportunities Weaknesses Threats
Industry, Company, and Competitive Analysis SWOT analysis—a methodology that surveys the opportunities and threats in the external environment and relates them to the organization’s particular strengths and weaknesses l SWOT Analysis l ¡ ¡ Strengths Opportunities Weaknesses Threats
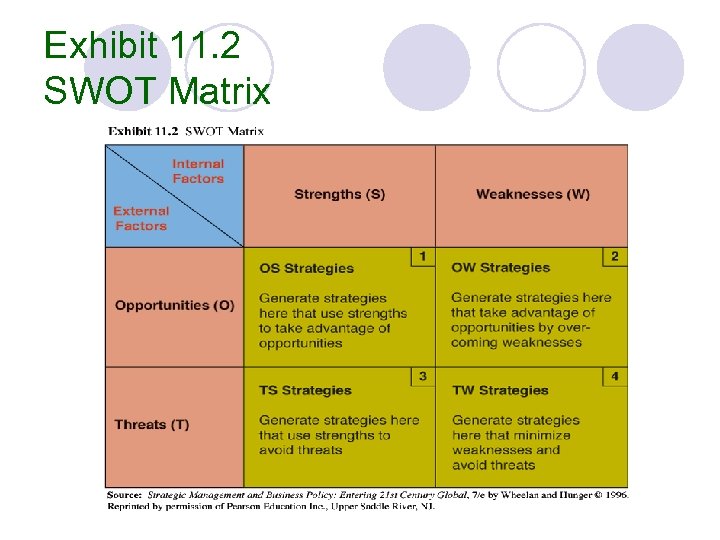 Exhibit 11. 2 SWOT Matrix
Exhibit 11. 2 SWOT Matrix
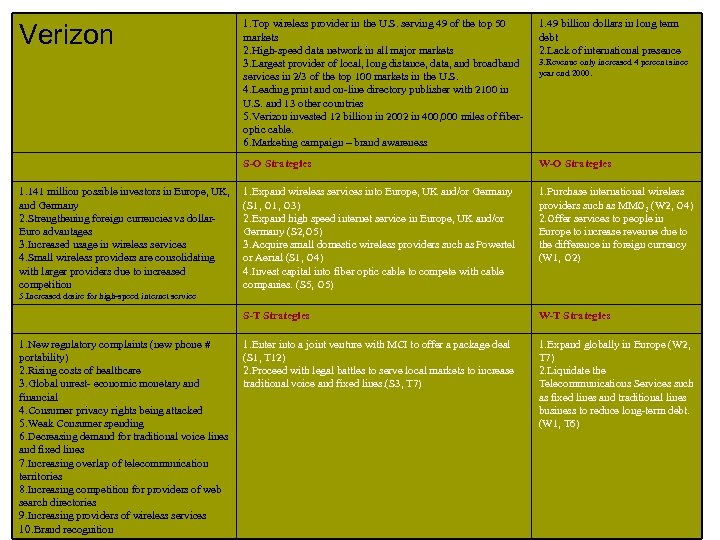 W-O Strategies 1. Expand wireless services into Europe, UK and/or Germany (S 1, O 3) 2. Expand high speed internet service in Europe, UK and/or Germany (S 2, O 5) 3. Acquire small domestic wireless providers such as Powertel or Aerial (S 1, O 4) 4. Invest capital into fiber optic cable to compete with cable companies. (S 5, O 5) 1. Purchase international wireless providers such as MMO 2 (W 2, O 4) 2. Offer services to people in Europe to increase revenue due to the difference in foreign currency (W 1, O 2) S-T Strategies 1. 141 million possible investors in Europe, UK, and Germany 2. Strengthening foreign currencies vs dollar. Euro advantages 3. Increased usage in wireless services 4. Small wireless providers are consolidating with larger providers due to increased competition 1. 49 billion dollars in long term debt 2. Lack of international presence S-O Strategies Verizon 1. Top wireless provider in the U. S. serving 49 of the top 50 markets 2. High-speed data network in all major markets 3. Largest provider of local, long distance, data, and broadband services in 2/3 of the top 100 markets in the U. S. 4. Leading print and on-line directory publisher with 2100 in U. S. and 13 other countries 5. Verizon invested 12 billion in 2002 in 400, 000 miles of fiberoptic cable. 6. Marketing campaign – brand awareness W-T Strategies 1. Enter into a joint venture with MCI to offer a package deal (S 1, T 12) 2. Proceed with legal battles to serve local markets to increase traditional voice and fixed lines. (S 3, T 7) 1. Expand globally in Europe (W 2, T 7) 2. Liquidate the Telecommunications Services such as fixed lines and traditional lines business to reduce long-term debt. (W 1, T 6) 3. Revenue only increased 4 percent since year end 2000. 5. Increased desire for high-speed internet service 1. New regulatory complaints (new phone # portability) 2. Rising costs of healthcare 3. Global unrest- economic monetary and financial 4. Consumer privacy rights being attacked 5. Weak Consumer spending 6. Decreasing demand for traditional voice lines and fixed lines 7. Increasing overlap of telecommunication territories 8. Increasing competition for providers of web search directories 9. Increasing providers of wireless services 10. Brand recognition
W-O Strategies 1. Expand wireless services into Europe, UK and/or Germany (S 1, O 3) 2. Expand high speed internet service in Europe, UK and/or Germany (S 2, O 5) 3. Acquire small domestic wireless providers such as Powertel or Aerial (S 1, O 4) 4. Invest capital into fiber optic cable to compete with cable companies. (S 5, O 5) 1. Purchase international wireless providers such as MMO 2 (W 2, O 4) 2. Offer services to people in Europe to increase revenue due to the difference in foreign currency (W 1, O 2) S-T Strategies 1. 141 million possible investors in Europe, UK, and Germany 2. Strengthening foreign currencies vs dollar. Euro advantages 3. Increased usage in wireless services 4. Small wireless providers are consolidating with larger providers due to increased competition 1. 49 billion dollars in long term debt 2. Lack of international presence S-O Strategies Verizon 1. Top wireless provider in the U. S. serving 49 of the top 50 markets 2. High-speed data network in all major markets 3. Largest provider of local, long distance, data, and broadband services in 2/3 of the top 100 markets in the U. S. 4. Leading print and on-line directory publisher with 2100 in U. S. and 13 other countries 5. Verizon invested 12 billion in 2002 in 400, 000 miles of fiberoptic cable. 6. Marketing campaign – brand awareness W-T Strategies 1. Enter into a joint venture with MCI to offer a package deal (S 1, T 12) 2. Proceed with legal battles to serve local markets to increase traditional voice and fixed lines. (S 3, T 7) 1. Expand globally in Europe (W 2, T 7) 2. Liquidate the Telecommunications Services such as fixed lines and traditional lines business to reduce long-term debt. (W 1, T 6) 3. Revenue only increased 4 percent since year end 2000. 5. Increased desire for high-speed internet service 1. New regulatory complaints (new phone # portability) 2. Rising costs of healthcare 3. Global unrest- economic monetary and financial 4. Consumer privacy rights being attacked 5. Weak Consumer spending 6. Decreasing demand for traditional voice lines and fixed lines 7. Increasing overlap of telecommunication territories 8. Increasing competition for providers of web search directories 9. Increasing providers of wireless services 10. Brand recognition
 Competitive Intelligence on the Internet l Internet can play a major role as a source of competitive information (competitive intelligence) ¡ ¡ Review competitors’ Web sites Examine publicly available financial documents l ¡ Edgar Online, Valueline Ask the customers—award prizes to those who best describe your competitors’ strengths and weaknesses
Competitive Intelligence on the Internet l Internet can play a major role as a source of competitive information (competitive intelligence) ¡ ¡ Review competitors’ Web sites Examine publicly available financial documents l ¡ Edgar Online, Valueline Ask the customers—award prizes to those who best describe your competitors’ strengths and weaknesses
 Competitive Intelligence on the Internet (cont. ) ¡ Analyze related discussion groups Find out what people think about a company and its products and competitor's products l Reaction to new ideas and products l ¡ Use information delivery services Find out what it published on the Internet l Known as push technologies l ¡ Corporate research companies provide information about your competitors: ¡ Examine chat rooms
Competitive Intelligence on the Internet (cont. ) ¡ Analyze related discussion groups Find out what people think about a company and its products and competitor's products l Reaction to new ideas and products l ¡ Use information delivery services Find out what it published on the Internet l Known as push technologies l ¡ Corporate research companies provide information about your competitors: ¡ Examine chat rooms
 Issues in Strategy Initiation To be a first mover or a follower? l Advantages ¡ ¡ ¡ Chance to capture large markets Establishing a brand name Exclusive strategic alliances l Disadvantages ¡ ¡ Cost of developing EC initiative is usually very high Chance of failure is high System may be obsolete as compared to second wave arrivals No support services are available at the beginning
Issues in Strategy Initiation To be a first mover or a follower? l Advantages ¡ ¡ ¡ Chance to capture large markets Establishing a brand name Exclusive strategic alliances l Disadvantages ¡ ¡ Cost of developing EC initiative is usually very high Chance of failure is high System may be obsolete as compared to second wave arrivals No support services are available at the beginning
 Should You Have a Separate Online Company? l Advantages ¡ ¡ Reducing or eliminating internal conflicts Providing more freedom to management in pricing, advertising, etc. Can create new brands quickly Take the e-business to an IPO and make a fortune l Disadvantages ¡ ¡ ¡ May be very costly and risky Collaboration with offline business may be difficult Lose expertise of business functions unless you use close collaboration
Should You Have a Separate Online Company? l Advantages ¡ ¡ Reducing or eliminating internal conflicts Providing more freedom to management in pricing, advertising, etc. Can create new brands quickly Take the e-business to an IPO and make a fortune l Disadvantages ¡ ¡ ¡ May be very costly and risky Collaboration with offline business may be difficult Lose expertise of business functions unless you use close collaboration
 Strategy Formulation l Strategy formulation Development of long-range and strategic plans to exploit opportunities and manage threats in the business environment in light of corporate strengths and weaknesses l Includes examining or redefining EC mission ¡ Specifying achievable objectives ¡ Developing strategies ¡ Setting implementation guidelines
Strategy Formulation l Strategy formulation Development of long-range and strategic plans to exploit opportunities and manage threats in the business environment in light of corporate strengths and weaknesses l Includes examining or redefining EC mission ¡ Specifying achievable objectives ¡ Developing strategies ¡ Setting implementation guidelines
 Discovering EC Opportunities l 3 common mistakes in allocating EC investment ¡ Let a thousand flowers bloom—fund many projects indiscriminately ¡ Bet it all—put everything on a single high-stake initiative ¡ Trend-surf—follow the crowd toward the next “big thing” l Any of the above can be risky and costly
Discovering EC Opportunities l 3 common mistakes in allocating EC investment ¡ Let a thousand flowers bloom—fund many projects indiscriminately ¡ Bet it all—put everything on a single high-stake initiative ¡ Trend-surf—follow the crowd toward the next “big thing” l Any of the above can be risky and costly
 Discovering EC Opportunities (cont. ) l Approaches to identifying EC opportunities ¡ Problem-driven ¡ Technology-driven ¡ Market-driven—waiting competitors will do ¡ Fear or greed-driven to see what the Afraid if they do not practice EC they will be big losers l Think they can make lots of money going into EC l
Discovering EC Opportunities (cont. ) l Approaches to identifying EC opportunities ¡ Problem-driven ¡ Technology-driven ¡ Market-driven—waiting competitors will do ¡ Fear or greed-driven to see what the Afraid if they do not practice EC they will be big losers l Think they can make lots of money going into EC l
 Determining an Appropriate EC Application Portfolio l Find the most appropriate portfolio in order to share limited resources Combine long-term speculative investments in new potentially high-growth business ¡ With short-term investments in existing, profitmaking businesses ¡ l Boston Consulting Group’s matrix Cash cows ¡ Starts ¡ Questionable projects Dogs
Determining an Appropriate EC Application Portfolio l Find the most appropriate portfolio in order to share limited resources Combine long-term speculative investments in new potentially high-growth business ¡ With short-term investments in existing, profitmaking businesses ¡ l Boston Consulting Group’s matrix Cash cows ¡ Starts ¡ Questionable projects Dogs
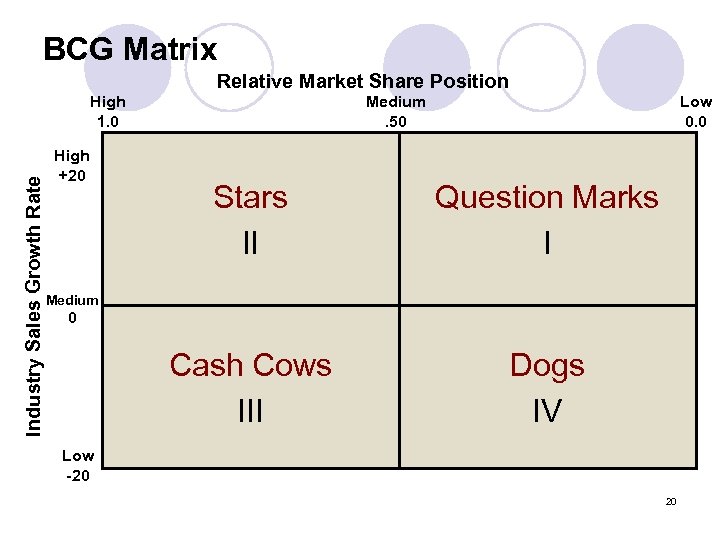 BCG Matrix Relative Market Share Position Industry Sales Growth Rate High 1. 0 High +20 Medium. 50 Low 0. 0 Stars II Question Marks I Cash Cows III Dogs IV Medium 0 Low -20 20
BCG Matrix Relative Market Share Position Industry Sales Growth Rate High 1. 0 High +20 Medium. 50 Low 0. 0 Stars II Question Marks I Cash Cows III Dogs IV Medium 0 Low -20 20
 Making the Business Case for EC l Business case—written document that is used by managers to garner funding for specific applications or projects by providing justification for investments ¡ Provides foundation for tactical decision making and technology by management ¡ Helps clarify the company’s use of its resources to accomplish the e-strategy
Making the Business Case for EC l Business case—written document that is used by managers to garner funding for specific applications or projects by providing justification for investments ¡ Provides foundation for tactical decision making and technology by management ¡ Helps clarify the company’s use of its resources to accomplish the e-strategy
 Content of an E-Business Case l Business case for EC approach for garnering funding for projects used to: ¡ Provide justification for investments ¡ Provides bridge between EC plan and the execution ¡ Provides foundation for tactical decision making and technology risk management ¡ Clarifies how the organization will use resources to accomplish the e-strategy
Content of an E-Business Case l Business case for EC approach for garnering funding for projects used to: ¡ Provide justification for investments ¡ Provides bridge between EC plan and the execution ¡ Provides foundation for tactical decision making and technology risk management ¡ Clarifies how the organization will use resources to accomplish the e-strategy
 Content of an E-Business Case (cont. ) l Content of an E-business case ¡ Strategic justification—”where are we going? ” ¡ Generational justification—”how will we get there? ” ¡ Technical justification—”when will we get there? ” ¡ Financial justification—”why will we win? ”
Content of an E-Business Case (cont. ) l Content of an E-business case ¡ Strategic justification—”where are we going? ” ¡ Generational justification—”how will we get there? ” ¡ Technical justification—”when will we get there? ” ¡ Financial justification—”why will we win? ”
 Cost-Benefit and Risk Analysis l How to conduct an e-business case ¡ ¡ Develop goal statement Set measurable goals Develop short- and long-term action plans Gain approval and support l Revenue model ¡ ¡ ¡ Properly planned revenue model is a critical success factor Revenues from sales depend on customer acquisition cost and advertisement Must be figured into the analysis
Cost-Benefit and Risk Analysis l How to conduct an e-business case ¡ ¡ Develop goal statement Set measurable goals Develop short- and long-term action plans Gain approval and support l Revenue model ¡ ¡ ¡ Properly planned revenue model is a critical success factor Revenues from sales depend on customer acquisition cost and advertisement Must be figured into the analysis
 Cost-Benefit and Risk Analysis (cont. ) l It is difficult to justify EC investment due to many intangible variables ¡ Return on investment (ROI) ¡ Discounted cash flow l Two common methods ¡ Value proposition ¡ Risk analysis
Cost-Benefit and Risk Analysis (cont. ) l It is difficult to justify EC investment due to many intangible variables ¡ Return on investment (ROI) ¡ Discounted cash flow l Two common methods ¡ Value proposition ¡ Risk analysis
 Value Proposition l Value proposition—the benefit a company can derive from implementing a new project, such as EC, usually by increasing its competitiveness and by providing better service to its customers
Value Proposition l Value proposition—the benefit a company can derive from implementing a new project, such as EC, usually by increasing its competitiveness and by providing better service to its customers
 Risk Analysis l Risk analysis program should ¡ ¡ Identify all potential risks Assess potential damage Evaluate possibility of protection (insurance) Evaluate cost of protection vs. benefits l E-business risks ¡ ¡ ¡ Strategic risks Financial risks Operational risks
Risk Analysis l Risk analysis program should ¡ ¡ Identify all potential risks Assess potential damage Evaluate possibility of protection (insurance) Evaluate cost of protection vs. benefits l E-business risks ¡ ¡ ¡ Strategic risks Financial risks Operational risks
 Issues in Strategy Formulation l How ¡ Let to handle channel conflicts established old-economy-type dealers handle e-business fulfillment ¡ Sell some products only online ¡ Help your intermediaries (e. g. , build portals) ¡ Sell online and off-line ¡ Do not sell online
Issues in Strategy Formulation l How ¡ Let to handle channel conflicts established old-economy-type dealers handle e-business fulfillment ¡ Sell some products only online ¡ Help your intermediaries (e. g. , build portals) ¡ Sell online and off-line ¡ Do not sell online
 Issues in Strategy Formulation (cont. ) l How to handle conflict between off-line and online businesses ¡ Clear support of top management ¡ Use of innovative processes that support collaboration ¡ Clear strategy of “what and how”
Issues in Strategy Formulation (cont. ) l How to handle conflict between off-line and online businesses ¡ Clear support of top management ¡ Use of innovative processes that support collaboration ¡ Clear strategy of “what and how”
 Issues in Strategy Formulation (cont. ) l Pricing strategy ¡ Setting prices lower than off-line business may lead to internal conflict ¡ Setting prices at the same level may hurt competitiveness l Should you get financing from big venture capital firms? ¡ Venture capital financing causes loss of control over business ¡ Benefit: access to various VC experts and get the cash you need
Issues in Strategy Formulation (cont. ) l Pricing strategy ¡ Setting prices lower than off-line business may lead to internal conflict ¡ Setting prices at the same level may hurt competitiveness l Should you get financing from big venture capital firms? ¡ Venture capital financing causes loss of control over business ¡ Benefit: access to various VC experts and get the cash you need
 Strategy Implementation l Strategy implementation--The execution of the e-strategy plan, in which detailed, short-term plans are developed for attaining strategic goals ¡ Establish a Web team that continues the execution of the plan ¡ Start with a pilot project ¡ Planning for resources
Strategy Implementation l Strategy implementation--The execution of the e-strategy plan, in which detailed, short-term plans are developed for attaining strategic goals ¡ Establish a Web team that continues the execution of the plan ¡ Start with a pilot project ¡ Planning for resources
 Strategy Implementation (cont. ) l Strategy implementation issues ¡ Evaluating outsourcing Build an in-house EC infrastructure l Purchase a commercial EC software package or EC suite l Use a Web hosting company l ¡ Partners’ strategy ¡ How to coordinate B 2 B and B 2 C
Strategy Implementation (cont. ) l Strategy implementation issues ¡ Evaluating outsourcing Build an in-house EC infrastructure l Purchase a commercial EC software package or EC suite l Use a Web hosting company l ¡ Partners’ strategy ¡ How to coordinate B 2 B and B 2 C
 Strategy and Project Assessment Strategy assessment—the periodic formal evaluation of progress toward the organization's strategic goals; may include needed actions and strategy reformulation l Objectives of assessment l ¡ ¡ ¡ Find out if EC project delivers what it was supposed to deliver Adjust plans if necessary Determine if EC project is still viable Reassess initial strategy in order to learn from mistakes and improve future planning Identify failing projects as soon as possible and determine reasons for failure
Strategy and Project Assessment Strategy assessment—the periodic formal evaluation of progress toward the organization's strategic goals; may include needed actions and strategy reformulation l Objectives of assessment l ¡ ¡ ¡ Find out if EC project delivers what it was supposed to deliver Adjust plans if necessary Determine if EC project is still viable Reassess initial strategy in order to learn from mistakes and improve future planning Identify failing projects as soon as possible and determine reasons for failure
 Measuring Results & Using Metrics l Metric—a measurable standard or a target against which actual performance is compared Response time to customers’ enquiries ¡ Response quality ¡ Security/trust level ¡ Download time, ¡ Timeliness of fulfillment ¡ How up-to-date information ¡ Availability ¡ Site effectiveness, ease of use, and navigability ¡
Measuring Results & Using Metrics l Metric—a measurable standard or a target against which actual performance is compared Response time to customers’ enquiries ¡ Response quality ¡ Security/trust level ¡ Download time, ¡ Timeliness of fulfillment ¡ How up-to-date information ¡ Availability ¡ Site effectiveness, ease of use, and navigability ¡
 Measuring Results & Using Metrics (cont. ) l Balanced scorecard—a structured methodology for measuring performance in organizations, using metrics in four areas ¡ Finance ¡ Customers’ assessments ¡ Internal business processes ¡ Learning and growth
Measuring Results & Using Metrics (cont. ) l Balanced scorecard—a structured methodology for measuring performance in organizations, using metrics in four areas ¡ Finance ¡ Customers’ assessments ¡ Internal business processes ¡ Learning and growth
 Measuring Results & Using Metrics (cont. ) l Performance dashboard—a structured methodology proposed by Rayport and Jaworski (2001) for measuring EC performance using: ¡ Desired outcomes ¡ Corresponding metrics ¡ Leading and lagging indicators of performance
Measuring Results & Using Metrics (cont. ) l Performance dashboard—a structured methodology proposed by Rayport and Jaworski (2001) for measuring EC performance using: ¡ Desired outcomes ¡ Corresponding metrics ¡ Leading and lagging indicators of performance
 Performance Dashboard
Performance Dashboard
 EC Failures & Lessons Learned l E-Tailing failures ¡ ¡ l Exchange failures ¡ ¡ l Lack of funding Incorrect revenue model Revenue growth too slow Need to move to new business model EC initiatives failures Levi Strauss stopped online direct sales of its apparel (levistrauss. com) when major distributors and retailers put pressure on the company not to compete with their brick-and-mortar outlets
EC Failures & Lessons Learned l E-Tailing failures ¡ ¡ l Exchange failures ¡ ¡ l Lack of funding Incorrect revenue model Revenue growth too slow Need to move to new business model EC initiatives failures Levi Strauss stopped online direct sales of its apparel (levistrauss. com) when major distributors and retailers put pressure on the company not to compete with their brick-and-mortar outlets
 Success Stories & Lessons Learned l Reasons for success: ¡ Brick-and-mortar companies add online channels ¡ Mergers and acquisitions ¡ Peter Drucker: Analyze the opportunities l Go out to look l keep it focused l Start small (one thing at a time) l Aim at market leadership l
Success Stories & Lessons Learned l Reasons for success: ¡ Brick-and-mortar companies add online channels ¡ Mergers and acquisitions ¡ Peter Drucker: Analyze the opportunities l Go out to look l keep it focused l Start small (one thing at a time) l Aim at market leadership l
 Success Stories & Lessons Learned (cont. ) ¡ Asian CEOs CSFs: Select robust business models l Understand dot-com future l Foster e-innovation l Evaluate a spin-off strategy l Co-brand l Employ ex-dot-com staffers l Focus on the e-generation as your market l ¡ Get the technology right, avoid expensive technology and technology malfunctions
Success Stories & Lessons Learned (cont. ) ¡ Asian CEOs CSFs: Select robust business models l Understand dot-com future l Foster e-innovation l Evaluate a spin-off strategy l Co-brand l Employ ex-dot-com staffers l Focus on the e-generation as your market l ¡ Get the technology right, avoid expensive technology and technology malfunctions
 Virtual Communities Virtual community—a group of people with similar interests who interact with one another using the Internet Elements of interaction: Communication—bulletin boards, chat rooms/threaded discussions, e-mail and instant messaging ¡ Information—directories and yellow pages, search engine, member-generated content ¡ EC elements—e-catalogs, shopping carts, ads, auctions of all types
Virtual Communities Virtual community—a group of people with similar interests who interact with one another using the Internet Elements of interaction: Communication—bulletin boards, chat rooms/threaded discussions, e-mail and instant messaging ¡ Information—directories and yellow pages, search engine, member-generated content ¡ EC elements—e-catalogs, shopping carts, ads, auctions of all types
 Virtual Communities (cont. ) Communities of transactions— facilitate buying and selling l Communities of interest—people interact with each other on a specific topic l Communities of relations (practice)— organized around certain life experiences l Communities of fantasy—share imaginary environments l
Virtual Communities (cont. ) Communities of transactions— facilitate buying and selling l Communities of interest—people interact with each other on a specific topic l Communities of relations (practice)— organized around certain life experiences l Communities of fantasy—share imaginary environments l
 Virtual Communities (cont. ) l Commercial aspects of community: ¡ Understand a particular niche industry ¡ Build a site that provides valuable information ¡ Site should mirror the steps a user goes through in the information-gathering and decision-making process ¡ Build a community that relies on the site for decision support ¡ Start selling products and services that fit into the decision-support process
Virtual Communities (cont. ) l Commercial aspects of community: ¡ Understand a particular niche industry ¡ Build a site that provides valuable information ¡ Site should mirror the steps a user goes through in the information-gathering and decision-making process ¡ Build a community that relies on the site for decision support ¡ Start selling products and services that fit into the decision-support process
 Exhibit 11. 9 Value Creation in E-Communities
Exhibit 11. 9 Value Creation in E-Communities
 Virtual Communities (cont. ) l Financial viability of communities ¡ Based on sponsorship and advertisement ¡ Expenses are very high because of the need to provide: Fresh content l Free services l Free membership l ¡ This model did not work well, many companies sustained heavy losses in 2000 -2001; too few members, too few purchases
Virtual Communities (cont. ) l Financial viability of communities ¡ Based on sponsorship and advertisement ¡ Expenses are very high because of the need to provide: Fresh content l Free services l Free membership l ¡ This model did not work well, many companies sustained heavy losses in 2000 -2001; too few members, too few purchases
 Virtual Communities (cont. ) l Key strategies for successful online communities 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Increase traffic and participation Focus on the needs of the members (facilitators and coordinators) Encourage free sharing of opinions and information Financial sponsorship is a must Consider the cultural environment Provide tools and activities for member use Community members involved in activities and recruiting Guide discussions, provoke controversy, and raise sticky issues
Virtual Communities (cont. ) l Key strategies for successful online communities 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Increase traffic and participation Focus on the needs of the members (facilitators and coordinators) Encourage free sharing of opinions and information Financial sponsorship is a must Consider the cultural environment Provide tools and activities for member use Community members involved in activities and recruiting Guide discussions, provoke controversy, and raise sticky issues
 Going Global l Decision to go global is a strategic one ¡ Geographical borders are falling ¡ Artificial borders are being erected through Local language preferences, l Local regulations l Access limitations l
Going Global l Decision to go global is a strategic one ¡ Geographical borders are falling ¡ Artificial borders are being erected through Local language preferences, l Local regulations l Access limitations l
 Benefits and Extent of Operations Major advantage of EC—ability to do business any time, anywhere, rapidly at a reasonable cost l Success stories l ¡ ¡ ¡ E*TRADE or boom. com as your broker for stock trading Amazon. com Small companies sell to hundreds of customers worldwide (virtualvine. com) Increasing number of out-of-the-country vendors participate in electronic requests for quotes Successful employees recruitment Successful collaboration in B 2 B exchanges
Benefits and Extent of Operations Major advantage of EC—ability to do business any time, anywhere, rapidly at a reasonable cost l Success stories l ¡ ¡ ¡ E*TRADE or boom. com as your broker for stock trading Amazon. com Small companies sell to hundreds of customers worldwide (virtualvine. com) Increasing number of out-of-the-country vendors participate in electronic requests for quotes Successful employees recruitment Successful collaboration in B 2 B exchanges
 Barriers to Global Electronic Commerce l Legal Issues Uncoordinated actions must be avoided an international policy of cooperation should be encouraged l Market Access Issues Companies starting e-commerce need to evaluate bandwidth needs by analyzing the data required, time constraints, access demands, and user technology limitations l Financial Issues ¡ ¡ Customs and taxation Electronic payment systems
Barriers to Global Electronic Commerce l Legal Issues Uncoordinated actions must be avoided an international policy of cooperation should be encouraged l Market Access Issues Companies starting e-commerce need to evaluate bandwidth needs by analyzing the data required, time constraints, access demands, and user technology limitations l Financial Issues ¡ ¡ Customs and taxation Electronic payment systems
 Small Business Goes Global l Cardiac Science—trying to break into the international market for years ¡ Within 2 years after Internet inception in the company, it was shipping its products to 46 countries ¡ Today, 85 percent of the company’s revenue is international, much of this is executed at (cardiacscience. com)
Small Business Goes Global l Cardiac Science—trying to break into the international market for years ¡ Within 2 years after Internet inception in the company, it was shipping its products to 46 countries ¡ Today, 85 percent of the company’s revenue is international, much of this is executed at (cardiacscience. com)
 Small Business Goes Global (cont. ) l Advice for small businesses going global at: ¡ Universal Business Exchange (unibex. com) ¡ Several government agencies (stat-usa. gov) l Cardiac’s CEO “crafting a solid export strategy takes a lot more commitment than putting up a snazzy Web site and waiting for the world to show up at our door. It’s all about building relationships. ”
Small Business Goes Global (cont. ) l Advice for small businesses going global at: ¡ Universal Business Exchange (unibex. com) ¡ Several government agencies (stat-usa. gov) l Cardiac’s CEO “crafting a solid export strategy takes a lot more commitment than putting up a snazzy Web site and waiting for the world to show up at our door. It’s all about building relationships. ”
 Barriers to Global Electronic Commerce (cont. ) l Other Issues ¡ Language and translation Primary problems are cost, speed, inaccuracy ¡ Localization Adapt local business practices ¡ Culture Multiple cultures warrant different marketing approaches
Barriers to Global Electronic Commerce (cont. ) l Other Issues ¡ Language and translation Primary problems are cost, speed, inaccuracy ¡ Localization Adapt local business practices ¡ Culture Multiple cultures warrant different marketing approaches
 Breaking down the Global EC Barriers l l l Value the human touch Be strategic Know your audience Be a perfectionist Remember, it’s the Web Integrate properly Keep the site flexible and up-to-date l Synchronize content l OECD (oecd. org) read “Dismantling the Barriers to Global EC” l
Breaking down the Global EC Barriers l l l Value the human touch Be strategic Know your audience Be a perfectionist Remember, it’s the Web Integrate properly Keep the site flexible and up-to-date l Synchronize content l OECD (oecd. org) read “Dismantling the Barriers to Global EC” l
 EC in SMEs l Advantages/benefits of EC in SMEs ¡ Inexpensive Source of information l Advertising l Conducting market research l Build (or rent) a storefront l Low transaction costs l Niche markets are best l Provide catalogs l Way to reach worldwide customers l
EC in SMEs l Advantages/benefits of EC in SMEs ¡ Inexpensive Source of information l Advertising l Conducting market research l Build (or rent) a storefront l Low transaction costs l Niche markets are best l Provide catalogs l Way to reach worldwide customers l
 EC in SMEs (cont. ) l Disadvantages/risks ¡ Inability to use EDI, unless it is EDI/Internet ¡ Lack of resources to fully exploit the Web ¡ Lack of expertise in legal issues, advertisement ¡ Less risk tolerance than a large company ¡ Disadvantage when a commodity is the product (for example, CDs) ¡ No more personal contact, which is a strong point of a small business ¡ No advantage to being in a local community
EC in SMEs (cont. ) l Disadvantages/risks ¡ Inability to use EDI, unless it is EDI/Internet ¡ Lack of resources to fully exploit the Web ¡ Lack of expertise in legal issues, advertisement ¡ Less risk tolerance than a large company ¡ Disadvantage when a commodity is the product (for example, CDs) ¡ No more personal contact, which is a strong point of a small business ¡ No advantage to being in a local community
 Critical Success Factors for SMEs l l l l Capital investment must be small Inventory should be minimal or non-existent Electronic payments scheme Payment methods must be flexible Logistical services must be quick and reliable The Web site should be submitted to directory-based search engine services Join an online service or mall and do banner exchange Design a Web site that is functional and provides all needed services to consumers
Critical Success Factors for SMEs l l l l Capital investment must be small Inventory should be minimal or non-existent Electronic payments scheme Payment methods must be flexible Logistical services must be quick and reliable The Web site should be submitted to directory-based search engine services Join an online service or mall and do banner exchange Design a Web site that is functional and provides all needed services to consumers
 Supporting Small Business Technical support from IBM (for a fee of only $25 per month) at ibm. com. search: businesscenter l Digital’s virtual stores l Microsoft’s Personal Web Server (PWS) l Gartner Group provides access to online research material at gartner. com l
Supporting Small Business Technical support from IBM (for a fee of only $25 per month) at ibm. com. search: businesscenter l Digital’s virtual stores l Microsoft’s Personal Web Server (PWS) l Gartner Group provides access to online research material at gartner. com l
 Business Process Reengineering (BPR) l Organizational transformation—the process of completely or drastically transforming an entire organization to a new mode of operation l Business process reengineering (BPR) —a methodology for comprehensive redesign of an enterprise’s processes
Business Process Reengineering (BPR) l Organizational transformation—the process of completely or drastically transforming an entire organization to a new mode of operation l Business process reengineering (BPR) —a methodology for comprehensive redesign of an enterprise’s processes
 BPR (cont. ) l Redesign of the enterprise process and BPR ¡ ¡ ¡ Does not make sense to automate poorly designed process—so restructure Necessary to change processes to fit commercially available software Fit is required between systems and processes of different companies Change processes to fit procedures and standards of public e-marketplaces Adjust procedures and processes to align with available services (logistics, payments, security) Changes to assure flexibility and scalability
BPR (cont. ) l Redesign of the enterprise process and BPR ¡ ¡ ¡ Does not make sense to automate poorly designed process—so restructure Necessary to change processes to fit commercially available software Fit is required between systems and processes of different companies Change processes to fit procedures and standards of public e-marketplaces Adjust procedures and processes to align with available services (logistics, payments, security) Changes to assure flexibility and scalability
 Workflow Technologies l Workflow system—software programs that manage all the steps in a business process from start to finish, including all exception conditions l Two categories: ¡ Collaborative workflow—products address project-oriented and collaborative processes ¡ Production workflow—tools address missioncritical, transaction-oriented processes
Workflow Technologies l Workflow system—software programs that manage all the steps in a business process from start to finish, including all exception conditions l Two categories: ¡ Collaborative workflow—products address project-oriented and collaborative processes ¡ Production workflow—tools address missioncritical, transaction-oriented processes
 Virtual Corporations Virtual corporation—an organization composed of several business partners (some of whom may be pure-play EC players) sharing costs and resources for the production or purchasing of a product or service l Major attributes of VCs: l ¡ Utilization ¡ Opportunism ¡ Trust ¡ Technology Excellence Lack of borders Adaptability to change
Virtual Corporations Virtual corporation—an organization composed of several business partners (some of whom may be pure-play EC players) sharing costs and resources for the production or purchasing of a product or service l Major attributes of VCs: l ¡ Utilization ¡ Opportunism ¡ Trust ¡ Technology Excellence Lack of borders Adaptability to change
 The Future of EC (CSF’s) l l l l Internet usage Opportunities for buying M-commerce Purchasing incentives Increased security and trust Efficient information handing Innovative organizations Virtual Communities l l l l Payment systems Business-to-business B 2 B exchanges Auctions Going global E-government-comprehensive Intrabusiness EC E-learning
The Future of EC (CSF’s) l l l l Internet usage Opportunities for buying M-commerce Purchasing incentives Increased security and trust Efficient information handing Innovative organizations Virtual Communities l l l l Payment systems Business-to-business B 2 B exchanges Auctions Going global E-government-comprehensive Intrabusiness EC E-learning
 EC Technology Trends l l l Clients Embedded clients Servers Networks Wireless communications l l l EC software and services Search engines P 2 P technology Integration Wearable devices
EC Technology Trends l l l Clients Embedded clients Servers Networks Wireless communications l l l EC software and services Search engines P 2 P technology Integration Wearable devices
 The Digital Divide Digital divide—the gap between those who have and those who do not have the ability to access electronic technology in general, and the Internet and EC in particular l 90% of all Internet computers are where 15% of the world’s population live l
The Digital Divide Digital divide—the gap between those who have and those who do not have the ability to access electronic technology in general, and the Internet and EC in particular l 90% of all Internet computers are where 15% of the world’s population live l
 Integrating Marketplace and Marketspace l Click-and-mortar organization ¡ How to cooperate in planning, advertising, logistics, resource allocation ¡ How to align the strategic plans ¡ B 2 C ordering systems l The impact of EC on our lives may be as much as, or more than that of the Industrial Revolution
Integrating Marketplace and Marketspace l Click-and-mortar organization ¡ How to cooperate in planning, advertising, logistics, resource allocation ¡ How to align the strategic plans ¡ B 2 C ordering systems l The impact of EC on our lives may be as much as, or more than that of the Industrial Revolution


