117582a5530eb6b8ade8b9b397d74bf2.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 15
 Elasticity
Elasticity
 What is Price Elasticity? When you hear “Elasticity”… it is referring to Price Elasticity s Elasticity: A measure of the responsiveness of Qd or Qs to a change in Price s There are four types of Elasticity you will need to master for the AP Exam are: s Price Elasticity of Demand s Income Elasticity (of Demand) s Cross Elasticity (of Demand) s Price Elasticity of Supply
What is Price Elasticity? When you hear “Elasticity”… it is referring to Price Elasticity s Elasticity: A measure of the responsiveness of Qd or Qs to a change in Price s There are four types of Elasticity you will need to master for the AP Exam are: s Price Elasticity of Demand s Income Elasticity (of Demand) s Cross Elasticity (of Demand) s Price Elasticity of Supply
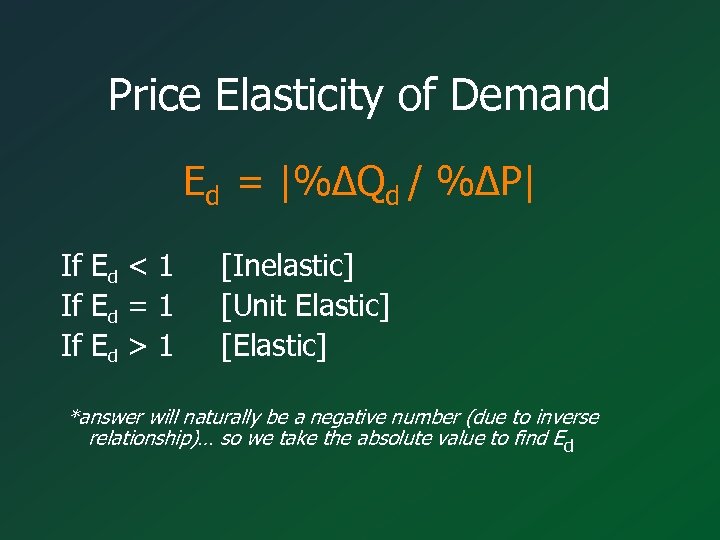 Price Elasticity of Demand Ed = |%∆Qd / %∆P| If Ed < 1 If Ed = 1 If Ed > 1 [Inelastic] [Unit Elastic] [Elastic] *answer will naturally be a negative number (due to inverse relationship)… so we take the absolute value to find Ed
Price Elasticity of Demand Ed = |%∆Qd / %∆P| If Ed < 1 If Ed = 1 If Ed > 1 [Inelastic] [Unit Elastic] [Elastic] *answer will naturally be a negative number (due to inverse relationship)… so we take the absolute value to find Ed
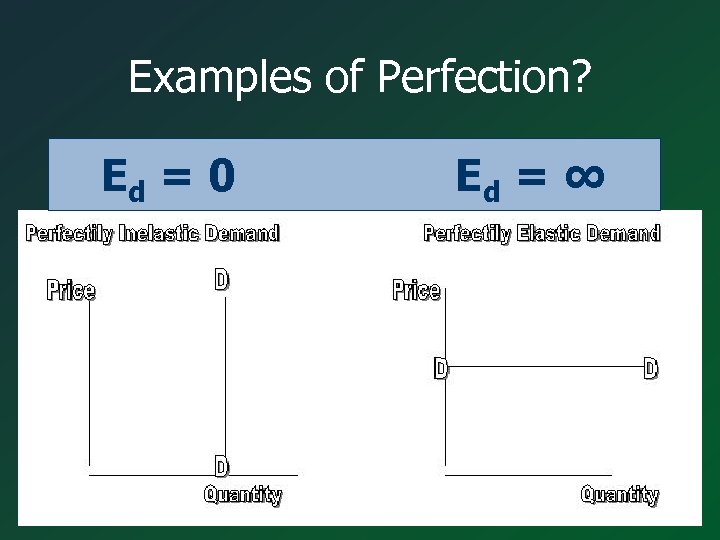 Examples of Perfection? Ed = 0 Ed = ∞
Examples of Perfection? Ed = 0 Ed = ∞
 DETERMINANTS of DEMAND Ed tends to be ELASTIC if… s Substitutes are available s Product price makes up a larger portion of the consumer’s income s The product is a luxury s The consumer has adjustment time to make changes in behavior, making the product less necessary
DETERMINANTS of DEMAND Ed tends to be ELASTIC if… s Substitutes are available s Product price makes up a larger portion of the consumer’s income s The product is a luxury s The consumer has adjustment time to make changes in behavior, making the product less necessary
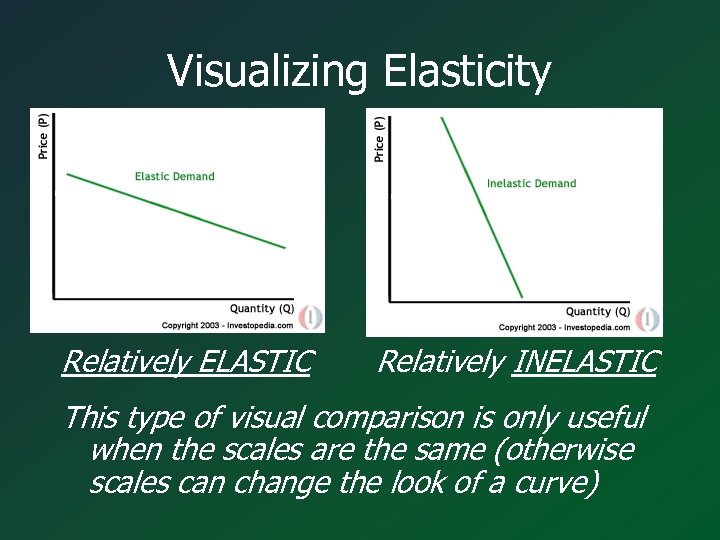 Visualizing Elasticity Relatively ELASTIC Relatively INELASTIC This type of visual comparison is only useful when the scales are the same (otherwise scales can change the look of a curve)
Visualizing Elasticity Relatively ELASTIC Relatively INELASTIC This type of visual comparison is only useful when the scales are the same (otherwise scales can change the look of a curve)
 Income Elasticity (of Demand) EI = %∆Qd/ %∆Income s If answer is positive: s NORMAL good s If answer is negative: s INFERIOR good
Income Elasticity (of Demand) EI = %∆Qd/ %∆Income s If answer is positive: s NORMAL good s If answer is negative: s INFERIOR good
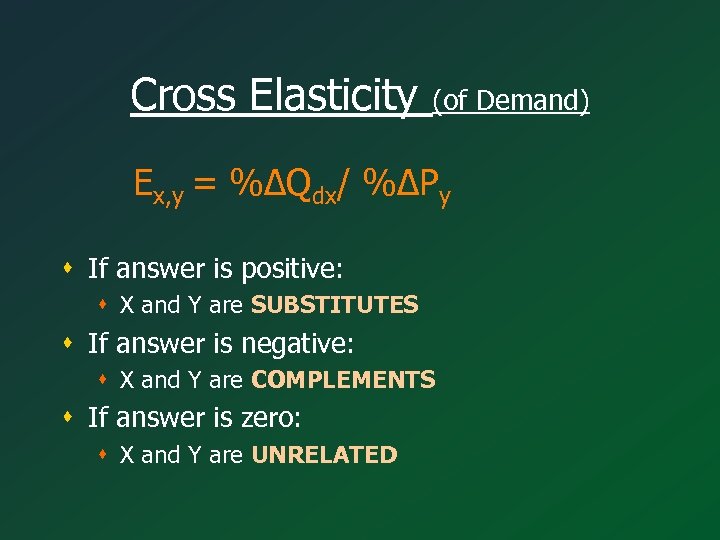 Cross Elasticity (of Demand) Ex, y = %∆Qdx/ %∆Py s If answer is positive: s X and Y are SUBSTITUTES s If answer is negative: s X and Y are COMPLEMENTS s If answer is zero: s X and Y are UNRELATED
Cross Elasticity (of Demand) Ex, y = %∆Qdx/ %∆Py s If answer is positive: s X and Y are SUBSTITUTES s If answer is negative: s X and Y are COMPLEMENTS s If answer is zero: s X and Y are UNRELATED
 Price Elasticity of Supply Es = %∆Qs / %∆P If Es < 1 If Es = 1 If Es > 1 [Inelastic] [Unit Elastic] [Elastic] *answer should never be less than zero
Price Elasticity of Supply Es = %∆Qs / %∆P If Es < 1 If Es = 1 If Es > 1 [Inelastic] [Unit Elastic] [Elastic] *answer should never be less than zero
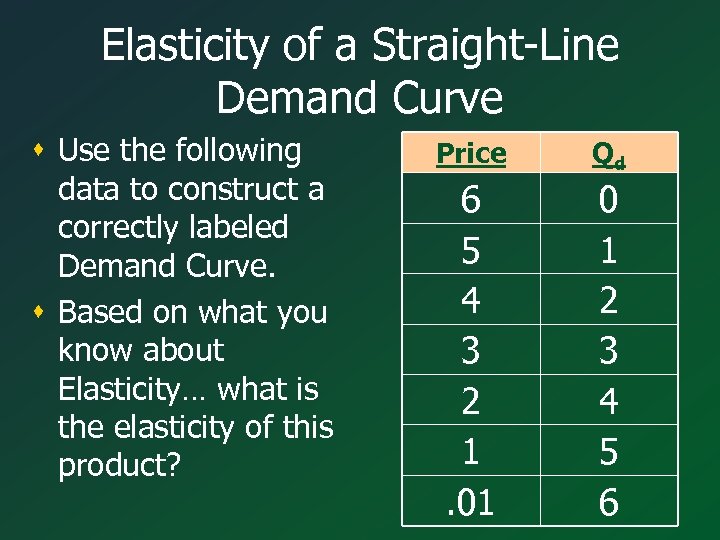 Elasticity of a Straight-Line Demand Curve s Use the following data to construct a correctly labeled Demand Curve. s Based on what you know about Elasticity… what is the elasticity of this product? Price Qd 6 5 4 3 2 1. 01 0 1 2 3 4 5 6
Elasticity of a Straight-Line Demand Curve s Use the following data to construct a correctly labeled Demand Curve. s Based on what you know about Elasticity… what is the elasticity of this product? Price Qd 6 5 4 3 2 1. 01 0 1 2 3 4 5 6
![Total Revenue Test [TR=P*Q] If price is decreasing and total revenue is increasing then Total Revenue Test [TR=P*Q] If price is decreasing and total revenue is increasing then](https://present5.com/presentation/117582a5530eb6b8ade8b9b397d74bf2/image-11.jpg) Total Revenue Test [TR=P*Q] If price is decreasing and total revenue is increasing then the product is ELASTIC _________ If price is decreases and total revenue decreases then the product is INELASTIC _________ If price changes, but total revenue stays the same the product is UNIT ELASTIC
Total Revenue Test [TR=P*Q] If price is decreasing and total revenue is increasing then the product is ELASTIC _________ If price is decreases and total revenue decreases then the product is INELASTIC _________ If price changes, but total revenue stays the same the product is UNIT ELASTIC

 Summary: Elasticity s s Definition Factors that determine Price Elasticity How to calculate the 4 types of Elasticity How elasticity affects relationships between goods. s Normal vs. Inferior Goods s Compliment vs. Substitutes s Using the Total Revenue Test s Relationship between… s TR, MR, and point of Ed=0 [preview for next unit]
Summary: Elasticity s s Definition Factors that determine Price Elasticity How to calculate the 4 types of Elasticity How elasticity affects relationships between goods. s Normal vs. Inferior Goods s Compliment vs. Substitutes s Using the Total Revenue Test s Relationship between… s TR, MR, and point of Ed=0 [preview for next unit]
 Free Response Question Once upon a time there was a college student who had to stay up studying many nights in a row. Soon the student had a caffeine addiction and bought Starbucks coffee. He would buy 35 coffees per semester at $2. 00 each. When the student came back in the spring he found coffee to now be $3. 00. Due to the income effect, he can no longer afford as many coffees even though he is addicted. He now only buys 20 coffees per semester. s 1) Is the Ed elastic or inelastic for Coffee? s 2) Calculate the Ed for Coffee for this college student
Free Response Question Once upon a time there was a college student who had to stay up studying many nights in a row. Soon the student had a caffeine addiction and bought Starbucks coffee. He would buy 35 coffees per semester at $2. 00 each. When the student came back in the spring he found coffee to now be $3. 00. Due to the income effect, he can no longer afford as many coffees even though he is addicted. He now only buys 20 coffees per semester. s 1) Is the Ed elastic or inelastic for Coffee? s 2) Calculate the Ed for Coffee for this college student
 Multiple Choice If the price of lunch at the school cafeteria increases and the cafeteria’s total revenue from lunches remains constant, we can conclude that the elasticity of demand for a school lunch is… a) Elastic b) Perfectly Elastic c) Perfectly Inelastic d) Unit Elastic e) Inelastic
Multiple Choice If the price of lunch at the school cafeteria increases and the cafeteria’s total revenue from lunches remains constant, we can conclude that the elasticity of demand for a school lunch is… a) Elastic b) Perfectly Elastic c) Perfectly Inelastic d) Unit Elastic e) Inelastic


