a01bdf712059bfb395418e44ee4e17f5.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 40
 Elasticity. . . Demand elasticity is a measure of how much buyers respond to changes price, income, and other things. u. Supply elasticity is a measure of how much sellers respond to changes in price and other things. u Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
Elasticity. . . Demand elasticity is a measure of how much buyers respond to changes price, income, and other things. u. Supply elasticity is a measure of how much sellers respond to changes in price and other things. u Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
 Flavors of elasticity Price Elasticity of Demand n Income Elasticity of Demand n Advertising Elasticity of Demand n Price Elasticity of Supply n Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
Flavors of elasticity Price Elasticity of Demand n Income Elasticity of Demand n Advertising Elasticity of Demand n Price Elasticity of Supply n Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
 Price Elasticity of Demand • Price elasticity of demand: • the percent change in quantity demanded in response to a percent change in price. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
Price Elasticity of Demand • Price elasticity of demand: • the percent change in quantity demanded in response to a percent change in price. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
 Price Elasticity of Demand tends to be more elastic : u. The larger the number of close substitutes. • the longer the time period. • the more narrowly defined the market. u If the good is a luxury. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
Price Elasticity of Demand tends to be more elastic : u. The larger the number of close substitutes. • the longer the time period. • the more narrowly defined the market. u If the good is a luxury. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
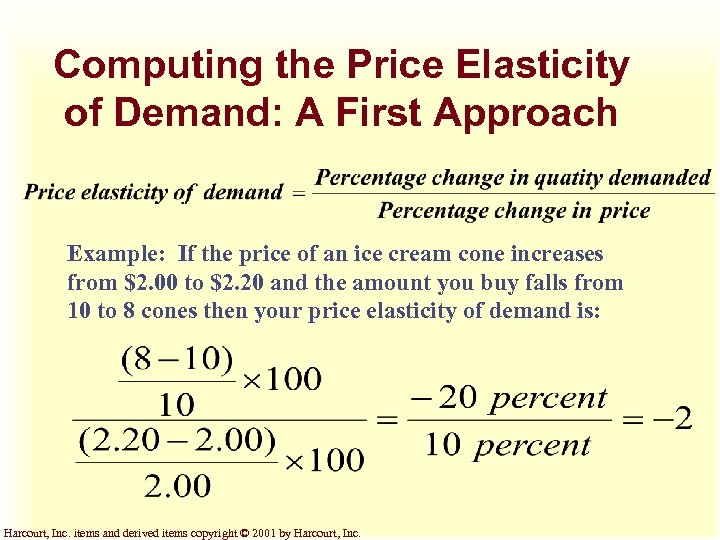 Computing the Price Elasticity of Demand: A First Approach Example: If the price of an ice cream cone increases from $2. 00 to $2. 20 and the amount you buy falls from 10 to 8 cones then your price elasticity of demand is: Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
Computing the Price Elasticity of Demand: A First Approach Example: If the price of an ice cream cone increases from $2. 00 to $2. 20 and the amount you buy falls from 10 to 8 cones then your price elasticity of demand is: Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
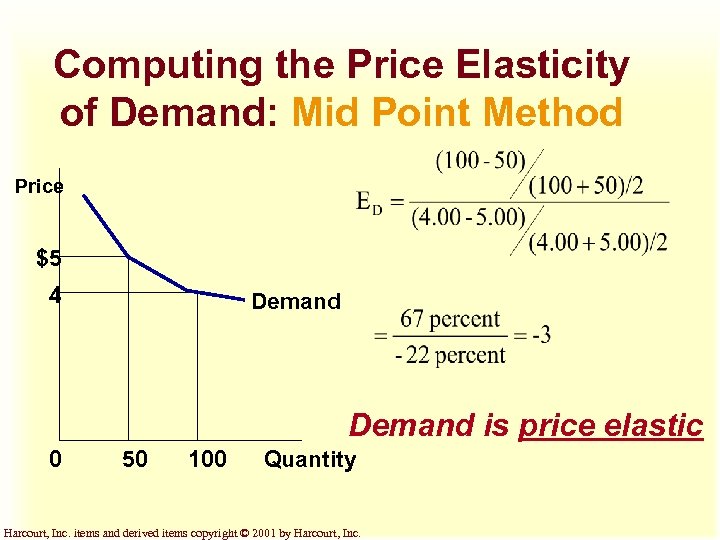 Computing the Price Elasticity of Demand: Mid Point Method Price $5 4 Demand is price elastic 0 50 100 Quantity Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
Computing the Price Elasticity of Demand: Mid Point Method Price $5 4 Demand is price elastic 0 50 100 Quantity Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
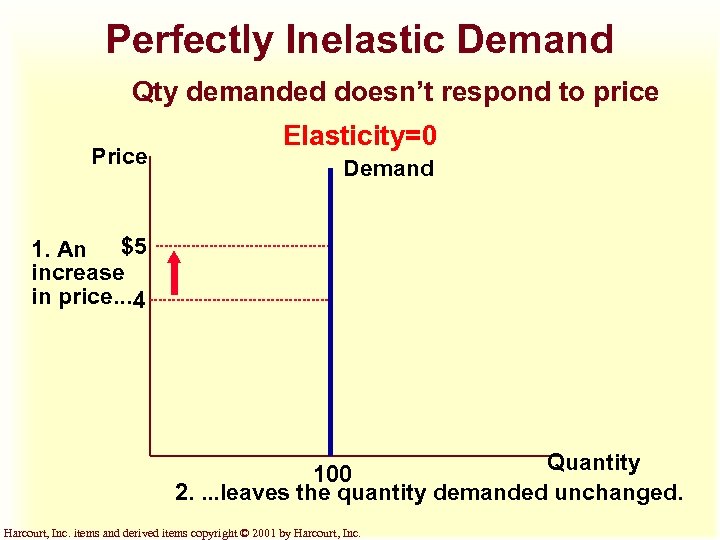 Perfectly Inelastic Demand Qty demanded doesn’t respond to price Price Elasticity=0 Demand 1. An $5 increase in price. . . 4 Quantity 100 2. . leaves the quantity demanded unchanged. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
Perfectly Inelastic Demand Qty demanded doesn’t respond to price Price Elasticity=0 Demand 1. An $5 increase in price. . . 4 Quantity 100 2. . leaves the quantity demanded unchanged. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
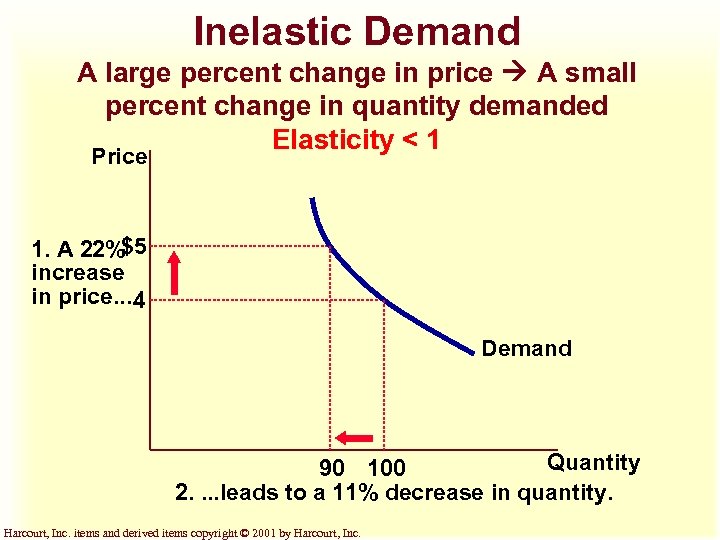 Inelastic Demand A large percent change in price A small percent change in quantity demanded Elasticity < 1 Price 1. A 22%$5 increase in price. . . 4 Demand Quantity 90 100 2. . leads to a 11% decrease in quantity. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
Inelastic Demand A large percent change in price A small percent change in quantity demanded Elasticity < 1 Price 1. A 22%$5 increase in price. . . 4 Demand Quantity 90 100 2. . leads to a 11% decrease in quantity. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
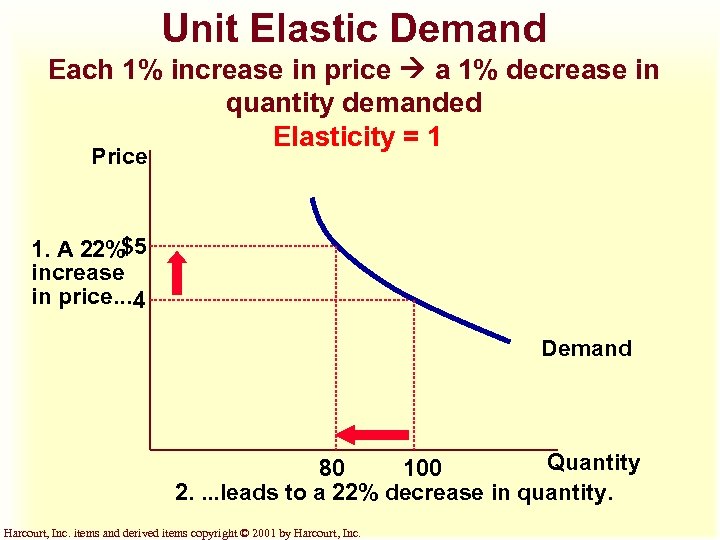 Unit Elastic Demand Each 1% increase in price a 1% decrease in quantity demanded Elasticity = 1 Price 1. A 22%$5 increase in price. . . 4 Demand Quantity 80 100 2. . leads to a 22% decrease in quantity. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
Unit Elastic Demand Each 1% increase in price a 1% decrease in quantity demanded Elasticity = 1 Price 1. A 22%$5 increase in price. . . 4 Demand Quantity 80 100 2. . leads to a 22% decrease in quantity. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
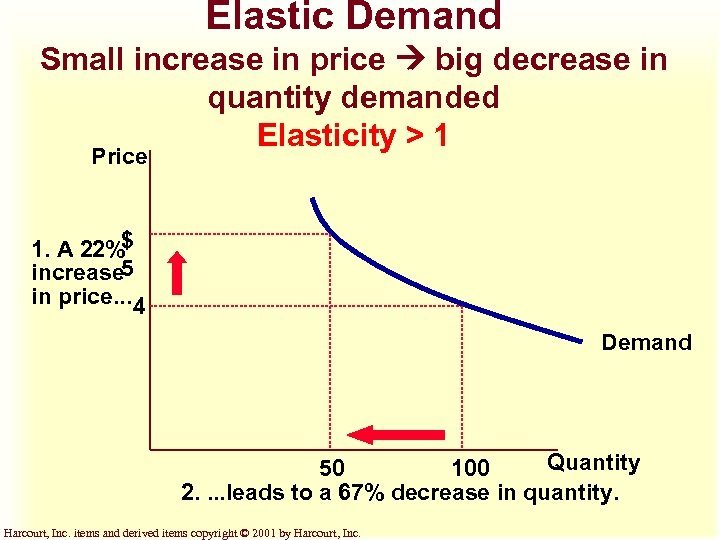 Elastic Demand Small increase in price big decrease in quantity demanded Elasticity > 1 Price 1. A 22%$ increase 5 in price. . . 4 Demand Quantity 50 100 2. . leads to a 67% decrease in quantity. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
Elastic Demand Small increase in price big decrease in quantity demanded Elasticity > 1 Price 1. A 22%$ increase 5 in price. . . 4 Demand Quantity 50 100 2. . leads to a 67% decrease in quantity. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
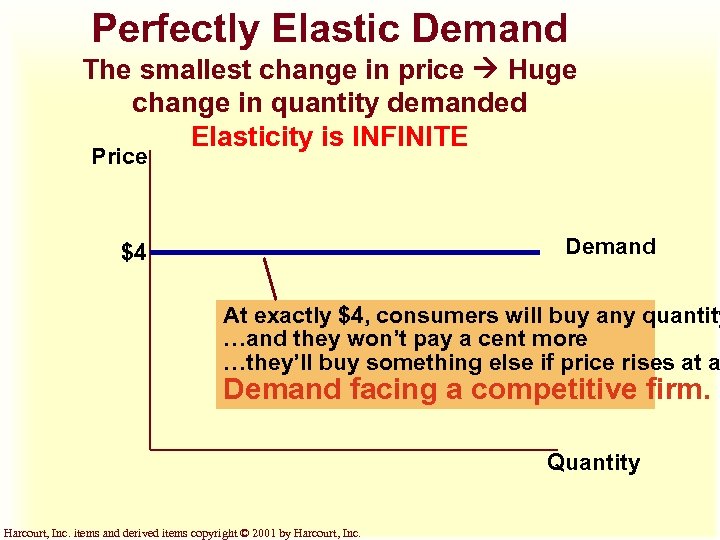 Perfectly Elastic Demand The smallest change in price Huge change in quantity demanded Elasticity is INFINITE Price Demand $4 At exactly $4, consumers will buy any quantity …and they won’t pay a cent more …they’ll buy something else if price rises at a Demand facing a competitive firm. Quantity Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
Perfectly Elastic Demand The smallest change in price Huge change in quantity demanded Elasticity is INFINITE Price Demand $4 At exactly $4, consumers will buy any quantity …and they won’t pay a cent more …they’ll buy something else if price rises at a Demand facing a competitive firm. Quantity Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
 Price Elasticity and Total Revenue u. Total revenue is the price of a good multiplied by the quantity sold. TR = P x Q Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
Price Elasticity and Total Revenue u. Total revenue is the price of a good multiplied by the quantity sold. TR = P x Q Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
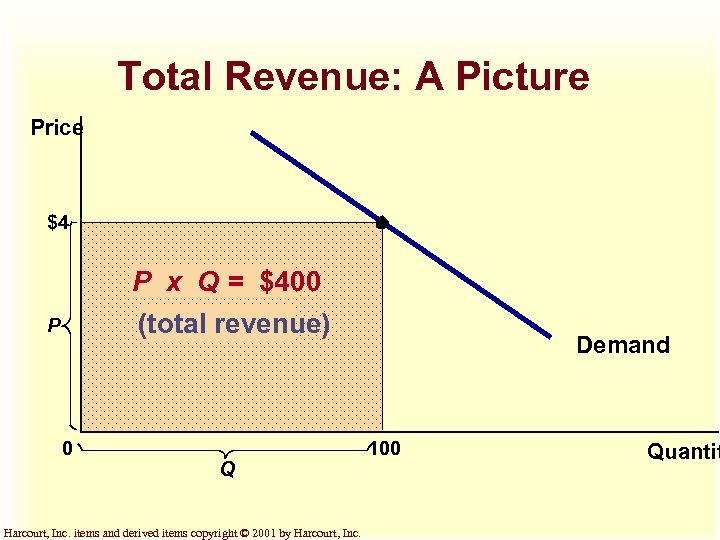 Total Revenue: A Picture Price $4 P x Q = $400 (total revenue) P 0 Q Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc. Demand 100 Quantit
Total Revenue: A Picture Price $4 P x Q = $400 (total revenue) P 0 Q Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc. Demand 100 Quantit
 Elasticity and Total Revenue n. With inelastic demand, an increase in price leads to a small decrease in quantity demanded. n. Total revenue increases when price rises. P x Q Increases when P rises Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
Elasticity and Total Revenue n. With inelastic demand, an increase in price leads to a small decrease in quantity demanded. n. Total revenue increases when price rises. P x Q Increases when P rises Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
 Elasticity and Total Revenue n. With elastic demand, a small increase in price leads to a big decrease in quantity demanded. n. T otal revenue decreases when price rises. P x Q decreases when P rises Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
Elasticity and Total Revenue n. With elastic demand, a small increase in price leads to a big decrease in quantity demanded. n. T otal revenue decreases when price rises. P x Q decreases when P rises Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
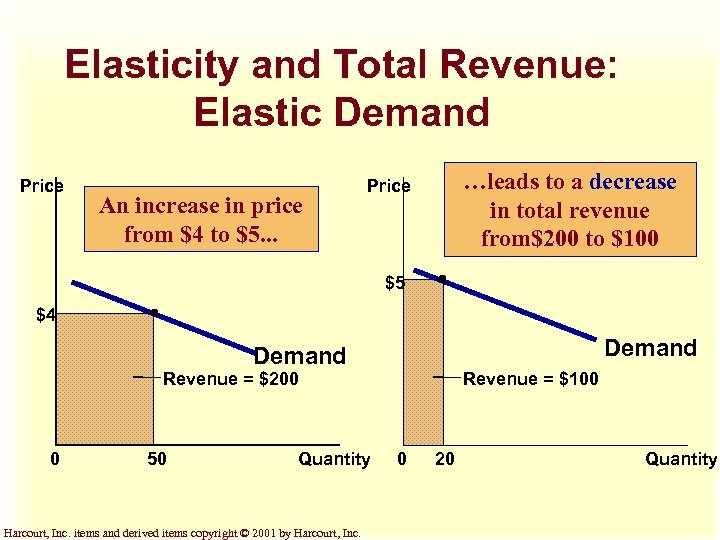 Elasticity and Total Revenue: Elastic Demand Price An increase in price from $4 to $5. . . …leads to a decrease in total revenue from$200 to $100 Price $5 $4 Demand Revenue = $200 0 50 Quantity Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc. Revenue = $100 0 20 Quantity
Elasticity and Total Revenue: Elastic Demand Price An increase in price from $4 to $5. . . …leads to a decrease in total revenue from$200 to $100 Price $5 $4 Demand Revenue = $200 0 50 Quantity Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc. Revenue = $100 0 20 Quantity
 Income Elasticity of Demand u. Quantity demanded responds to consumer income. u. Income elasticity of demand: upercentage change in quantity demanded divided by the percentage change in income. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
Income Elasticity of Demand u. Quantity demanded responds to consumer income. u. Income elasticity of demand: upercentage change in quantity demanded divided by the percentage change in income. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
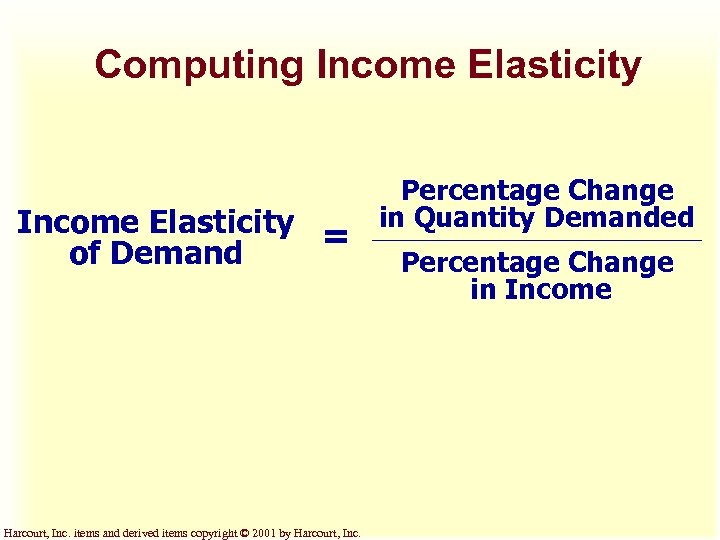 Computing Income Elasticity = of Demand Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc. Percentage Change in Quantity Demanded Percentage Change in Income
Computing Income Elasticity = of Demand Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc. Percentage Change in Quantity Demanded Percentage Change in Income
 Income Elasticity - Types of Goods u. Necessities are income inelastic Examples: food, fuel, clothing, utilities, medical care. u. Luxuries are income elastic. Examples: sports cars, jewelry, gourmet foods. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
Income Elasticity - Types of Goods u. Necessities are income inelastic Examples: food, fuel, clothing, utilities, medical care. u. Luxuries are income elastic. Examples: sports cars, jewelry, gourmet foods. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
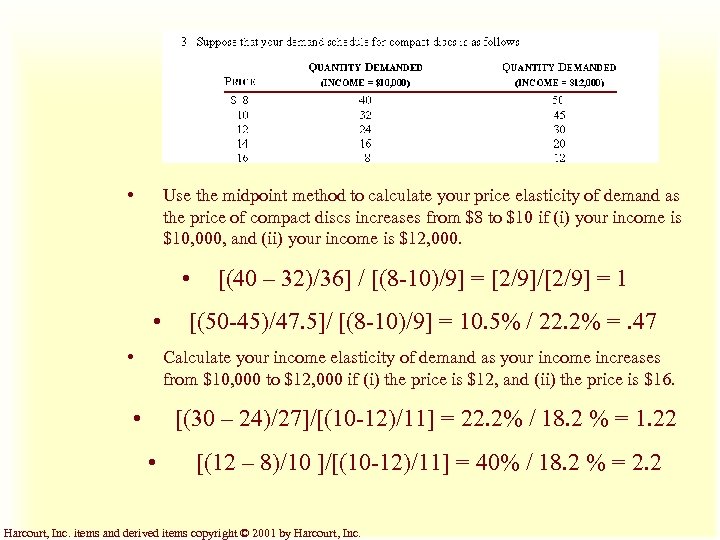 • Use the midpoint method to calculate your price elasticity of demand as the price of compact discs increases from $8 to $10 if (i) your income is $10, 000, and (ii) your income is $12, 000. • • • [(40 – 32)/36] / [(8 -10)/9] = [2/9]/[2/9] = 1 [(50 -45)/47. 5]/ [(8 -10)/9] = 10. 5% / 22. 2% =. 47 Calculate your income elasticity of demand as your income increases from $10, 000 to $12, 000 if (i) the price is $12, and (ii) the price is $16. • [(30 – 24)/27]/[(10 -12)/11] = 22. 2% / 18. 2 % = 1. 22 • [(12 – 8)/10 ]/[(10 -12)/11] = 40% / 18. 2 % = 2. 2 Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
• Use the midpoint method to calculate your price elasticity of demand as the price of compact discs increases from $8 to $10 if (i) your income is $10, 000, and (ii) your income is $12, 000. • • • [(40 – 32)/36] / [(8 -10)/9] = [2/9]/[2/9] = 1 [(50 -45)/47. 5]/ [(8 -10)/9] = 10. 5% / 22. 2% =. 47 Calculate your income elasticity of demand as your income increases from $10, 000 to $12, 000 if (i) the price is $12, and (ii) the price is $16. • [(30 – 24)/27]/[(10 -12)/11] = 22. 2% / 18. 2 % = 1. 22 • [(12 – 8)/10 ]/[(10 -12)/11] = 40% / 18. 2 % = 2. 2 Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
 Price Elasticity of Supply u. Quantity supplied responds to price. u. Price elasticity of supply the percentage change in quantity supplied resulting from a percent change in price. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
Price Elasticity of Supply u. Quantity supplied responds to price. u. Price elasticity of supply the percentage change in quantity supplied resulting from a percent change in price. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
 Computing the Price Elasticity of Supply The percentage change in quantity supplied divided by the percentage change in price. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
Computing the Price Elasticity of Supply The percentage change in quantity supplied divided by the percentage change in price. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
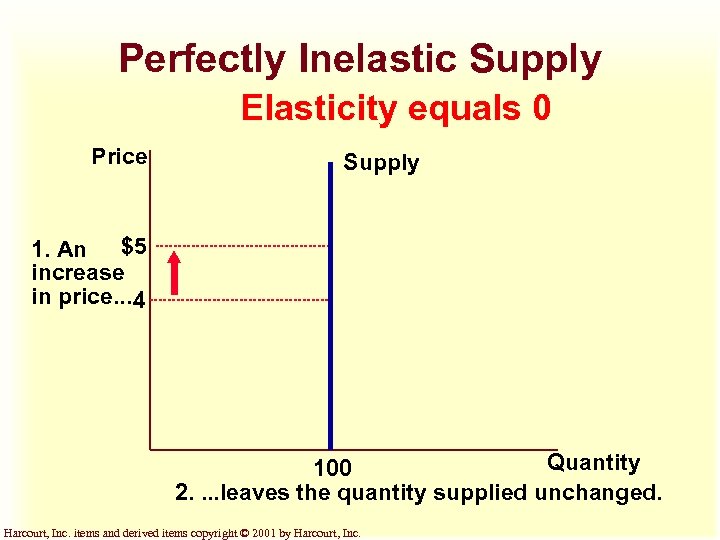 Perfectly Inelastic Supply Elasticity equals 0 Price Supply 1. An $5 increase in price. . . 4 Quantity 100 2. . leaves the quantity supplied unchanged. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
Perfectly Inelastic Supply Elasticity equals 0 Price Supply 1. An $5 increase in price. . . 4 Quantity 100 2. . leaves the quantity supplied unchanged. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
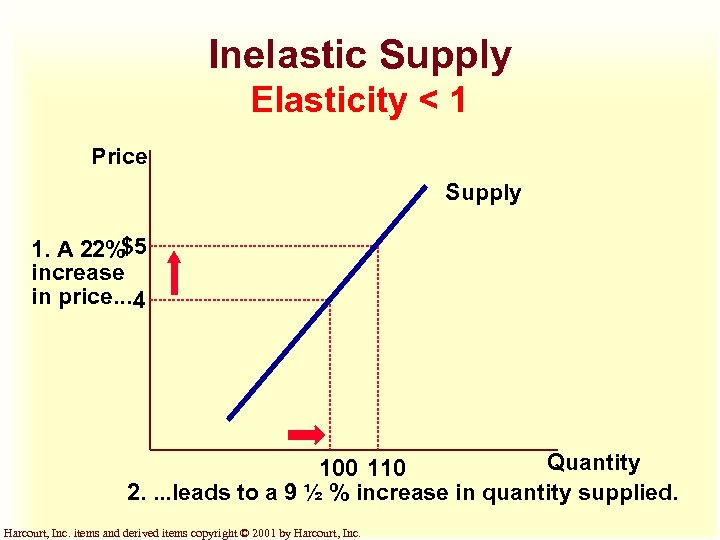 Inelastic Supply Elasticity < 1 Price Supply 1. A 22%$5 increase in price. . . 4 Quantity 100 110 2. . leads to a 9 ½ % increase in quantity supplied. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
Inelastic Supply Elasticity < 1 Price Supply 1. A 22%$5 increase in price. . . 4 Quantity 100 110 2. . leads to a 9 ½ % increase in quantity supplied. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
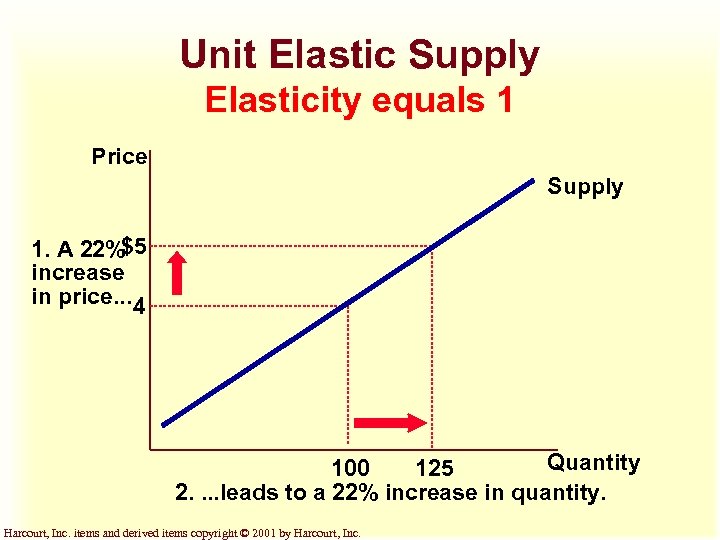 Unit Elastic Supply Elasticity equals 1 Price Supply 1. A 22%$5 increase in price. . . 4 Quantity 100 125 2. . leads to a 22% increase in quantity. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
Unit Elastic Supply Elasticity equals 1 Price Supply 1. A 22%$5 increase in price. . . 4 Quantity 100 125 2. . leads to a 22% increase in quantity. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
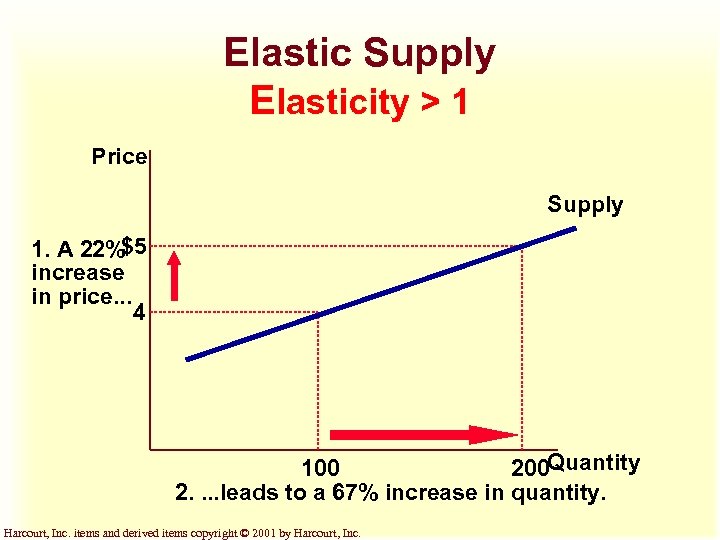 Elastic Supply Elasticity > 1 Price Supply 1. A 22%$5 increase in price. . . 4 100 200 Quantity 2. . leads to a 67% increase in quantity. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
Elastic Supply Elasticity > 1 Price Supply 1. A 22%$5 increase in price. . . 4 100 200 Quantity 2. . leads to a 67% increase in quantity. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
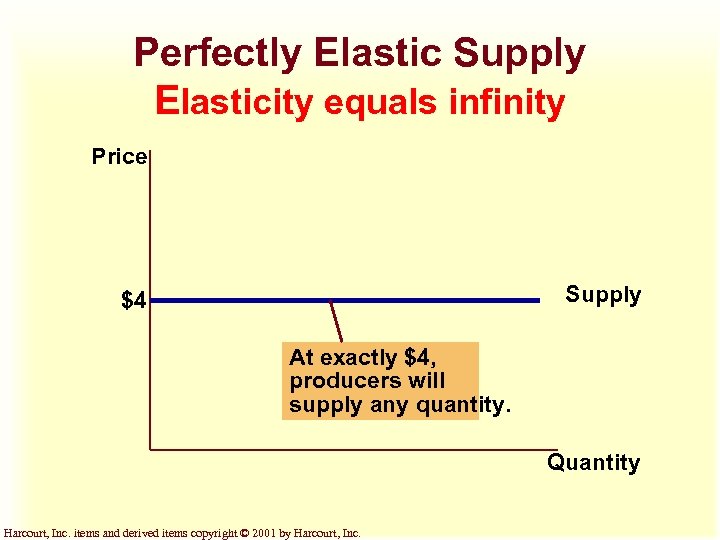 Perfectly Elastic Supply Elasticity equals infinity Price Supply $4 At exactly $4, producers will supply any quantity. Quantity Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
Perfectly Elastic Supply Elasticity equals infinity Price Supply $4 At exactly $4, producers will supply any quantity. Quantity Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
 Determinants of Elasticity of Supply Ability of sellers to change the amount they produce • • Beach-front land is inelastic. Books, cars, or manufactured goods are elastic. Time period • Supply is more elastic in the long run than in the short run. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
Determinants of Elasticity of Supply Ability of sellers to change the amount they produce • • Beach-front land is inelastic. Books, cars, or manufactured goods are elastic. Time period • Supply is more elastic in the long run than in the short run. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
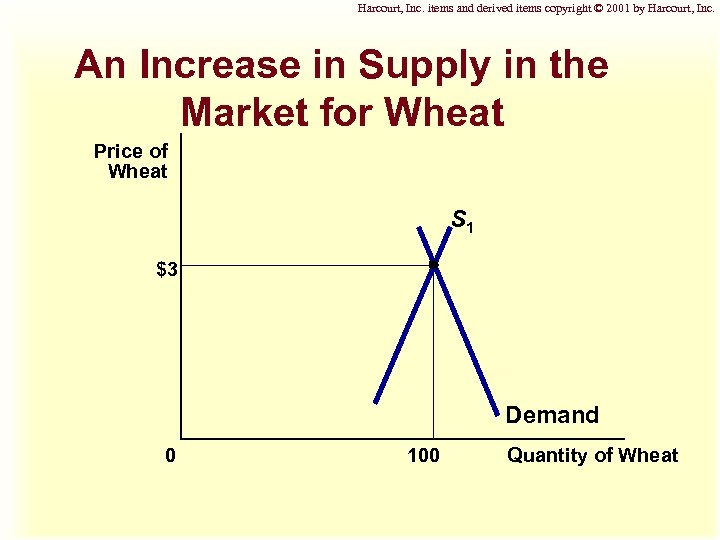 Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc. An Increase in Supply in the Market for Wheat Price of Wheat S 1 $3 Demand 0 100 Quantity of Wheat
Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc. An Increase in Supply in the Market for Wheat Price of Wheat S 1 $3 Demand 0 100 Quantity of Wheat
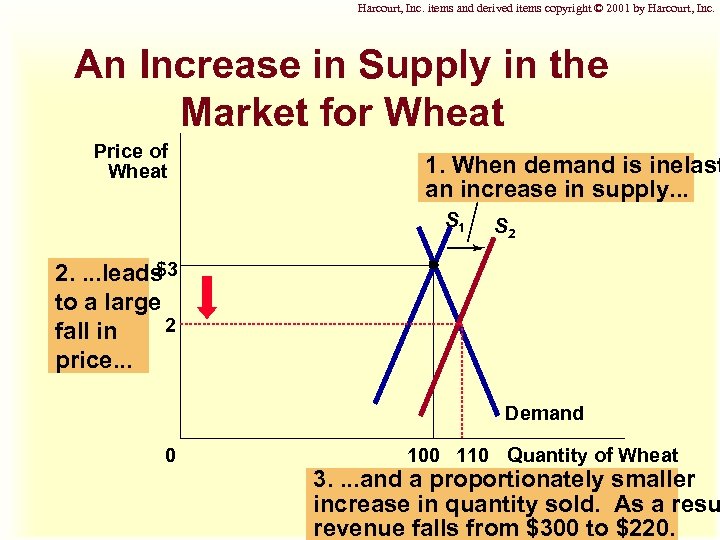 Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc. An Increase in Supply in the Market for Wheat Price of Wheat 1. When demand is inelast an increase in supply. . . S 1 S 2 $3 2. . leads to a large 2 fall in price. . . Demand 0 100 110 Quantity of Wheat 3. . and a proportionately smaller increase in quantity sold. As a resu revenue falls from $300 to $220.
Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc. An Increase in Supply in the Market for Wheat Price of Wheat 1. When demand is inelast an increase in supply. . . S 1 S 2 $3 2. . leads to a large 2 fall in price. . . Demand 0 100 110 Quantity of Wheat 3. . and a proportionately smaller increase in quantity sold. As a resu revenue falls from $300 to $220.
 Summary u. Price elasticity of demand measures how much the quantity demanded responds to changes in the price. u. If a demand curve is elastic, total revenue falls when the price rises. u. If it is inelastic, total revenue rises as the price rises. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
Summary u. Price elasticity of demand measures how much the quantity demanded responds to changes in the price. u. If a demand curve is elastic, total revenue falls when the price rises. u. If it is inelastic, total revenue rises as the price rises. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
 Summary u. The price elasticity of supply measures how much the quantity supplied responds to changes in the price. u. In most markets, supply is more elastic in the long run than in the short run. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
Summary u. The price elasticity of supply measures how much the quantity supplied responds to changes in the price. u. In most markets, supply is more elastic in the long run than in the short run. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
 Graphical Review Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
Graphical Review Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
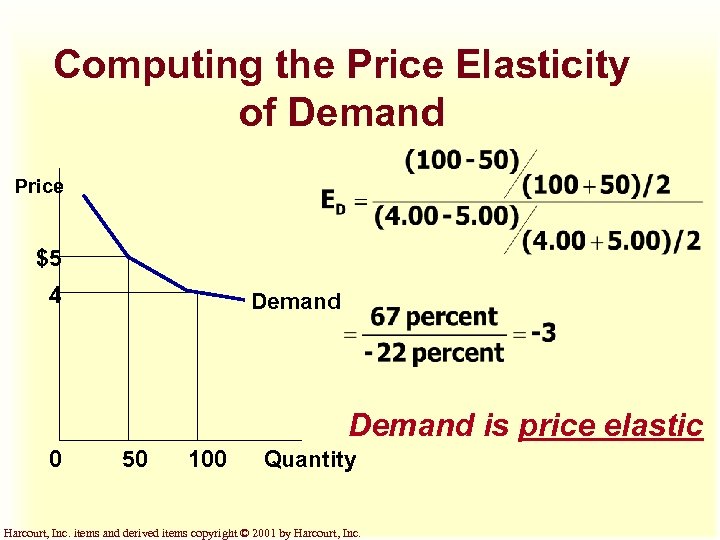 Computing the Price Elasticity of Demand Price $5 4 Demand is price elastic 0 50 100 Quantity Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
Computing the Price Elasticity of Demand Price $5 4 Demand is price elastic 0 50 100 Quantity Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
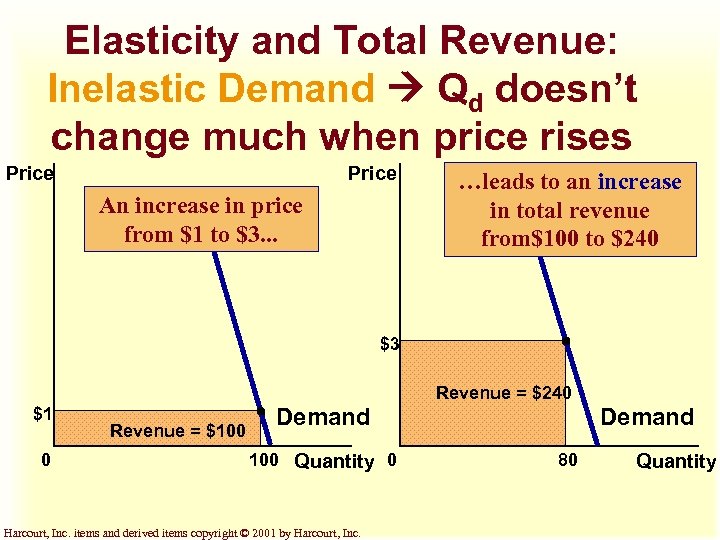 Elasticity and Total Revenue: Inelastic Demand Qd doesn’t change much when price rises Price An increase in price from $1 to $3. . . …leads to an increase in total revenue from$100 to $240 $3 Revenue = $240 $1 0 Revenue = $100 Demand 100 Quantity 0 Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc. Demand 80 Quantity
Elasticity and Total Revenue: Inelastic Demand Qd doesn’t change much when price rises Price An increase in price from $1 to $3. . . …leads to an increase in total revenue from$100 to $240 $3 Revenue = $240 $1 0 Revenue = $100 Demand 100 Quantity 0 Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc. Demand 80 Quantity
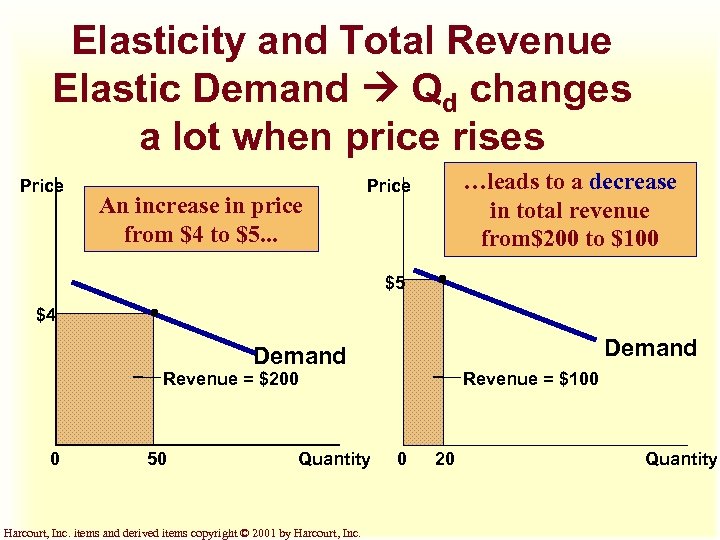 Elasticity and Total Revenue Elastic Demand Qd changes a lot when price rises Price An increase in price from $4 to $5. . . …leads to a decrease in total revenue from$200 to $100 Price $5 $4 Demand Revenue = $200 0 50 Quantity Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc. Revenue = $100 0 20 Quantity
Elasticity and Total Revenue Elastic Demand Qd changes a lot when price rises Price An increase in price from $4 to $5. . . …leads to a decrease in total revenue from$200 to $100 Price $5 $4 Demand Revenue = $200 0 50 Quantity Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc. Revenue = $100 0 20 Quantity
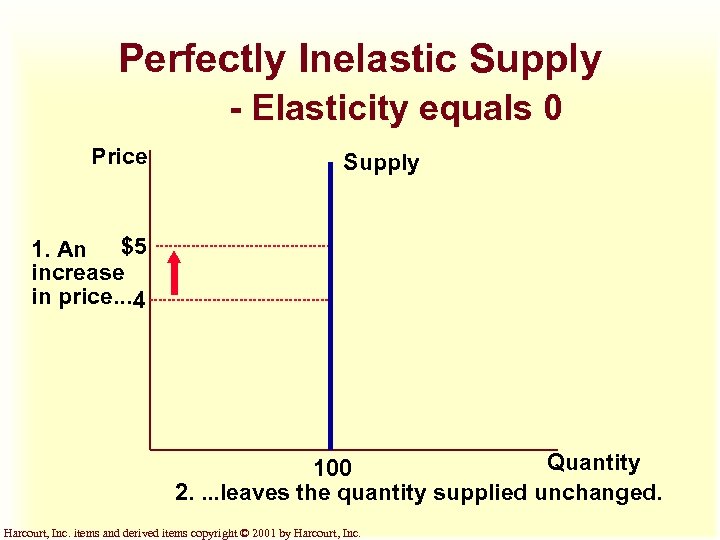 Perfectly Inelastic Supply - Elasticity equals 0 Price Supply 1. An $5 increase in price. . . 4 Quantity 100 2. . leaves the quantity supplied unchanged. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
Perfectly Inelastic Supply - Elasticity equals 0 Price Supply 1. An $5 increase in price. . . 4 Quantity 100 2. . leaves the quantity supplied unchanged. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
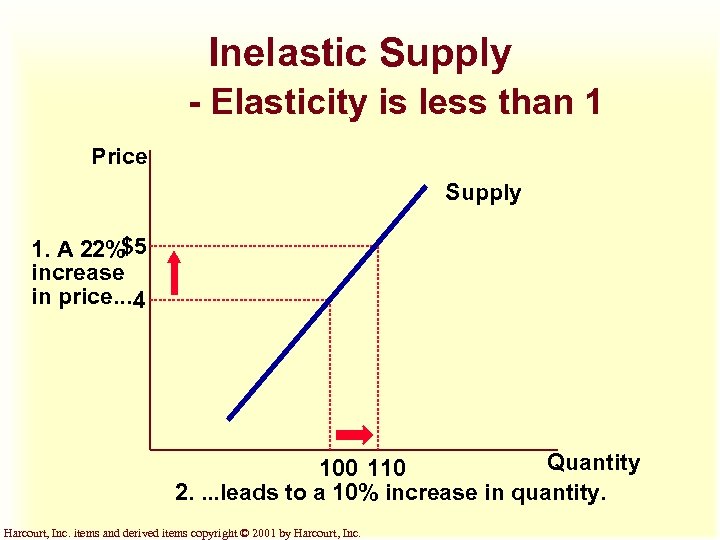 Inelastic Supply - Elasticity is less than 1 Price Supply 1. A 22%$5 increase in price. . . 4 Quantity 100 110 2. . leads to a 10% increase in quantity. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
Inelastic Supply - Elasticity is less than 1 Price Supply 1. A 22%$5 increase in price. . . 4 Quantity 100 110 2. . leads to a 10% increase in quantity. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
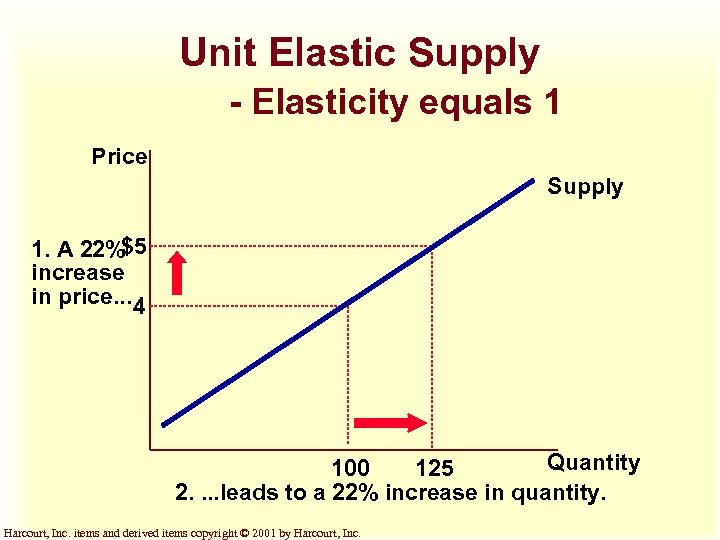 Unit Elastic Supply - Elasticity equals 1 Price Supply 1. A 22%$5 increase in price. . . 4 Quantity 100 125 2. . leads to a 22% increase in quantity. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
Unit Elastic Supply - Elasticity equals 1 Price Supply 1. A 22%$5 increase in price. . . 4 Quantity 100 125 2. . leads to a 22% increase in quantity. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
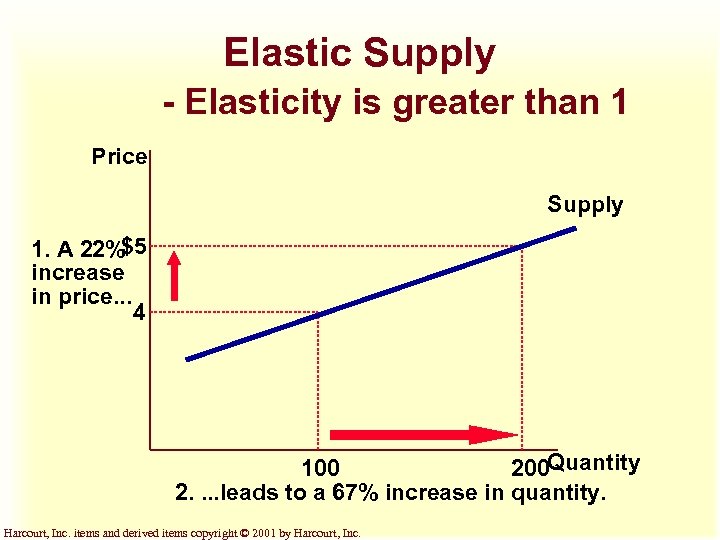 Elastic Supply - Elasticity is greater than 1 Price Supply 1. A 22%$5 increase in price. . . 4 100 200 Quantity 2. . leads to a 67% increase in quantity. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
Elastic Supply - Elasticity is greater than 1 Price Supply 1. A 22%$5 increase in price. . . 4 100 200 Quantity 2. . leads to a 67% increase in quantity. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.


