 Эксплуатационная прочность и надежность конструкций в магистерской программе 08. 04. 01 Egyptian Bridge collapse in SPb in 1905. Chain suspended bridge failure was caused by marching in step of a military division which induced forced vibration and failure of the bridge
Эксплуатационная прочность и надежность конструкций в магистерской программе 08. 04. 01 Egyptian Bridge collapse in SPb in 1905. Chain suspended bridge failure was caused by marching in step of a military division which induced forced vibration and failure of the bridge
 Reliability? In-Service Reliability? The In-service Strength and Reliability of Structures Course is focused on mechanisms of structural degradation, mostly on explanation of the fatigue damage and the methodology of fatigue assessment of structures. Reliability is the capability of a structure to fulfill the intended functions without operational failures through the prescribed life. Reliability is composed of Durability provided by the design, proper selection of materials, permanence, provided by the design and maintenance, accessibility for inspection and reparability of structural components which might be affected by the material and structure degradation processes in service.
Reliability? In-Service Reliability? The In-service Strength and Reliability of Structures Course is focused on mechanisms of structural degradation, mostly on explanation of the fatigue damage and the methodology of fatigue assessment of structures. Reliability is the capability of a structure to fulfill the intended functions without operational failures through the prescribed life. Reliability is composed of Durability provided by the design, proper selection of materials, permanence, provided by the design and maintenance, accessibility for inspection and reparability of structural components which might be affected by the material and structure degradation processes in service.
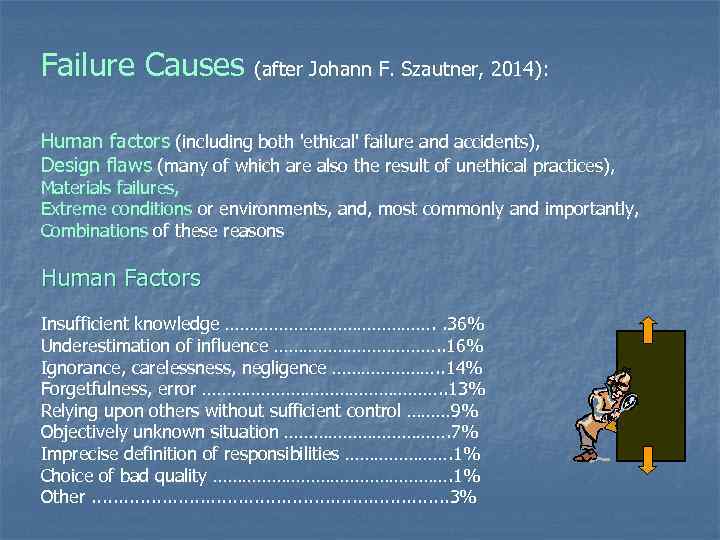 Failure Causes (after Johann F. Szautner, 2014): Human factors (including both 'ethical' failure and accidents), Design flaws (many of which are also the result of unethical practices), Materials failures, Extreme conditions or environments, and, most commonly and importantly, Combinations of these reasons Human Factors Insufficient knowledge …………………. . 36% Underestimation of influence ………………. . 16% Ignorance, carelessness, negligence …………………. . 14% Forgetfulness, error ……………………. . 13% Relying upon others without sufficient control ……… 9% Objectively unknown situation ………………. 7% Imprecise definition of responsibilities …………………. 1% Choice of bad quality ……………………. 1% Other. . . . 3%
Failure Causes (after Johann F. Szautner, 2014): Human factors (including both 'ethical' failure and accidents), Design flaws (many of which are also the result of unethical practices), Materials failures, Extreme conditions or environments, and, most commonly and importantly, Combinations of these reasons Human Factors Insufficient knowledge …………………. . 36% Underestimation of influence ………………. . 16% Ignorance, carelessness, negligence …………………. . 14% Forgetfulness, error ……………………. . 13% Relying upon others without sufficient control ……… 9% Objectively unknown situation ………………. 7% Imprecise definition of responsibilities …………………. 1% Choice of bad quality ……………………. 1% Other. . . . 3%
 DISASTROUS ACCIDENTS FROM EARLY EVIDENCES UP TO PRESENT May 1842: Crash of the train on the way from Versailles to Paris caused by fatigue fracture of the leading locomotive axle. Passengers were locked in carriages; 55 of them were lost in fire, including famous explorer of Pacific J. Dumont d’Urville. Scottish engineer JWM RANKINE was the first who recognized detrimental effect of stress concentration on fatigue
DISASTROUS ACCIDENTS FROM EARLY EVIDENCES UP TO PRESENT May 1842: Crash of the train on the way from Versailles to Paris caused by fatigue fracture of the leading locomotive axle. Passengers were locked in carriages; 55 of them were lost in fire, including famous explorer of Pacific J. Dumont d’Urville. Scottish engineer JWM RANKINE was the first who recognized detrimental effect of stress concentration on fatigue
 DISASTROUS ACCIDENTS FROM EARLY EVIDENCES UP TO PRESENT The ICE «Eschede» train disaster, 1998 The «Eschede» train disaster was the world's deadliest high-speed train accident on 3 June 1998, near the village of Eschede in the Lower Saxony, Germany. The toll of 101 people dead and 88 (estimated) injured. The accident was caused by a single fatigue crack in one wheel which, when it finally failed, caused the train to derail at a rail switch
DISASTROUS ACCIDENTS FROM EARLY EVIDENCES UP TO PRESENT The ICE «Eschede» train disaster, 1998 The «Eschede» train disaster was the world's deadliest high-speed train accident on 3 June 1998, near the village of Eschede in the Lower Saxony, Germany. The toll of 101 people dead and 88 (estimated) injured. The accident was caused by a single fatigue crack in one wheel which, when it finally failed, caused the train to derail at a rail switch
 Tacoma Narrows Bridge Failure, 1940 Photographer Clifford of the Tacoma News snapped a few shots and run
Tacoma Narrows Bridge Failure, 1940 Photographer Clifford of the Tacoma News snapped a few shots and run
 Tacoma Narrows Bridge Failure, 1940 Spectacular failure of the bridge caused by excessive torsional vibration of structure induced by wind gusts
Tacoma Narrows Bridge Failure, 1940 Spectacular failure of the bridge caused by excessive torsional vibration of structure induced by wind gusts
 The Collapse of the Highway Bridge in central Minneapolis in 2007 The findings of investigation (2008): The primary cause was the under-sized gusset plates, 13 mm thick. Contributing factors were: 51 mm of concrete added to the road surface over the years, increasing the DEAD LOAD by 20%. Also contributing were…
The Collapse of the Highway Bridge in central Minneapolis in 2007 The findings of investigation (2008): The primary cause was the under-sized gusset plates, 13 mm thick. Contributing factors were: 51 mm of concrete added to the road surface over the years, increasing the DEAD LOAD by 20%. Also contributing were…