6c001eae8b552386800918b6519c1116.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 23
 EIONET interest group Land use and spatial planning Andrus Meiner, EEA
EIONET interest group Land use and spatial planning Andrus Meiner, EEA
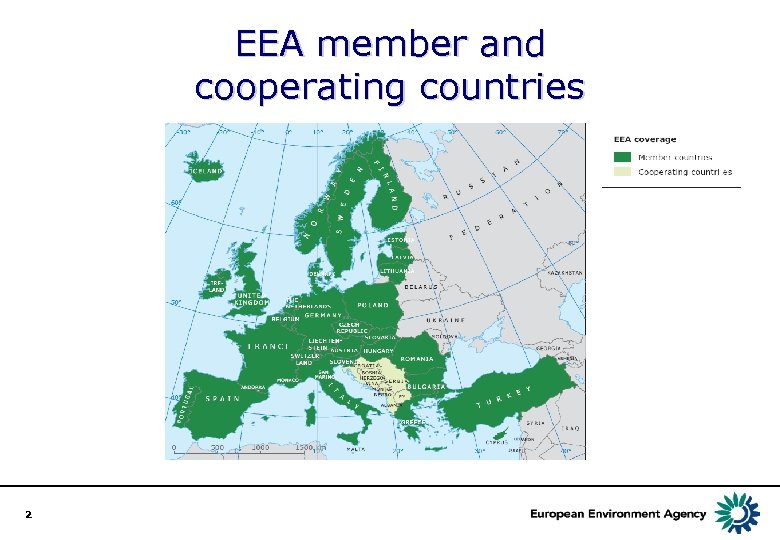 EEA member and cooperating countries Member countries 2
EEA member and cooperating countries Member countries 2
 Setting the scene • • What is the context of existing EU policies and organisation structures? • What are links to relevant data production and maintenance activities? • 3 Why we deal with new EIONET interest group Land use and Spatial planning? What methodologies are available for land use analysis?
Setting the scene • • What is the context of existing EU policies and organisation structures? • What are links to relevant data production and maintenance activities? • 3 Why we deal with new EIONET interest group Land use and Spatial planning? What methodologies are available for land use analysis?
 Background • EEA Multi-annual work programme 2009 -2013 • • emphasizes environmental and cross-cutting strategic areas so to improve integrated assessments formation of a new EEA cross-cutting work area Land use and spatial planning on land/territorial assessments • In July 2009 the EEA Management Board envisaged the creation of a separate EIONET interest group LUSP • NFP meeting 26 May 2010 adopted the profile of NRC LUSP • • 4 new network is called to support the work area 2. 6 Land in the EEA Strategy new IG LUSP complements existing EIONET IG Land cover
Background • EEA Multi-annual work programme 2009 -2013 • • emphasizes environmental and cross-cutting strategic areas so to improve integrated assessments formation of a new EEA cross-cutting work area Land use and spatial planning on land/territorial assessments • In July 2009 the EEA Management Board envisaged the creation of a separate EIONET interest group LUSP • NFP meeting 26 May 2010 adopted the profile of NRC LUSP • • 4 new network is called to support the work area 2. 6 Land in the EEA Strategy new IG LUSP complements existing EIONET IG Land cover
 European policy context • • Relevant data structures: • • 5 EU environmental policies (thematic and horizontal) Territorial cohesion / Territorial Action Plan 2020 Sectoral policies driving land use e. g. CAP 2 nd pillar, mobility Climate Action (carbon sequestration, adaptation) GMES Land Service (and GMES In-situ component) INSPIRE directive implementation CORINE Land cover and High Resolution Layers (5) Land use data centre (SEIS thematic data hub) European Topic Centre for Spatial information and analysis FP 7 research projects / EU and global partnerships
European policy context • • Relevant data structures: • • 5 EU environmental policies (thematic and horizontal) Territorial cohesion / Territorial Action Plan 2020 Sectoral policies driving land use e. g. CAP 2 nd pillar, mobility Climate Action (carbon sequestration, adaptation) GMES Land Service (and GMES In-situ component) INSPIRE directive implementation CORINE Land cover and High Resolution Layers (5) Land use data centre (SEIS thematic data hub) European Topic Centre for Spatial information and analysis FP 7 research projects / EU and global partnerships
 Socio-economic data • Eurostat as contributor of regional statistics for socioeconomic activities and population distribution – LUCAS data base • Designing territorial analysis domain – Regional governance (macro-regions, river basins, eco-regions) – Guiding typologies (urban/rural, agglomerations/UMZ) • 6 Other sources of geo-spatial socio-economic information (territorial indicators, ESPON)
Socio-economic data • Eurostat as contributor of regional statistics for socioeconomic activities and population distribution – LUCAS data base • Designing territorial analysis domain – Regional governance (macro-regions, river basins, eco-regions) – Guiding typologies (urban/rural, agglomerations/UMZ) • 6 Other sources of geo-spatial socio-economic information (territorial indicators, ESPON)
 Consolidation of data elements • Existing land indicators, CORINE Land cover, geo-spatial reference layers, hydro-systems data base, territorial indicators, Urban Atlas database • New data streams from GMES Land service including 5 high resolution datasets on imperviousness, forest, wetland, grassland water land cover • Access to shared data and case studies • 7 Benefit from cooperation with Member states and European Commission services e. g. DG Joint Research Centre
Consolidation of data elements • Existing land indicators, CORINE Land cover, geo-spatial reference layers, hydro-systems data base, territorial indicators, Urban Atlas database • New data streams from GMES Land service including 5 high resolution datasets on imperviousness, forest, wetland, grassland water land cover • Access to shared data and case studies • 7 Benefit from cooperation with Member states and European Commission services e. g. DG Joint Research Centre
 ECOSYSTEM-BASED MANAGEMENT APPROACH SPATIAL PLANNING EU TERRITORIAL COHESION POLICY Place-based management 8
ECOSYSTEM-BASED MANAGEMENT APPROACH SPATIAL PLANNING EU TERRITORIAL COHESION POLICY Place-based management 8
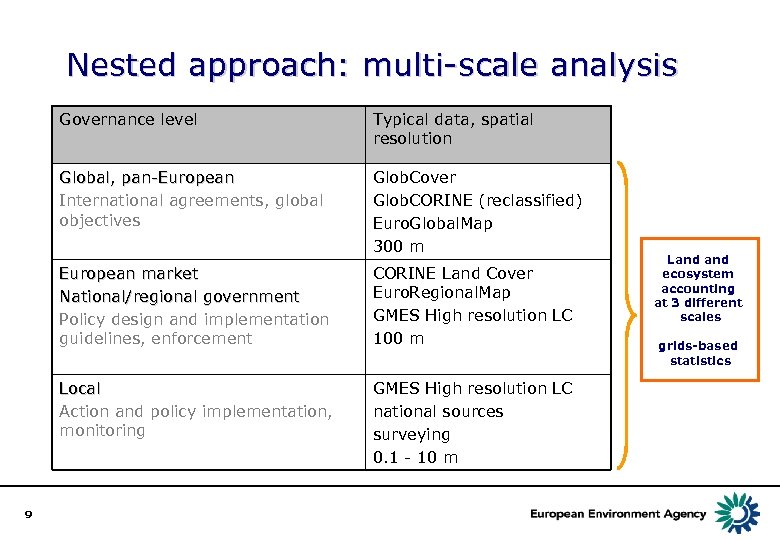 Nested approach: multi-scale analysis Governance level Typical data, spatial resolution Global, pan-European International agreements, global objectives Glob. Cover Glob. CORINE (reclassified) Euro. Global. Map 300 m European market National/regional government Policy design and implementation guidelines, enforcement Local Action and policy implementation, monitoring 9 CORINE Land Cover Euro. Regional. Map GMES High resolution LC 100 m GMES High resolution LC national sources surveying 0. 1 - 10 m Land ecosystem accounting at 3 different scales grids-based statistics
Nested approach: multi-scale analysis Governance level Typical data, spatial resolution Global, pan-European International agreements, global objectives Glob. Cover Glob. CORINE (reclassified) Euro. Global. Map 300 m European market National/regional government Policy design and implementation guidelines, enforcement Local Action and policy implementation, monitoring 9 CORINE Land Cover Euro. Regional. Map GMES High resolution LC 100 m GMES High resolution LC national sources surveying 0. 1 - 10 m Land ecosystem accounting at 3 different scales grids-based statistics
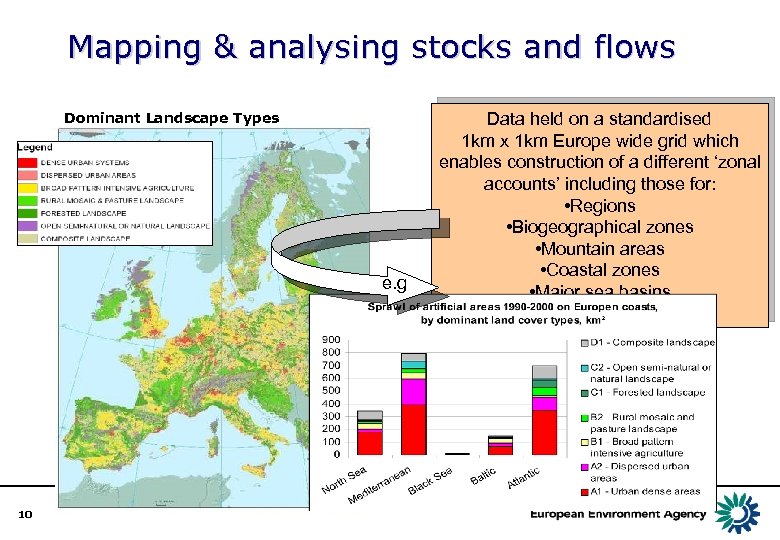 Mapping & analysing stocks and flows Dominant Landscape Types e. g 10 Data held on a standardised 1 km x 1 km Europe wide grid which enables construction of a different ‘zonal accounts’ including those for: • Regions • Biogeographical zones • Mountain areas • Coastal zones • Major sea basins • Dominant landscape types…
Mapping & analysing stocks and flows Dominant Landscape Types e. g 10 Data held on a standardised 1 km x 1 km Europe wide grid which enables construction of a different ‘zonal accounts’ including those for: • Regions • Biogeographical zones • Mountain areas • Coastal zones • Major sea basins • Dominant landscape types…
 How does spatial planning fit into EIONET IG LUSP agenda? • Monitoring and evaluating performance of spatial planning • Agreed spatial planning objectives and management outcomes will normally need: • • 11 indicator baseline target data collection strategy data analysis reporting plan identified users Facilitating exchange of experience and good practice
How does spatial planning fit into EIONET IG LUSP agenda? • Monitoring and evaluating performance of spatial planning • Agreed spatial planning objectives and management outcomes will normally need: • • 11 indicator baseline target data collection strategy data analysis reporting plan identified users Facilitating exchange of experience and good practice
 Main objective of the workshop • Main objective of the workshop is to inform the countries and allow for exchange of views on scope and role of a new forming network of National Reference Centers 12
Main objective of the workshop • Main objective of the workshop is to inform the countries and allow for exchange of views on scope and role of a new forming network of National Reference Centers 12
 Task and some considerations Mobilize new EIONET IG Land use and spatial planning and clarify its scope; cooperate with other existing EIONET networks • Business as usual would mean low EIONET involvement in EEA work on land use analysis; good example of cooperation exist: SOER 2010 Country assessments Land use • Complement the existing EIONET IG Land cover with land use and planning elements to enforce integrated assessment across full DPSIR chain • • • 13 Land use /planning Land cover DPSIR Analogy with Maritime – NFPs endorsed complement ‘Marine & coastal environment’ with ‘Maritime’
Task and some considerations Mobilize new EIONET IG Land use and spatial planning and clarify its scope; cooperate with other existing EIONET networks • Business as usual would mean low EIONET involvement in EEA work on land use analysis; good example of cooperation exist: SOER 2010 Country assessments Land use • Complement the existing EIONET IG Land cover with land use and planning elements to enforce integrated assessment across full DPSIR chain • • • 13 Land use /planning Land cover DPSIR Analogy with Maritime – NFPs endorsed complement ‘Marine & coastal environment’ with ‘Maritime’
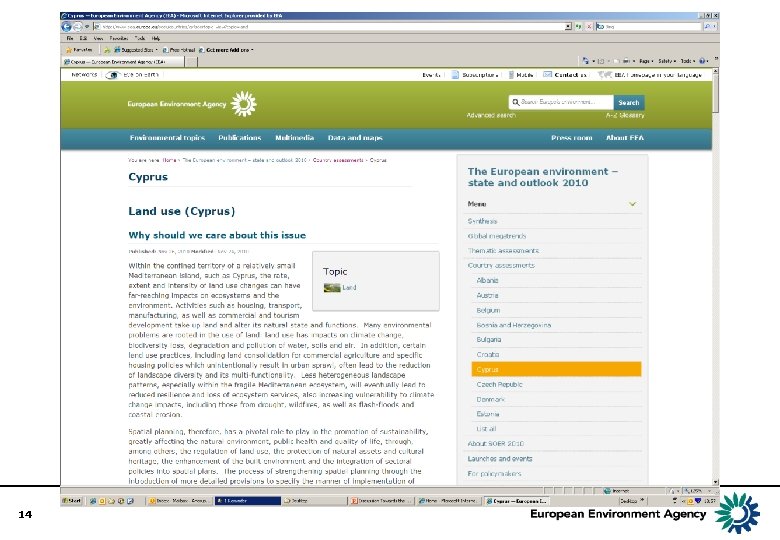 14
14
 Task and some considerations Mobilize new EIONET IG Land use and spatial planning and clarify its scope; cooperate with other existing EIONET networks • Business as usual would mean low EIONET involvement in EEA work on land use analysis; good example of cooperation exist: SOER 2010 Country assessments Land use • Complement the existing EIONET IG Land cover with land use and planning elements to enforce integrated assessment across full DPSIR chain • • • 15 Land use /planning Land cover DPSIR Analogy with Maritime – NFPs endorsed complement ‘Marine & coastal environment’ with ‘Maritime’
Task and some considerations Mobilize new EIONET IG Land use and spatial planning and clarify its scope; cooperate with other existing EIONET networks • Business as usual would mean low EIONET involvement in EEA work on land use analysis; good example of cooperation exist: SOER 2010 Country assessments Land use • Complement the existing EIONET IG Land cover with land use and planning elements to enforce integrated assessment across full DPSIR chain • • • 15 Land use /planning Land cover DPSIR Analogy with Maritime – NFPs endorsed complement ‘Marine & coastal environment’ with ‘Maritime’
 Profile for a National Reference Centre of EIONET • • Expertise – key topics • Skills - five types of ‘skills’ (Technology, Monitoring/Data/Information, Assessment/Reporting/ Knowledge, Communication, Policy). • Policy processes to be supported • Input and contributions from the NRC-s in 2010 (2011 -2013) – reviews and comments; participation on workshops; data delivery (tbd) • 16 Name of NRC network Other relevant organisations and European networks – contact, cooperation, partnership
Profile for a National Reference Centre of EIONET • • Expertise – key topics • Skills - five types of ‘skills’ (Technology, Monitoring/Data/Information, Assessment/Reporting/ Knowledge, Communication, Policy). • Policy processes to be supported • Input and contributions from the NRC-s in 2010 (2011 -2013) – reviews and comments; participation on workshops; data delivery (tbd) • 16 Name of NRC network Other relevant organisations and European networks – contact, cooperation, partnership
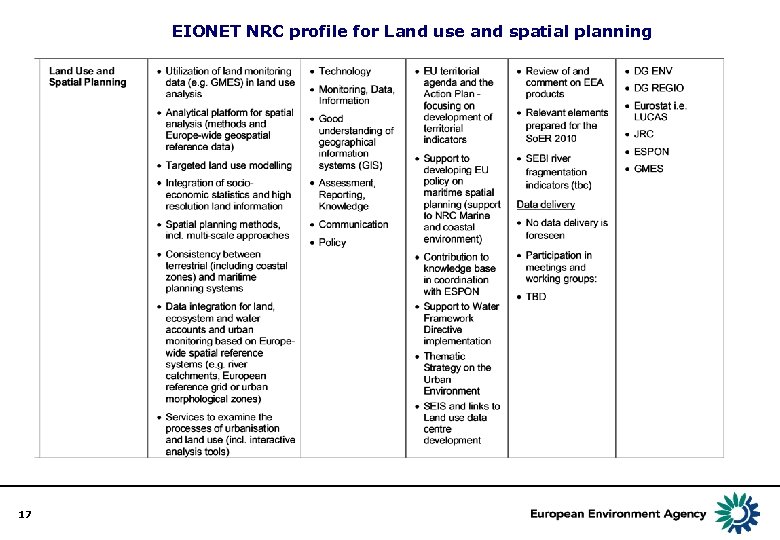 EIONET NRC profile for Land use and spatial planning 17
EIONET NRC profile for Land use and spatial planning 17
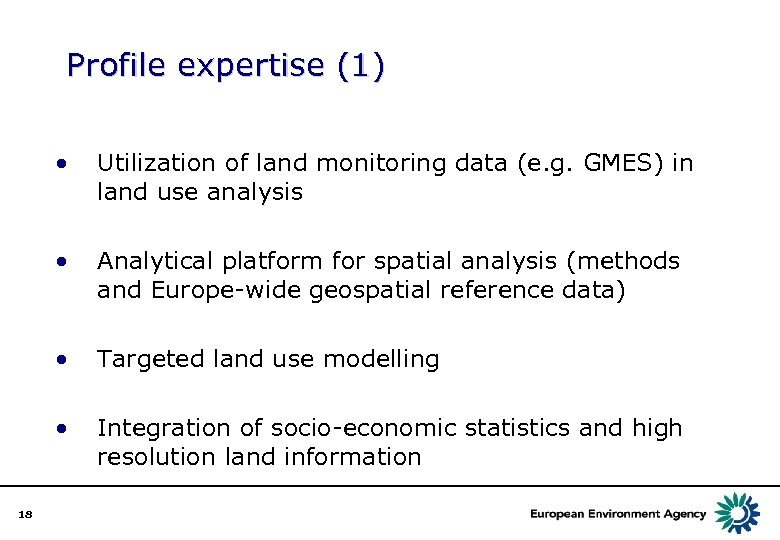 Profile expertise (1) • • Analytical platform for spatial analysis (methods and Europe-wide geospatial reference data) • Targeted land use modelling • 18 Utilization of land monitoring data (e. g. GMES) in land use analysis Integration of socio-economic statistics and high resolution land information
Profile expertise (1) • • Analytical platform for spatial analysis (methods and Europe-wide geospatial reference data) • Targeted land use modelling • 18 Utilization of land monitoring data (e. g. GMES) in land use analysis Integration of socio-economic statistics and high resolution land information
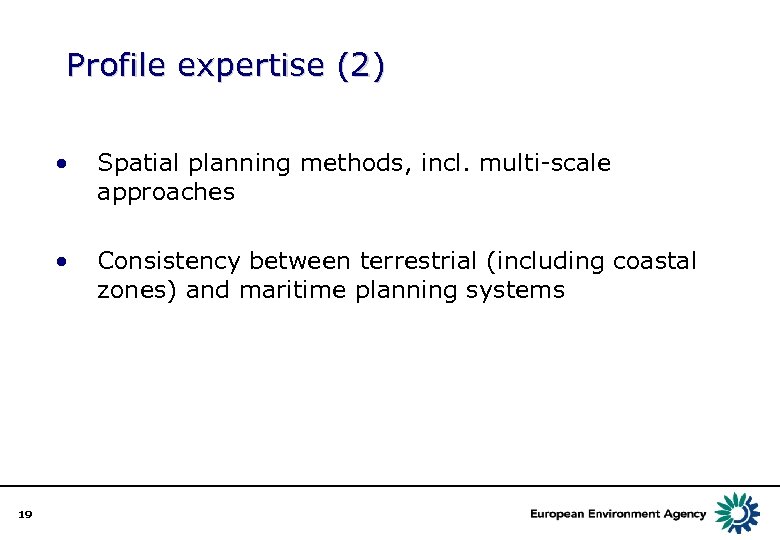 Profile expertise (2) • • 19 Spatial planning methods, incl. multi-scale approaches Consistency between terrestrial (including coastal zones) and maritime planning systems
Profile expertise (2) • • 19 Spatial planning methods, incl. multi-scale approaches Consistency between terrestrial (including coastal zones) and maritime planning systems
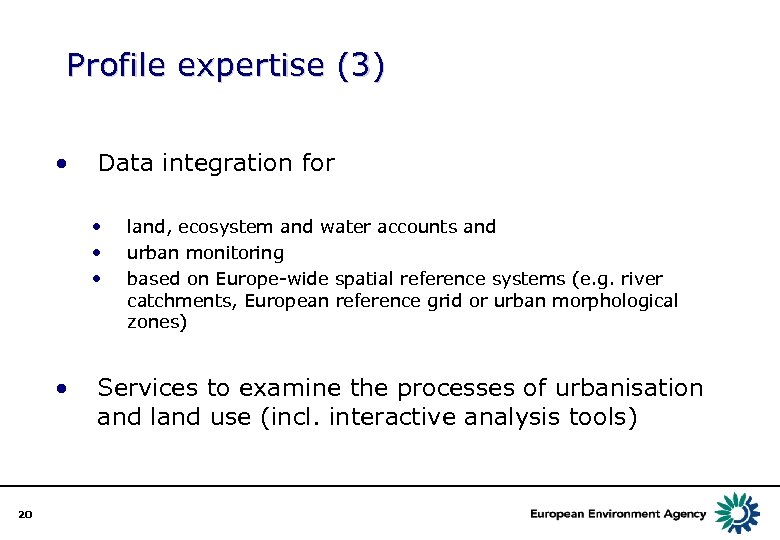 Profile expertise (3) • Data integration for • • 20 land, ecosystem and water accounts and urban monitoring based on Europe-wide spatial reference systems (e. g. river catchments, European reference grid or urban morphological zones) Services to examine the processes of urbanisation and land use (incl. interactive analysis tools)
Profile expertise (3) • Data integration for • • 20 land, ecosystem and water accounts and urban monitoring based on Europe-wide spatial reference systems (e. g. river catchments, European reference grid or urban morphological zones) Services to examine the processes of urbanisation and land use (incl. interactive analysis tools)
 Possible cooperation activities • Review of territorial planning tools across EIONET – – – • Existing country assessments – review & update – – • SOER 2010 Land use (country contributions) CORINE LC 2000 -2006 trends (EEA analysis) State & Outlook of Environment Report European thematic assessment Land use – – 21 Contributing with experience, good practice, case studies Possible survey questionnaire Test cases: using HRL data in national context; combine European data with natinoal data – date model SOER 2010 Land use – comments towards SOER 2015 ETC SIA gap analysis of SOER 2010 (2012 -2013)
Possible cooperation activities • Review of territorial planning tools across EIONET – – – • Existing country assessments – review & update – – • SOER 2010 Land use (country contributions) CORINE LC 2000 -2006 trends (EEA analysis) State & Outlook of Environment Report European thematic assessment Land use – – 21 Contributing with experience, good practice, case studies Possible survey questionnaire Test cases: using HRL data in national context; combine European data with natinoal data – date model SOER 2010 Land use – comments towards SOER 2015 ETC SIA gap analysis of SOER 2010 (2012 -2013)
 Thank you! Contact: Andrus. Meiner@eea. europa. eu http: //www. eea. europa. eu 22
Thank you! Contact: Andrus. Meiner@eea. europa. eu http: //www. eea. europa. eu 22
 Questions for discussion III • What are the policy processes most relevant to proposed EIONET IG LUSP? • What is the data and information content for proposed EIONET IG LUSP? – – • Conceptual development of integrated land assessments – – – 23 European level and natrional/planning level Land use indicators? Trade-off of land allocation Land accounting (support to ecosystem capital accounts) Other methodological issues
Questions for discussion III • What are the policy processes most relevant to proposed EIONET IG LUSP? • What is the data and information content for proposed EIONET IG LUSP? – – • Conceptual development of integrated land assessments – – – 23 European level and natrional/planning level Land use indicators? Trade-off of land allocation Land accounting (support to ecosystem capital accounts) Other methodological issues


