063e94d39bffac6c3ce855295789110b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 23
 Efficient Capital Markets 1
Efficient Capital Markets 1
 Efficient Capital Markets n n Stock prices are in equilibrium or are “fairly” priced If this is true, then you should not be able to earn “abnormal” or “excess” returns, in expectation. Efficient markets DO NOT imply that investors cannot earn a positive return in the stock market. They do mean that, on average, you will earn a return that is appropriate for the risk undertaken and there is not a bias in prices that can be exploited to earn excess returns. 2
Efficient Capital Markets n n Stock prices are in equilibrium or are “fairly” priced If this is true, then you should not be able to earn “abnormal” or “excess” returns, in expectation. Efficient markets DO NOT imply that investors cannot earn a positive return in the stock market. They do mean that, on average, you will earn a return that is appropriate for the risk undertaken and there is not a bias in prices that can be exploited to earn excess returns. 2
 What is the Efficient Market Hypothesis (EMH)? n n n Securities are normally in equilibrium and are “fairly priced. ” Investors cannot “beat the market” except through good luck or better information. Levels of market efficiency n n n Weak-form efficiency Semistrong-form efficiency Strong-form efficiency 3
What is the Efficient Market Hypothesis (EMH)? n n n Securities are normally in equilibrium and are “fairly priced. ” Investors cannot “beat the market” except through good luck or better information. Levels of market efficiency n n n Weak-form efficiency Semistrong-form efficiency Strong-form efficiency 3
 3 Levels of Market Efficiency n Weak Form Efficiency n n Semi-Strong Form Efficiency n n Market prices reflect all historical price information Market prices reflect all publicly available information Strong Form Efficiency n Market prices reflect all information, both public and private 4
3 Levels of Market Efficiency n Weak Form Efficiency n n Semi-Strong Form Efficiency n n Market prices reflect all historical price information Market prices reflect all publicly available information Strong Form Efficiency n Market prices reflect all information, both public and private 4
 Weak-form efficiency n n Can’t profit by looking at past price trends. A recent decline is no reason to think stocks will go up (or down) in the future. There is no predictable price pattern based on price path. Real world evidence supports weakform EMH, but “technical analysis” is still used by some people. 5
Weak-form efficiency n n Can’t profit by looking at past price trends. A recent decline is no reason to think stocks will go up (or down) in the future. There is no predictable price pattern based on price path. Real world evidence supports weakform EMH, but “technical analysis” is still used by some people. 5
 Random Walk Theory n n The movement of stock prices from day to day DO NOT reflect any pattern. Statistically speaking, the movement of stock prices is random (skewed positive over the long term). 6
Random Walk Theory n n The movement of stock prices from day to day DO NOT reflect any pattern. Statistically speaking, the movement of stock prices is random (skewed positive over the long term). 6
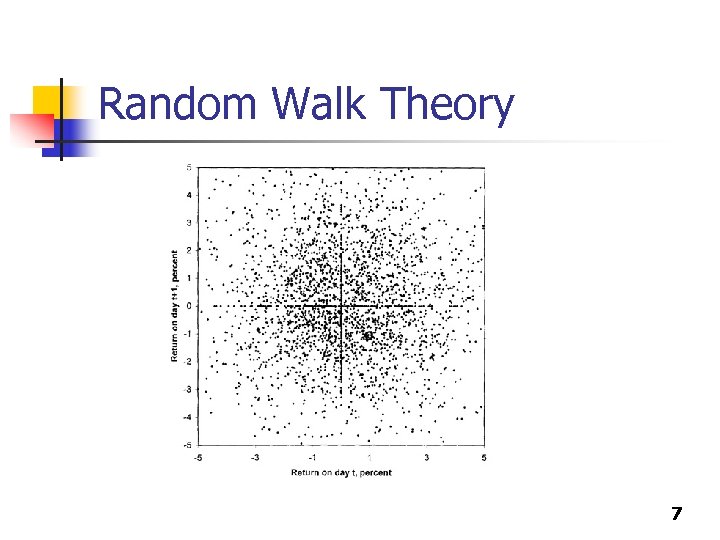 Random Walk Theory 7
Random Walk Theory 7
 Efficient Market Theory n Technical Analysts n Forecast stock prices based on the watching the fluctuations in historical prices (thus “wiggle watchers”) 8
Efficient Market Theory n Technical Analysts n Forecast stock prices based on the watching the fluctuations in historical prices (thus “wiggle watchers”) 8
 Semistrong-form efficiency n n All publicly available information is reflected in stock prices, so it doesn’t pay to over-analyze annual reports looking for undervalued stocks. Largely true in real world, but superior analysts can still profit by finding and using new information 9
Semistrong-form efficiency n n All publicly available information is reflected in stock prices, so it doesn’t pay to over-analyze annual reports looking for undervalued stocks. Largely true in real world, but superior analysts can still profit by finding and using new information 9
 Semi-strong form efficiency n Fundamental Analysts n n Research the value of stocks by delving into detailed accounting and operating numbers. These guys do not believe in semi-strong form of market efficiency. 10
Semi-strong form efficiency n Fundamental Analysts n n Research the value of stocks by delving into detailed accounting and operating numbers. These guys do not believe in semi-strong form of market efficiency. 10
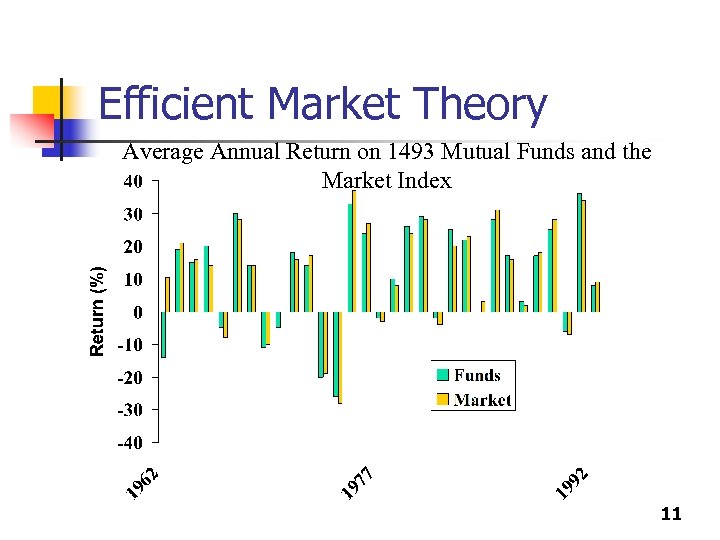 Efficient Market Theory Average Annual Return on 1493 Mutual Funds and the Market Index 11
Efficient Market Theory Average Annual Return on 1493 Mutual Funds and the Market Index 11
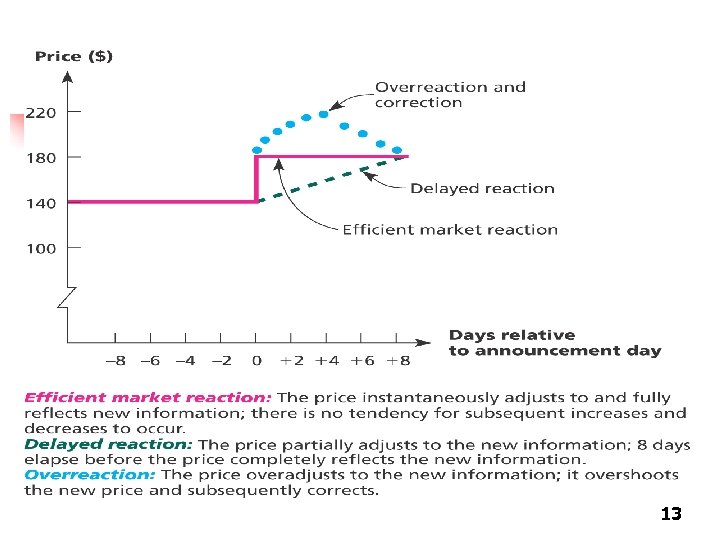
 Implications of market efficiency n You hear in the news that a medical research company received FDA approval for one of its products. If the market is semi-strong efficient, can you expect to take advantage of this information by purchasing the stock? n No – if the market is semi-strong efficient, this information will already have been incorporated into the company’s stock price. So, it’s probably too late … 12
Implications of market efficiency n You hear in the news that a medical research company received FDA approval for one of its products. If the market is semi-strong efficient, can you expect to take advantage of this information by purchasing the stock? n No – if the market is semi-strong efficient, this information will already have been incorporated into the company’s stock price. So, it’s probably too late … 12
 13
13
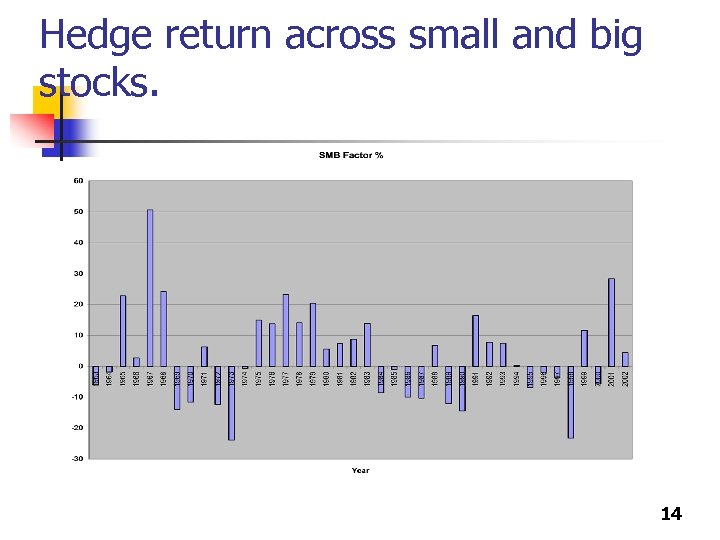 Hedge return across small and big stocks. 14
Hedge return across small and big stocks. 14
 Hedge return across high B/M and low B/M stocks. 15
Hedge return across high B/M and low B/M stocks. 15
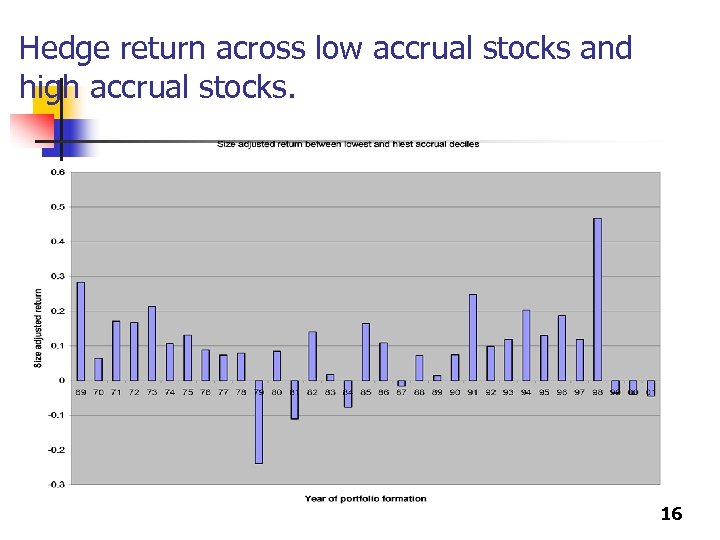 Hedge return across low accrual stocks and high accrual stocks. 16
Hedge return across low accrual stocks and high accrual stocks. 16
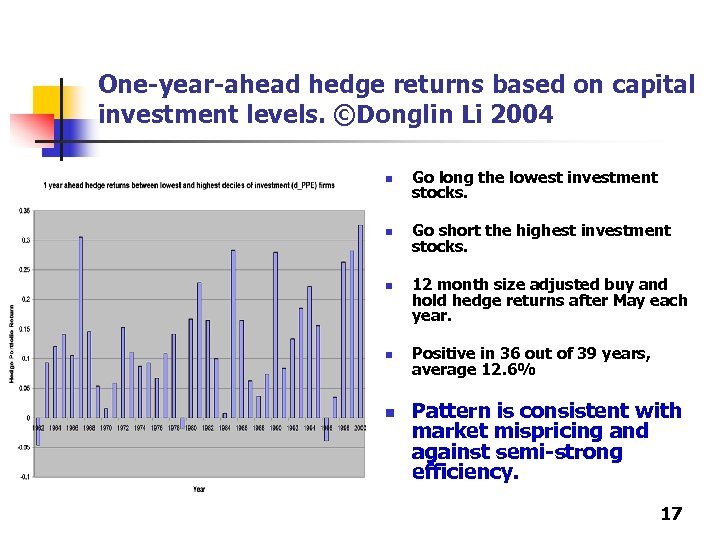 One-year-ahead hedge returns based on capital investment levels. ©Donglin Li 2004 n Go long the lowest investment stocks. n Go short the highest investment stocks. n n n 12 month size adjusted buy and hold hedge returns after May each year. Positive in 36 out of 39 years, average 12. 6% Pattern is consistent with market mispricing and against semi-strong efficiency. 17
One-year-ahead hedge returns based on capital investment levels. ©Donglin Li 2004 n Go long the lowest investment stocks. n Go short the highest investment stocks. n n n 12 month size adjusted buy and hold hedge returns after May each year. Positive in 36 out of 39 years, average 12. 6% Pattern is consistent with market mispricing and against semi-strong efficiency. 17
 Strong-form efficiency n n All information, even inside information, is embedded in stock prices. That is, one cannot profit even on private information. Not true--insiders can gain by trading on the basis of insider information, but that’s illegal. 18
Strong-form efficiency n n All information, even inside information, is embedded in stock prices. That is, one cannot profit even on private information. Not true--insiders can gain by trading on the basis of insider information, but that’s illegal. 18
 Is the stock market efficient? n Empirical studies have tried to test the three forms of efficiency. n n n Highly efficient in the weak form. Reasonably efficient in the semistrong form. Not efficient in the strong form. Insiders could and did make abnormal (and sometimes illegal) profits. 19
Is the stock market efficient? n Empirical studies have tried to test the three forms of efficiency. n n n Highly efficient in the weak form. Reasonably efficient in the semistrong form. Not efficient in the strong form. Insiders could and did make abnormal (and sometimes illegal) profits. 19
 What Makes Markets Efficient? n There are many investors out there doing research As new information comes to market, this information is analyzed and trades are made based on this information n Therefore, prices should reflect all available public information, and almost instantly. n 20
What Makes Markets Efficient? n There are many investors out there doing research As new information comes to market, this information is analyzed and trades are made based on this information n Therefore, prices should reflect all available public information, and almost instantly. n 20
 Exercises 1. You purchase a stock expecting the price to rise 10% in the coming year. After one year, the stock has actually increased in value by 30%, due primarily to new information released during the year concerning unexpectedly higher sales. Which of the following describes this result? A) This is a violation of weak form efficiency. B) This is a violation of semi-strong form efficiency. C) This is a violation of strong form efficiency. D) This is not a violation of market efficiency. 21
Exercises 1. You purchase a stock expecting the price to rise 10% in the coming year. After one year, the stock has actually increased in value by 30%, due primarily to new information released during the year concerning unexpectedly higher sales. Which of the following describes this result? A) This is a violation of weak form efficiency. B) This is a violation of semi-strong form efficiency. C) This is a violation of strong form efficiency. D) This is not a violation of market efficiency. 21
 2. You track the liquidity of companies and find that you can consistently earn unusually high returns by purchasing the shares of firms whose stock price falls below the cash value per share as indicated on the balance sheet. Which of the following describes this strategy? A) This would not be a violation of market efficiency. B) This would be a violation of weak form efficiency. C) This would be a violation of semi-strong form efficiency. 22
2. You track the liquidity of companies and find that you can consistently earn unusually high returns by purchasing the shares of firms whose stock price falls below the cash value per share as indicated on the balance sheet. Which of the following describes this strategy? A) This would not be a violation of market efficiency. B) This would be a violation of weak form efficiency. C) This would be a violation of semi-strong form efficiency. 22
 3. You have discovered from looking at charts of past stock prices that if you buy just after a stock price has declined for three consecutive days, you make money every time! This is clearly a violation of _____ market efficiency. A) weak form B) semi-weak form C) semi-strong form D) strong form 23
3. You have discovered from looking at charts of past stock prices that if you buy just after a stock price has declined for three consecutive days, you make money every time! This is clearly a violation of _____ market efficiency. A) weak form B) semi-weak form C) semi-strong form D) strong form 23


