860646212ddac4b9f00e3f0795cfacfa.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25
 Effects Of Animal Identification On Cattle Market Structure Prepared by: Darrell R. Mark, Ph. D. Asst. Professor & Extension Livestock Marketing Specialist Department of Agricultural Economics University of Nebraska-Lincoln 402 -472 -1796 Email: dmark 2@unl. edu Web: http: //agecon. unl. edu/mark Western Extension Marketing Committee Western Center for Risk Management Education
Effects Of Animal Identification On Cattle Market Structure Prepared by: Darrell R. Mark, Ph. D. Asst. Professor & Extension Livestock Marketing Specialist Department of Agricultural Economics University of Nebraska-Lincoln 402 -472 -1796 Email: dmark 2@unl. edu Web: http: //agecon. unl. edu/mark Western Extension Marketing Committee Western Center for Risk Management Education
 Structural Change Is: 1. Change In Number Of Firms 2. Change In Size Of Those Firms 3. Change In Geographic Location Of The Firms • Because NAIS Continues To Be Developed & Implemented, Impacts On Beef Industry Structural Change Is Currently Uncertain
Structural Change Is: 1. Change In Number Of Firms 2. Change In Size Of Those Firms 3. Change In Geographic Location Of The Firms • Because NAIS Continues To Be Developed & Implemented, Impacts On Beef Industry Structural Change Is Currently Uncertain
 Cow-Calf Sector
Cow-Calf Sector
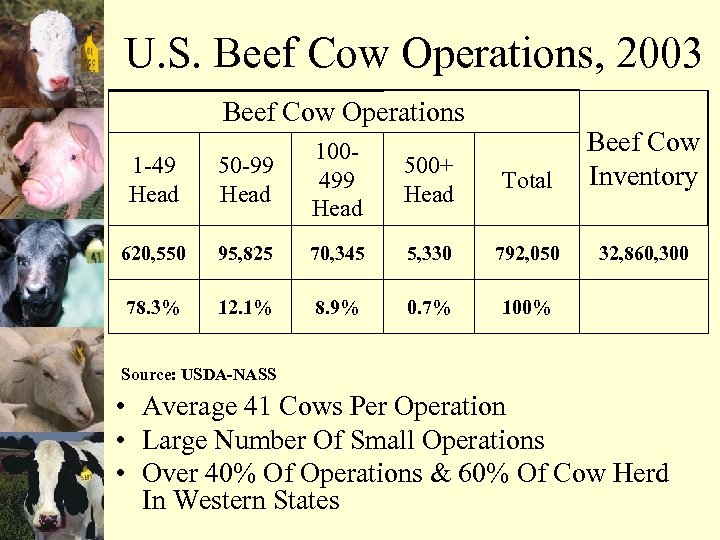 U. S. Beef Cow Operations, 2003 Beef Cow Operations 500+ Head Total Beef Cow Inventory 32, 860, 300 1 -49 Head 50 -99 Head 100499 Head 620, 550 95, 825 70, 345 5, 330 792, 050 78. 3% 12. 1% 8. 9% 0. 7% 100% Source: USDA-NASS • Average 41 Cows Per Operation • Large Number Of Small Operations • Over 40% Of Operations & 60% Of Cow Herd In Western States
U. S. Beef Cow Operations, 2003 Beef Cow Operations 500+ Head Total Beef Cow Inventory 32, 860, 300 1 -49 Head 50 -99 Head 100499 Head 620, 550 95, 825 70, 345 5, 330 792, 050 78. 3% 12. 1% 8. 9% 0. 7% 100% Source: USDA-NASS • Average 41 Cows Per Operation • Large Number Of Small Operations • Over 40% Of Operations & 60% Of Cow Herd In Western States
 Costs Will Vary For Operations • Some Will Not Participate Unless ID Becomes Mandatory – No Increase In Costs, But May Jeopardize Market Access • Some Will Only Obtain Premises ID Number, But Not Do Individual Head ID – Will Keep Costs Low – Potential Benefits Would Be Low
Costs Will Vary For Operations • Some Will Not Participate Unless ID Becomes Mandatory – No Increase In Costs, But May Jeopardize Market Access • Some Will Only Obtain Premises ID Number, But Not Do Individual Head ID – Will Keep Costs Low – Potential Benefits Would Be Low
 Group/Individual Head ID • Small Herd Sizes – Variable Costs (Tagging, Scanning): $2 -5/head – Fixed Costs (Electronic Readers): $4 -25/head – Costs Per Head Will Decrease With Increasing Herd Size Source: Blasi et al.
Group/Individual Head ID • Small Herd Sizes – Variable Costs (Tagging, Scanning): $2 -5/head – Fixed Costs (Electronic Readers): $4 -25/head – Costs Per Head Will Decrease With Increasing Herd Size Source: Blasi et al.
 Third-Party Technology Provider • Collect Traceability Information Required By NAIS & Report It • Collect Production & Management Information – Birth Dates & Weights, Vaccination Records, etc. – Provide Summary Reports & Benchmark Information To Producer – Beneficial Only If Producers Use It To Make Better Production Management Or Marketing Decisions
Third-Party Technology Provider • Collect Traceability Information Required By NAIS & Report It • Collect Production & Management Information – Birth Dates & Weights, Vaccination Records, etc. – Provide Summary Reports & Benchmark Information To Producer – Beneficial Only If Producers Use It To Make Better Production Management Or Marketing Decisions
 Costs For Third-Party Providers • Depends On: – Amount & Type Of Hardware & Software – Individual Tags & Recordkeeping Charges – Decreases In Technology Costs Over Time
Costs For Third-Party Providers • Depends On: – Amount & Type Of Hardware & Software – Individual Tags & Recordkeeping Charges – Decreases In Technology Costs Over Time
 Small Sized Operations Three Alternatives 1. Contract With Third Party 2. Forgo ID As Long As It Is Voluntary & They Maintain Market Access 3. Cooperatively Own Hardware & Software With Other Producers • As Long As NAIS Is Voluntary & Technology Neutral, Costs Should Remain Low (<$5/head)
Small Sized Operations Three Alternatives 1. Contract With Third Party 2. Forgo ID As Long As It Is Voluntary & They Maintain Market Access 3. Cooperatively Own Hardware & Software With Other Producers • As Long As NAIS Is Voluntary & Technology Neutral, Costs Should Remain Low (<$5/head)
 Medium & Large Sized Operations • Larger Herd Sizes Can Distribute Fixed Costs Over More Cattle • Medium Sized Operations Must Determine Whether To Use Third-Party Provider Or Invest Themselves
Medium & Large Sized Operations • Larger Herd Sizes Can Distribute Fixed Costs Over More Cattle • Medium Sized Operations Must Determine Whether To Use Third-Party Provider Or Invest Themselves
 Structural Change • All Operations Will Adapt In Least-Cost Manner – Each Size Has Advantages & Disadvantages • Structural Change Will Be Led By How Producers Use The Individual Head Production Records – Not Required By NAIS – Better Tracking Of Productivity May Provide Comparative Advantage, This Return Could Be Reinvested In Operation To Increase Its Size
Structural Change • All Operations Will Adapt In Least-Cost Manner – Each Size Has Advantages & Disadvantages • Structural Change Will Be Led By How Producers Use The Individual Head Production Records – Not Required By NAIS – Better Tracking Of Productivity May Provide Comparative Advantage, This Return Could Be Reinvested In Operation To Increase Its Size
 Market Access & Price Differentials • If Program Is: 1. Voluntary 2. Some Producers Don’t Participate 3. There Are Benefits To ID • Stocker Or Finishing Operations Or Packers Will Eventually Discount Cattle Without Tags Or ID Records Or Possibly Not Buy Them
Market Access & Price Differentials • If Program Is: 1. Voluntary 2. Some Producers Don’t Participate 3. There Are Benefits To ID • Stocker Or Finishing Operations Or Packers Will Eventually Discount Cattle Without Tags Or ID Records Or Possibly Not Buy Them
 Liability • If Improved Traceability Exposes Producers To Additional Liability For Quality Or Safety, Smaller Sized Operations Would Be More Impacted By This Risk • Geographic Differences May Exist Depending On State Laws To Provide Protection
Liability • If Improved Traceability Exposes Producers To Additional Liability For Quality Or Safety, Smaller Sized Operations Would Be More Impacted By This Risk • Geographic Differences May Exist Depending On State Laws To Provide Protection
 Seed Stock Sector
Seed Stock Sector
 Structural Changes • Likely Minimal Because Some Type Of Individual ID Is Already Used – Don’t Need Technology To Quickly Read Large Numbers Of Cattle • NAIS May Provide A Way To Verify Breeding & Genetics Of A Particular Line That Might Have A Valuable Attribute
Structural Changes • Likely Minimal Because Some Type Of Individual ID Is Already Used – Don’t Need Technology To Quickly Read Large Numbers Of Cattle • NAIS May Provide A Way To Verify Breeding & Genetics Of A Particular Line That Might Have A Valuable Attribute
 Stocker Sector
Stocker Sector
 Stocker Operators • NAIS Guidelines Would Have Cattle Tagged Before Being Sold, So Stockers Should Not Have These Costs, At Least After System Is Functioning • Buyers Of Cattle Have Responsibility To Report The New Location • Stocker Operators That Use Multiple Premises Sites May Have To Report Movements That Do Not Include Change Of Ownership
Stocker Operators • NAIS Guidelines Would Have Cattle Tagged Before Being Sold, So Stockers Should Not Have These Costs, At Least After System Is Functioning • Buyers Of Cattle Have Responsibility To Report The New Location • Stocker Operators That Use Multiple Premises Sites May Have To Report Movements That Do Not Include Change Of Ownership
 Sourcing Cattle From Multiple Locations • Results In Cattle With Different Types Of Tags & Different Technology – It Is Hard To Make The Different Technologies & Software Work Together Seamlessly – Will Stockers Have To Re-Tag Or Buy Cattle With Only One Type Of Tag? • Some Cattle Purchased Will Continue To Be Serviced Throughout Their Life By The Original Third-Party Provider
Sourcing Cattle From Multiple Locations • Results In Cattle With Different Types Of Tags & Different Technology – It Is Hard To Make The Different Technologies & Software Work Together Seamlessly – Will Stockers Have To Re-Tag Or Buy Cattle With Only One Type Of Tag? • Some Cattle Purchased Will Continue To Be Serviced Throughout Their Life By The Original Third-Party Provider
 Feeding Sector
Feeding Sector
 Feed Yard Operators • Have Same Issue With Multiple Sources Of Cattle & Different Technologies – To Get Useful Individual Head Data, They Need All Information Aggregated Into One System • More Difficult With Producers Retaining Ownership • Have Incentive To Build Relationship With Feeder Cattle Suppliers – Lower Costs, Consistent Technology, Liability Protection
Feed Yard Operators • Have Same Issue With Multiple Sources Of Cattle & Different Technologies – To Get Useful Individual Head Data, They Need All Information Aggregated Into One System • More Difficult With Producers Retaining Ownership • Have Incentive To Build Relationship With Feeder Cattle Suppliers – Lower Costs, Consistent Technology, Liability Protection
 Costs By Size • Small Yards Likely Need Only One Panel Reader & One Hand-Held Reader • Large Yards May Need Multiple Panel Readers & Hand-Held Readers – Can Spread Hardware, Software, & Technology Costs Across More Cattle & Pounds Gained To Create Economies Of Scale – If They Realize A Benefit From The Data Collected, They Will Likely Gain The Most
Costs By Size • Small Yards Likely Need Only One Panel Reader & One Hand-Held Reader • Large Yards May Need Multiple Panel Readers & Hand-Held Readers – Can Spread Hardware, Software, & Technology Costs Across More Cattle & Pounds Gained To Create Economies Of Scale – If They Realize A Benefit From The Data Collected, They Will Likely Gain The Most
 Implications
Implications
 Vertical Coordination • Animal Identification Creates Strong Incentive For Linkages Between Cow. Calf, Stocker, & Finishing Sectors That Would Share Information – Easier Liability Transfer – Do Business With As Few Firms As Possible • May Reduce Liability & Improve Product Quality & Safety
Vertical Coordination • Animal Identification Creates Strong Incentive For Linkages Between Cow. Calf, Stocker, & Finishing Sectors That Would Share Information – Easier Liability Transfer – Do Business With As Few Firms As Possible • May Reduce Liability & Improve Product Quality & Safety
 Sales Method • Direct Sales/Private Treaty Will Be Easier To Transfer & Exchange Information – Fed Cattle Market Will Be Less Affected • Central Markets Present Numerous Issues For Traceback
Sales Method • Direct Sales/Private Treaty Will Be Easier To Transfer & Exchange Information – Fed Cattle Market Will Be Less Affected • Central Markets Present Numerous Issues For Traceback
 Public vs. Private Benefit • Public Benefit From 48 -Hour Trace back – Avoid Negative Demand Shock From Animal Disease Problem • Private Benefit From Using “Extra” Production Management Data – The Greater These Benefits, The More Disparity Between Producers Using Individual Animal ID Data & Those Who Do Not
Public vs. Private Benefit • Public Benefit From 48 -Hour Trace back – Avoid Negative Demand Shock From Animal Disease Problem • Private Benefit From Using “Extra” Production Management Data – The Greater These Benefits, The More Disparity Between Producers Using Individual Animal ID Data & Those Who Do Not


