fecfcb474e30331e85024f8e80ec3e4e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 110
 EEE 264 -5: 3 G Wireless Networks
EEE 264 -5: 3 G Wireless Networks
 3 G Wireless Networks • History and Evolution of Mobile Radio • Evolving Network Architectures • Evolving Services • Applications
3 G Wireless Networks • History and Evolution of Mobile Radio • Evolving Network Architectures • Evolving Services • Applications
 First Mobile Radio Telephone 1924 Courtesy of Rich Howard
First Mobile Radio Telephone 1924 Courtesy of Rich Howard
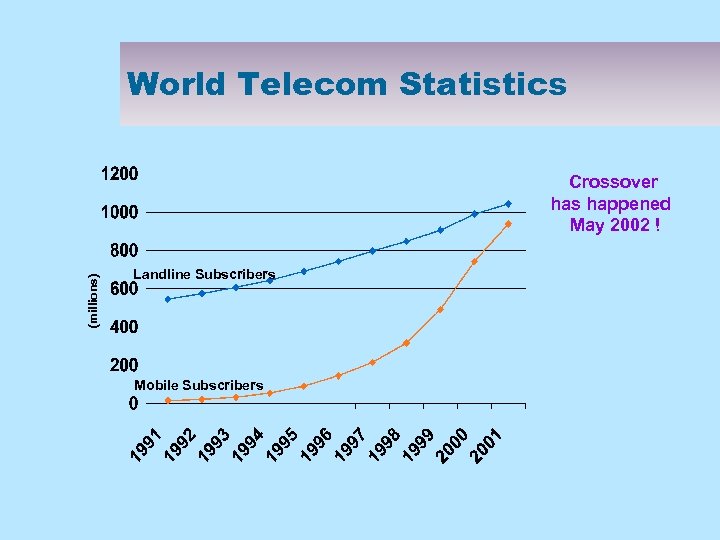 World Telecom Statistics (millions) Crossover has happened May 2002 ! Landline Subscribers Mobile Subscribers
World Telecom Statistics (millions) Crossover has happened May 2002 ! Landline Subscribers Mobile Subscribers
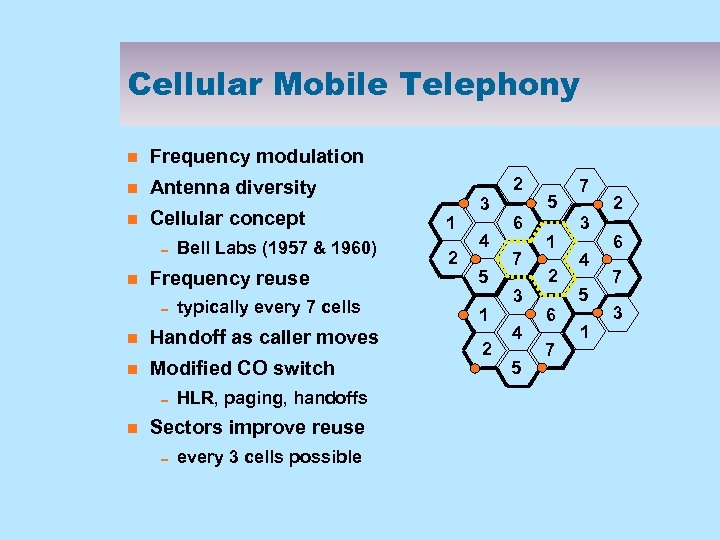 Cellular Mobile Telephony n Frequency modulation n Antenna diversity n Cellular concept 0 Bell Labs (1957 & 1960) n Frequency reuse 0 typically every 7 cells n Handoff as caller moves n Modified CO switch 0 HLR, paging, handoffs n Sectors improve reuse 0 every 3 cells possible 2 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 6 7 3 4 5 5 1 2 6 7 7 3 4 5 1 2 6 7 3
Cellular Mobile Telephony n Frequency modulation n Antenna diversity n Cellular concept 0 Bell Labs (1957 & 1960) n Frequency reuse 0 typically every 7 cells n Handoff as caller moves n Modified CO switch 0 HLR, paging, handoffs n Sectors improve reuse 0 every 3 cells possible 2 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 6 7 3 4 5 5 1 2 6 7 7 3 4 5 1 2 6 7 3
 Mobile Communication Using Satellites (MSAT) n Iridium n ICO (Project 21, Immarsat-P) n Immarsat-M n Globalstar n Odyssey n Teledesic n Ellipso n Constellation (Aries) n VSAT/MSS
Mobile Communication Using Satellites (MSAT) n Iridium n ICO (Project 21, Immarsat-P) n Immarsat-M n Globalstar n Odyssey n Teledesic n Ellipso n Constellation (Aries) n VSAT/MSS
 First Generation – 1 G Cellular n Advanced Mobile Phone Service (AMPS) 0 US trials 1978; deployed in Japan (’ 79) & US (’ 83) 0 800 MHz band – two 20 MHz bands n Nordic Mobile Telephony (NMT) 0 Sweden, Norway, Demark & Finland 0 Launched 1981; 0 450 MHz; later at 900 MHz (NMT 900) n Total Access Communications System (TACS) 0 British design; similar to AMPS; deployed 1985
First Generation – 1 G Cellular n Advanced Mobile Phone Service (AMPS) 0 US trials 1978; deployed in Japan (’ 79) & US (’ 83) 0 800 MHz band – two 20 MHz bands n Nordic Mobile Telephony (NMT) 0 Sweden, Norway, Demark & Finland 0 Launched 1981; 0 450 MHz; later at 900 MHz (NMT 900) n Total Access Communications System (TACS) 0 British design; similar to AMPS; deployed 1985
 Second Generation – 2 G n n Digital systems Leveraged technology to increase capacity 0 Speech compression; digital signal processing n n Utilized “Intelligent Network” concepts Improved fraud prevention Added new services Wide diversity of 2 G systems 0 IS-54/ IS-136 North American TDMA; PDC (Japan) 0 i. DEN 0 DECT and PHS 0 IS-95 CDMA (cdma. One) 0 GSM
Second Generation – 2 G n n Digital systems Leveraged technology to increase capacity 0 Speech compression; digital signal processing n n Utilized “Intelligent Network” concepts Improved fraud prevention Added new services Wide diversity of 2 G systems 0 IS-54/ IS-136 North American TDMA; PDC (Japan) 0 i. DEN 0 DECT and PHS 0 IS-95 CDMA (cdma. One) 0 GSM
 D-AMPS/ TDMA & PDC n Speech coded as digital bit stream 0 compression plus error protection bits 0 aggressive compression limits voice quality n Time division multiple access (TDMA) 0 3 calls per radio channel using repeating time slices n Deployed 1993 (PDC 1994) 0 Development through 1980 s n IS-54 / IS-136 standards in US
D-AMPS/ TDMA & PDC n Speech coded as digital bit stream 0 compression plus error protection bits 0 aggressive compression limits voice quality n Time division multiple access (TDMA) 0 3 calls per radio channel using repeating time slices n Deployed 1993 (PDC 1994) 0 Development through 1980 s n IS-54 / IS-136 standards in US
 i. DEN n n Used by Nextel Motorola proprietary system 0 time division multiple access technology 0 based on GSM architecture n 800 MHz private mobile radio (PMR) spectrum 0 just below 800 MHz cellular band n Special protocol supported fast “Push-to. Talk” 0 digital replacement for old PMR services
i. DEN n n Used by Nextel Motorola proprietary system 0 time division multiple access technology 0 based on GSM architecture n 800 MHz private mobile radio (PMR) spectrum 0 just below 800 MHz cellular band n Special protocol supported fast “Push-to. Talk” 0 digital replacement for old PMR services
 DECT and PHS n n Also based on time division multiple access Digital European Cordless Telephony 0 focused on business use, i. e. wireless PBX (private branch exchange) 0 very small cells; in building propagation issues 0 wide bandwidth (32 Kbps channels) 0 high quality voice and/or ISDN (Integrated Services Digital Network) data n Personal Handiphone Service 0 similar performance (32 Kbps channels) 0 deployed across Japanese cities (high pop. density) 0 4 channel base station uses one ISDN BRI (Basic Rate Interface) line 0 Base stations on top of phone booths 0 legacy in Japan; deployed in China
DECT and PHS n n Also based on time division multiple access Digital European Cordless Telephony 0 focused on business use, i. e. wireless PBX (private branch exchange) 0 very small cells; in building propagation issues 0 wide bandwidth (32 Kbps channels) 0 high quality voice and/or ISDN (Integrated Services Digital Network) data n Personal Handiphone Service 0 similar performance (32 Kbps channels) 0 deployed across Japanese cities (high pop. density) 0 4 channel base station uses one ISDN BRI (Basic Rate Interface) line 0 Base stations on top of phone booths 0 legacy in Japan; deployed in China
 North American CDMA (cdma. One) n Code Division Multiple Access 0 all users share same frequency band 0 CDMA is basis for 3 G common air interface n Qualcomm demo in 1989 0 claimed improved capacity & simplified planning n n n First deployment in Hong Kong late 1994 Major success in Korea (1 M subs by 1996, 20 M by 2001) Used by Verizon and Sprint in US
North American CDMA (cdma. One) n Code Division Multiple Access 0 all users share same frequency band 0 CDMA is basis for 3 G common air interface n Qualcomm demo in 1989 0 claimed improved capacity & simplified planning n n n First deployment in Hong Kong late 1994 Major success in Korea (1 M subs by 1996, 20 M by 2001) Used by Verizon and Sprint in US
 cdma. One -- IS-95 n n TIA standard IS-95 (ANSI-95) in 1993 IS-95 deployed in the 800 MHz cellular band 0 J-STD-08 variant deployed in 1900 MHz US “PCS” band n Evolution fixes bugs and adds data 0 IS-95 A provides data rates up to 14. 4 kbps 0 IS-95 B provides rates up to 64 kbps (2. 5 G) 0 Both A and B are compatible with J-STD-08. n All variants designed for TIA IS-41 core networks (ANSI 41) * ANSI – 41: the North American standard for wireless telecommunications network signaling
cdma. One -- IS-95 n n TIA standard IS-95 (ANSI-95) in 1993 IS-95 deployed in the 800 MHz cellular band 0 J-STD-08 variant deployed in 1900 MHz US “PCS” band n Evolution fixes bugs and adds data 0 IS-95 A provides data rates up to 14. 4 kbps 0 IS-95 B provides rates up to 64 kbps (2. 5 G) 0 Both A and B are compatible with J-STD-08. n All variants designed for TIA IS-41 core networks (ANSI 41) * ANSI – 41: the North American standard for wireless telecommunications network signaling
 GSM n « Groupe Special Mobile » , later changed to « Global System for Mobile » 0 joint European effort beginning in 1982 0 focus on seamless roaming across Europe n Services launched 1991 0 time division multiple access (8 users per 200 KHz) 0 900 MHz band; later extended to 1800 MHz 0 added 1900 MHz (US PCS bands) n GSM was dominant world standard 0 well defined interfaces; many competitors 0 network effect (Metcalfe’s law) took hold in late 1990 s 0 tri-band GSM phone can roam the world today * Metcalfe’s law: The community value of a network grows as the square of the number of its users increase.
GSM n « Groupe Special Mobile » , later changed to « Global System for Mobile » 0 joint European effort beginning in 1982 0 focus on seamless roaming across Europe n Services launched 1991 0 time division multiple access (8 users per 200 KHz) 0 900 MHz band; later extended to 1800 MHz 0 added 1900 MHz (US PCS bands) n GSM was dominant world standard 0 well defined interfaces; many competitors 0 network effect (Metcalfe’s law) took hold in late 1990 s 0 tri-band GSM phone can roam the world today * Metcalfe’s law: The community value of a network grows as the square of the number of its users increase.
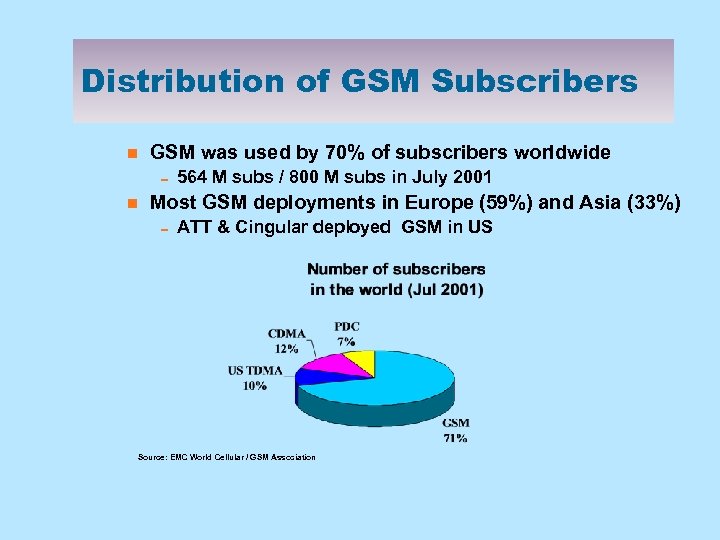 Distribution of GSM Subscribers n GSM was used by 70% of subscribers worldwide 0 564 M subs / 800 M subs in July 2001 n Most GSM deployments in Europe (59%) and Asia (33%) 0 ATT & Cingular deployed GSM in US Source: EMC World Cellular / GSM Association
Distribution of GSM Subscribers n GSM was used by 70% of subscribers worldwide 0 564 M subs / 800 M subs in July 2001 n Most GSM deployments in Europe (59%) and Asia (33%) 0 ATT & Cingular deployed GSM in US Source: EMC World Cellular / GSM Association
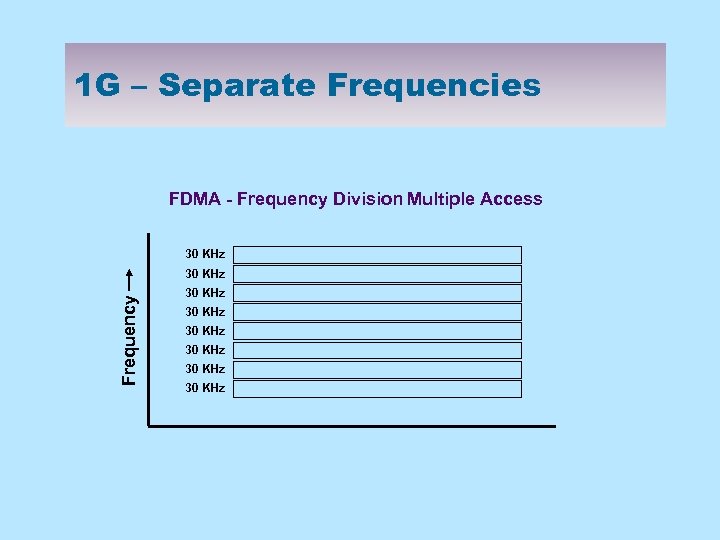 1 G – Separate Frequencies FDMA - Frequency Division Multiple Access 30 KHz Frequency 30 KHz 30 KHz
1 G – Separate Frequencies FDMA - Frequency Division Multiple Access 30 KHz Frequency 30 KHz 30 KHz
 2 G – TDMA – Time Division Multiple Access One timeslot = 0. 577 ms One TDMA frame = 8 timeslots Frequency 200 KHz Time
2 G – TDMA – Time Division Multiple Access One timeslot = 0. 577 ms One TDMA frame = 8 timeslots Frequency 200 KHz Time
 2 G & 3 G – CDMA – Code Division Multiple Access n Spread spectrum modulation 0 originally developed for the military 0 resists jamming and many kinds of interference 0 coded modulation hidden from those w/o the code n All users share same (large) block of spectrum 0 one for one frequency reuse 0 soft handoffs possible n Almost all accepted 3 G radio standards are based on CDMA 0 CDMA 2000, W-CDMA and TD-SCDMA
2 G & 3 G – CDMA – Code Division Multiple Access n Spread spectrum modulation 0 originally developed for the military 0 resists jamming and many kinds of interference 0 coded modulation hidden from those w/o the code n All users share same (large) block of spectrum 0 one for one frequency reuse 0 soft handoffs possible n Almost all accepted 3 G radio standards are based on CDMA 0 CDMA 2000, W-CDMA and TD-SCDMA
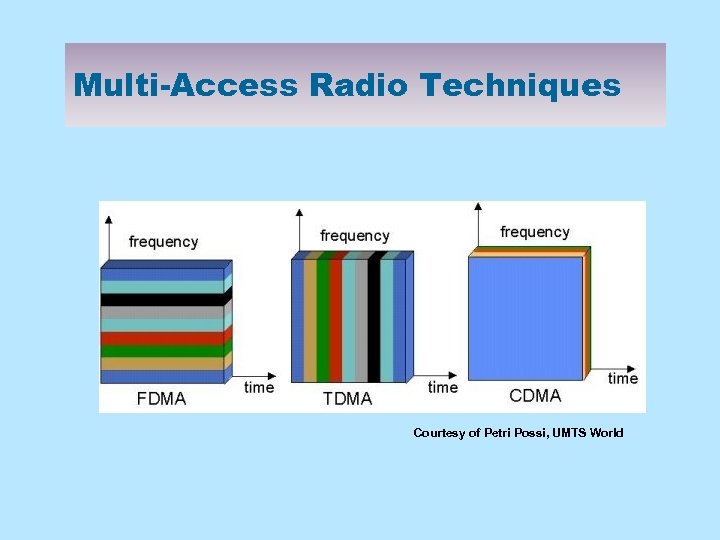 Multi-Access Radio Techniques Courtesy of Petri Possi, UMTS World
Multi-Access Radio Techniques Courtesy of Petri Possi, UMTS World
 3 G Vision n Universal global roaming n Multimedia (voice, data & video) n Increased data rates 0 384 Kbps while moving 0 2 Mbps when stationary at specific locations n Increased capacity (more spectrally efficient) n IP (Internet Protocol) architecture
3 G Vision n Universal global roaming n Multimedia (voice, data & video) n Increased data rates 0 384 Kbps while moving 0 2 Mbps when stationary at specific locations n Increased capacity (more spectrally efficient) n IP (Internet Protocol) architecture
 International Standardization n ITU (International Telecommunication Union) 0 radio standards and spectrum n IMT-2000 0 ITU’s umbrella name for 3 G which stands for International Mobile Telecommunications 2000 n National and regional standards bodies are collaborating in 3 G partnership projects 0 ARIB, TIA, TTC, CWTS. T 1, ETSI n 3 G Partnership Projects (3 GPP & 3 GPP 2) 0 focused on evolution of access and core networks
International Standardization n ITU (International Telecommunication Union) 0 radio standards and spectrum n IMT-2000 0 ITU’s umbrella name for 3 G which stands for International Mobile Telecommunications 2000 n National and regional standards bodies are collaborating in 3 G partnership projects 0 ARIB, TIA, TTC, CWTS. T 1, ETSI n 3 G Partnership Projects (3 GPP & 3 GPP 2) 0 focused on evolution of access and core networks
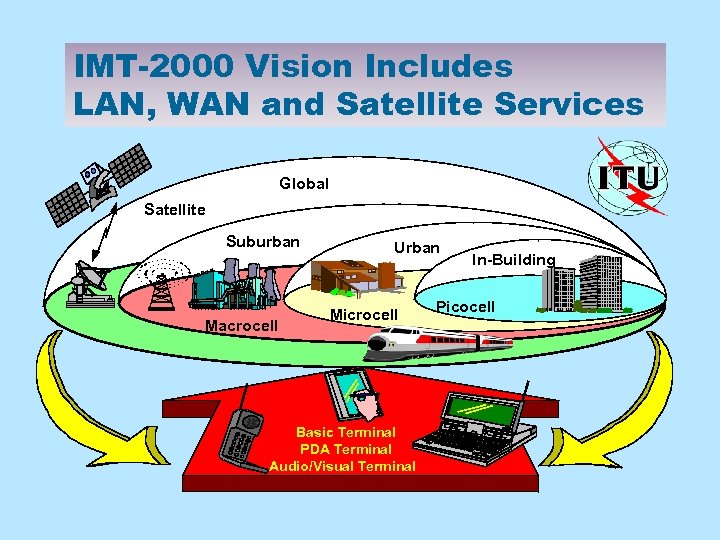 IMT-2000 Vision Includes LAN, WAN and Satellite Services Global Satellite Suburban Macrocell Urban Microcell Basic Terminal PDA Terminal Audio/Visual Terminal In-Building Picocell
IMT-2000 Vision Includes LAN, WAN and Satellite Services Global Satellite Suburban Macrocell Urban Microcell Basic Terminal PDA Terminal Audio/Visual Terminal In-Building Picocell
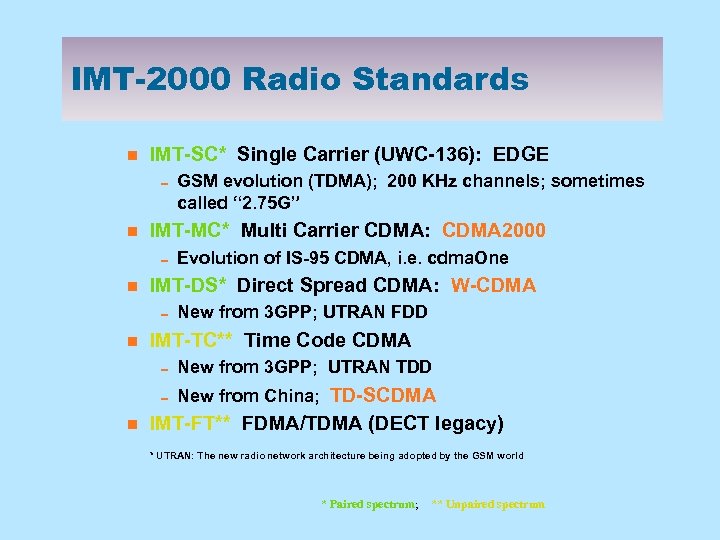 IMT-2000 Radio Standards n IMT-SC* Single Carrier (UWC-136): EDGE 0 GSM evolution (TDMA); 200 KHz channels; sometimes called “ 2. 75 G” n IMT-MC* Multi Carrier CDMA: CDMA 2000 0 Evolution of IS-95 CDMA, i. e. cdma. One n IMT-DS* Direct Spread CDMA: W-CDMA 0 New from 3 GPP; UTRAN FDD n IMT-TC** Time Code CDMA 0 New from 3 GPP; UTRAN TDD 0 New from China; TD-SCDMA n IMT-FT** FDMA/TDMA (DECT legacy) * UTRAN: The new radio network architecture being adopted by the GSM world * Paired spectrum; ** Unpaired spectrum
IMT-2000 Radio Standards n IMT-SC* Single Carrier (UWC-136): EDGE 0 GSM evolution (TDMA); 200 KHz channels; sometimes called “ 2. 75 G” n IMT-MC* Multi Carrier CDMA: CDMA 2000 0 Evolution of IS-95 CDMA, i. e. cdma. One n IMT-DS* Direct Spread CDMA: W-CDMA 0 New from 3 GPP; UTRAN FDD n IMT-TC** Time Code CDMA 0 New from 3 GPP; UTRAN TDD 0 New from China; TD-SCDMA n IMT-FT** FDMA/TDMA (DECT legacy) * UTRAN: The new radio network architecture being adopted by the GSM world * Paired spectrum; ** Unpaired spectrum
 cdma 2000 Pros and Cons n Evolution from original Qualcomm CDMA 0 from cdma. One or IS-95 n Better migration story from 2 G to 3 G 0 cdma. One operators don’t need additional spectrum 0 3 x promises higher data rates than UMTS, i. e. W- CDMA n n Better spectral efficiency than W-CDMA cdma 2000 core network less mature 0 cmda. One interfaces were vendor-specific 0 Compliance of cdma 2000 vendors with 3 GPP 2
cdma 2000 Pros and Cons n Evolution from original Qualcomm CDMA 0 from cdma. One or IS-95 n Better migration story from 2 G to 3 G 0 cdma. One operators don’t need additional spectrum 0 3 x promises higher data rates than UMTS, i. e. W- CDMA n n Better spectral efficiency than W-CDMA cdma 2000 core network less mature 0 cmda. One interfaces were vendor-specific 0 Compliance of cdma 2000 vendors with 3 GPP 2
 W-CDMA (UMTS) Pros and Cons n Wideband CDMA 0 Standard for Universal Mobile Telephone Service (UMTS) n Committed standard for Europe and migration path for other GSM operators 0 leveraged GSM’s dominant position n Requires substantial new spectrum 0 5 MHz each way (symmetric) n n Legally mandated in Europe and elsewhere Sales of new spectrum completed in Europe
W-CDMA (UMTS) Pros and Cons n Wideband CDMA 0 Standard for Universal Mobile Telephone Service (UMTS) n Committed standard for Europe and migration path for other GSM operators 0 leveraged GSM’s dominant position n Requires substantial new spectrum 0 5 MHz each way (symmetric) n n Legally mandated in Europe and elsewhere Sales of new spectrum completed in Europe
 TD-SCDMA n n Time division synchronous CDMA Chinese development Good match for asymmetrical traffic Single spectral band 0 unpaired spectrum; as little as 1. 6 MHz; 0 time division duplex (TDD) with high spectral efficiency n Costs relatively low 0 Handset smaller and may cost less 0 Power consumption lower n Power amplifiers must be very linear 0 relatively hard to meet specifications
TD-SCDMA n n Time division synchronous CDMA Chinese development Good match for asymmetrical traffic Single spectral band 0 unpaired spectrum; as little as 1. 6 MHz; 0 time division duplex (TDD) with high spectral efficiency n Costs relatively low 0 Handset smaller and may cost less 0 Power consumption lower n Power amplifiers must be very linear 0 relatively hard to meet specifications
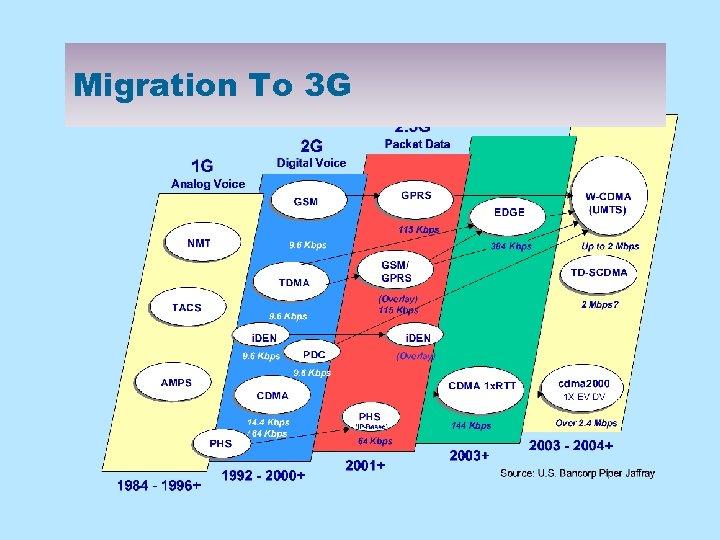 Migration To 3 G
Migration To 3 G
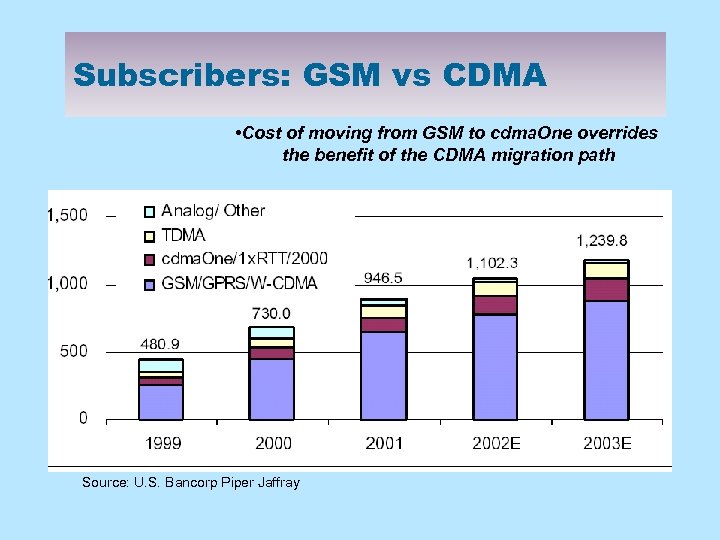 Subscribers: GSM vs CDMA • Cost of moving from GSM to cdma. One overrides the benefit of the CDMA migration path Source: U. S. Bancorp Piper Jaffray
Subscribers: GSM vs CDMA • Cost of moving from GSM to cdma. One overrides the benefit of the CDMA migration path Source: U. S. Bancorp Piper Jaffray
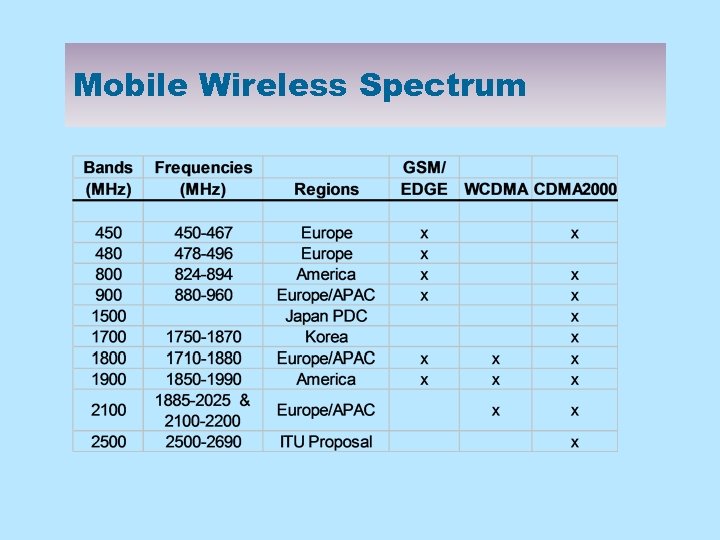 Mobile Wireless Spectrum
Mobile Wireless Spectrum
 Prospects for Global Roaming n Multiple vocoders: Adaptive Multi-Rate (AMR), Enhanced Variable Rate CODEC (EVRC), Selectable Mode Vocoder (SMV) n Six or more spectral bands 0 800, 900, 1800, 1900, 2100, 2500 MHz n At least three modulation variants 0 W-CDMA, CDMA 2000, TD-SCMDA The handset approach n n n Advanced silicon Software defined radio Improved batteries
Prospects for Global Roaming n Multiple vocoders: Adaptive Multi-Rate (AMR), Enhanced Variable Rate CODEC (EVRC), Selectable Mode Vocoder (SMV) n Six or more spectral bands 0 800, 900, 1800, 1900, 2100, 2500 MHz n At least three modulation variants 0 W-CDMA, CDMA 2000, TD-SCMDA The handset approach n n n Advanced silicon Software defined radio Improved batteries
 3 G Wireless Networks • History and Evolution of Mobile Radio • Evolving Network Architectures • Evolving Services • Applications
3 G Wireless Networks • History and Evolution of Mobile Radio • Evolving Network Architectures • Evolving Services • Applications
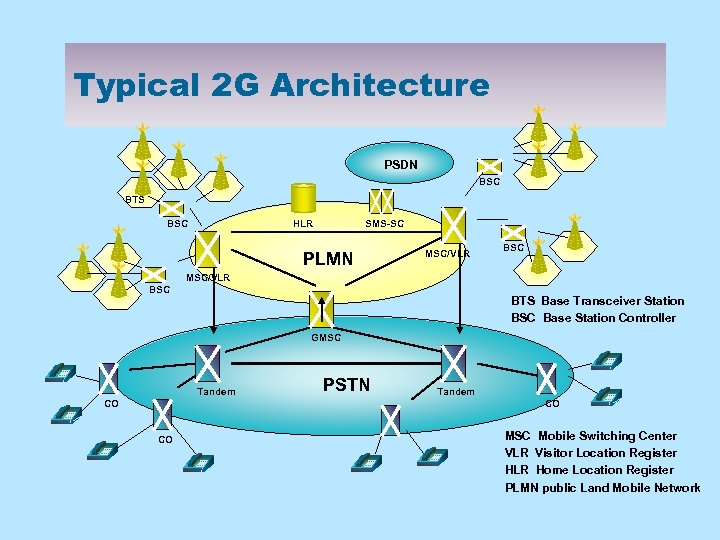 Typical 2 G Architecture PSDN BSC BTS BSC HLR SMS-SC PLMN MSC/VLR BSC BTS Base Transceiver Station BSC Base Station Controller GMSC Tandem CO PSTN Tandem CO CO MSC Mobile Switching Center VLR Visitor Location Register HLR Home Location Register PLMN public Land Mobile Network
Typical 2 G Architecture PSDN BSC BTS BSC HLR SMS-SC PLMN MSC/VLR BSC BTS Base Transceiver Station BSC Base Station Controller GMSC Tandem CO PSTN Tandem CO CO MSC Mobile Switching Center VLR Visitor Location Register HLR Home Location Register PLMN public Land Mobile Network
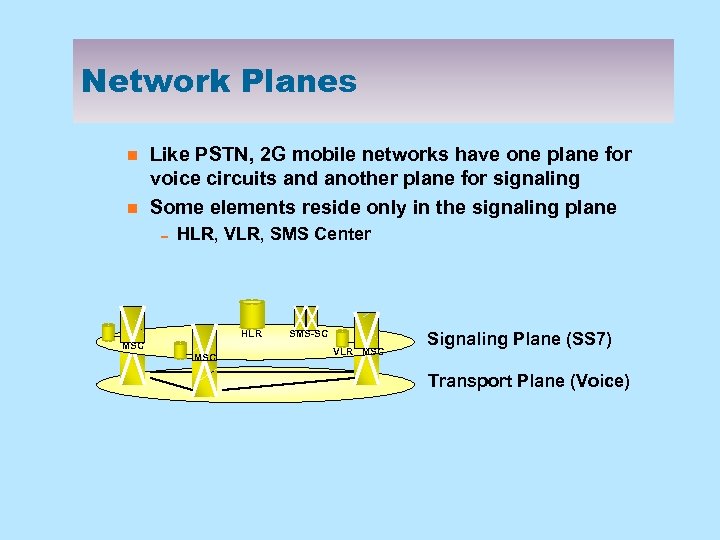 Network Planes n n Like PSTN, 2 G mobile networks have one plane for voice circuits and another plane for signaling Some elements reside only in the signaling plane 0 HLR, VLR, SMS Center HLR MSC SMS-SC VLR MSC Signaling Plane (SS 7) Transport Plane (Voice)
Network Planes n n Like PSTN, 2 G mobile networks have one plane for voice circuits and another plane for signaling Some elements reside only in the signaling plane 0 HLR, VLR, SMS Center HLR MSC SMS-SC VLR MSC Signaling Plane (SS 7) Transport Plane (Voice)
 Signaling in Core Network n Based on SS 7 (Signaling system 7) 0 ISUP (ISDN Signaling User Part) and specific Application Parts n GSM MAP and ANSI-41 services 0 mobility, call-handling, O&M 0 authentication, supplementary services 0 SMS n Location registers for mobility management 0 HLR: home location register; has permanent data 0 VLR: visitor location register ; keeps local copy for roamers * Common Channel Signaling System No. 7 (i. e. , SS 7 or C 7) * The ISDN User Part (ISUP) defines the protocol and procedures used to set-up, manage, and release trunk circuits that carry voice and data calls over the public switched telephone network (PSTN). ISUP is used for both ISDN and non-ISDN calls
Signaling in Core Network n Based on SS 7 (Signaling system 7) 0 ISUP (ISDN Signaling User Part) and specific Application Parts n GSM MAP and ANSI-41 services 0 mobility, call-handling, O&M 0 authentication, supplementary services 0 SMS n Location registers for mobility management 0 HLR: home location register; has permanent data 0 VLR: visitor location register ; keeps local copy for roamers * Common Channel Signaling System No. 7 (i. e. , SS 7 or C 7) * The ISDN User Part (ISUP) defines the protocol and procedures used to set-up, manage, and release trunk circuits that carry voice and data calls over the public switched telephone network (PSTN). ISUP is used for both ISDN and non-ISDN calls
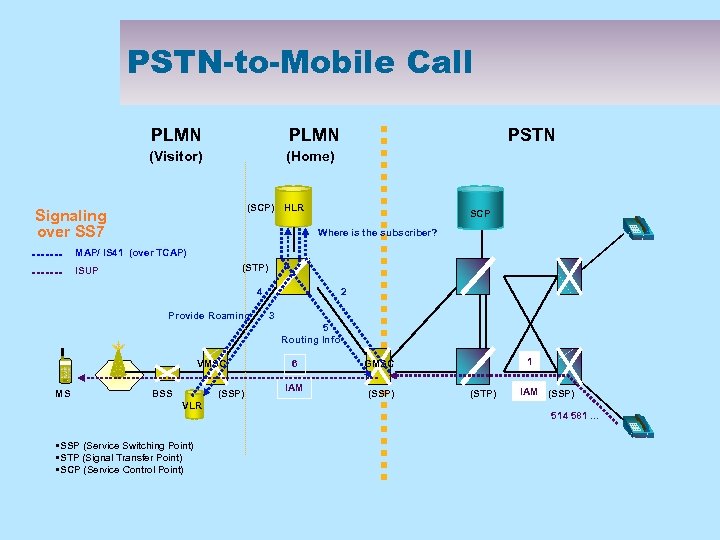 PSTN-to-Mobile Call PLMN (Visitor) PSTN (Home) (SCP) HLR Signaling over SS 7 SCP Where is the subscriber? MAP/ IS 41 (over TCAP) (STP) ISUP 4 Provide Roaming 2 3 5 Routing Info VMSC MS BSS (SSP) VLR • SSP (Service Switching Point) • STP (Signal Transfer Point) • SCP (Service Control Point) 6 IAM 1 GMSC (SSP) (STP) IAM (SSP) 514 581. . .
PSTN-to-Mobile Call PLMN (Visitor) PSTN (Home) (SCP) HLR Signaling over SS 7 SCP Where is the subscriber? MAP/ IS 41 (over TCAP) (STP) ISUP 4 Provide Roaming 2 3 5 Routing Info VMSC MS BSS (SSP) VLR • SSP (Service Switching Point) • STP (Signal Transfer Point) • SCP (Service Control Point) 6 IAM 1 GMSC (SSP) (STP) IAM (SSP) 514 581. . .
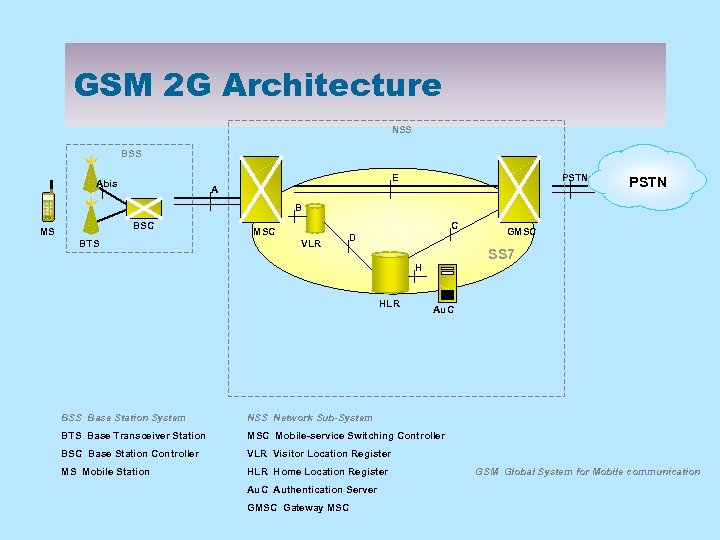 GSM 2 G Architecture NSS BSS E Abis PSTN A PSTN B BSC MS BTS C MSC VLR D SS 7 H HLR GMSC Au. C BSS Base Station System NSS Network Sub-System BTS Base Transceiver Station MSC Mobile-service Switching Controller BSC Base Station Controller VLR Visitor Location Register MS Mobile Station HLR Home Location Register Au. C Authentication Server GMSC Gateway MSC GSM Global System for Mobile communication
GSM 2 G Architecture NSS BSS E Abis PSTN A PSTN B BSC MS BTS C MSC VLR D SS 7 H HLR GMSC Au. C BSS Base Station System NSS Network Sub-System BTS Base Transceiver Station MSC Mobile-service Switching Controller BSC Base Station Controller VLR Visitor Location Register MS Mobile Station HLR Home Location Register Au. C Authentication Server GMSC Gateway MSC GSM Global System for Mobile communication
 Enhancing GSM n n New technology since mid-90 s Global standard - most widely deployed 0 significant payback for enhancements n Frequency hopping 0 overcome fading n Synchronization between cells 0 DFCA: dynamic frequency and channel assignment allocate radio resources to minimize interference 0 Also used to determine mobile’s location n n TFO – Tandem Free Operation
Enhancing GSM n n New technology since mid-90 s Global standard - most widely deployed 0 significant payback for enhancements n Frequency hopping 0 overcome fading n Synchronization between cells 0 DFCA: dynamic frequency and channel assignment allocate radio resources to minimize interference 0 Also used to determine mobile’s location n n TFO – Tandem Free Operation
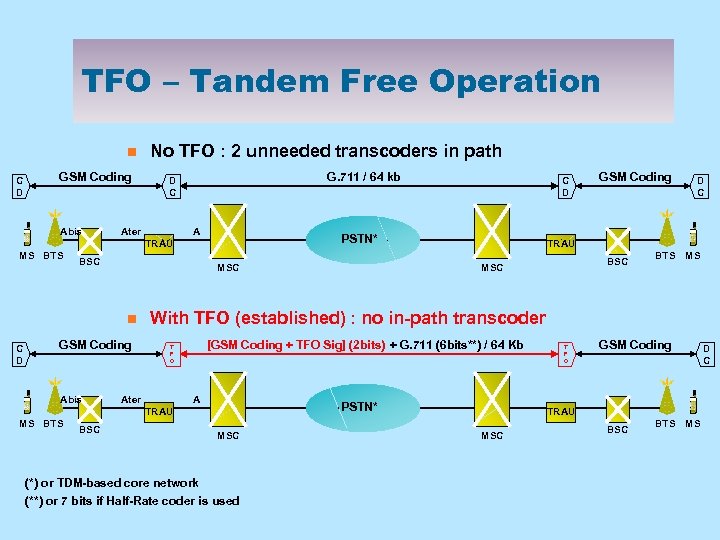 TFO – Tandem Free Operation n C D GSM Coding Abis No TFO : 2 unneeded transcoders in path G. 711 / 64 kb D C Ater A PSTN* TRAU MS BTS BSC MSC n C D GSM Coding Abis BSC GSM Coding D C TRAU BSC MSC BTS MS With TFO (established) : no in-path transcoder [GSM Coding + TFO Sig] (2 bits) + G. 711 (6 bits**) / 64 Kb T F O Ater A PSTN* TRAU MS BTS C D MSC (*) or TDM-based core network (**) or 7 bits if Half-Rate coder is used T F O GSM Coding D C TRAU MSC BTS MS
TFO – Tandem Free Operation n C D GSM Coding Abis No TFO : 2 unneeded transcoders in path G. 711 / 64 kb D C Ater A PSTN* TRAU MS BTS BSC MSC n C D GSM Coding Abis BSC GSM Coding D C TRAU BSC MSC BTS MS With TFO (established) : no in-path transcoder [GSM Coding + TFO Sig] (2 bits) + G. 711 (6 bits**) / 64 Kb T F O Ater A PSTN* TRAU MS BTS C D MSC (*) or TDM-based core network (**) or 7 bits if Half-Rate coder is used T F O GSM Coding D C TRAU MSC BTS MS
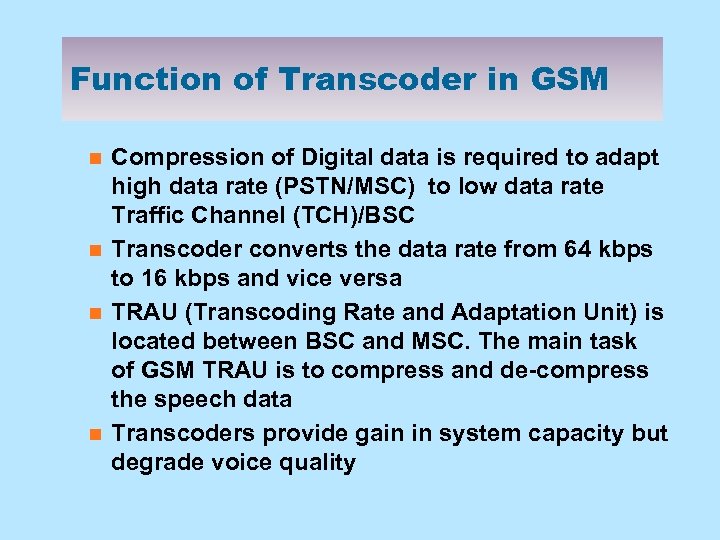 Function of Transcoder in GSM n n Compression of Digital data is required to adapt high data rate (PSTN/MSC) to low data rate Traffic Channel (TCH)/BSC Transcoder converts the data rate from 64 kbps to 16 kbps and vice versa TRAU (Transcoding Rate and Adaptation Unit) is located between BSC and MSC. The main task of GSM TRAU is to compress and de-compress the speech data Transcoders provide gain in system capacity but degrade voice quality
Function of Transcoder in GSM n n Compression of Digital data is required to adapt high data rate (PSTN/MSC) to low data rate Traffic Channel (TCH)/BSC Transcoder converts the data rate from 64 kbps to 16 kbps and vice versa TRAU (Transcoding Rate and Adaptation Unit) is located between BSC and MSC. The main task of GSM TRAU is to compress and de-compress the speech data Transcoders provide gain in system capacity but degrade voice quality
 TFO Working Principle n n n TFO steals least significant bits (LSBs) from GSM coding to embed the bits from encoded stream. Since GSM codec rates are 16 kbit/s maximum, one needs to steal only about 1 or 2 LSBs of total 8 bits If TFO connection breaks down, then the upper most significant bits (MSBs) can still be used to carry transcoded G. 711/PCM sample values without loss The remote transcoder equipment then extracts the encoded stream from LSBs and reconstructs it as codec frames This avoids two iterations of trancoding.
TFO Working Principle n n n TFO steals least significant bits (LSBs) from GSM coding to embed the bits from encoded stream. Since GSM codec rates are 16 kbit/s maximum, one needs to steal only about 1 or 2 LSBs of total 8 bits If TFO connection breaks down, then the upper most significant bits (MSBs) can still be used to carry transcoded G. 711/PCM sample values without loss The remote transcoder equipment then extracts the encoded stream from LSBs and reconstructs it as codec frames This avoids two iterations of trancoding.
 TFO Pros and Cons n n Improves voice quality by disabling unneeded transcoders during mobile-to-mobile calls Operate with existing networks (BSCs, MSCs) 0 New TRAU negotiates TFO in-band after call setup 0 TFO frames use LSBits of 64 Kbps circuit to carry compressed speech frames and TFO signaling 0 MSBits still carry normal G. 711 speech samples n Limitations 0 Same speech codec in each handset 0 Digital transparency in core network 0 TFO disabled upon cell handover, call transfer, in-band DTMF, announcements or conferencing
TFO Pros and Cons n n Improves voice quality by disabling unneeded transcoders during mobile-to-mobile calls Operate with existing networks (BSCs, MSCs) 0 New TRAU negotiates TFO in-band after call setup 0 TFO frames use LSBits of 64 Kbps circuit to carry compressed speech frames and TFO signaling 0 MSBits still carry normal G. 711 speech samples n Limitations 0 Same speech codec in each handset 0 Digital transparency in core network 0 TFO disabled upon cell handover, call transfer, in-band DTMF, announcements or conferencing
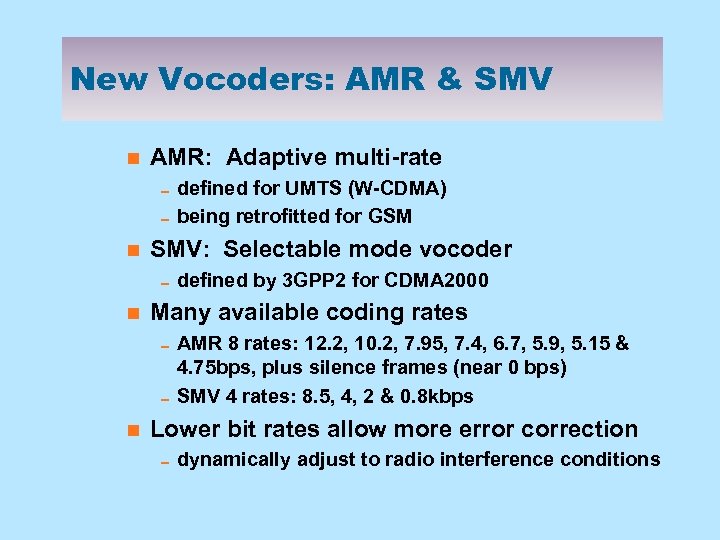 New Vocoders: AMR & SMV n AMR: Adaptive multi-rate 0 defined for UMTS (W-CDMA) 0 being retrofitted for GSM n SMV: Selectable mode vocoder 0 defined by 3 GPP 2 for CDMA 2000 n Many available coding rates 0 AMR 8 rates: 12. 2, 10. 2, 7. 95, 7. 4, 6. 7, 5. 9, 5. 15 & 4. 75 bps, plus silence frames (near 0 bps) 0 SMV 4 rates: 8. 5, 4, 2 & 0. 8 kbps n Lower bit rates allow more error correction 0 dynamically adjust to radio interference conditions
New Vocoders: AMR & SMV n AMR: Adaptive multi-rate 0 defined for UMTS (W-CDMA) 0 being retrofitted for GSM n SMV: Selectable mode vocoder 0 defined by 3 GPP 2 for CDMA 2000 n Many available coding rates 0 AMR 8 rates: 12. 2, 10. 2, 7. 95, 7. 4, 6. 7, 5. 9, 5. 15 & 4. 75 bps, plus silence frames (near 0 bps) 0 SMV 4 rates: 8. 5, 4, 2 & 0. 8 kbps n Lower bit rates allow more error correction 0 dynamically adjust to radio interference conditions
 GPRS - 2. 5 G for GSM n General packet radio service 0 first introduction of packet technology n Aggregate radio channels 0 support higher data rates (115 Kbps) 0 subject to channel availability n n n Share aggregate channels among multiple users All new IP-based data infrastructure No changes to voice network
GPRS - 2. 5 G for GSM n General packet radio service 0 first introduction of packet technology n Aggregate radio channels 0 support higher data rates (115 Kbps) 0 subject to channel availability n n n Share aggregate channels among multiple users All new IP-based data infrastructure No changes to voice network
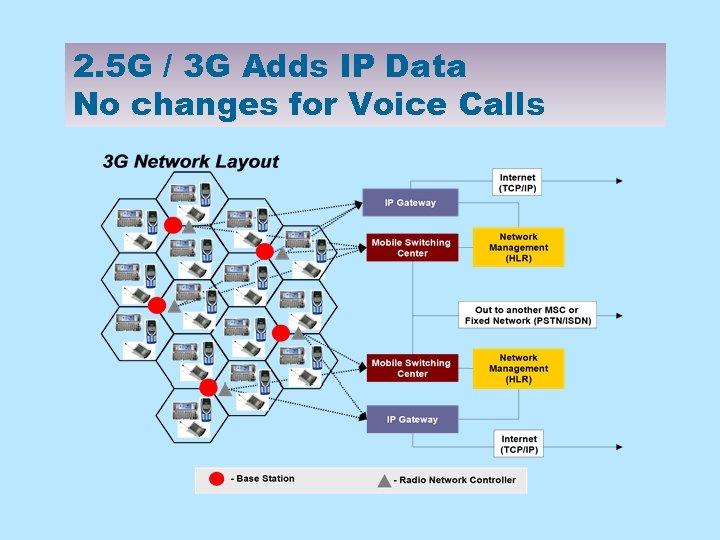 2. 5 G / 3 G Adds IP Data No changes for Voice Calls
2. 5 G / 3 G Adds IP Data No changes for Voice Calls
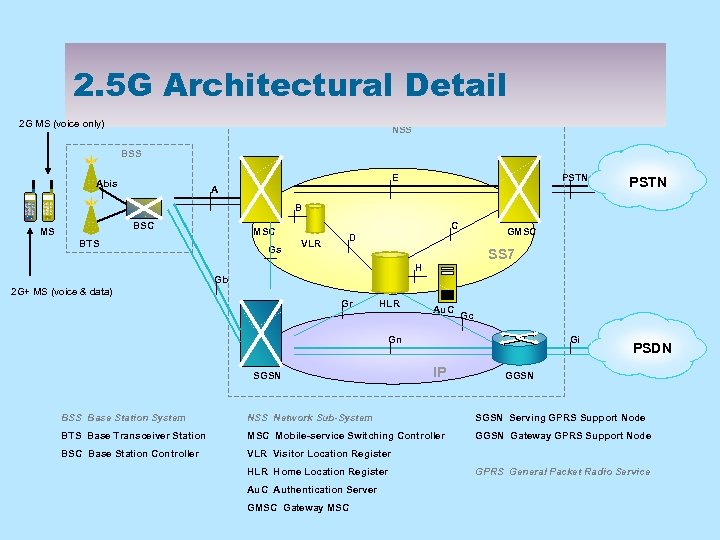 2. 5 G Architectural Detail 2 G MS (voice only) NSS BSS E Abis PSTN A PSTN B BSC MSC BTS Gs GMSC D VLR SS 7 H Gb 2 G+ MS (voice & data) Gr HLR Au. C Gc Gi Gn SGSN IP PSDN GGSN BSS Base Station System NSS Network Sub-System SGSN Serving GPRS Support Node BTS Base Transceiver Station MSC Mobile-service Switching Controller GGSN Gateway GPRS Support Node BSC Base Station Controller VLR Visitor Location Register HLR Home Location Register Au. C Authentication Server GMSC Gateway MSC GPRS General Packet Radio Service
2. 5 G Architectural Detail 2 G MS (voice only) NSS BSS E Abis PSTN A PSTN B BSC MSC BTS Gs GMSC D VLR SS 7 H Gb 2 G+ MS (voice & data) Gr HLR Au. C Gc Gi Gn SGSN IP PSDN GGSN BSS Base Station System NSS Network Sub-System SGSN Serving GPRS Support Node BTS Base Transceiver Station MSC Mobile-service Switching Controller GGSN Gateway GPRS Support Node BSC Base Station Controller VLR Visitor Location Register HLR Home Location Register Au. C Authentication Server GMSC Gateway MSC GPRS General Packet Radio Service
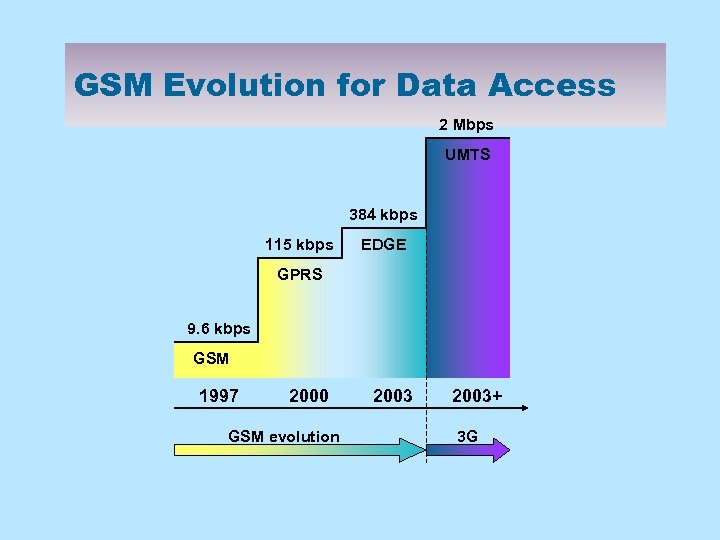 GSM Evolution for Data Access 2 Mbps UMTS 384 kbps 115 kbps EDGE GPRS 9. 6 kbps GSM 1997 2000 GSM evolution 2003+ 3 G
GSM Evolution for Data Access 2 Mbps UMTS 384 kbps 115 kbps EDGE GPRS 9. 6 kbps GSM 1997 2000 GSM evolution 2003+ 3 G
 EDGE n n Enhanced Data rates for Global Evolution Increased data rates with GSM compatibility 0 still 200 KHz bands; still TDMA 0 8 -PSK modulation: 3 bits/symbol give 3 X data rate 0 shorter range (more sensitive to noise/interference) n GAIT - GSM/ANSI-136 interoperability team 0 allows IS-136 TDMA operators to migrate to EDGE 0 new GSM/ EDGE radios but evolved ANSI-41 core network
EDGE n n Enhanced Data rates for Global Evolution Increased data rates with GSM compatibility 0 still 200 KHz bands; still TDMA 0 8 -PSK modulation: 3 bits/symbol give 3 X data rate 0 shorter range (more sensitive to noise/interference) n GAIT - GSM/ANSI-136 interoperability team 0 allows IS-136 TDMA operators to migrate to EDGE 0 new GSM/ EDGE radios but evolved ANSI-41 core network
 3 G Partnership Project (3 GPP) n 3 GPP defining migration from GSM to UMTS (W-CDMA) 0 core network evolves from GSM-only to support GSM, GPRS and new W-CDMA facilities n n 3 GPP Release 99 - Adds 3 G radios 3 GPP Release 4 0 Adds softswitch/ voice gateways and packet core n 3 GPP Release 5 0 First IP Multimedia Services (IMS) w/ SIP & Qo. S n 3 GPP Release 6 0 “All IP” network; contents of r 6 still being defined
3 G Partnership Project (3 GPP) n 3 GPP defining migration from GSM to UMTS (W-CDMA) 0 core network evolves from GSM-only to support GSM, GPRS and new W-CDMA facilities n n 3 GPP Release 99 - Adds 3 G radios 3 GPP Release 4 0 Adds softswitch/ voice gateways and packet core n 3 GPP Release 5 0 First IP Multimedia Services (IMS) w/ SIP & Qo. S n 3 GPP Release 6 0 “All IP” network; contents of r 6 still being defined
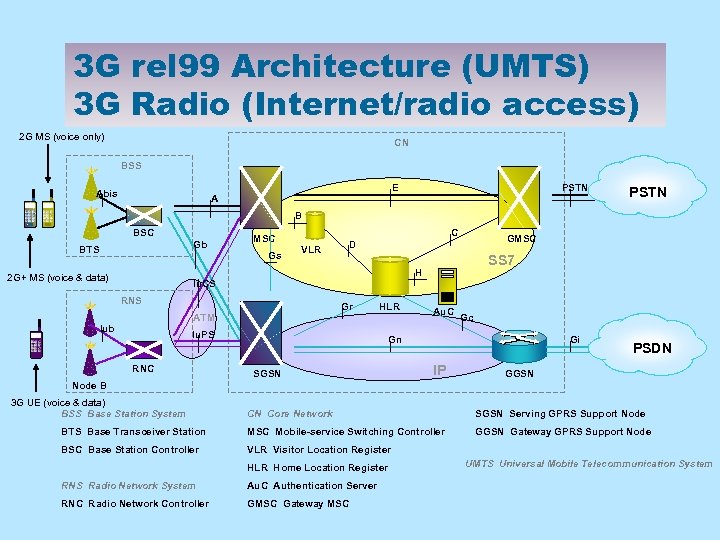 3 G rel 99 Architecture (UMTS) 3 G Radio (Internet/radio access) 2 G MS (voice only) CN BSS E Abis PSTN A PSTN B BSC Gb BTS C MSC Gs GMSC D VLR SS 7 H 2 G+ MS (voice & data) Iu. CS RNS Gr HLR ATM Iub Iu. PS RNC Au. C Gc Gn SGSN Gi IP PSDN GGSN Node B 3 G UE (voice & data) BSS Base Station System CN Core Network SGSN Serving GPRS Support Node BTS Base Transceiver Station MSC Mobile-service Switching Controller GGSN Gateway GPRS Support Node BSC Base Station Controller VLR Visitor Location Register HLR Home Location Register RNS Radio Network System Au. C Authentication Server RNC Radio Network Controller GMSC Gateway MSC UMTS Universal Mobile Telecommunication System
3 G rel 99 Architecture (UMTS) 3 G Radio (Internet/radio access) 2 G MS (voice only) CN BSS E Abis PSTN A PSTN B BSC Gb BTS C MSC Gs GMSC D VLR SS 7 H 2 G+ MS (voice & data) Iu. CS RNS Gr HLR ATM Iub Iu. PS RNC Au. C Gc Gn SGSN Gi IP PSDN GGSN Node B 3 G UE (voice & data) BSS Base Station System CN Core Network SGSN Serving GPRS Support Node BTS Base Transceiver Station MSC Mobile-service Switching Controller GGSN Gateway GPRS Support Node BSC Base Station Controller VLR Visitor Location Register HLR Home Location Register RNS Radio Network System Au. C Authentication Server RNC Radio Network Controller GMSC Gateway MSC UMTS Universal Mobile Telecommunication System
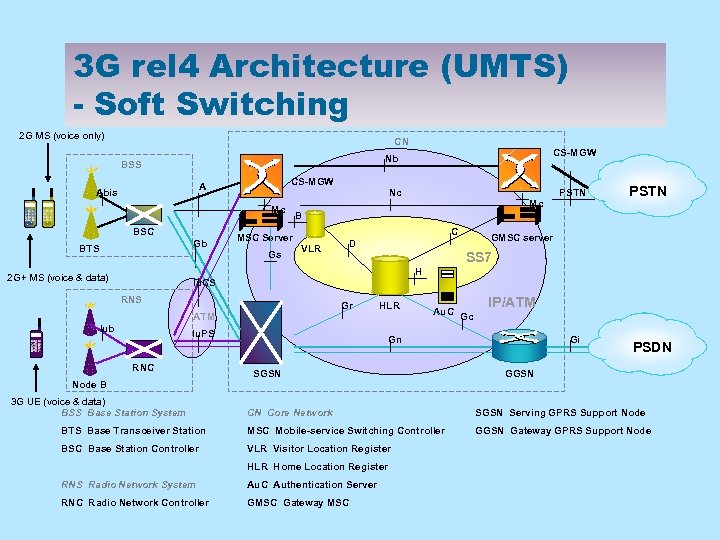 3 G rel 4 Architecture (UMTS) - Soft Switching 2 G MS (voice only) CN CS-MGW A Abis Nc Mc BSC Gb BTS CS-MGW Nb BSS PSTN B C MSC Server Gs PSTN Mc GMSC server D VLR SS 7 H 2 G+ MS (voice & data) Iu. CS RNS Gr HLR ATM Iub Iu. PS RNC Au. C IP/ATM Gc Gn SGSN Gi PSDN GGSN Node B 3 G UE (voice & data) BSS Base Station System CN Core Network SGSN Serving GPRS Support Node BTS Base Transceiver Station MSC Mobile-service Switching Controller GGSN Gateway GPRS Support Node BSC Base Station Controller VLR Visitor Location Register HLR Home Location Register RNS Radio Network System Au. C Authentication Server RNC Radio Network Controller GMSC Gateway MSC
3 G rel 4 Architecture (UMTS) - Soft Switching 2 G MS (voice only) CN CS-MGW A Abis Nc Mc BSC Gb BTS CS-MGW Nb BSS PSTN B C MSC Server Gs PSTN Mc GMSC server D VLR SS 7 H 2 G+ MS (voice & data) Iu. CS RNS Gr HLR ATM Iub Iu. PS RNC Au. C IP/ATM Gc Gn SGSN Gi PSDN GGSN Node B 3 G UE (voice & data) BSS Base Station System CN Core Network SGSN Serving GPRS Support Node BTS Base Transceiver Station MSC Mobile-service Switching Controller GGSN Gateway GPRS Support Node BSC Base Station Controller VLR Visitor Location Register HLR Home Location Register RNS Radio Network System Au. C Authentication Server RNC Radio Network Controller GMSC Gateway MSC
 Benefits of Media Gateways • Media gateway -translation device or service that converts media streams between different technologies such as SS 7, 2 G, 2. 5 G and 3 G radio access networks) or PBX systems • Media gateways enable communications across packet networks using transport protocols such as Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) and Internet Protocol (IP) • Media gateway function is to convert between different transmission and coding techniques
Benefits of Media Gateways • Media gateway -translation device or service that converts media streams between different technologies such as SS 7, 2 G, 2. 5 G and 3 G radio access networks) or PBX systems • Media gateways enable communications across packet networks using transport protocols such as Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) and Internet Protocol (IP) • Media gateway function is to convert between different transmission and coding techniques
 Transcoder Free Operation (Tr. FO) n Improve voice quality by avoiding unneeded transcoders 0 like TFO but using packet-based core network n Out-of-band negotiation 0 Select same codec at both ends during call setup 0 Supports sudden channel rearrangement (handovers, etc. ) via signaling procedures 0 When Tr. FO impossible, TFO can be attempted e. g. transit between packet-based and circuit-based core networks
Transcoder Free Operation (Tr. FO) n Improve voice quality by avoiding unneeded transcoders 0 like TFO but using packet-based core network n Out-of-band negotiation 0 Select same codec at both ends during call setup 0 Supports sudden channel rearrangement (handovers, etc. ) via signaling procedures 0 When Tr. FO impossible, TFO can be attempted e. g. transit between packet-based and circuit-based core networks
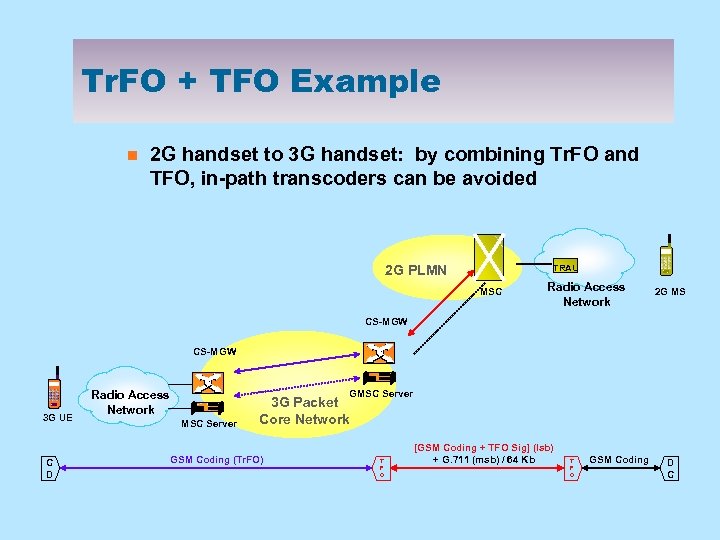 Tr. FO + TFO Example n 2 G handset to 3 G handset: by combining Tr. FO and TFO, in-path transcoders can be avoided 2 G PLMN TRAU MSC Radio Access Network 2 G MS CS-MGW 3 G UE C D GMSC Server Radio Access Network MSC Server 3 G Packet Core Network GSM Coding (Tr. FO) T F O [GSM Coding + TFO Sig] (lsb) + G. 711 (msb) / 64 Kb T F O GSM Coding D C
Tr. FO + TFO Example n 2 G handset to 3 G handset: by combining Tr. FO and TFO, in-path transcoders can be avoided 2 G PLMN TRAU MSC Radio Access Network 2 G MS CS-MGW 3 G UE C D GMSC Server Radio Access Network MSC Server 3 G Packet Core Network GSM Coding (Tr. FO) T F O [GSM Coding + TFO Sig] (lsb) + G. 711 (msb) / 64 Kb T F O GSM Coding D C
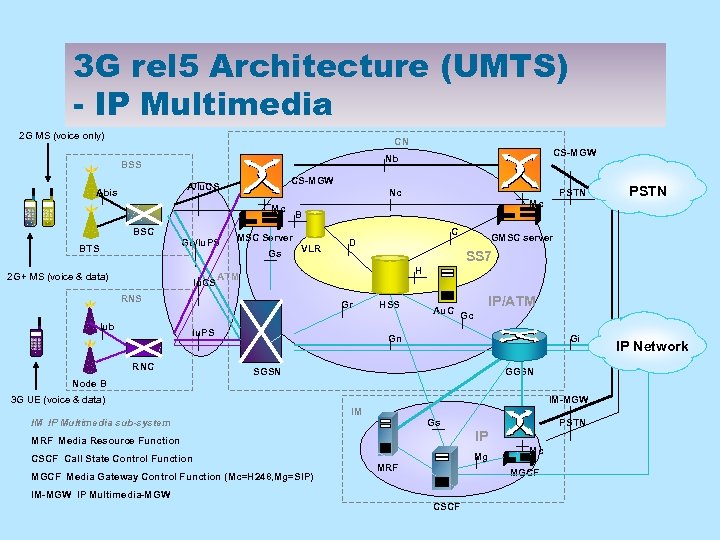 3 G rel 5 Architecture (UMTS) - IP Multimedia 2 G MS (voice only) CN CS-MGW A/Iu. CS Abis Nc Mc BSC BTS Gb/Iu. PS 2 G+ MS (voice & data) Iu. CS PSTN B C VLR GMSC server D SS 7 H ATM RNS Gr Iu. PS RNC PSTN Mc MSC Server Gs Iub CS-MGW Nb BSS HSS Au. C IP/ATM Gc Gn Gi SGSN GGSN Node B 3 G UE (voice & data) IM-MGW IM Gs IM IP Multimedia sub-system PSTN MRF Media Resource Function IP CSCF Call State Control Function Mg MGCF Media Gateway Control Function (Mc=H 248, Mg=SIP) MRF Mc MGCF IM-MGW IP Multimedia-MGW CSCF IP Network
3 G rel 5 Architecture (UMTS) - IP Multimedia 2 G MS (voice only) CN CS-MGW A/Iu. CS Abis Nc Mc BSC BTS Gb/Iu. PS 2 G+ MS (voice & data) Iu. CS PSTN B C VLR GMSC server D SS 7 H ATM RNS Gr Iu. PS RNC PSTN Mc MSC Server Gs Iub CS-MGW Nb BSS HSS Au. C IP/ATM Gc Gn Gi SGSN GGSN Node B 3 G UE (voice & data) IM-MGW IM Gs IM IP Multimedia sub-system PSTN MRF Media Resource Function IP CSCF Call State Control Function Mg MGCF Media Gateway Control Function (Mc=H 248, Mg=SIP) MRF Mc MGCF IM-MGW IP Multimedia-MGW CSCF IP Network
 3 GPP Rel. 6 Objectives n IP Multimedia Services, phase 2 0 IMS messaging and group management n n Wireless LAN interworking Speech enabled services 0 distributed speech recognition (DSR) n Number portability Other enhancements n Scope and definition in progress n
3 GPP Rel. 6 Objectives n IP Multimedia Services, phase 2 0 IMS messaging and group management n n Wireless LAN interworking Speech enabled services 0 distributed speech recognition (DSR) n Number portability Other enhancements n Scope and definition in progress n
 3 GPP 2 Defines IS-41 Evolution n 3 rd Generation Partnership Project “Two” 0 Separate organization, as 3 GPP closely tied to GSM and UMTS 0 Goal of ultimate merger (3 GPP + 3 GPP 2) remains n Evolution of IS-41 to “all IP” more direct but not any faster 0 skips ATM stage n n n 1 x. RTT - IP packet support (like GPRS) 1 x. EVDV - Adds softswitch/ voice gateways 3 x – Triples radio data rates Spring 2004
3 GPP 2 Defines IS-41 Evolution n 3 rd Generation Partnership Project “Two” 0 Separate organization, as 3 GPP closely tied to GSM and UMTS 0 Goal of ultimate merger (3 GPP + 3 GPP 2) remains n Evolution of IS-41 to “all IP” more direct but not any faster 0 skips ATM stage n n n 1 x. RTT - IP packet support (like GPRS) 1 x. EVDV - Adds softswitch/ voice gateways 3 x – Triples radio data rates Spring 2004
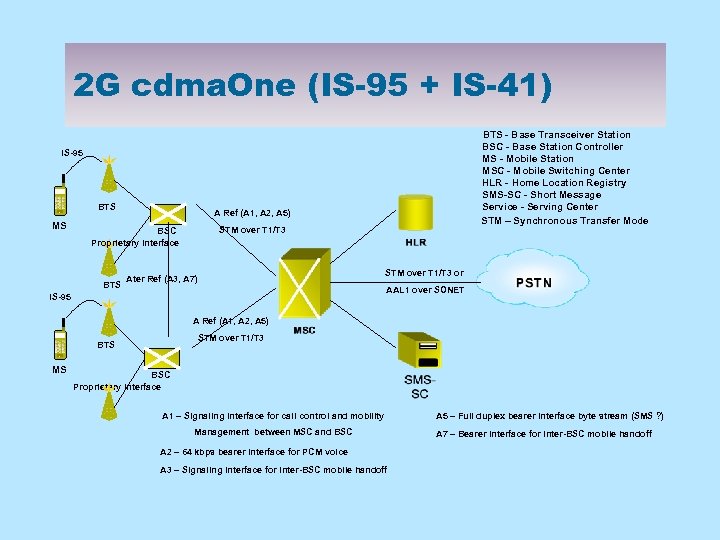 2 G cdma. One (IS-95 + IS-41) BTS - Base Transceiver Station BSC - Base Station Controller MS - Mobile Station MSC - Mobile Switching Center HLR - Home Location Registry SMS-SC - Short Message Service - Serving Center STM – Synchronous Transfer Mode IS-95 BTS MS A Ref (A 1, A 2, A 5) STM over T 1/T 3 BSC Proprietary Interface BTS STM over T 1/T 3 or Ater Ref (A 3, A 7) AAL 1 over SONET IS-95 A Ref (A 1, A 2, A 5) STM over T 1/T 3 BTS MS BSC Proprietary Interface A 1 – Signaling interface for call control and mobility Management between MSC and BSC A 2 – 64 kbps bearer interface for PCM voice A 3 – Signaling interface for inter-BSC mobile handoff A 5 – Full duplex bearer interface byte stream (SMS ? ) A 7 – Bearer interface for inter-BSC mobile handoff
2 G cdma. One (IS-95 + IS-41) BTS - Base Transceiver Station BSC - Base Station Controller MS - Mobile Station MSC - Mobile Switching Center HLR - Home Location Registry SMS-SC - Short Message Service - Serving Center STM – Synchronous Transfer Mode IS-95 BTS MS A Ref (A 1, A 2, A 5) STM over T 1/T 3 BSC Proprietary Interface BTS STM over T 1/T 3 or Ater Ref (A 3, A 7) AAL 1 over SONET IS-95 A Ref (A 1, A 2, A 5) STM over T 1/T 3 BTS MS BSC Proprietary Interface A 1 – Signaling interface for call control and mobility Management between MSC and BSC A 2 – 64 kbps bearer interface for PCM voice A 3 – Signaling interface for inter-BSC mobile handoff A 5 – Full duplex bearer interface byte stream (SMS ? ) A 7 – Bearer interface for inter-BSC mobile handoff
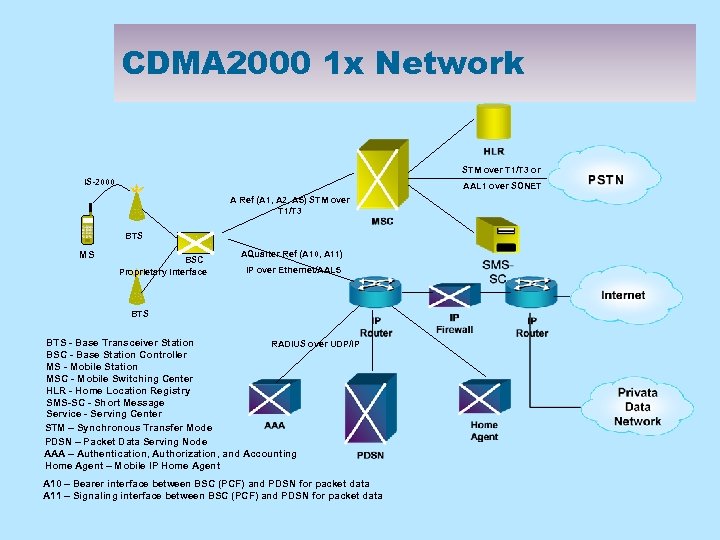 CDMA 2000 1 x Network STM over T 1/T 3 or IS-2000 AAL 1 over SONET A Ref (A 1, A 2, A 5) STM over T 1/T 3 BTS MS BSC Proprietary Interface AQuarter Ref (A 10, A 11) IP over Ethernet/AAL 5 BTS - Base Transceiver Station RADIUS over UDP/IP BSC - Base Station Controller MS - Mobile Station MSC - Mobile Switching Center HLR - Home Location Registry SMS-SC - Short Message Service - Serving Center STM – Synchronous Transfer Mode PDSN – Packet Data Serving Node AAA – Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting Home Agent – Mobile IP Home Agent A 10 – Bearer interface between BSC (PCF) and PDSN for packet data A 11 – Signaling interface between BSC (PCF) and PDSN for packet data
CDMA 2000 1 x Network STM over T 1/T 3 or IS-2000 AAL 1 over SONET A Ref (A 1, A 2, A 5) STM over T 1/T 3 BTS MS BSC Proprietary Interface AQuarter Ref (A 10, A 11) IP over Ethernet/AAL 5 BTS - Base Transceiver Station RADIUS over UDP/IP BSC - Base Station Controller MS - Mobile Station MSC - Mobile Switching Center HLR - Home Location Registry SMS-SC - Short Message Service - Serving Center STM – Synchronous Transfer Mode PDSN – Packet Data Serving Node AAA – Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting Home Agent – Mobile IP Home Agent A 10 – Bearer interface between BSC (PCF) and PDSN for packet data A 11 – Signaling interface between BSC (PCF) and PDSN for packet data
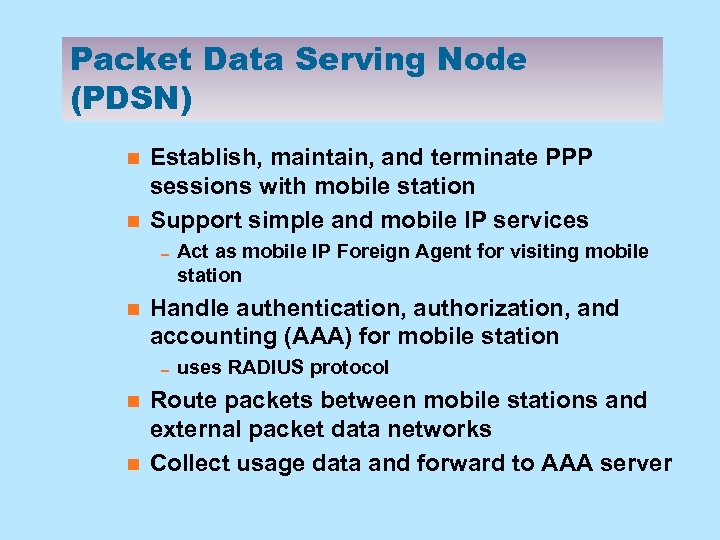 Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) n n Establish, maintain, and terminate PPP sessions with mobile station Support simple and mobile IP services 0 Act as mobile IP Foreign Agent for visiting mobile station n Handle authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA) for mobile station 0 uses RADIUS protocol n n Route packets between mobile stations and external packet data networks Collect usage data and forward to AAA server
Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) n n Establish, maintain, and terminate PPP sessions with mobile station Support simple and mobile IP services 0 Act as mobile IP Foreign Agent for visiting mobile station n Handle authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA) for mobile station 0 uses RADIUS protocol n n Route packets between mobile stations and external packet data networks Collect usage data and forward to AAA server
 AAA Server and Home Agent n AAA server 0 Authentication: PPP and mobile IP connections 0 Authorization: service profile and security key distribution and management 0 Accounting: usage data for billing n Mobile IP Home Agent 0 Track location of mobile IP subscribers when they move from one network to another 0 Receive packets on behalf of the mobile node when node is attached to a foreign network and deliver packets to mobile’s current point of attachment
AAA Server and Home Agent n AAA server 0 Authentication: PPP and mobile IP connections 0 Authorization: service profile and security key distribution and management 0 Accounting: usage data for billing n Mobile IP Home Agent 0 Track location of mobile IP subscribers when they move from one network to another 0 Receive packets on behalf of the mobile node when node is attached to a foreign network and deliver packets to mobile’s current point of attachment
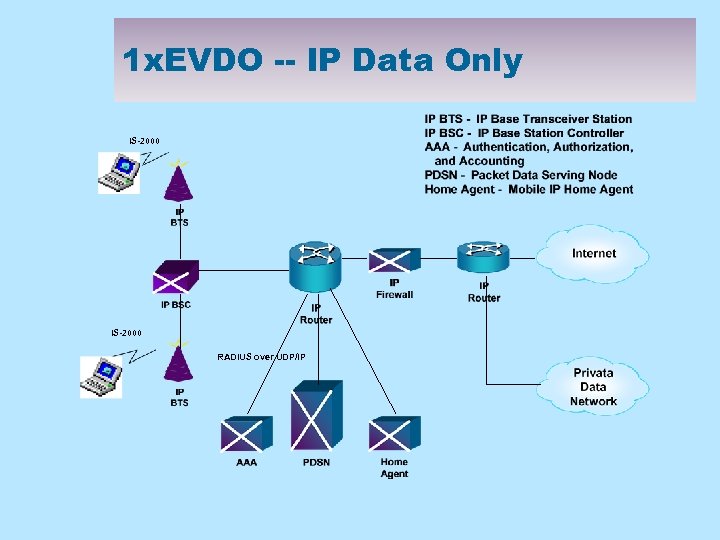 1 x. EVDO -- IP Data Only IS-2000 RADIUS over UDP/IP
1 x. EVDO -- IP Data Only IS-2000 RADIUS over UDP/IP
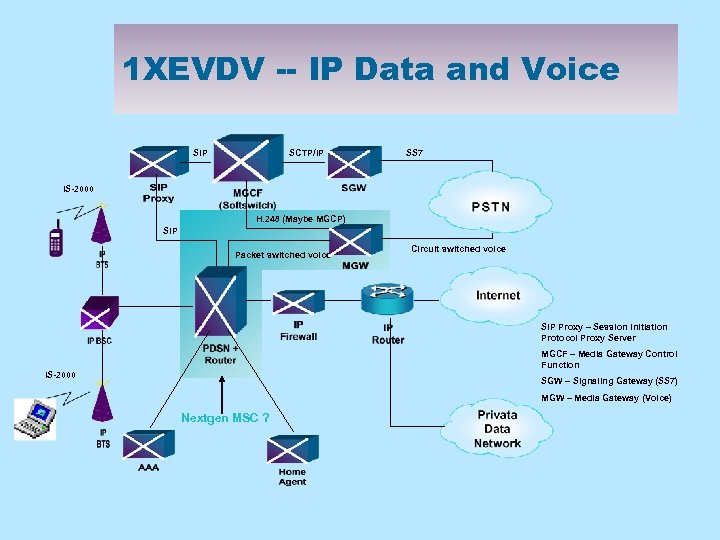 1 XEVDV -- IP Data and Voice SIP SCTP/IP SS 7 IS-2000 H. 248 (Maybe MGCP) SIP Packet switched voice Circuit switched voice SIP Proxy – Session Initiation Protocol Proxy Server MGCF – Media Gateway Control Function IS-2000 SGW – Signaling Gateway (SS 7) MGW – Media Gateway (Voice) Nextgen MSC ?
1 XEVDV -- IP Data and Voice SIP SCTP/IP SS 7 IS-2000 H. 248 (Maybe MGCP) SIP Packet switched voice Circuit switched voice SIP Proxy – Session Initiation Protocol Proxy Server MGCF – Media Gateway Control Function IS-2000 SGW – Signaling Gateway (SS 7) MGW – Media Gateway (Voice) Nextgen MSC ?
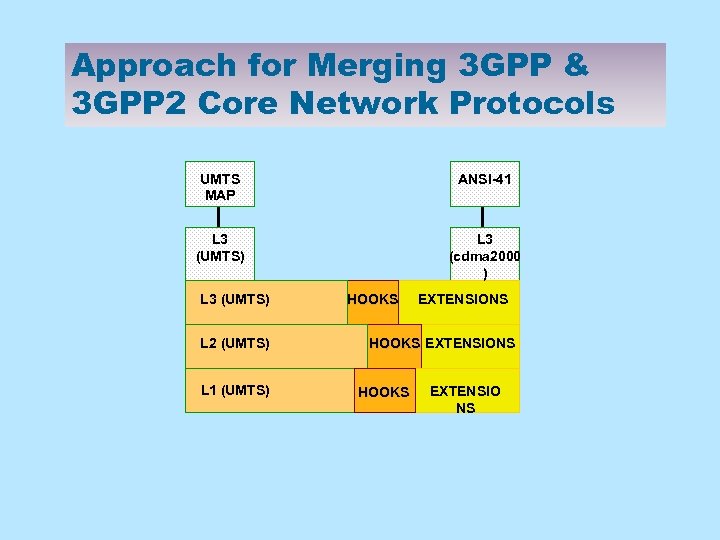 Approach for Merging 3 GPP & 3 GPP 2 Core Network Protocols UMTS MAP ANSI-41 L 3 (UMTS) L 3 (cdma 2000 ) L 3 (UMTS) L 2 (UMTS) L 1 (UMTS) HOOKS EXTENSIONS HOOKS EXTENSIO NS
Approach for Merging 3 GPP & 3 GPP 2 Core Network Protocols UMTS MAP ANSI-41 L 3 (UMTS) L 3 (cdma 2000 ) L 3 (UMTS) L 2 (UMTS) L 1 (UMTS) HOOKS EXTENSIONS HOOKS EXTENSIO NS
 Gateway Location Register n n Gateway between differing LR standards Introduced between VLR/SGSN and HLR 0 Single point for “hooks and extensions” 0 Controls traffic between visited mobile system and home mobile system n Visited network’s VLR/SGSN 0 treats GLR as roaming user’s HLR n Home network’s HLR 0 treats GLR as VLR/SGSN at visited network n GLR physically located in visited network 0 interacts with all VLRs in visited network
Gateway Location Register n n Gateway between differing LR standards Introduced between VLR/SGSN and HLR 0 Single point for “hooks and extensions” 0 Controls traffic between visited mobile system and home mobile system n Visited network’s VLR/SGSN 0 treats GLR as roaming user’s HLR n Home network’s HLR 0 treats GLR as VLR/SGSN at visited network n GLR physically located in visited network 0 interacts with all VLRs in visited network
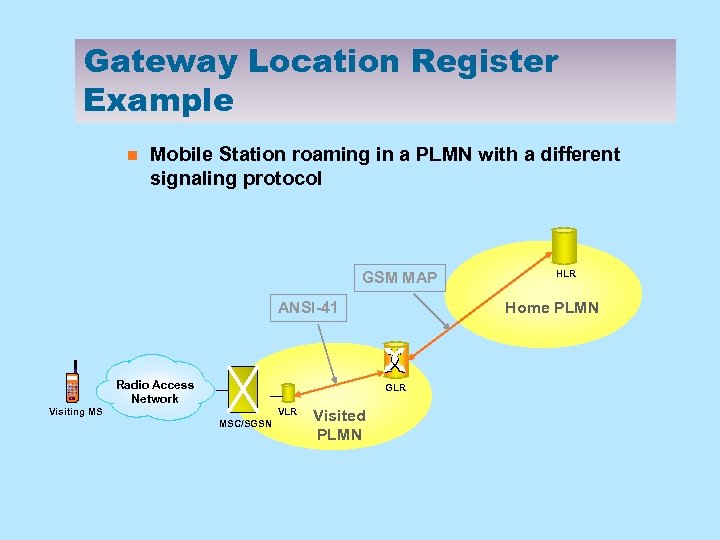 Gateway Location Register Example n Mobile Station roaming in a PLMN with a different signaling protocol GSM MAP ANSI-41 Radio Access Network Home PLMN GLR Visiting MS VLR MSC/SGSN Visited PLMN HLR
Gateway Location Register Example n Mobile Station roaming in a PLMN with a different signaling protocol GSM MAP ANSI-41 Radio Access Network Home PLMN GLR Visiting MS VLR MSC/SGSN Visited PLMN HLR
 3 GPP / 3 GPP 2 Harmonization n Joint meetings address interoperability and roaming 0 Handsets, radio network, core network n « Hooks and Extensions » help to converge 0 Near term fix n Target all-IP core harmonization 0 Leverage common specifications (esp. IETF RFCs) 0 Align terms, interfaces and functional entities 0 Developing Harmonization Reference Model (HRM) n 3 GPP’s IP Multimedia Services and 3 GPP 2’s Multi-Media Domain almost aligned
3 GPP / 3 GPP 2 Harmonization n Joint meetings address interoperability and roaming 0 Handsets, radio network, core network n « Hooks and Extensions » help to converge 0 Near term fix n Target all-IP core harmonization 0 Leverage common specifications (esp. IETF RFCs) 0 Align terms, interfaces and functional entities 0 Developing Harmonization Reference Model (HRM) n 3 GPP’s IP Multimedia Services and 3 GPP 2’s Multi-Media Domain almost aligned
 3 G Wireless Networks • History and Evolution of Mobile Radio • Evolving Network Architectures • Evolving Services • Applications
3 G Wireless Networks • History and Evolution of Mobile Radio • Evolving Network Architectures • Evolving Services • Applications
 Up and Coming Mobile Services n n n SMS, EMS, MMS Location-based services 3 G-324 M Video Vo. IP w/o Qo. S; Push-to-Talk IP Multimedia Services (w/ Qo. S) Converged “All IP” networks – the Vision
Up and Coming Mobile Services n n n SMS, EMS, MMS Location-based services 3 G-324 M Video Vo. IP w/o Qo. S; Push-to-Talk IP Multimedia Services (w/ Qo. S) Converged “All IP” networks – the Vision
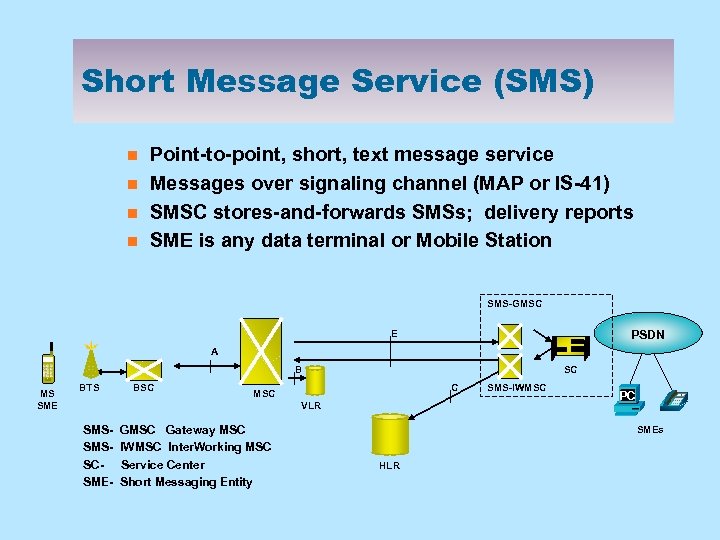 Short Message Service (SMS) n n Point-to-point, short, text message service Messages over signaling channel (MAP or IS-41) SMSC stores-and-forwards SMSs; delivery reports SME is any data terminal or Mobile Station SMS-GMSC E PSDN A B MS SME BTS BSC SC C MSC VLR SMS- GMSC Gateway MSC SMS- IWMSC Inter. Working MSC SC- Service Center SME- Short Messaging Entity SMS-IWMSC PC SMEs HLR
Short Message Service (SMS) n n Point-to-point, short, text message service Messages over signaling channel (MAP or IS-41) SMSC stores-and-forwards SMSs; delivery reports SME is any data terminal or Mobile Station SMS-GMSC E PSDN A B MS SME BTS BSC SC C MSC VLR SMS- GMSC Gateway MSC SMS- IWMSC Inter. Working MSC SC- Service Center SME- Short Messaging Entity SMS-IWMSC PC SMEs HLR
 SMS Principles n Basic services : 0 SM MT (Mobile Terminated) 0 SM MO (Mobile Originated) 0 (3 GPP 2) SM MO can be cancelled 0 (3 GPP 2) User can acknowledge n SM Service Center (3 GPP) aka Message Center (3 GPP 2) 0 relays and store-and-forwards SMSs n Payload of up to 140 bytes, but 0 Can be compressed (MS-to-MS) 0 And/or segmented in several SMs
SMS Principles n Basic services : 0 SM MT (Mobile Terminated) 0 SM MO (Mobile Originated) 0 (3 GPP 2) SM MO can be cancelled 0 (3 GPP 2) User can acknowledge n SM Service Center (3 GPP) aka Message Center (3 GPP 2) 0 relays and store-and-forwards SMSs n Payload of up to 140 bytes, but 0 Can be compressed (MS-to-MS) 0 And/or segmented in several SMs
 SMS Transport n Delivery / Submission report 0 Optional in 3 GPP 2 n Messages-Waiting 0 SC informs HLR/VLR that a message could not be delivered to MS n Alert-SC 0 HLR informs SC that the MS is again ready to receive n All messages over signaling channels 0 usually SS 7; SMSC may have IP option
SMS Transport n Delivery / Submission report 0 Optional in 3 GPP 2 n Messages-Waiting 0 SC informs HLR/VLR that a message could not be delivered to MS n Alert-SC 0 HLR informs SC that the MS is again ready to receive n All messages over signaling channels 0 usually SS 7; SMSC may have IP option
 EMS Principles n n n Enhanced Message Service Leverages SMS infrastructure Formatting attributes in payload allow: 0 Text formatting (alignment, font size, style, colour…) 0 Pictures (e. g. 255 x 255 color) or vector-based graphics 0 Animations 0 Sounds n Interoperable with 2 G SMS mobiles 0 2 G SMS spec had room for payload formatting 0 2 G MS ignore special formats
EMS Principles n n n Enhanced Message Service Leverages SMS infrastructure Formatting attributes in payload allow: 0 Text formatting (alignment, font size, style, colour…) 0 Pictures (e. g. 255 x 255 color) or vector-based graphics 0 Animations 0 Sounds n Interoperable with 2 G SMS mobiles 0 2 G SMS spec had room for payload formatting 0 2 G MS ignore special formats
 MMS Principles (1) n Non-real-time, multi-media message service 0 Text; Speech (AMR coding) 0 Audio (MP 3, synthetic MIDI) 0 Image, graphics (JPEG, GIF, PNG) 0 Video (MPEG 4, H. 263) 0 Will evolve with multimedia technologies n Uses IP data path & IP protocols (not SS 7) 0 WAP, HTTP, SMTP, etc. n Adapts to terminal capabilities 0 media format conversions (JPEG to GIF) 0 media type conversions (fax to image) 0 SMS (2 G) terminal inter-working
MMS Principles (1) n Non-real-time, multi-media message service 0 Text; Speech (AMR coding) 0 Audio (MP 3, synthetic MIDI) 0 Image, graphics (JPEG, GIF, PNG) 0 Video (MPEG 4, H. 263) 0 Will evolve with multimedia technologies n Uses IP data path & IP protocols (not SS 7) 0 WAP, HTTP, SMTP, etc. n Adapts to terminal capabilities 0 media format conversions (JPEG to GIF) 0 media type conversions (fax to image) 0 SMS (2 G) terminal inter-working
 MMS Principles (2) n n MMs can be forwarded (w/o downloading), and may have a validity period One or multiple addressees Addressing by phone number (E. 164) or email address (RFC 822) Extended reporting 0 submission, storage, delivery, reading, deletion n n Supports an MMBox, i. e. a mail box Optional support of media streaming (RTP/RTSP)
MMS Principles (2) n n MMs can be forwarded (w/o downloading), and may have a validity period One or multiple addressees Addressing by phone number (E. 164) or email address (RFC 822) Extended reporting 0 submission, storage, delivery, reading, deletion n n Supports an MMBox, i. e. a mail box Optional support of media streaming (RTP/RTSP)
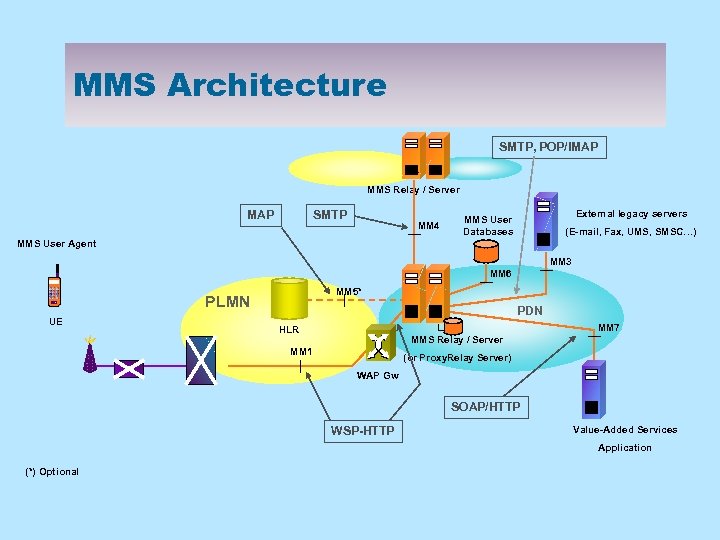 MMS Architecture SMTP, POP/IMAP SN SN MMS Relay / Server MAP SMTP MM 4 External legacy servers MMS User Databases SN MMS User Agent (E-mail, Fax, UMS, SMSC…) MM 3 MM 6 MM 5* PLMN UE PDN SN SN MM 7 HLR MMS Relay / Server MM 1 (or Proxy. Relay Server) WAP Gw SOAP/HTTP WSP-HTTP SN Value-Added Services Application (*) Optional
MMS Architecture SMTP, POP/IMAP SN SN MMS Relay / Server MAP SMTP MM 4 External legacy servers MMS User Databases SN MMS User Agent (E-mail, Fax, UMS, SMSC…) MM 3 MM 6 MM 5* PLMN UE PDN SN SN MM 7 HLR MMS Relay / Server MM 1 (or Proxy. Relay Server) WAP Gw SOAP/HTTP WSP-HTTP SN Value-Added Services Application (*) Optional
 Location n Driven by e 911 requirements in US 0 FCC mandated; not yet functioning as desired 0 most operators are operating under “waivers” n n Potential revenue from location-based services Several technical approaches 0 in network technologies (measurements at cell sites) 0 handset technologies 0 network-assisted handset approaches n Plus additional core network infrastructure 0 location computation and mobile location servers n Significant privacy issues
Location n Driven by e 911 requirements in US 0 FCC mandated; not yet functioning as desired 0 most operators are operating under “waivers” n n Potential revenue from location-based services Several technical approaches 0 in network technologies (measurements at cell sites) 0 handset technologies 0 network-assisted handset approaches n Plus additional core network infrastructure 0 location computation and mobile location servers n Significant privacy issues
 Location Technology n n Cell identity: crude but available today Based on timing 0 TA: Timing Advance (distance from GSM BTS) n Based on timing and triangulation 0 TOA: Time of Arrival 0 TDOA: Time Difference of Arrival 0 EOTD: Enhanced Observed Time Difference 0 AOA: Angle of Arrival n Based on satellite navigation systems 0 GPS: Global Positioning System 0 A-GPS: Assisted GPS
Location Technology n n Cell identity: crude but available today Based on timing 0 TA: Timing Advance (distance from GSM BTS) n Based on timing and triangulation 0 TOA: Time of Arrival 0 TDOA: Time Difference of Arrival 0 EOTD: Enhanced Observed Time Difference 0 AOA: Angle of Arrival n Based on satellite navigation systems 0 GPS: Global Positioning System 0 A-GPS: Assisted GPS
 Location-Based Services n Emergency services 0 E 911 - Enhanced 911 n Value-added personal services 0 friend finder, directions n Commercial services 0 coupons or offers from nearby stores n Network internal 0 Traffic & coverage measurements n Lawful intercept extensions 0 law enforcement locates suspect
Location-Based Services n Emergency services 0 E 911 - Enhanced 911 n Value-added personal services 0 friend finder, directions n Commercial services 0 coupons or offers from nearby stores n Network internal 0 Traffic & coverage measurements n Lawful intercept extensions 0 law enforcement locates suspect
 Location Information n Location (in 3 D), speed and direction 0 with timestamp n n Accuracy of measurement Response time 0 a Qo. S measure n Security & Privacy 0 authorized clients 0 secure info exchange 0 privacy control by user and/or operator
Location Information n Location (in 3 D), speed and direction 0 with timestamp n n Accuracy of measurement Response time 0 a Qo. S measure n Security & Privacy 0 authorized clients 0 secure info exchange 0 privacy control by user and/or operator
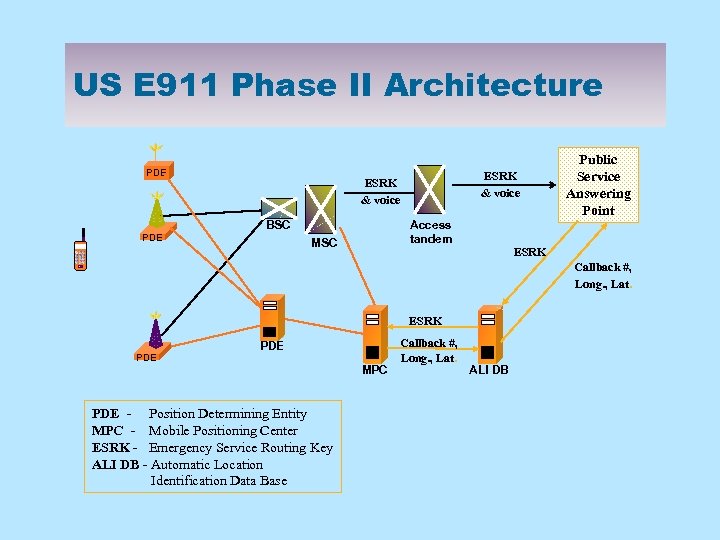 US E 911 Phase II Architecture PDE ESRK & voice Access tandem BSC MSC Public Service Answering Point ESRK Callback #, Long. , Lat. PDE SN PDE - Position Determining Entity MPC - Mobile Positioning Center ESRK - Emergency Service Routing Key ALI DB - Automatic Location Identification Data Base ESRK SN MPC Callback #, Long. , Lat. SN ALI DB
US E 911 Phase II Architecture PDE ESRK & voice Access tandem BSC MSC Public Service Answering Point ESRK Callback #, Long. , Lat. PDE SN PDE - Position Determining Entity MPC - Mobile Positioning Center ESRK - Emergency Service Routing Key ALI DB - Automatic Location Identification Data Base ESRK SN MPC Callback #, Long. , Lat. SN ALI DB
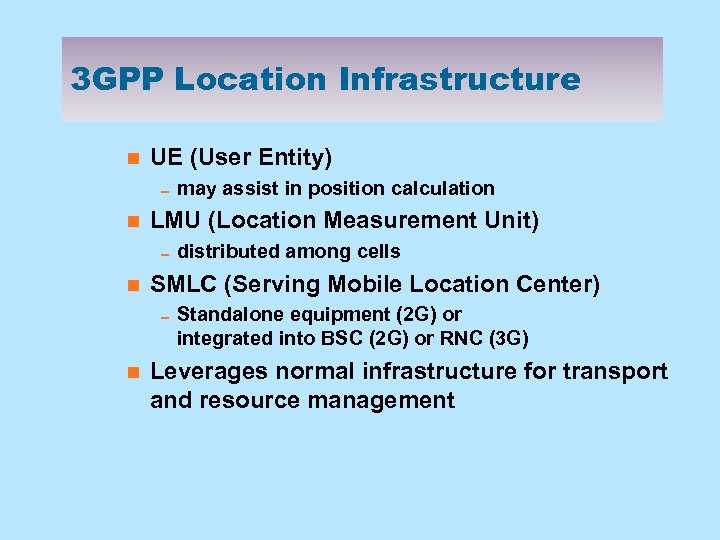 3 GPP Location Infrastructure n UE (User Entity) 0 may assist in position calculation n LMU (Location Measurement Unit) 0 distributed among cells n SMLC (Serving Mobile Location Center) 0 Standalone equipment (2 G) or integrated into BSC (2 G) or RNC (3 G) n Leverages normal infrastructure for transport and resource management
3 GPP Location Infrastructure n UE (User Entity) 0 may assist in position calculation n LMU (Location Measurement Unit) 0 distributed among cells n SMLC (Serving Mobile Location Center) 0 Standalone equipment (2 G) or integrated into BSC (2 G) or RNC (3 G) n Leverages normal infrastructure for transport and resource management
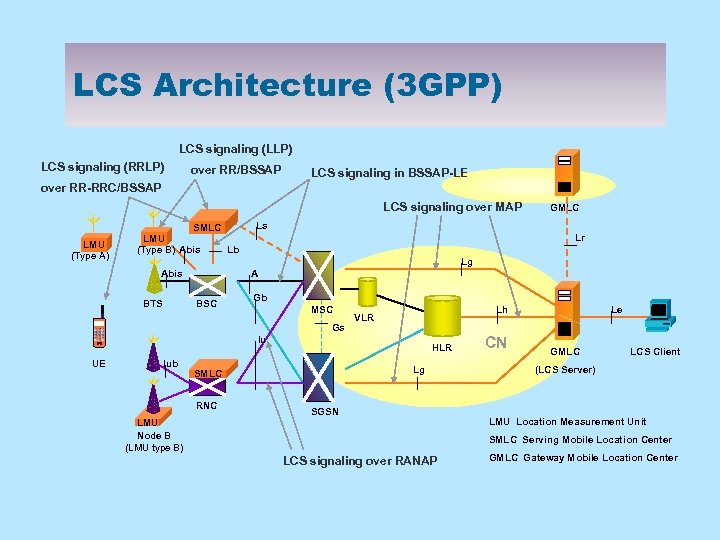 LCS Architecture (3 GPP) LCS signaling (LLP) LCS signaling (RRLP) over RR/BSSAP LCS signaling in BSSAP-LE SN over RR-RRC/BSSAP LCS signaling over MAP LMU (Type A) SMLC LMU (Type B) Abis Lb Ls Lr Lg Abis BTS A BSC Gb MSC Gs Lh VLR Iu UE GMLC Iub HLR Lg SMLC RNC SGSN LMU Node B (LMU type B) CN Le SN GMLC LCS Client (LCS Server) LMU Location Measurement Unit SMLC Serving Mobile Location Center LCS signaling over RANAP GMLC Gateway Mobile Location Center
LCS Architecture (3 GPP) LCS signaling (LLP) LCS signaling (RRLP) over RR/BSSAP LCS signaling in BSSAP-LE SN over RR-RRC/BSSAP LCS signaling over MAP LMU (Type A) SMLC LMU (Type B) Abis Lb Ls Lr Lg Abis BTS A BSC Gb MSC Gs Lh VLR Iu UE GMLC Iub HLR Lg SMLC RNC SGSN LMU Node B (LMU type B) CN Le SN GMLC LCS Client (LCS Server) LMU Location Measurement Unit SMLC Serving Mobile Location Center LCS signaling over RANAP GMLC Gateway Mobile Location Center
 Location Request n MLP – Mobile Location Protocol 0 from Location Interop Forum 0 based on HTTP/SSL/XML 0 allows Internet clients to request location services n n GMLC is the Location Server Interrogates HLR to find visited MSC/SGSN 0 Roaming user can be located 0 UE can be idle, but not off ! n Immediate or deferred result
Location Request n MLP – Mobile Location Protocol 0 from Location Interop Forum 0 based on HTTP/SSL/XML 0 allows Internet clients to request location services n n GMLC is the Location Server Interrogates HLR to find visited MSC/SGSN 0 Roaming user can be located 0 UE can be idle, but not off ! n Immediate or deferred result
 3 G-324 M Video Services n Initial mobile video service uses 3 G data bandwidth w/o IP multimedia infrastructure 0 deployed by Do. Co. Mo in Japan today n Leverage high speed circuit-switch data path 0 64 Kbps H. 324 video structure 0 MPEG 4 video coding 0 AMR audio coding n Supports video clips, video streaming and live video conversations 0 MS to MS 0 MS to Internet or ISDN with gateways
3 G-324 M Video Services n Initial mobile video service uses 3 G data bandwidth w/o IP multimedia infrastructure 0 deployed by Do. Co. Mo in Japan today n Leverage high speed circuit-switch data path 0 64 Kbps H. 324 video structure 0 MPEG 4 video coding 0 AMR audio coding n Supports video clips, video streaming and live video conversations 0 MS to MS 0 MS to Internet or ISDN with gateways
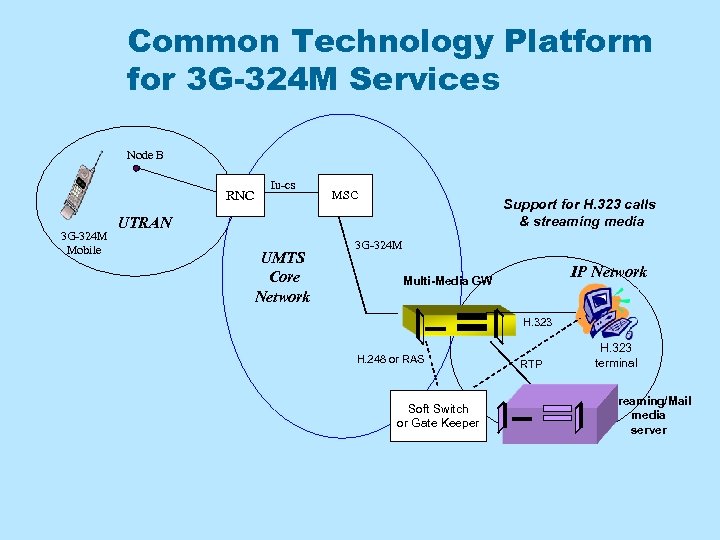 Common Technology Platform for 3 G-324 M Services Node B RNC 3 G-324 M Mobile Iu-cs MSC Support for H. 323 calls & streaming media UTRAN UMTS Core Network 3 G-324 M IP Network Multi-Media GW H. 323 H. 248 or RAS Soft Switch or Gate Keeper RTP H. 323 terminal Streaming/Mail media server
Common Technology Platform for 3 G-324 M Services Node B RNC 3 G-324 M Mobile Iu-cs MSC Support for H. 323 calls & streaming media UTRAN UMTS Core Network 3 G-324 M IP Network Multi-Media GW H. 323 H. 248 or RAS Soft Switch or Gate Keeper RTP H. 323 terminal Streaming/Mail media server
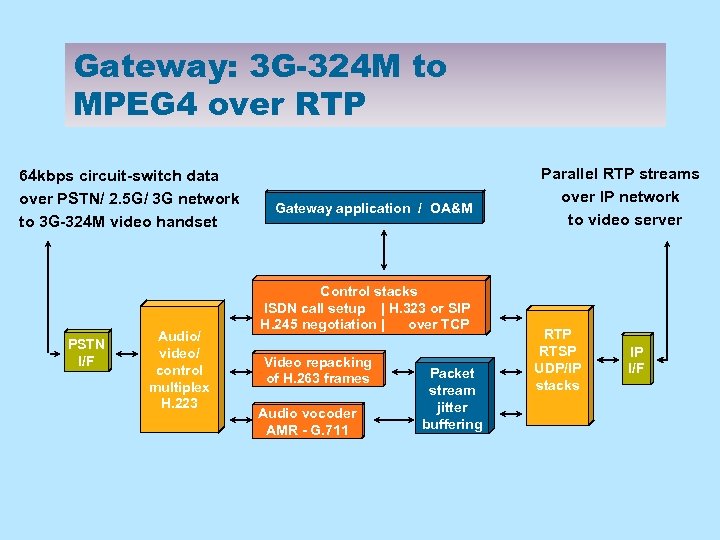 Gateway: 3 G-324 M to MPEG 4 over RTP 64 kbps circuit-switch data over PSTN/ 2. 5 G/ 3 G network to 3 G-324 M video handset PSTN I/F Audio/ video/ control multiplex H. 223 Gateway application / OA&M Control stacks ISDN call setup | H. 323 or SIP H. 245 negotiation | over TCP Video repacking of H. 263 frames Audio vocoder AMR - G. 711 Packet stream jitter buffering Parallel RTP streams over IP network to video server RTP RTSP UDP/IP stacks IP I/F
Gateway: 3 G-324 M to MPEG 4 over RTP 64 kbps circuit-switch data over PSTN/ 2. 5 G/ 3 G network to 3 G-324 M video handset PSTN I/F Audio/ video/ control multiplex H. 223 Gateway application / OA&M Control stacks ISDN call setup | H. 323 or SIP H. 245 negotiation | over TCP Video repacking of H. 263 frames Audio vocoder AMR - G. 711 Packet stream jitter buffering Parallel RTP streams over IP network to video server RTP RTSP UDP/IP stacks IP I/F
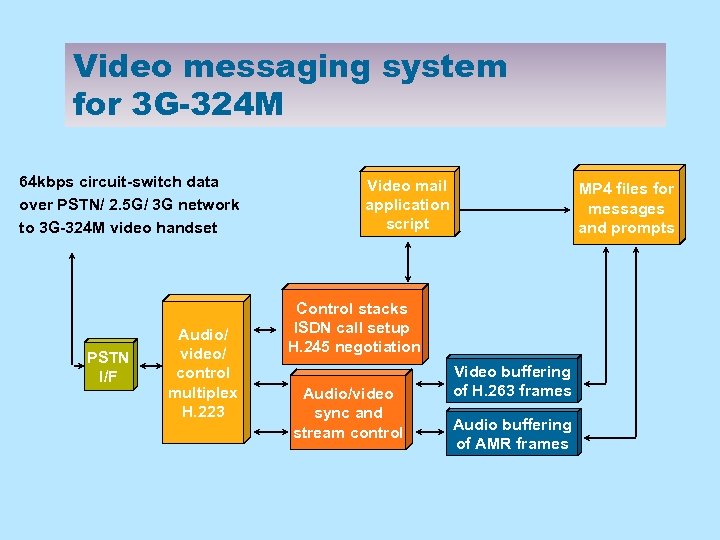 Video messaging system for 3 G-324 M 64 kbps circuit-switch data over PSTN/ 2. 5 G/ 3 G network to 3 G-324 M video handset PSTN I/F Audio/ video/ control multiplex H. 223 Video mail application script MP 4 files for messages and prompts Control stacks ISDN call setup H. 245 negotiation Audio/video sync and stream control Video buffering of H. 263 frames Audio buffering of AMR frames
Video messaging system for 3 G-324 M 64 kbps circuit-switch data over PSTN/ 2. 5 G/ 3 G network to 3 G-324 M video handset PSTN I/F Audio/ video/ control multiplex H. 223 Video mail application script MP 4 files for messages and prompts Control stacks ISDN call setup H. 245 negotiation Audio/video sync and stream control Video buffering of H. 263 frames Audio buffering of AMR frames
 Push-to. Talk Vo. IP before Qo. S is Available n Nextel’s “Direct Connect” service credited with getting them 20 -25% extra ARPU 0 Based on totally proprietary i. DEN 0 Other carriers extremely jealous n Push-to-talk is half duplex 0 Short delays OK n Issues remain 0 Always on IP isn’t always on; radio connection suspended if unused; 2 -3 seconds to re-establish n Sprint has announced they will be offering a push-to-talk service on their 1 x. RTT network
Push-to. Talk Vo. IP before Qo. S is Available n Nextel’s “Direct Connect” service credited with getting them 20 -25% extra ARPU 0 Based on totally proprietary i. DEN 0 Other carriers extremely jealous n Push-to-talk is half duplex 0 Short delays OK n Issues remain 0 Always on IP isn’t always on; radio connection suspended if unused; 2 -3 seconds to re-establish n Sprint has announced they will be offering a push-to-talk service on their 1 x. RTT network
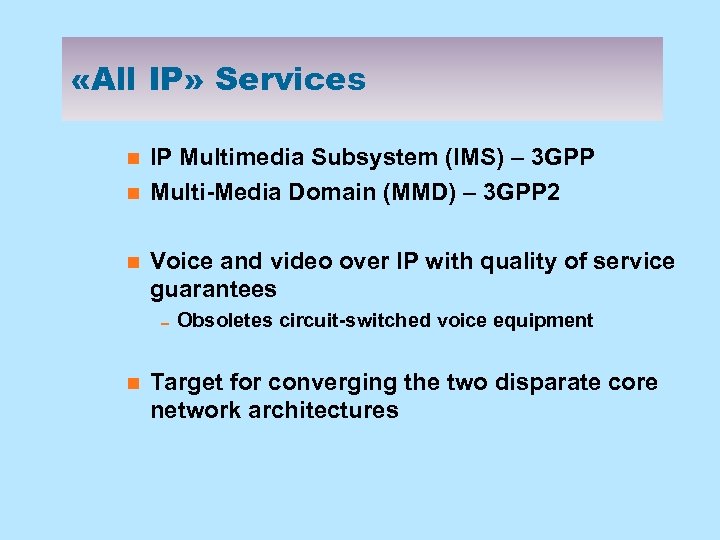 «All IP» Services n n n IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS) – 3 GPP Multi-Media Domain (MMD) – 3 GPP 2 Voice and video over IP with quality of service guarantees 0 Obsoletes circuit-switched voice equipment n Target for converging the two disparate core network architectures
«All IP» Services n n n IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS) – 3 GPP Multi-Media Domain (MMD) – 3 GPP 2 Voice and video over IP with quality of service guarantees 0 Obsoletes circuit-switched voice equipment n Target for converging the two disparate core network architectures
 IMS / MMD Services n n n Presence Location Instant Messaging (voice+video) Conferencing Media Streaming / Annoucements Multi-player gaming with voice channel
IMS / MMD Services n n n Presence Location Instant Messaging (voice+video) Conferencing Media Streaming / Annoucements Multi-player gaming with voice channel
 3 G Qo. S n n Substantial new requirements on the radio access network Traffic classes 0 conversational, streaming, interactive, background n Ability to specify 0 traffic handling priority 0 allocation/retention priority 0 error rates (bits and/ or SDUs) 0 transfer delay 0 data rates (maximum and guaranteed) 0 deliver in order (Y/N)
3 G Qo. S n n Substantial new requirements on the radio access network Traffic classes 0 conversational, streaming, interactive, background n Ability to specify 0 traffic handling priority 0 allocation/retention priority 0 error rates (bits and/ or SDUs) 0 transfer delay 0 data rates (maximum and guaranteed) 0 deliver in order (Y/N)
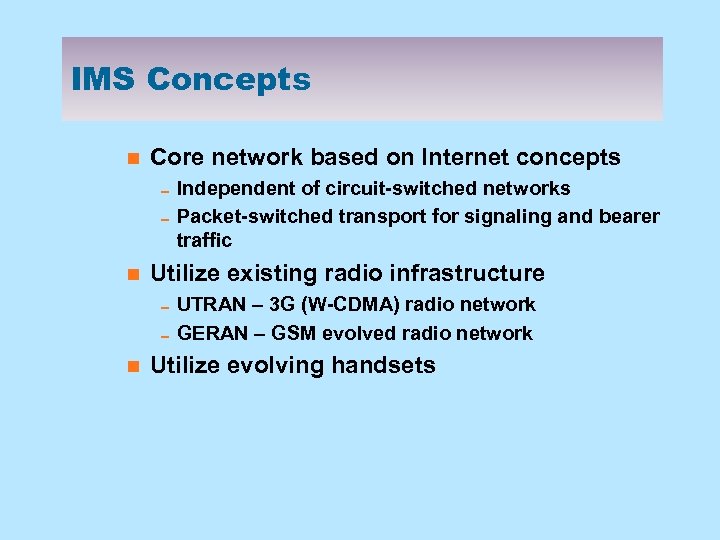 IMS Concepts n Core network based on Internet concepts 0 Independent of circuit-switched networks 0 Packet-switched transport for signaling and bearer traffic n Utilize existing radio infrastructure 0 UTRAN – 3 G (W-CDMA) radio network 0 GERAN – GSM evolved radio network n Utilize evolving handsets
IMS Concepts n Core network based on Internet concepts 0 Independent of circuit-switched networks 0 Packet-switched transport for signaling and bearer traffic n Utilize existing radio infrastructure 0 UTRAN – 3 G (W-CDMA) radio network 0 GERAN – GSM evolved radio network n Utilize evolving handsets
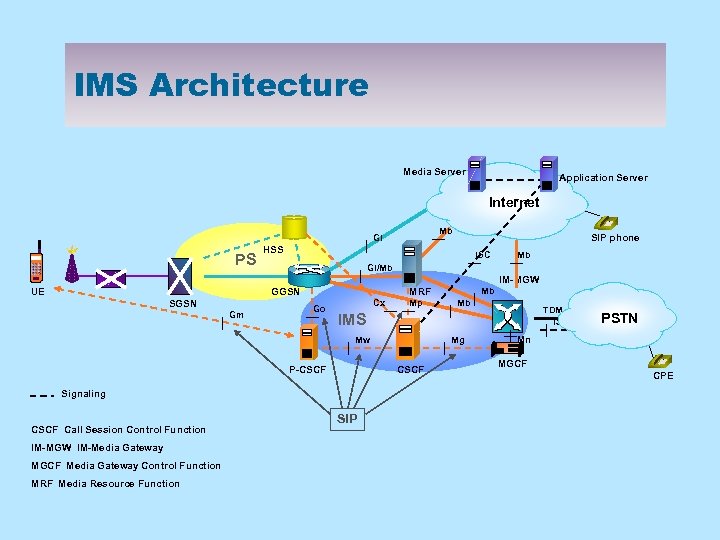 IMS Architecture Media Server Application Server Internet Mb Gi PS SIP phone HSS ISC Mb Gi/Mb IM-MGW UE GGSN SGSN Gm Go Cx Mp P-CSCF MGCF Media Gateway Control Function MRF Media Resource Function Mg CSCF Signaling IM-MGW IM-Media Gateway Mb TDM ISUP IMS Mw CSCF Call Session Control Function Mb MRF SIP PSTN Mn MGCF CPE
IMS Architecture Media Server Application Server Internet Mb Gi PS SIP phone HSS ISC Mb Gi/Mb IM-MGW UE GGSN SGSN Gm Go Cx Mp P-CSCF MGCF Media Gateway Control Function MRF Media Resource Function Mg CSCF Signaling IM-MGW IM-Media Gateway Mb TDM ISUP IMS Mw CSCF Call Session Control Function Mb MRF SIP PSTN Mn MGCF CPE
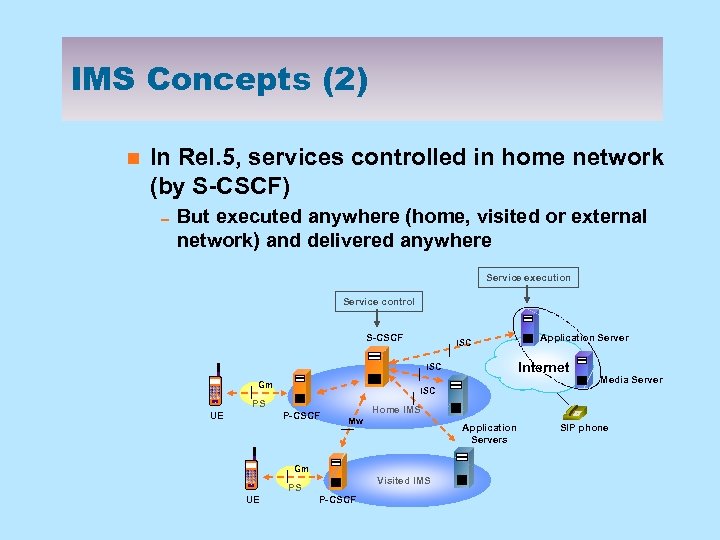 IMS Concepts (2) n In Rel. 5, services controlled in home network (by S-CSCF) 0 But executed anywhere (home, visited or external network) and delivered anywhere Service execution Service control S-CSCF ISC Internet ISC Gm P-CSCF Home IMS Mw Application Servers Gm Visited IMS PS UE Media Server ISC PS UE Application Server P-CSCF SIP phone
IMS Concepts (2) n In Rel. 5, services controlled in home network (by S-CSCF) 0 But executed anywhere (home, visited or external network) and delivered anywhere Service execution Service control S-CSCF ISC Internet ISC Gm P-CSCF Home IMS Mw Application Servers Gm Visited IMS PS UE Media Server ISC PS UE Application Server P-CSCF SIP phone
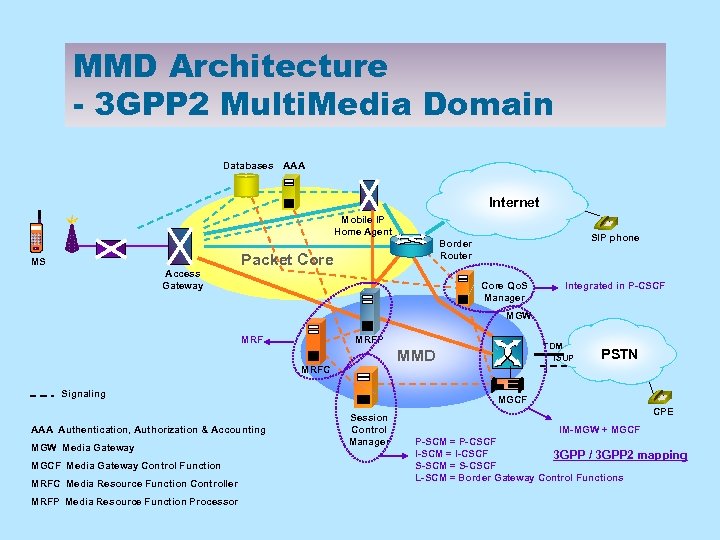 MMD Architecture - 3 GPP 2 Multi. Media Domain Databases AAA Internet Mobile IP Home Agent MS Access Gateway SIP phone Border Router Packet Core Qo. S Manager Integrated in P-CSCF MGW MRFP MRFC Signaling AAA Authentication, Authorization & Accounting MGW Media Gateway MGCF Media Gateway Control Function MRFC Media Resource Function Controller MRFP Media Resource Function Processor TDM ISUP MMD PSTN MGCF Session Control Manager CPE IM-MGW + MGCF P-SCM = P-CSCF I-SCM = I-CSCF 3 GPP / 3 GPP 2 mapping S-SCM = S-CSCF L-SCM = Border Gateway Control Functions
MMD Architecture - 3 GPP 2 Multi. Media Domain Databases AAA Internet Mobile IP Home Agent MS Access Gateway SIP phone Border Router Packet Core Qo. S Manager Integrated in P-CSCF MGW MRFP MRFC Signaling AAA Authentication, Authorization & Accounting MGW Media Gateway MGCF Media Gateway Control Function MRFC Media Resource Function Controller MRFP Media Resource Function Processor TDM ISUP MMD PSTN MGCF Session Control Manager CPE IM-MGW + MGCF P-SCM = P-CSCF I-SCM = I-CSCF 3 GPP / 3 GPP 2 mapping S-SCM = S-CSCF L-SCM = Border Gateway Control Functions
 3 G Wireless Networks • History and Evolution of Mobile Radio • Evolving Network Architectures • Evolving Services • Applications
3 G Wireless Networks • History and Evolution of Mobile Radio • Evolving Network Architectures • Evolving Services • Applications
 Multimodal Services and Multi-Application Platforms n Combined voice and data applications 0 Today, without “all IP” infrastructure 0 Text messaging plus speech recognition-enabled voice services 0 Evolve from as new services become available n Multi-application platform 0 Integrate TDM voice and IP data 0 Support multiple applications 0 Flexible billing and provisioning
Multimodal Services and Multi-Application Platforms n Combined voice and data applications 0 Today, without “all IP” infrastructure 0 Text messaging plus speech recognition-enabled voice services 0 Evolve from as new services become available n Multi-application platform 0 Integrate TDM voice and IP data 0 Support multiple applications 0 Flexible billing and provisioning
 Sample Multimodal Applications n Travel information 0 Make request via voice 0 Receive response in text n Directions 0 Make request via voice 0 Receive initial response in text 0 Get updates while traveling via voice or SMS or rich graphics n One-to-many messaging 0 Record message via voice or text 0 Deliver message via voice, SMS, WAP, or email
Sample Multimodal Applications n Travel information 0 Make request via voice 0 Receive response in text n Directions 0 Make request via voice 0 Receive initial response in text 0 Get updates while traveling via voice or SMS or rich graphics n One-to-many messaging 0 Record message via voice or text 0 Deliver message via voice, SMS, WAP, or email
 More Multimodal Examples n Purchasing famous person’s voice for your personal answering message 0 Text or voice menus 0 Voice to hear message 0 Voice or text to select (and authorize payment) n Unified communications 0 While listening to a voice message from a customer, obtain a text display of recent customer activity n Emergency response team 0 SMS and voice alert 0 Voice conference, and text updates, while traveling to site of emergency
More Multimodal Examples n Purchasing famous person’s voice for your personal answering message 0 Text or voice menus 0 Voice to hear message 0 Voice or text to select (and authorize payment) n Unified communications 0 While listening to a voice message from a customer, obtain a text display of recent customer activity n Emergency response team 0 SMS and voice alert 0 Voice conference, and text updates, while traveling to site of emergency
 Early Deployments n Cricket matches (Hutchinson India) 0 SMS alert at start of coverage 0 Live voice coverage or text updates n Information delivery (SFR France) 0 SMS broadcast with phone # & URL 0 Choice of text display or voice (text-to-speech) n Yellow pages (Platinet Israel) 0 Adding voice menus to existing text-based service 0 Voice flattens menus, eases access
Early Deployments n Cricket matches (Hutchinson India) 0 SMS alert at start of coverage 0 Live voice coverage or text updates n Information delivery (SFR France) 0 SMS broadcast with phone # & URL 0 Choice of text display or voice (text-to-speech) n Yellow pages (Platinet Israel) 0 Adding voice menus to existing text-based service 0 Voice flattens menus, eases access
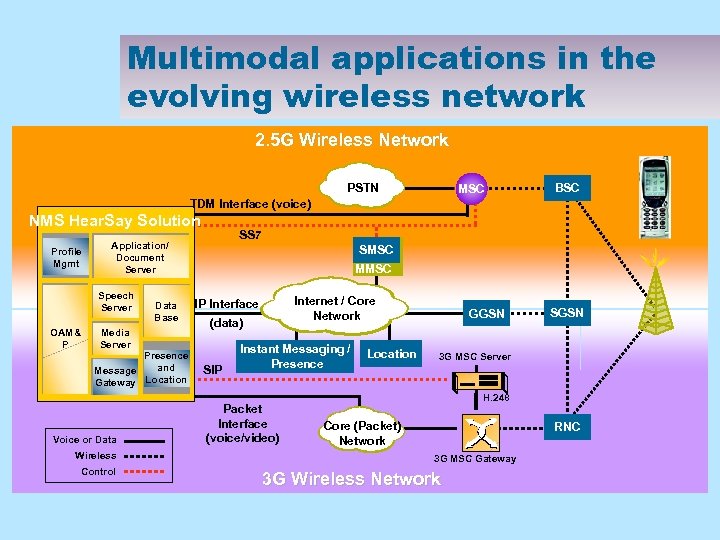 Multimodal applications in the evolving wireless network 2. 5 G Wireless Network PSTN MSC BSC TDM Interface (voice) NMS Hear. Say Solution Profile Mgmt Speech Server OAM& P SS 7 Application/ Document Server Data Base Media Server Presence and Message Location Gateway Voice or Data Wireless Control SMSC MMSC Internet / Core Network IP Interface (data) SIP Instant Messaging / Presence Packet Interface (voice/video) Location GGSN SGSN 3 G MSC Server H. 248 Core (Packet) Network RNC 3 G MSC Gateway 3 G Wireless Network
Multimodal applications in the evolving wireless network 2. 5 G Wireless Network PSTN MSC BSC TDM Interface (voice) NMS Hear. Say Solution Profile Mgmt Speech Server OAM& P SS 7 Application/ Document Server Data Base Media Server Presence and Message Location Gateway Voice or Data Wireless Control SMSC MMSC Internet / Core Network IP Interface (data) SIP Instant Messaging / Presence Packet Interface (voice/video) Location GGSN SGSN 3 G MSC Server H. 248 Core (Packet) Network RNC 3 G MSC Gateway 3 G Wireless Network
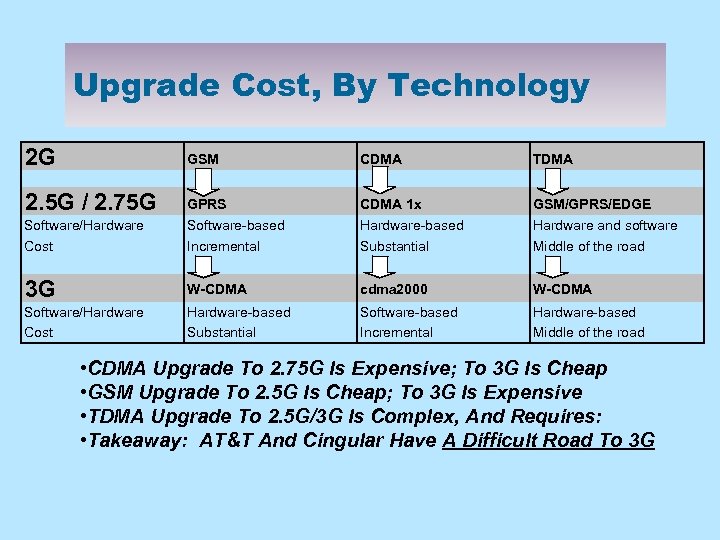 Upgrade Cost, By Technology 2 G GSM CDMA TDMA Software/Hardware GPRS Software-based CDMA 1 x Hardware-based GSM/GPRS/EDGE Hardware and software Cost Incremental Substantial Middle of the road 3 G W-CDMA cdma 2000 W-CDMA Software/Hardware Cost Hardware-based Substantial Software-based Incremental Hardware-based Middle of the road 2. 5 G / 2. 75 G • CDMA Upgrade To 2. 75 G Is Expensive; To 3 G Is Cheap • GSM Upgrade To 2. 5 G Is Cheap; To 3 G Is Expensive • TDMA Upgrade To 2. 5 G/3 G Is Complex, And Requires: • Takeaway: AT&T And Cingular Have A Difficult Road To 3 G
Upgrade Cost, By Technology 2 G GSM CDMA TDMA Software/Hardware GPRS Software-based CDMA 1 x Hardware-based GSM/GPRS/EDGE Hardware and software Cost Incremental Substantial Middle of the road 3 G W-CDMA cdma 2000 W-CDMA Software/Hardware Cost Hardware-based Substantial Software-based Incremental Hardware-based Middle of the road 2. 5 G / 2. 75 G • CDMA Upgrade To 2. 75 G Is Expensive; To 3 G Is Cheap • GSM Upgrade To 2. 5 G Is Cheap; To 3 G Is Expensive • TDMA Upgrade To 2. 5 G/3 G Is Complex, And Requires: • Takeaway: AT&T And Cingular Have A Difficult Road To 3 G
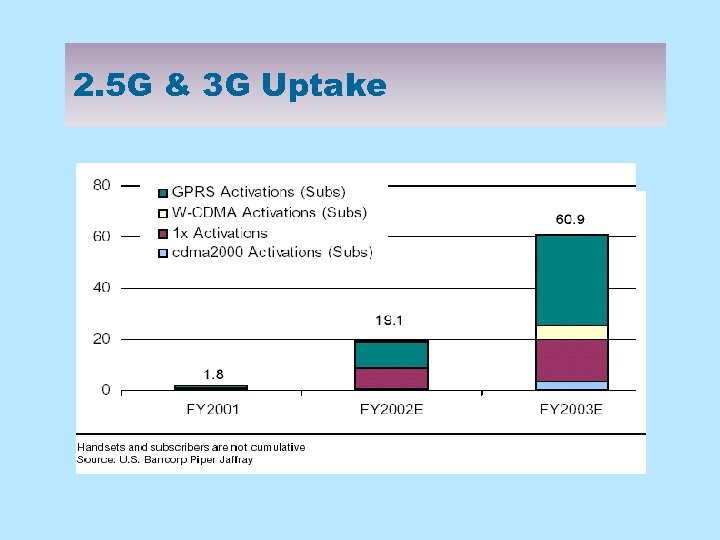 2. 5 G & 3 G Uptake
2. 5 G & 3 G Uptake
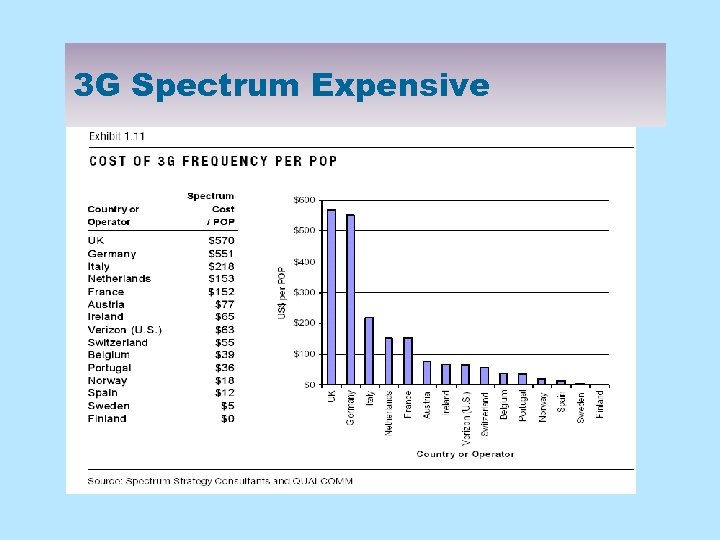 3 G Spectrum Expensive
3 G Spectrum Expensive
 Biggest Threat to Today’s 3 G: Wireless LANs ? n Faster than 3 G 0 11 or 56 Mbps vs. <2 Mbps for 3 G when stationary n Data experience matches the Internet 0 with the added convenience of mobile 0 same user interface (doesn’t rely on small screens) 0 same programs, files, applications, Websites. n Low cost, low barriers to entry. n Organizations can build own networks 0 Like the Internet, will grow virally.
Biggest Threat to Today’s 3 G: Wireless LANs ? n Faster than 3 G 0 11 or 56 Mbps vs. <2 Mbps for 3 G when stationary n Data experience matches the Internet 0 with the added convenience of mobile 0 same user interface (doesn’t rely on small screens) 0 same programs, files, applications, Websites. n Low cost, low barriers to entry. n Organizations can build own networks 0 Like the Internet, will grow virally.
 Additional Reference Material
Additional Reference Material
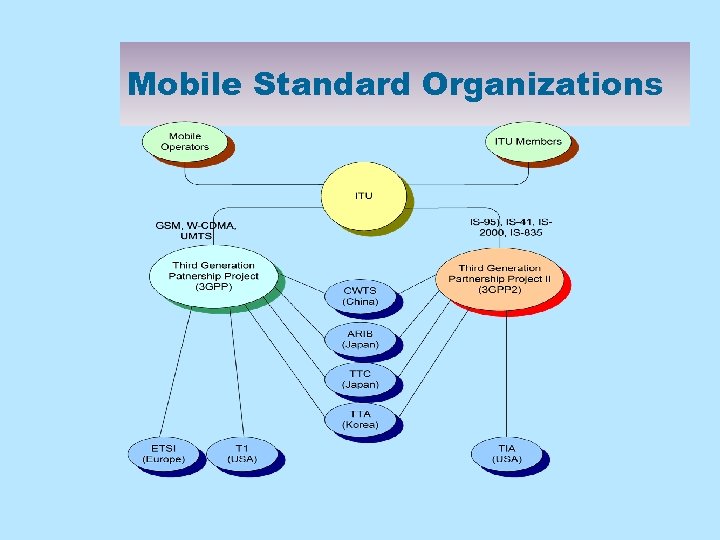 Mobile Standard Organizations
Mobile Standard Organizations
 Partnership Project and Forums ITU IMT-2000 https: //www. itu. int/osg/spu/imt-2000/technology. html n n Mobile Partnership Projects 0 3 GPP : http: //www. 3 gpp. org 0 3 GPP 2 : http: //www. 3 gpp 2. org n Mobile Technical Forums 0 3 G All IP Forum: http: //www. 3 gip. org 0 IPv 6 Forum: http: //www. ipv 6 forum. com n Mobile Marketing Forums 0 Global Mobile Supplier: http: //www. gsacom. com
Partnership Project and Forums ITU IMT-2000 https: //www. itu. int/osg/spu/imt-2000/technology. html n n Mobile Partnership Projects 0 3 GPP : http: //www. 3 gpp. org 0 3 GPP 2 : http: //www. 3 gpp 2. org n Mobile Technical Forums 0 3 G All IP Forum: http: //www. 3 gip. org 0 IPv 6 Forum: http: //www. ipv 6 forum. com n Mobile Marketing Forums 0 Global Mobile Supplier: http: //www. gsacom. com
 Mobile Standards Organizations n European Technical Standard Institute (Europe): 0 n Telecommunication Industry Association (USA): 0 n http: //www. arib. or. jp/english/index. html The Telecommunication Technology Committee (Japan): 0 n http: //www. ccsa. org. cn/english/ The Association of Radio Industries and Businesses (Japan): 0 n http: //www. tiaonline. org China Communications Standards Association: 0 n http: //www. etsi. org http: //www. ttc. or. jp/e/index. html The Telecommunication Technology Association (Korea): 0 http: //www. tta. or. kr/English/index. jsp
Mobile Standards Organizations n European Technical Standard Institute (Europe): 0 n Telecommunication Industry Association (USA): 0 n http: //www. arib. or. jp/english/index. html The Telecommunication Technology Committee (Japan): 0 n http: //www. ccsa. org. cn/english/ The Association of Radio Industries and Businesses (Japan): 0 n http: //www. tiaonline. org China Communications Standards Association: 0 n http: //www. etsi. org http: //www. ttc. or. jp/e/index. html The Telecommunication Technology Association (Korea): 0 http: //www. tta. or. kr/English/index. jsp
 Location-Related Organizations n OMA, Open Mobile Alliance 0 http: //www. openmobilealliance. org/ 0 Consolidates Open Mobile Architecture, WAP Forum, LIF, Sync. ML, MMS Interoperability Group, Wireless Village n Open GIS Consortium 0 http: //www. opengis. org/ 0 Focus on standards for spatial and location information
Location-Related Organizations n OMA, Open Mobile Alliance 0 http: //www. openmobilealliance. org/ 0 Consolidates Open Mobile Architecture, WAP Forum, LIF, Sync. ML, MMS Interoperability Group, Wireless Village n Open GIS Consortium 0 http: //www. opengis. org/ 0 Focus on standards for spatial and location information


