e4ed7c79df817e6c89e494f2071944ad.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 19

EECE 887 Distribution System Engineering CHAPTER 1 Power Delivery Systems
SUBSYSTEMS F Generation F Transmission F Subtransmission F Distribution

Billions of Dollars F Generation -- 40% F Transmission -- 20% F Distribution -- 20%

MISSION F Reach every customer F Meet demands of customers F Supply reliable power F Provide fluctuation free voltage F Provide power with low harmonics F Keep cost low
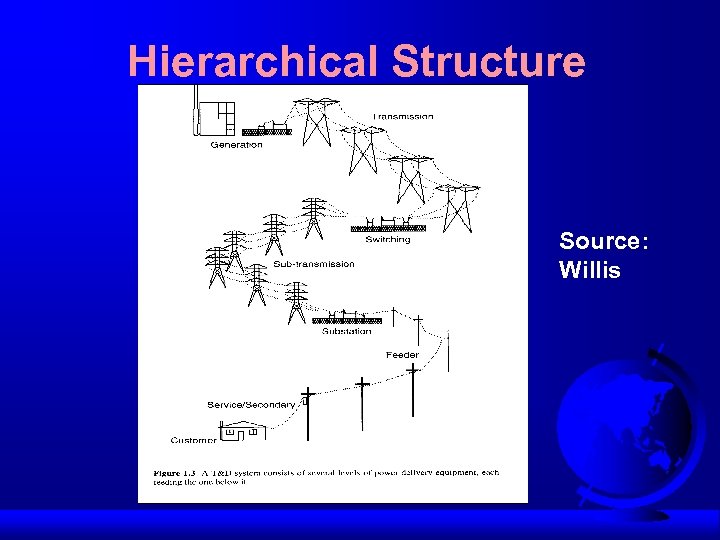
Hierarchical Structure Source: Willis
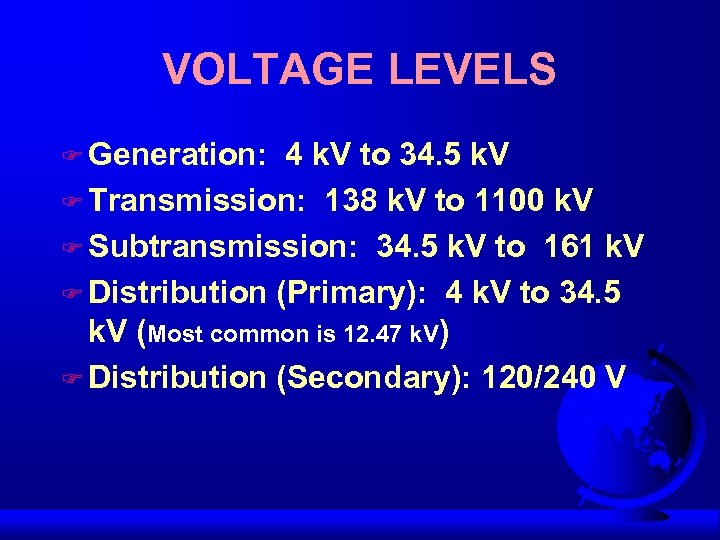
VOLTAGE LEVELS F Generation: 4 k. V to 34. 5 k. V F Transmission: 138 k. V to 1100 k. V F Subtransmission: 34. 5 k. V to 161 k. V F Distribution (Primary): 4 k. V to 34. 5 k. V (Most common is 12. 47 k. V) F Distribution (Secondary): 120/240 V

OBSERVATIONS F Transformers separate the levels F Equipment size and capacity decrease as we move down into the system. However, number of equipment increases. F Net capacity increases F Reliability drops as we move closer to customers

Distribution Service Transformer
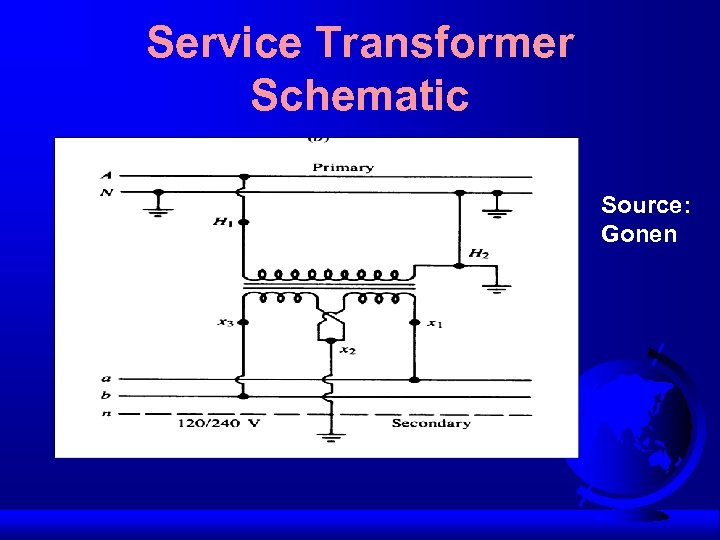
Service Transformer Schematic Source: Gonen
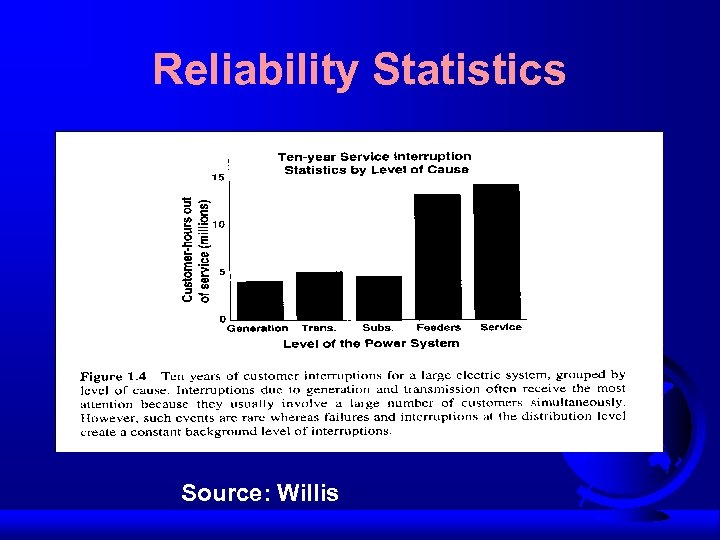
Reliability Statistics Source: Willis

Further Observations F Transmission Systems: – Very high capacity – Networked for high reliability – Designed to provide system stability F Subtransmission Systems: – Medium capacity – Networked for high reliability – Designed for stability as well as power delivery needs

Further Observations F Distribution Substations: – Link between transmission and distribution – 1 to 6 transformers of 5 MVA to 150 MVA (generally more than 1 for contingency) – The substation also has high and low voltage buses, circuit breakers, metering and protective equipment, and a control house.

Further Observations F Feeders: – Overhead lines mounted on wooden poles or underground cables (3 to 10 times more expensive than overhead) – Underground cables used for aesthetics and in dense urban areas. – 2 to 12 feeders per substation – 2 MVA to 30 MVA per feeder – Radial arrangement
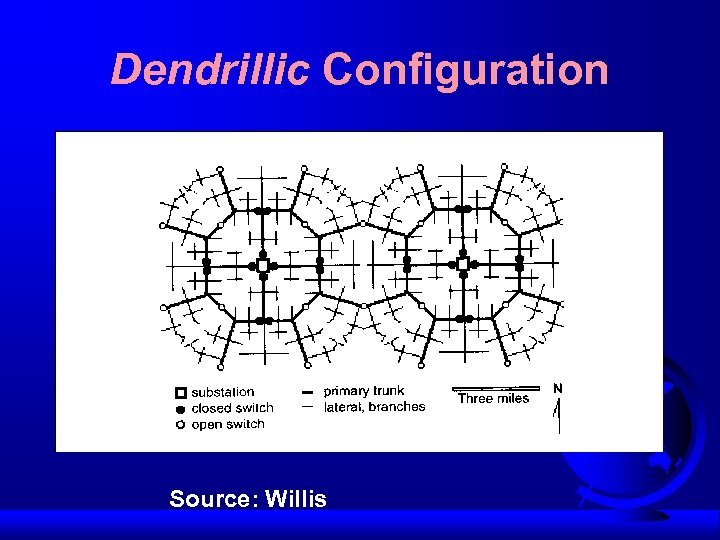
Dendrillic Configuration Source: Willis
Components of Distribution System (Primary side) F Primary trunk F Main branches – Trunk and main branches are usually three-phase F Switches – Normally Closed (NC) – Normally Open (NO) – NO switches are closed during emergencies

F Underground feeder get-away to prevent congestion of wires F Laterals – Branches off of main feeders – one or two phase – Different phases are tapped alternately to maintain balance – 10 k. VA to 2 MVA – Overhead or underground (buried directly)

Secondary System F Close to customers at utilization voltage F Radial F Feeds 1 to 12 customers (4 to 6 is more common)
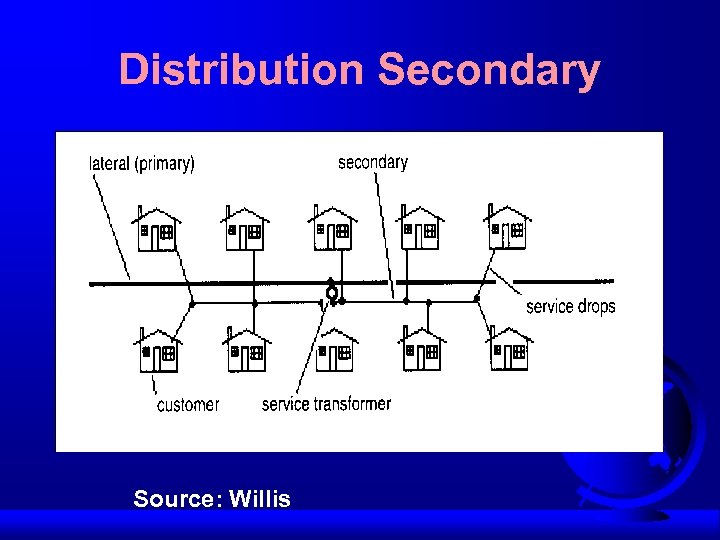
Distribution Secondary Source: Willis
What is Distribution System? – It consists of feeders, service transformers, and secondary system. – In some cases distribution substation is also included. – Other equipment: u Voltage regulators and tap changers to maintain voltage levels u Capacitors to compensate inductive loads
e4ed7c79df817e6c89e494f2071944ad.ppt