e7ab6bb7da11be22a3a95cf6ce70844e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 8

EE 314 Microprocessor Systems Chapter 1 Microprocessor-based systems Based on "An Introduction to the Intel Family of Microprocessors" by James L. Antonakos
1. 1 Introduction Examples of devices using microprocessors ( P) • Pocket calculators • Digital watches • Automatic tellers • Smart telephones • Compact disk players • Home security devices • Realistic video games • Toys • VCRs • Personal computers
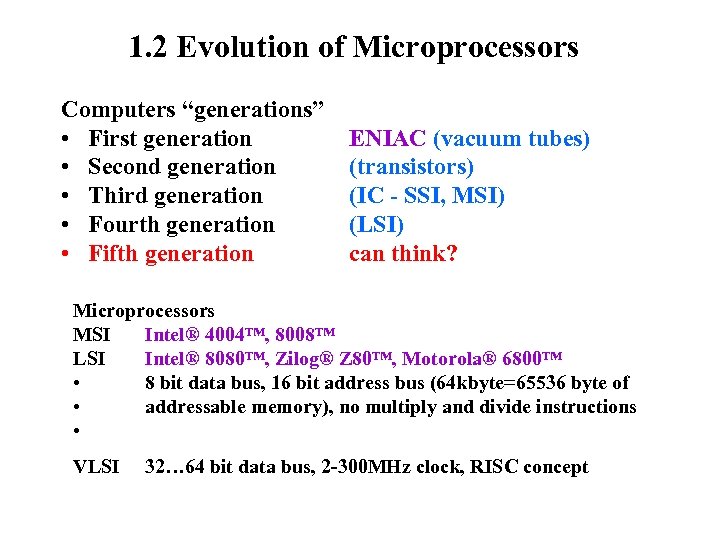
1. 2 Evolution of Microprocessors Computers “generations” • First generation • Second generation • Third generation • Fourth generation • Fifth generation ENIAC (vacuum tubes) (transistors) (IC - SSI, MSI) (LSI) can think? Microprocessors MSI Intel® 4004™, 8008™ LSI Intel® 8080™, Zilog® Z 80™, Motorola® 6800™ • 8 bit data bus, 16 bit address bus (64 kbyte=65536 byte of • addressable memory), no multiply and divide instructions • VLSI 32… 64 bit data bus, 2 -300 MHz clock, RISC concept
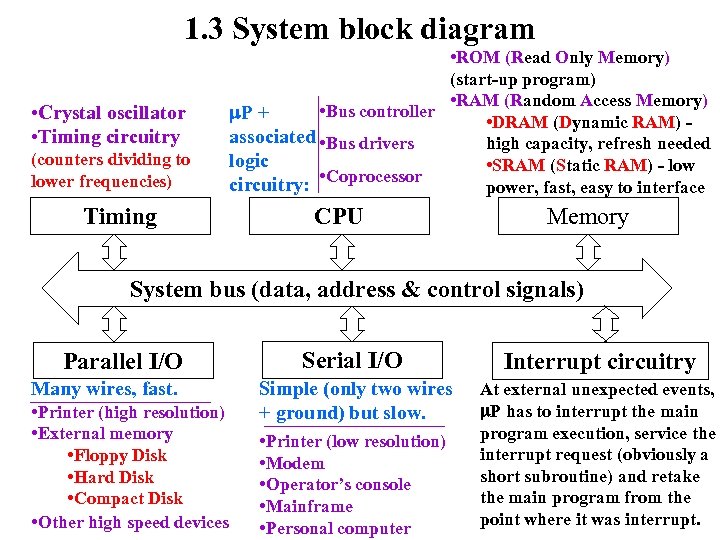
1. 3 System block diagram • Crystal oscillator • Timing circuitry (counters dividing to lower frequencies) Timing • ROM (Read Only Memory) (start-up program) • RAM (Random Access Memory) • Bus controller P + • DRAM (Dynamic RAM) associated • Bus drivers high capacity, refresh needed logic • SRAM (Static RAM) - low • Coprocessor circuitry: power, fast, easy to interface CPU Memory System bus (data, address & control signals) Parallel I/O Many wires, fast. • Printer (high resolution) • External memory • Floppy Disk • Hard Disk • Compact Disk • Other high speed devices Serial I/O Interrupt circuitry Simple (only two wires + ground) but slow. At external unexpected events, P has to interrupt the main program execution, service the interrupt request (obviously a short subroutine) and retake the main program from the point where it was interrupt. • Printer (low resolution) • Modem • Operator’s console • Mainframe • Personal computer
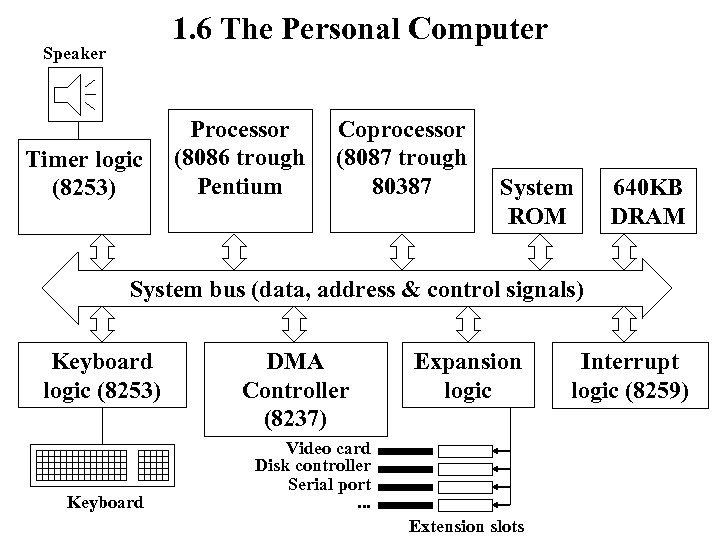
1. 6 The Personal Computer Speaker Timer logic (8253) Processor (8086 trough Pentium Coprocessor (8087 trough 80387 System ROM 640 KB DRAM System bus (data, address & control signals) Keyboard logic (8253) Keyboard DMA Controller (8237) Expansion logic Video card Disk controller Serial port. . . Extension slots Interrupt logic (8259)
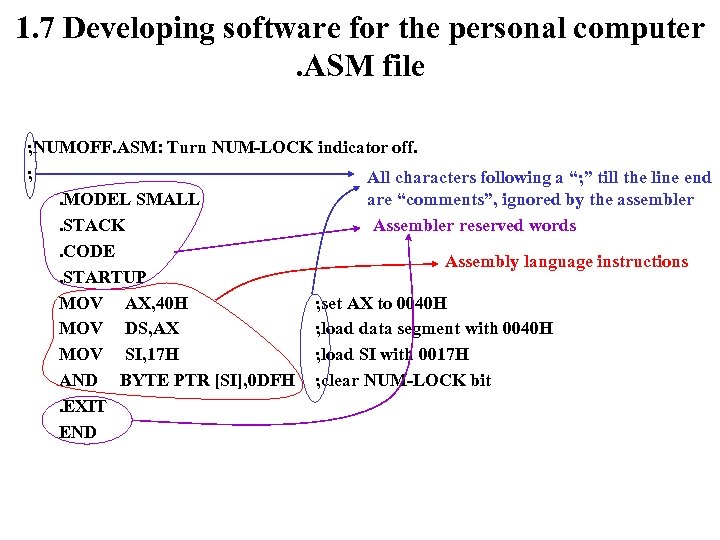
1. 7 Developing software for the personal computer. ASM file ; NUMOFF. ASM: Turn NUM-LOCK indicator off. ; All characters following a “; ” till the line end are “comments”, ignored by the assembler. MODEL SMALL. STACK Assembler reserved words. CODE Assembly language instructions. STARTUP MOV AX, 40 H ; set AX to 0040 H MOV DS, AX ; load data segment with 0040 H MOV SI, 17 H ; load SI with 0017 H AND BYTE PTR [SI], 0 DFH ; clear NUM-LOCK bit. EXIT END
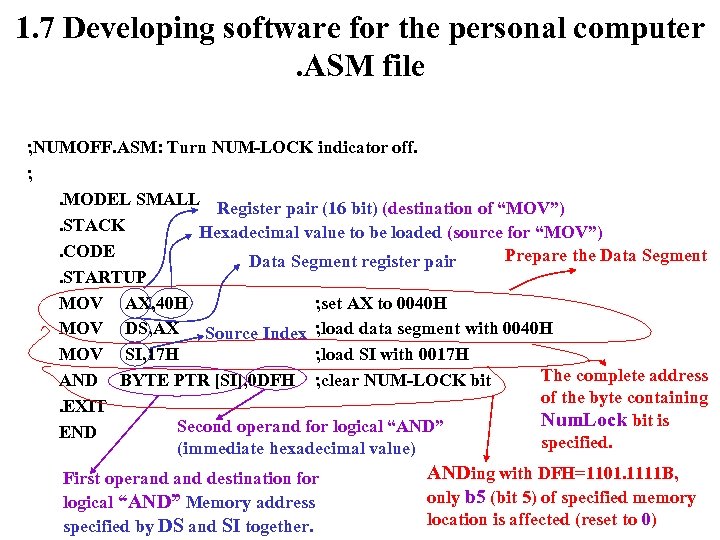
1. 7 Developing software for the personal computer. ASM file ; NUMOFF. ASM: Turn NUM-LOCK indicator off. ; . MODEL SMALL Register pair (16 bit) (destination of “MOV”). STACK Hexadecimal value to be loaded (source for “MOV”). CODE Prepare the Data Segment register pair. STARTUP MOV AX, 40 H ; set AX to 0040 H MOV DS, AX Source Index ; load data segment with 0040 H MOV SI, 17 H ; load SI with 0017 H The complete address AND BYTE PTR [SI], 0 DFH ; clear NUM-LOCK bit of the byte containing. EXIT Num. Lock bit is Second operand for logical “AND” END specified. (immediate hexadecimal value) ANDing with DFH=1101. 1111 B, First operand destination for only b 5 (bit 5) of specified memory logical “AND” Memory address location is affected (reset to 0) specified by DS and SI together.
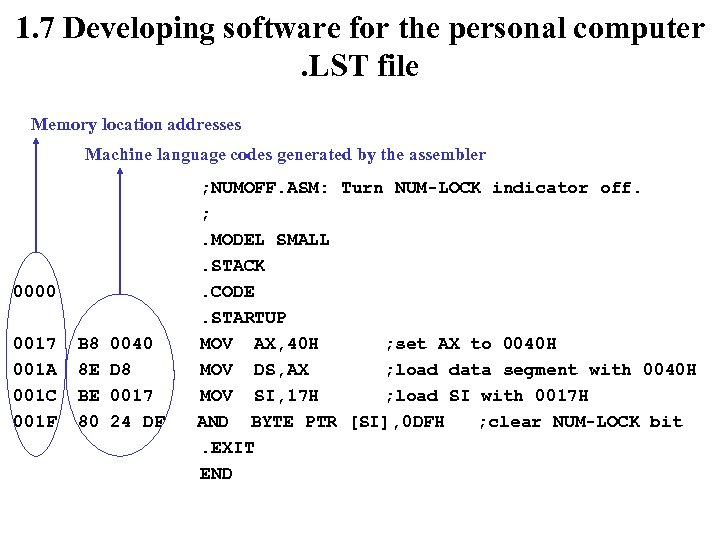
1. 7 Developing software for the personal computer. LST file Memory location addresses Machine language codes generated by the assembler 0000 0017 001 A 001 C 001 F B 8 8 E BE 80 0040 D 8 0017 24 DF ; NUMOFF. ASM: Turn NUM-LOCK indicator off. ; . MODEL SMALL. STACK. CODE. STARTUP MOV AX, 40 H ; set AX to 0040 H MOV DS, AX ; load data segment with 0040 H MOV SI, 17 H ; load SI with 0017 H AND BYTE PTR [SI], 0 DFH ; clear NUM-LOCK bit. EXIT END
e7ab6bb7da11be22a3a95cf6ce70844e.ppt