Practical lesson #8 Def.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 61

Education of children with behavior disorders Practical lesson #8

Practical lesson #8 • Aim: to train students to define and understand psychological and pedagogical peculiarities of teaching children with autism and behavior disorders. • Key special wordsautism, behavior, mood, : emotion, behavior disorders, epilepsy, bipolar disorder, hypergraphia, schizophrenia, eating disorders, anxiety disorders, conduct disorders, learning disorders, severe depression, disruptive behavioral disorders, dissociative disorders, emotional disorders, pervasive developmental disorders, Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD), Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD), Oppositional Defiant Disorder (ODD), Asperger's Syndrome, Tourette syndrome (GTS)

Key special words • • • • autism – аутизм behavior – поведение mood - настроение emotions- эмоции behavior disorders расстройства поведения – epilepsy- эпилепсия bipolar disorder– биполярное расстройство hypergraphia- гиперграфия schizophrenia- шизофрения eating disorders расстройства приема пищи – anxiety disorders тревожные расстройства – conduct disorders поведенческие расстройства – learning disorders расстройства, связанные с учением –


Key special words • severe depression глубокая депрессия – • disruptive behavioral disorders деструктивные – поведенческие расстройства • dissociative disorders диссоциативные расстройства – • emotional disorders эмоциональные расстройства – • pervasive developmental disordersобщие расстройства – развития • Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) – синдром дефицита внимания и гиперактивности (СДВГ) • Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD) обсессивно– компульсивное расстройство (ОКР) • Oppositional Defiant Disorder (ODD) оппозиционновызывающее расстройство (ОВР) • Asperger's Syndrome синдром Аспергера – • Tourette syndrome (GTS) синдром Туретта -
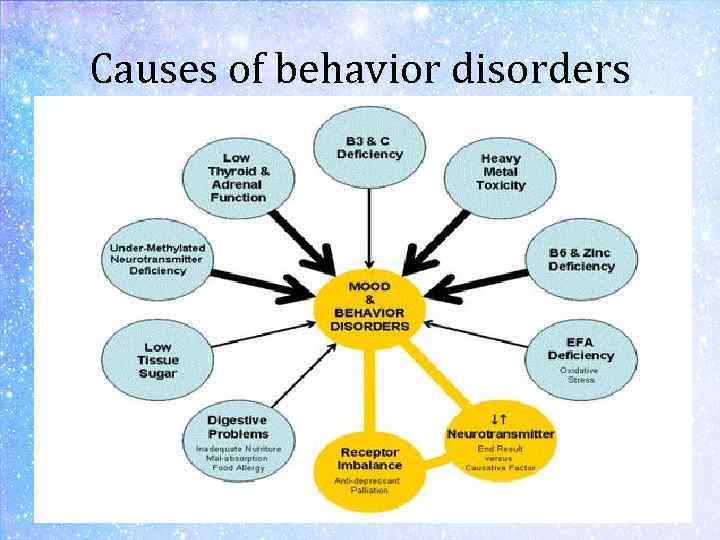
Causes of behavior disorders

Questions: • • What is behavior disorder ? What are types of behavioral disorders ? What are causes for behavioral disorders? What are the signs of behavioral disorders? What are emotional symptoms of behavioral disorders? What is autism? How can we help children with autism? What is Asperger's Syndrome ?
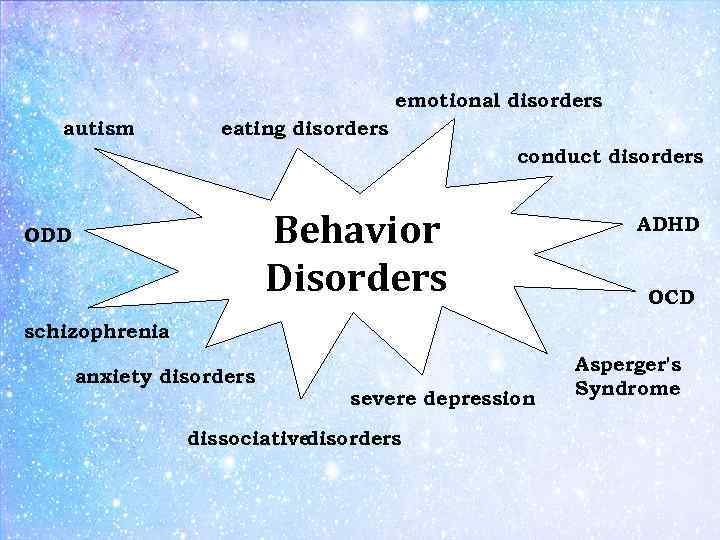
emotional disorders autism eating disorders conduct disorders Behavior Disorders ODD ADHD OCD schizophrenia anxiety disorders severe depression dissociative disorders Asperger's Syndrome
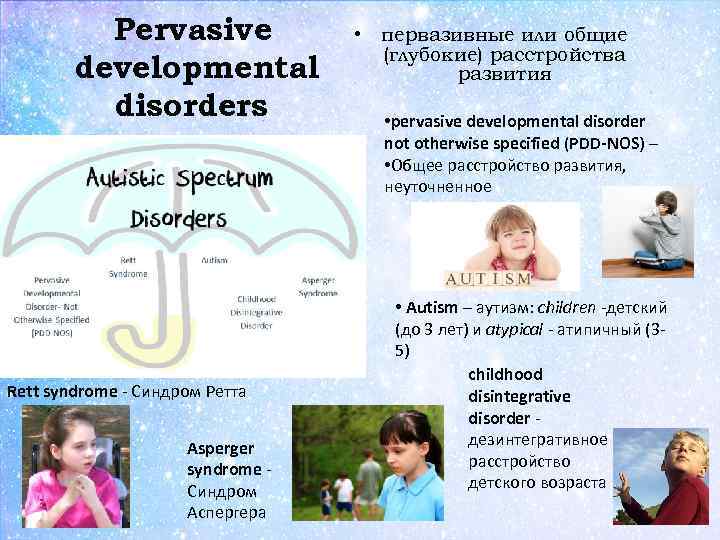
Pervasive developmental disorders Rett syndrome - Синдром Ретта Asperger syndrome - Синдром Аспергера • первазивные или общие (глубокие) расстройства развития • pervasive developmental disorder not otherwise specified (PDD-NOS) – • Общее расстройство развития, неуточненное • Autism – аутизм: children -детский (до 3 лет) и atypical - атипичный (35) childhood disintegrative disorder - дезинтегративное расстройство детского возраста

Autism • Autism (autistic disorder) is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by impaired social interaction, verbal and nonverbal communication, and restricted and repetitive behavior. • Children with autism have problems interacting and communicating with others (взаимодействии и общении с другими).

Asperger's Syndrome • Asperger syndrome (AS) is a developmental disorder characterized by significant difficulties in social interaction and nonverbal communication, along with restricted and repetitive patterns of behavior and interests. • It is an autism spectrum disorder (ASD) and differs from other disorders by relatively normal language and intelligence. • Синдро А спергера одно из м — общих нарушений развития, характеризующееся серьёзными трудностями в социальном взаимодействии, а также ограниченным, стереотипным, повторяющимся репертуаром интересов и занятий.

Asperger's Syndrome • Синдром получил название в честь австрийского психиатра и педиатра Ганса Аспергера ( ans Asperger H ), который в 1944 году описал детей, отличавшихся отсутствием способностей к невербальной коммуникации, ограниченной эмпатией по отношению к сверстникам и физической неловкостью. • Сам Аспергер использовал термин «аутистическая психопатия» . • От аутизма отличается он прежде всего тем, что речевые и когнитивные способности в целом остаются сохранными. Синдром часто характеризуется также выраженной неуклюжестью.

Severe Depression • Глубокая депрессия • Today, experts agree that severe depression can occur at any age. • The disorder is marked by changes in: • Emotions — Children often feel sad, cry, or feel worthless. • Motivation — Children lose interest in play activities, or schoolwork declines. • Physical well-being — Children may experience changes in appetite or sleeping patterns and may have vague physical complaints. • Thoughts — Children believe they are ugly, unable.

Bipolar Disorder • Bipolar disorder is a mental illness characterized by periods of depression and periods of elevated mood (excitedness). • Биполярное расстройство (manic depression- маниакально–депрессивный психоз) - психическое заболевание, которое характеризуется нетипичной сменой настроений, перепадами энергии и способности функционировать. • В отличие от нормальной смены настроений, с их взлетами и падениями, оно может привести к весьма серьезным последствиям (разрушить личные отношения, повлиять на качество работы или успеваемость в школе)

Eating Disorders • Children or adolescents who are intensely afraid of gaining weight and do not believe that they are underweight may have eating disorders. • anorexia - нервная анорексия (преднамеренное снижение веса, вызываемое и/или поддерживаемым самим пациентом, в целях похудения или для профилактики набора лишнего веса. ) • bulimia - нервная булимия (два основных признака: 1) непреодолимая тяга к перееданию и 2) рвота, которую намеренно вызывают у себя больные (иногда в сочетании со злоупотреблением слабительными), чтобы воспрепятствовать увеличению массы тела) • binge eating disorder - психогенное переедание (переедание, приводящее к появлению лишнего веса, и являющееся реакцией на дистресс) • pica – парорексия (бщее название нарушений пищевого поведения, при которых в силу различных причин поедаются несъедобные субстанции (известь, песок, бумага, мелкие камни, обломки кирпича и мн. др. )

Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) • Young people with attentiondeficit/hyperactivity disorder are unable to focus their attention and are often impulsive and easily distracted. Attentiondeficit/hyperactivity disorder occurs in up to five of every 100 children (U. S. Department of Health and Human Services, 1999).

Tourette syndrome (GTS) • Tourette syndrome (also called Tourette's syndrome, Tourette's disorder, Gilles de la Tourette syndrome, GTS or, more commonly, simply Tourette's or TS) is an inherited neuropsychiatric disorder with onset in childhood, characterized by multiple physical (motor) tics and at least one vocal (phonic) tic. • exclamation of obscene words or socially inappropriate and derogatory remarks • Синдром Туре тта (болезнь Туретта, синдром Жиля де ла Туретта) — генетически обусловленное расстройствоцентральной нервной системы, которое проявляется в детском возрасте и характеризуется множественными моторнымитиками и как минимум одним вокальным или механическим тиком. • Ранее синдром Туретта считался редким и странным синдромом, ассоциируемым с выкрикиванием нецензурных слов или социально неуместных и оскорбительных высказываний (копролалия).

Emotional disorders • An emotional behavioral disorder affects a person’s ability to be happy, control their emotions and pay attention in school. According to Gallaudet University, symptoms of an emotional behavioral disorder include: • Inappropriate actions or emotions under normal circumstances • Learning difficulties that are not caused by another health factor • Difficulty with interpersonal relationships, including relationships with teachers and peers • A general feeling of unhappiness or depression • Feelings of fear and anxiety related to personal or school matters

Anxiety disorders • Young people who experience excessive fear, worry, or uneasiness may have an anxiety disorder. • Phobias • Generalized anxiety disorder • Panic disorder ("panic attacks”) • Obsessive-compulsive disorder • Post-traumatic stress disorder

Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD) • OCD is characterized by fears and irrational thoughts that lead to obsessions, which, in turn, cause compulsions. If you have OCD, you engage in compulsive, repetitive behavior.

Dissociativedisorders • диссоциативные расстройства • Dissociativedisorders (DD) are conditions that involve disruptions or breakdowns of memory, awareness, identity, or perception. • Dissociation (диссоциация, разъединение) is a defense mechanism(защитный механизм). • They include: • dissociative amnesia – диссоциативная амнезия • dissociative identity disorder or multiple personality disorder - Диссоциативное расстройство идентичности (расстройство множественной личности, раздвоение личности) • dissociative fugue - Диссоциативная фуга (фуга – бегство) • depersonalization/derealisation disorder – деперсонализация/ дереализация

Disruptive behavior disorders • Деструктивное расстройство • Disruptive behavior disorders involve behaviors such as temper tantrums (истерики physical aggression ), (физическая агрессия) such as attacking other children, excessive argumentativeness (чрезмерное аргументированность), stealing (воровство) and other forms of defiance , or resistance to authority. • They include Oppositional Defiant Disorder and Conduct Disorder.

Oppositional Defiant Disorder (ODD) • оппозиционновызывающее расстройство (ОВР) • Oppositional Defiant Disorder (ODD) • ODD is a behavioral disorder characterized by hostile, irritable and uncooperative attitudes in children, according to Children’s Mental Health Ontario. Children with ODD may be spiteful or annoying on purpose, and they generally direct their negative actions at authority figures.

Conduct Disorder • Young people with conduct disorder usually have little concern for others and repeatedly violate the basic rights of others and the rules of society. • Conduct disorder causes children and adolescents to act out their feelings or impulses in destructive ways.

Schizophrenia is a mental disorder characterized by abnormal social behavior and failure to understand reality. • ü ü ü ü Common symptoms include: false beliefs (ложные убеждения) unclear or confused thinking hearing voices (слышать голоса в голове) lack of motivation (отсутствие мотивации) hallucinations (галлюцинации) withdrawal from others (отчуждение от других людей) loss of contact with reality (потеря контакта с реальностью)

Epilepsy • Epilepsy is a group of neurological diseases characterized by epileptic seizures. • одно из самых распространённых хронических неврологич еских заболеваний человека, проявляющееся в предрасположенности организма к внезапному возникновению судорожных приступов

Hypergraphia • Hypergraphia is a behavioral condition characterized by the intense desire to write. • Гиперграфия (Hypergraphia) — стиль письма, для которого характерно чрезмерное многословие, педантическая настойчивость в упоминании многих несущественных деталей и склонность к навязчивым вставкам; все это свидетельствует об имеющемся у человека нарушении психики, которое часто встречается у больных эпилепсией. Люди, у которых наблюдается гиперграфия, редко сами признают наличие у них проблем в общении.

What Causes a Behavioral Disorder? • • • Biological causes may include: Physical illness or disability Malnutrition Brain damage Hereditary factors Other factors related to an individual’s home life: Divorce or other emotional upset at home Coercion from parents Unhealthy or inconsistent discipline style Poor attitude toward education or schooling

Emotional Symptoms Easily getting annoyed or nervous Often appearing angry Putting blame on others Refusing to follow rules or questioning authority • Arguing and throwing temper tantrums • Having difficulty in handling frustration • •
Vincent Van Gogh • Vincent Van Gogh was born in Holland in 1853. Before becoming a painter he was a teacher. • He started painting when he was twenty-seven. • In 1886 he left Holland joined his young brother Theo, who lived in Paris. • Here he painted some of his most famous pictures. • After living there for two years he moved to the South of France, because the climate was warmer there.

Van Gogh Vincent Van Gogh • But Van Gogh was mentally ill. During one of his fits of madness he attacked his friend, the artist Paul Gaugin. • In another fit of madness, he cut off part of his own ear. • Eventually he went into a mental hospital but he didn’t get any better. • Finally, on Sunday 27 th July 1890, in the small village Vincent Van Gogh took a gun. • He went into a cornfield and shot himself. Thirty-six hours later Van Gogh died in his brother’s arms. Paul Gaugin

Vincent Van Gogh • His last words were: «I hope I did it properly» . Nobody has ever painted cornfields or sunflowers like Van Gogh. • His paintings are full of colour and sunlight. Today his paintings are worth millions of pounds but in his lifetime he only sold one. • Like his life, his art was always unusual and very emotional.

Questions: • When was Vincent Van Gogh born? • Was he a teacher before becoming a painter? • Why did he leave Paris? • Was Van Gogh mentally ill? • How many paintings did he sell during his lifetime?

Van Gogh’s mental health • His mental health: There are still several opinions about Van Gogh’s mental problems: • Epilepsy • Bipolar disorder • Hypergraphia • Schizophrenia

(1890) Portrait of Doctor Gachet

(1885) The Potato Eaters

(1888) Bedroom in Arles

(1888) Cafe Terrace at Night

(1888) The Red Vinyard

(1889) The Starry Night
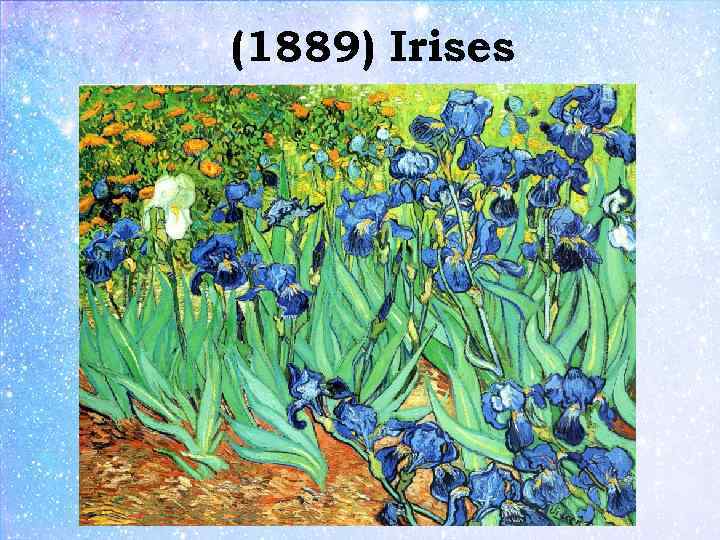

(1889) Irises

(1889) Still Life: Vase with Twelve Sunflowers

(1889) Portrait de l'artiste sans barbe

Video task: What disorder do they have (specify)? John tiles S Alex Vincent Marie

Complete (job, disorder, achievements): • • Lev Vygotsky Sigmund Freud Vincent van Gogh Winston Churchill Marilyn Monroe Ludwig van Beethoven Hellen Keller Alexander Graham Bell

Describe paintings (colors, emotions) • Orange and yellow are main colors. There is also green, red and brown. • When I look at this picture I feel happy and warm. • I can see sunflowers in the vase. • Sunflowers are like the Sun.
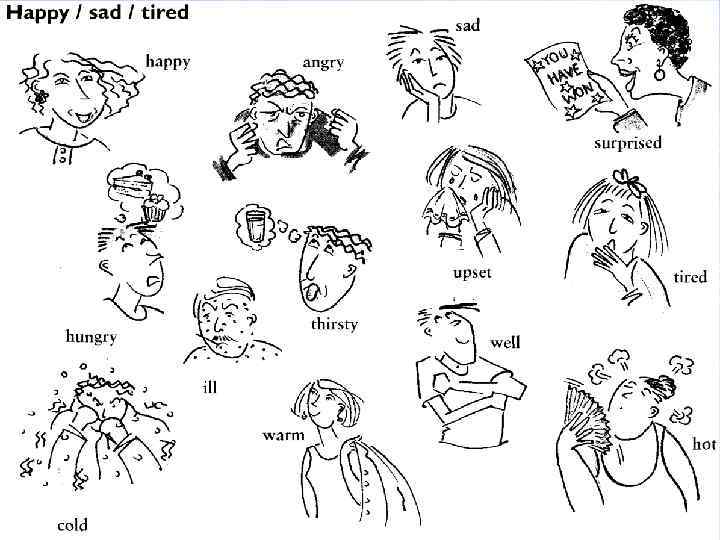


I feel good! Ø I am very sad today. Ø I feel happy. I’ve passed my exam. Ø I feel sad when I watch this film. Ø I’m bored. Let’s go out. Ø I feel tired and I’m hungry. Ø I feel angry with you. Why are you late? Ø People look surprised. They’ve never seen such performance. Ø Mary is scared. She is afraid of spiders.
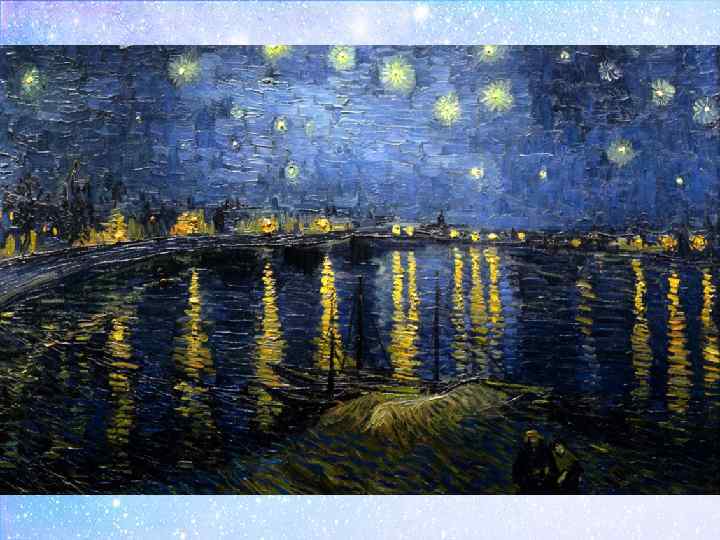
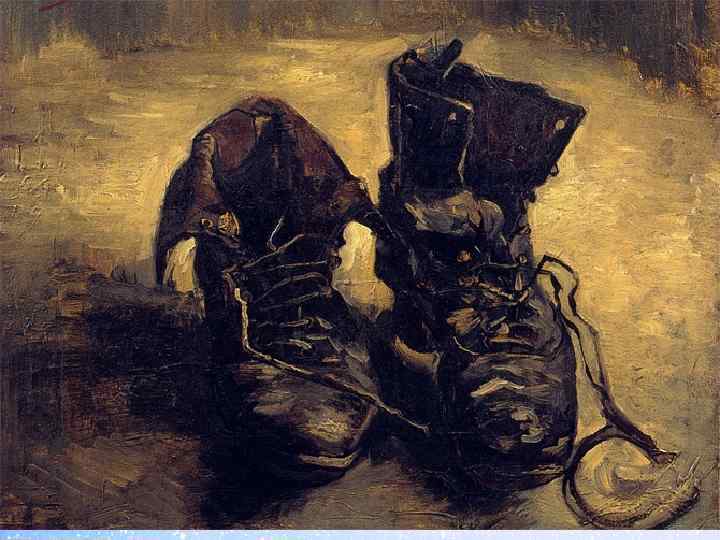
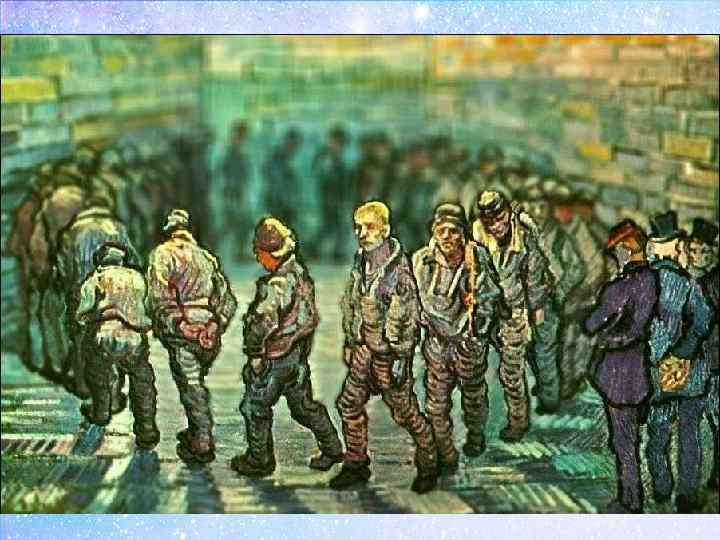






Didactic sinquain: • Topic – тақырыбы, атауы (не? кім? ) • 2 adjectives – 2 сын есімдер (қандай? • 3 verbs – 3 етістіктер (не істеп отыр/ жатыр/ тұр? ) • Your opinion (I like it or I don’t like it / It is disgusting/ terrible/ awesome …) – сіздің пікіріңіз (Сізге ұнай ма? ) • Emotions (I’m impressed/ I feel depressed, I feel scared/ I feel happy/ I feel sad) – эмоциялар

Didactic sinquain: • Topic – тема, название картины • 2 adjectives – 2 имени прилагательных (Which? - Какой? Какая? Какие? ) • 3 verbs – 3 глагола (What are they doing? - Что делает? Что делают? ) • Your opinion (I like it or I don’t like it / It is disgusting/ terrible/ awesome …) – ваше мнение (Do you like it? ) • Emotions (I’m impressed/ I feel depressed, I feel scared/ I feel happy/ I feel sad) – эмоции (How do you feel when you look at this painting? )

Didactic sinquain: • Butterfly in the space. • Cosmic, artificial. • Fly, float, go ahead. • I like it / It is amazing. • I feel excited.




Practical lesson #8 Def.pptx