96bd94fd4728c7bdf8f53650583142b4.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 42


Education is an admirable thing, but it is well to remember from time to time that nothing that is worth knowing can be taught. Oscar Wilde

As you know, education in England is one of the best well -developed education in the world. So, talking about education, we will begin with a brief survey of the development of free universal education since the middle ages, & then take a closer look at the main institutions in which British people are formally educated.

History of British Education

Common people Middle Ages Aristocracy The first schools were parish schools. They were taught hunting & manners, Schools were mostly religious & children rather than reading & writing were taught to read, learn prayers & psalms Girls were not normally educated except The grammar schools. The pupils, drawn that often they too were sent away from schools from the wealthier sections of town home to learn how to behave & care for society, were expected to be able to read a household. & write before they were admitted. They then went on to learn Latin grammar & compose Latin verse In the middle ages children often had to receive cruel punishment.

th century 17 Common people Dame schools were paid by the parish & usually run by women, there were taught children up to the age 7 reading, knitting & spinning. Aristocracy Grammar schools. There was schools provided further education in writing, Latin & Greek & even mathematics in the grammar schools. The Dissenting Academies where the religious teaching reflected their own beliefs Private boarding-schools

18 th century Dame schools continued Charity schools were established that stressed religion, moral teaching & vocational training. The grammar schools The public schools where the scenes of bullying & savage corporal punishment.

19 th century From the 19 th century limited & voluntary schooling to the present expanded & compulsory education system: Schools & teaching were provided for the children of enfranchised groups Schools were organised to run cheaply as possible Monitorial system - teacher teaches the monitors who then pass on their knowledge to the pupils The so-called Ragged Schools (supported by charity & provided education for the very poorest children of the cities. ) 1833 Education Act gave the first Government grant to schools.

20 th century to finance 1902 - Local Education Authorities had 1902 secondary schools 1907 - private secondary schools could get 1907 financial help from the government 1918 - the power of the LEAs increased: schooling 1918 was made compulsory up to the age of 14 and this reorganised the government grants to schools 1944 -all children should have an equal 1944 opportunity to participate in secondary education & it should be suited to their age.

The Education System The basic structure of British education system, particularly the 3 stages of education in modern Britain • School Education • Further Education • Higher Education

Basic Structure of British Education System • Pre-school education • Primary school • Secondary school • Universities, colleges of higher education
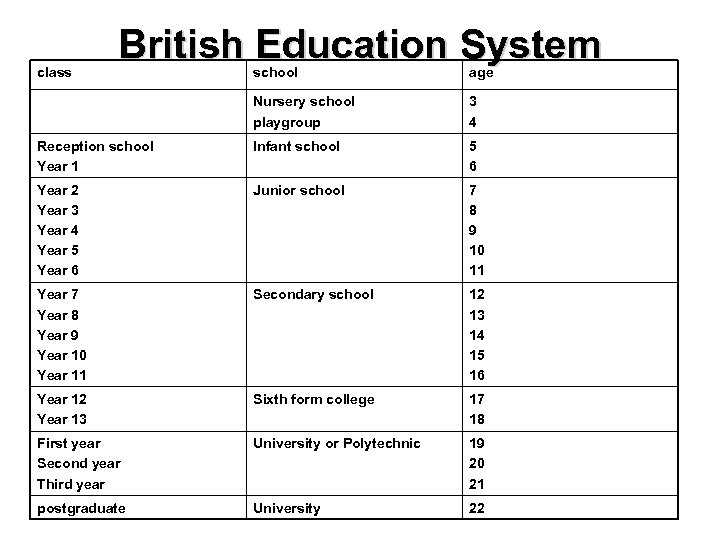
class British Education System school age Nursery school playgroup 3 4 Reception school Year 1 Infant school 5 6 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Year 5 Year 6 Junior school 7 8 9 10 11 Year 7 Year 8 Year 9 Year 10 Year 11 Secondary school 12 13 14 15 16 Year 12 Year 13 Sixth form college 17 18 First year Second year Third year University or Polytechnic 19 20 21 postgraduate University 22

Britain State Schools • The system of secondary education in Britain has been changed in recent years. Under the old system, children took an examination called the “eleven plus” at the age of 11. If they passed this examination, they went to a grammar school (high school) & if they failed, they went to a secondary modern school.

• Under the new system, there is no examination at the age of eleven • the grammar schools & secondary modern schools have been replaced by large comprehensive schools. • Some comprehensives are “streamed”; others are “unstreamed”. • In a streamed school, pupils are placed into classes according to their ability. Children of high ability are in the “A” stream, those of lesser ability in the “B” stream & so on. • In an unstreamed school, children of mixed ability are placed together in the classes.

Private education • Government does not support these schools financially. • People must pay for their education • Choice: day and boarding schools, single-sex schools • 2, 400 schools in Britain

“E d u c a t i o n brings a child the world” • Many British children start school at the age of 3 or 4 if there is a play school near their house. • These schools are nursery & they are not compulsory. • Children are taught to sing, draw, they play different creative games. • Compulsory education begins at the age of 5, when children go to primary school.

Pre-school Education • Compulsory schooling: every child in Britain must by law receive full-time education from the age of 5 to 16. • Children begin their education in the State system at the age of 5; some lucky children may attend Nursery schools (kindergartens) from 3 to 5, but most start their basic education in an Infants’ (the infants department of a junior school) or First School.

Primary Education • All children start primary school by the age of 5. Primary education lasts for six years. • They attend the infant school from 5 to 7 and then junior school until they are 11. • Some parents pay for their children to attend a private school but all children have the right to go to a state school which is free. • Private schools are called public schools. • Most of them are boarding schools. • More than 90% of British children attend state schools. • In English schools pupils have to address men teachers “Sir” and women teachers “Miss” or “Mrs”.

Primary School Subjects One teacher teaches: ШArt ШAnalysis ШDrama ШEnglish ШGeography ШHistory ШMathematics ШScottish Gaelic (in Scotland)
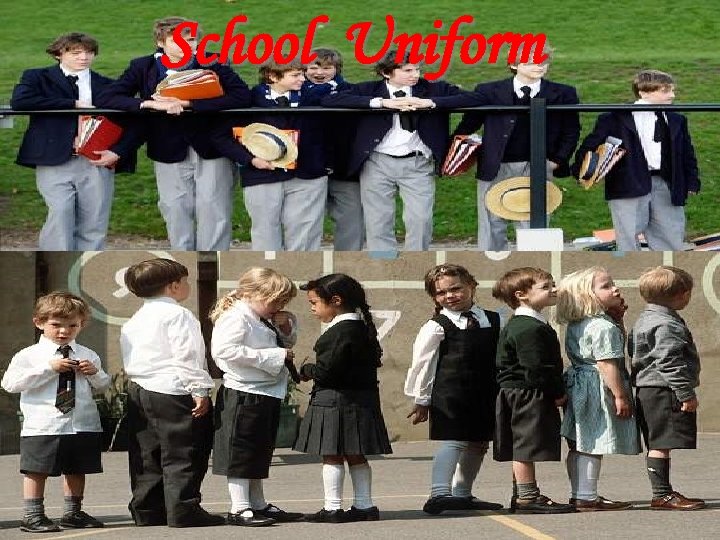

School Uniform

Young people in Britain often don't like their school uniform, especially the hats & shoes. Sometimes they do not wear the right clothes. Schools will often give them a warning the first time that this happens but then will punish them if they continue not to wear the correct uniform. Senior students don't have to wear their school uniform.

Secondary School • Compulsory education extends up to 16 years. Comprehensive schools are mostly mixed sex & cater for a mixed range of abilities. Their students come from a range of social classes & ethnic backgrounds. Students are often streamed into different ability groups. . • The main examination that all students should take at 16 is GCSE. Some students continue in the same school for a further 2 years of study leading to the examination of the General Certificate of Education, Advanced level (GCE A level). Usually 3 or 4 academic subjects are studied & 1 general studies paper. This is the main examination required for university entrance.

Secondary School Subjects • Mathematics • Science • Technology and design • Information Technology • English • Modern Languages (French, German, Spanish) • Geography • History • Social Education • Religion • Cooking • Music • Physical education • Greek and Latin (grammar and independent schools)
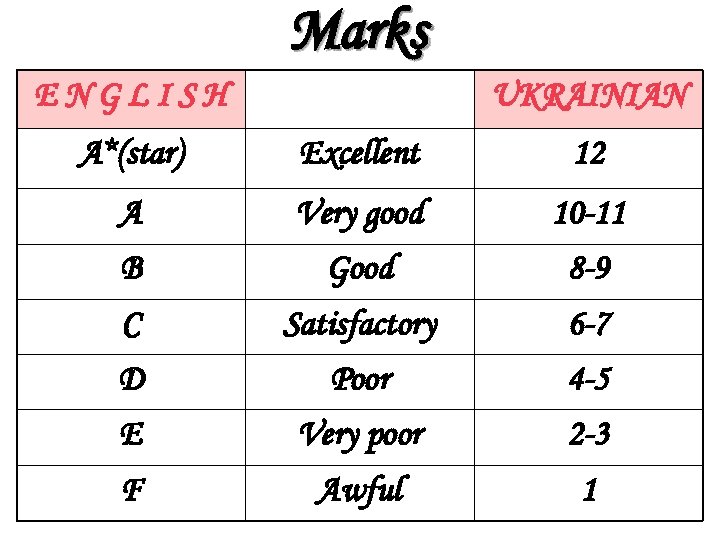
Marks ENGLISH UKRAINIAN А*(star) Excellent 12 A Very good 10 -11 B Good 8 -9 C Satisfactory 6 -7 D Poor 4 -5 E Very poor 2 -3 F Awful 1

General School Certificate • The General School Certificate (G. S. C) was a standardized school (public) examination in Britain. It was replaced by the General Certificate of Education (G. C. E) in 1965. • The G. C. E consists of two sets of examinations: the ordinary level & the advanced level. It is on the results of the advanced level examination that universities choose their students.

• At the age of 13 pupils begin preparing for the G. C. S. E in 8 or 9 subjects such as English, French, mathematics & history. • Then pupils may choose 2 or 3 subjects out of the 8 or 9 for a 2 -year course leading to the A level examinations. With 8 good grades in the G. C. S. E & 3 G. C. E. A level passes, students will stand a very good chance of being accepted by universities.

School Rules EVERY BRITISH SCHOOL HAS ITS RULES, FOR EXAMPLE: • • • • Be polite Say hello when you see a teacher Come to school on time Stand up when a teacher comes into the class Don’t eat or drink in the classroom Don’t run in the corridors Don’t bring mobile phones to class Don’t talk to people in lessons Appropriate school dress must de worn on all school occasions. Bicycles shall not be ridden in the school grounds. Ball games may not be played in areas close to unprotected windows. Radios and tape-recorders of any type must not be brought to school. No pupil is allowed to smoke on the school premises or on school visits, or to bring cigarettes.

Further education • Used to study academic subjects & explore recreational activities as well as to develop & upgrade work skills. • Usually for students between 16 and 18 • Prepares for university or for a vocation • At 18 some students take A-level examination because it is necessary to have A-levels in order to go to a university or Polytechnic. • But some pupils want to stay on at school to prepare for a vocational course or for a work rather than for A-level examinations.

Higher Education • • There are more than 88 universities in Britain Mostly teach a broad range of subjects Higher education begins at 18 & usually lasts three or four years. After getting A-level of GCSE students go to universities, polytechnics or colleges of higher education. The academic year is divided into three terms. Terminal examinations are held at the end of autumn, spring & summer terms. Only two reexaminations are allowed. British universities usually keep to the customs of the past. Upon graduation all the students have to wear long black gowns & “students caps”.

University of Higher Education • The old universities refer to those founded before 1600. Oxford & Cambridge are the oldest ones, dating from 1249 &1284. Until the 19 th century, they are the only 2 universities in England • The new universities are those founded since the 2 nd world war. They have their own independent & modern approaches to teaching • A private university (Buckingham). • A school which is devoted entirely to distance learning (the Open University).

Open University

• The open University is a non-residential university offering degree & other courses for adult students of all ages. It uses specially printed texts, correspondence tuition, TV & radio broadcast, audio & visual cassettes. There is also a network of study centers for contact with part-time counselors & fellow students. No formal academic qualifications are required to register for most courses, but standards of the University’s degrees are the same as those of other universities. They offer higher degrees & programs for professionals in education, health & welfare & for updating managers, scientists & technologists.

Classification of degrees • Degrees: BA (Bachelor of Arts) or BSc (Bachelor of Science); • MA (Master of Arts) or MSc (Master of Science); • Ph. D. (Doctor of Philosophy).

Undergraduate Courses • • • Usually only three years Specialise in one subject Entrance requirements Ш Good English profieciency Ш Previous examinations Postgraduate courses • Masters ШCan be teaching or research based ШUsually examined by dissertation ШOne or two years • Doctorate – Always research, never taught

Distance education • Learners are separated from the institution • Learning takes place outside the education establishment. • Students learn where and when it suits them, at their own pace. • Studies and private and professional commitments can be combined

The oldest universities of Great Britain : Oxford Cambridge
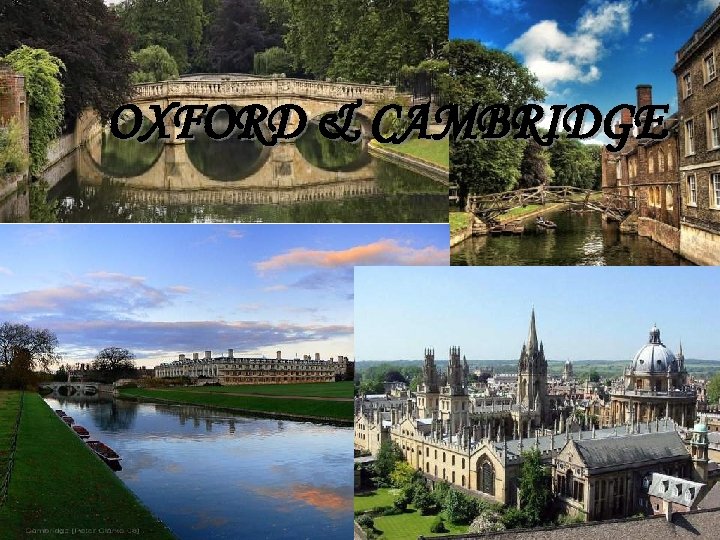

OXFORD & CAMBRIDGE
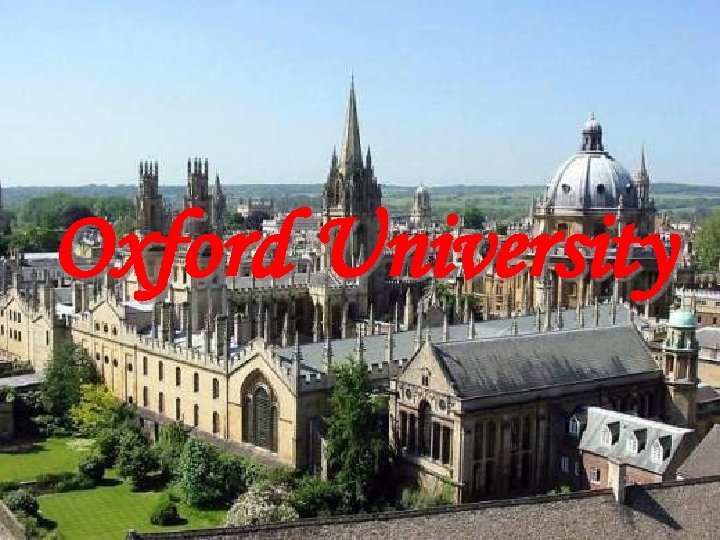

Oxford University
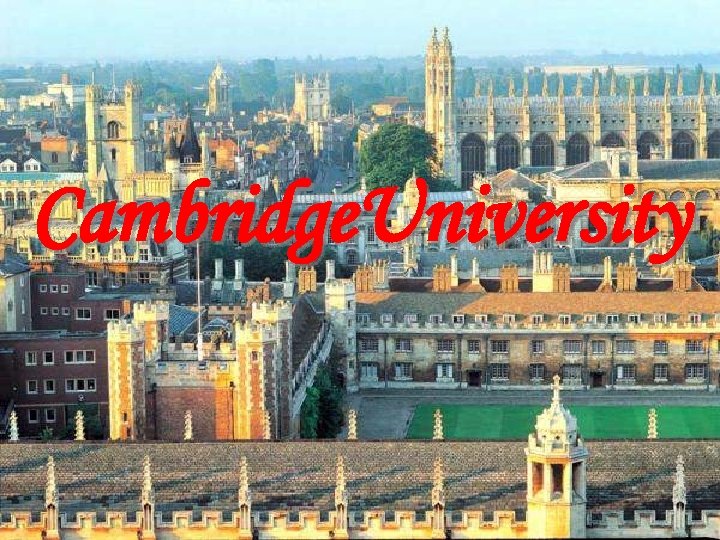

Cambridge. University

Education for Foreigners Language courses Summer schools (colleges)

Conclusion The studying in England is very prestigious, interesting and popular all over the world. Every year hundreds and thousands of students come to this place to get the best education. It is hard to find parents who don’t want to see their children as graduates of a British college or a University. What is the secret of its popularity? What are the main a dvantages of studying in Great Britain? • British certificates are considered to be the best and respected all over the world • The quality of the British Education is very prestigious in the world • The studying in Great Britain is cheaper than in other countries • The studying in Great Britain allows you to learn to speak and think as Englishmen

Study well and you’ll have a chance to enter these universities.
96bd94fd4728c7bdf8f53650583142b4.ppt