ac8ac883e7dff8741c4a8d616f8826ea.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 14
 Editing and Coding: Transforming Raw Data into Information (Source: W. G Zikmund, B. J Babin, J. C Carr and M. Griffin, Business Research Methods, 8 th Edition, U. S, South-Western Cengage Learning, 2008) 1
Editing and Coding: Transforming Raw Data into Information (Source: W. G Zikmund, B. J Babin, J. C Carr and M. Griffin, Business Research Methods, 8 th Edition, U. S, South-Western Cengage Learning, 2008) 1
 Objectives 1. Know when a response is really an error and should be edited 2. Appreciate coding of pure qualitative research 3. Understand the way data are represented in a data file 4. Understand the coding of structured responses including a dummy variable approach 5. Appreciate the ways that technological advances have simplified the coding process 2
Objectives 1. Know when a response is really an error and should be edited 2. Appreciate coding of pure qualitative research 3. Understand the way data are represented in a data file 4. Understand the coding of structured responses including a dummy variable approach 5. Appreciate the ways that technological advances have simplified the coding process 2
 Stages of Data Analysis n Raw Data q n Nonrespondent Error q n The unedited responses from a respondent exactly as indicated by that respondent. Error that the respondent is not responsible for creating, such as when the interviewer marks a response incorrectly. Data Integrity q The notion that the data file actually contains the information that the researcher is trying to obtain to adequately address research questions. 3
Stages of Data Analysis n Raw Data q n Nonrespondent Error q n The unedited responses from a respondent exactly as indicated by that respondent. Error that the respondent is not responsible for creating, such as when the interviewer marks a response incorrectly. Data Integrity q The notion that the data file actually contains the information that the researcher is trying to obtain to adequately address research questions. 3
 Editing n Editing q n Field Editing q n The process of checking the completeness, consistency, and legibility of data and making the data ready for coding and transfer to storage. Preliminary editing by a field supervisor on the same day as the interview to catch technical omissions, check legibility of handwriting, and clarify responses that are logically or conceptually inconsistent. In-House Editing q A rigorous editing job performed by a centralized office staff. 4
Editing n Editing q n Field Editing q n The process of checking the completeness, consistency, and legibility of data and making the data ready for coding and transfer to storage. Preliminary editing by a field supervisor on the same day as the interview to catch technical omissions, check legibility of handwriting, and clarify responses that are logically or conceptually inconsistent. In-House Editing q A rigorous editing job performed by a centralized office staff. 4
 Editing n n n Checking for Consistency q Respondents match defined population q Check for consistency within the data collection framework Taking Action When Response is Obviously in Error q Change/correct responses only when there are multiple pieces of evidence for doing so. Editing Technology q Computer routines can check for consistency automatically. 5
Editing n n n Checking for Consistency q Respondents match defined population q Check for consistency within the data collection framework Taking Action When Response is Obviously in Error q Change/correct responses only when there are multiple pieces of evidence for doing so. Editing Technology q Computer routines can check for consistency automatically. 5
 Editing for Completeness n Item Nonresponse q q The technical term for an unanswered question on an otherwise complete questionnaire resulting in missing data. Plug Value n n q An answer that an editor “plugs in” to replace blanks or missing values so as to permit data analysis. Choice of value is based on a predetermined decision rule. Impute n To fill in a missing data point through the use of a statistical process providing an educated guess for the missing response based on available information. 6
Editing for Completeness n Item Nonresponse q q The technical term for an unanswered question on an otherwise complete questionnaire resulting in missing data. Plug Value n n q An answer that an editor “plugs in” to replace blanks or missing values so as to permit data analysis. Choice of value is based on a predetermined decision rule. Impute n To fill in a missing data point through the use of a statistical process providing an educated guess for the missing response based on available information. 6
 Editing for Completeness (cont’d) n What about missing data? q List-wise deletion n q The entire record for a respondent that has left a response missing is excluded from use in statistical analysis. Pair-wise deletion n Only the actual variables for a respondent that do not contain information are eliminated from use in statistical analysis. 7
Editing for Completeness (cont’d) n What about missing data? q List-wise deletion n q The entire record for a respondent that has left a response missing is excluded from use in statistical analysis. Pair-wise deletion n Only the actual variables for a respondent that do not contain information are eliminated from use in statistical analysis. 7
 Facilitating the Coding Process n Editing And Tabulating “Don’t Know” Answers q q q Legitimate don’t know (no opinion) Reluctant don’t know (refusal to answer) Confused don’t know (does not understand) 8
Facilitating the Coding Process n Editing And Tabulating “Don’t Know” Answers q q q Legitimate don’t know (no opinion) Reluctant don’t know (refusal to answer) Confused don’t know (does not understand) 8
 Coding Qualitative Responses n n n Coding q The process of assigning a numerical score or other character symbol to previously edited data. Codes q Rules for interpreting, classifying, and recording data in the coding process. q The actual numerical or other character symbols assigned to raw data. Dummy Coding q Numeric “ 1” or “ 0” coding where each number represents an alternate response such as “female” or “male. ” 9
Coding Qualitative Responses n n n Coding q The process of assigning a numerical score or other character symbol to previously edited data. Codes q Rules for interpreting, classifying, and recording data in the coding process. q The actual numerical or other character symbols assigned to raw data. Dummy Coding q Numeric “ 1” or “ 0” coding where each number represents an alternate response such as “female” or “male. ” 9
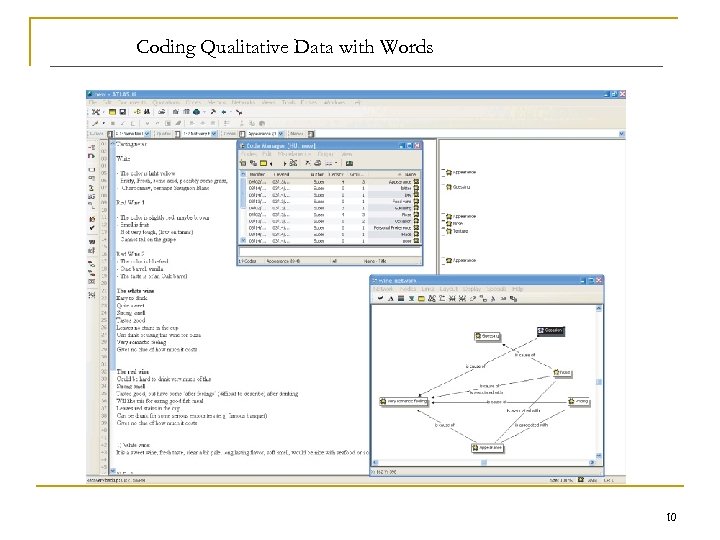 Coding Qualitative Data with Words 10
Coding Qualitative Data with Words 10
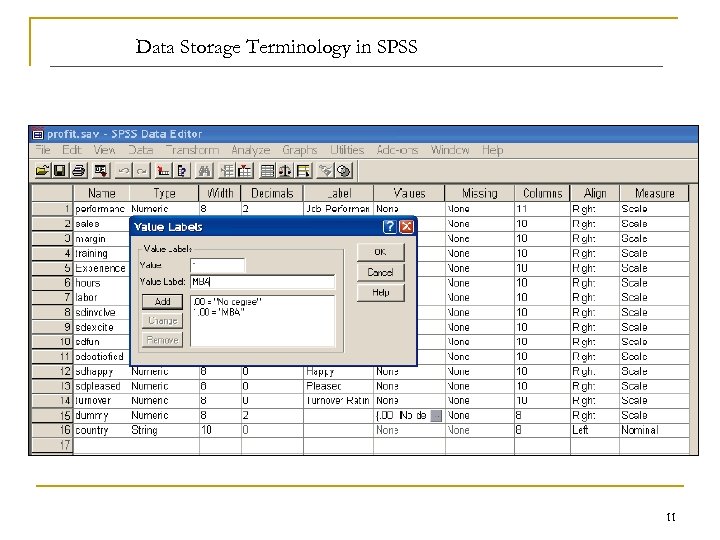 Data Storage Terminology in SPSS 11
Data Storage Terminology in SPSS 11
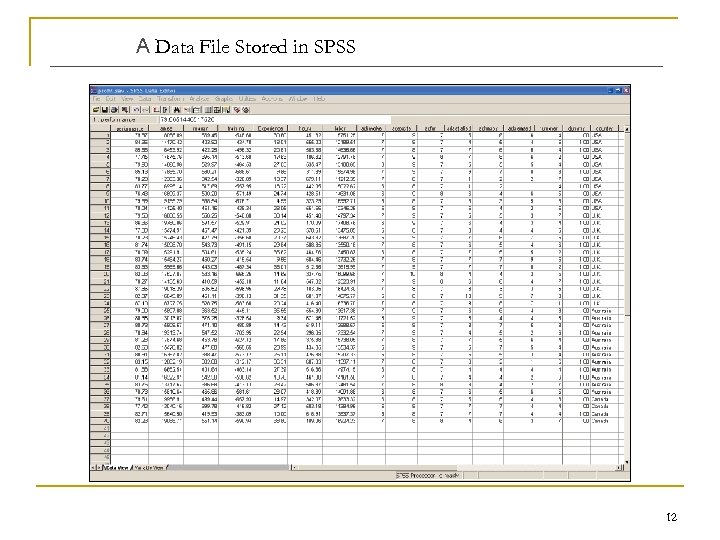 A Data File Stored in SPSS 12
A Data File Stored in SPSS 12
 Computerized Survey Data Processing n Data Entry q n The activity of transferring data from a research project to computers. Optical Scanning System q A data processing input device that reads material directly from mark-sensed questionnaires. 13
Computerized Survey Data Processing n Data Entry q n The activity of transferring data from a research project to computers. Optical Scanning System q A data processing input device that reads material directly from mark-sensed questionnaires. 13
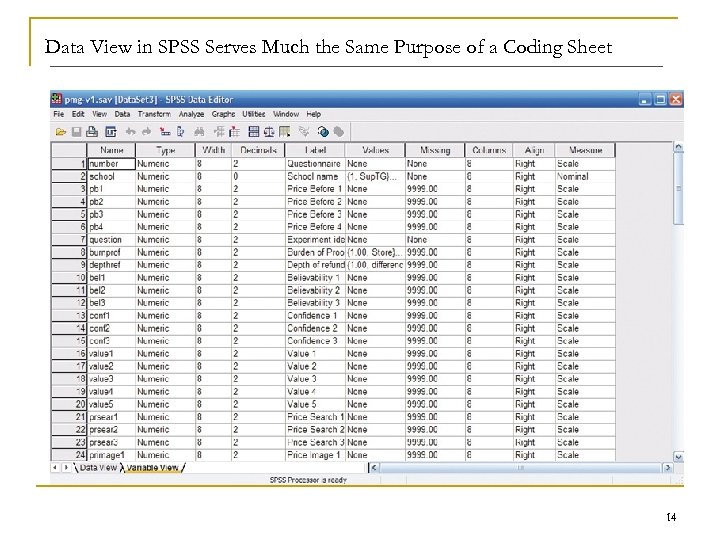 Data View in SPSS Serves Much the Same Purpose of a Coding Sheet 14
Data View in SPSS Serves Much the Same Purpose of a Coding Sheet 14


