afff110e5a6ee10eda2c740cfbbbe7e2.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 39
 EDI & POS Systems ATG 383 - Spring 2002
EDI & POS Systems ATG 383 - Spring 2002
 When to adopt technology? • “Things have to change to remain the same” • What do we want to accomplish? – Lower costs – Increase revenues – Comply with required standards
When to adopt technology? • “Things have to change to remain the same” • What do we want to accomplish? – Lower costs – Increase revenues – Comply with required standards
 3 Technologies We Will Consider • Electronic Data Interchange • POS Systems • e. Xtensible Markup Language & e. Xtensible Business Reporting Language
3 Technologies We Will Consider • Electronic Data Interchange • POS Systems • e. Xtensible Markup Language & e. Xtensible Business Reporting Language
 Electronic Data Interchange • Computer to computer exchange of business information in a standard format. • EDI is not faxes, email, or web sites.
Electronic Data Interchange • Computer to computer exchange of business information in a standard format. • EDI is not faxes, email, or web sites.
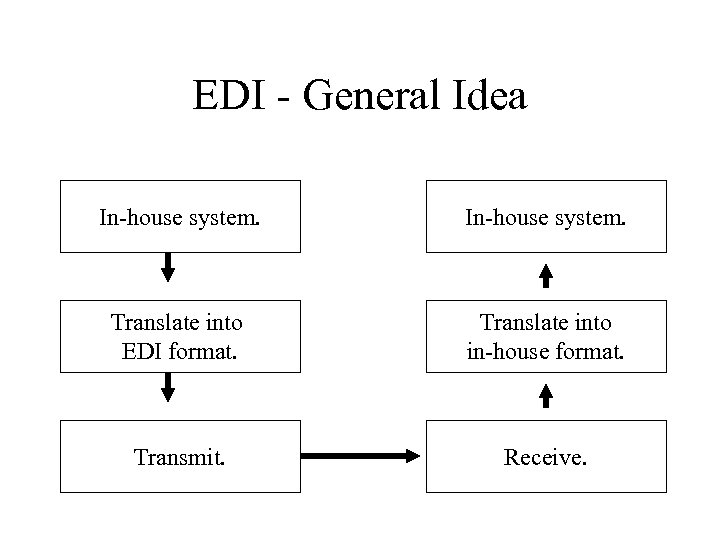 EDI - General Idea In-house system. Translate into EDI format. Translate into in-house format. Transmit. Receive.
EDI - General Idea In-house system. Translate into EDI format. Translate into in-house format. Transmit. Receive.
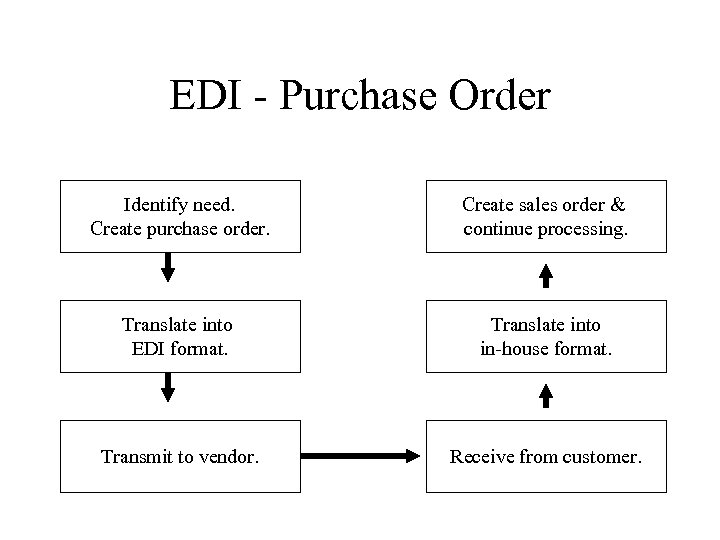 EDI - Purchase Order Identify need. Create purchase order. Create sales order & continue processing. Translate into EDI format. Translate into in-house format. Transmit to vendor. Receive from customer.
EDI - Purchase Order Identify need. Create purchase order. Create sales order & continue processing. Translate into EDI format. Translate into in-house format. Transmit to vendor. Receive from customer.
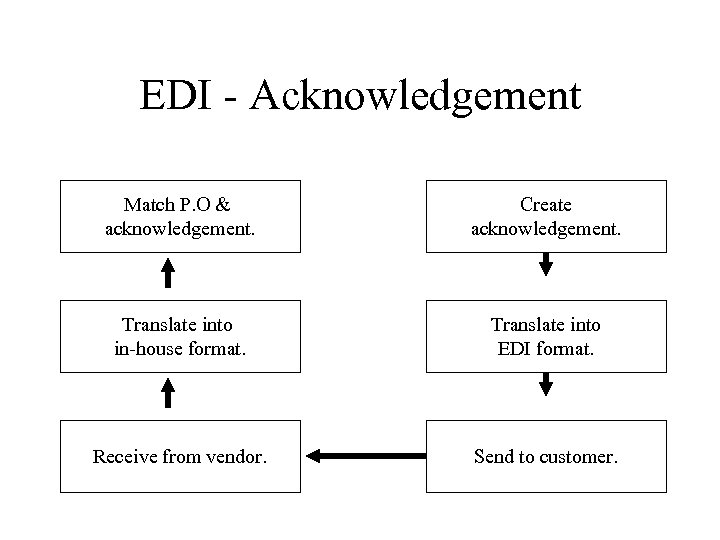 EDI - Acknowledgement Match P. O & acknowledgement. Create acknowledgement. Translate into in-house format. Translate into EDI format. Receive from vendor. Send to customer.
EDI - Acknowledgement Match P. O & acknowledgement. Create acknowledgement. Translate into in-house format. Translate into EDI format. Receive from vendor. Send to customer.
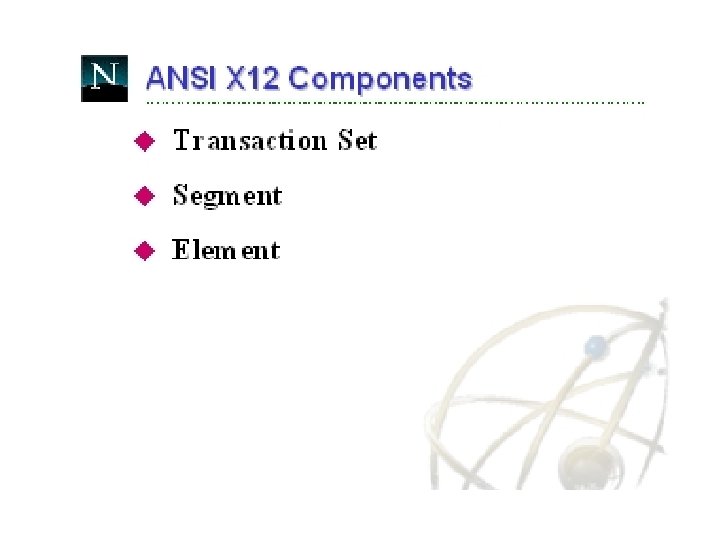
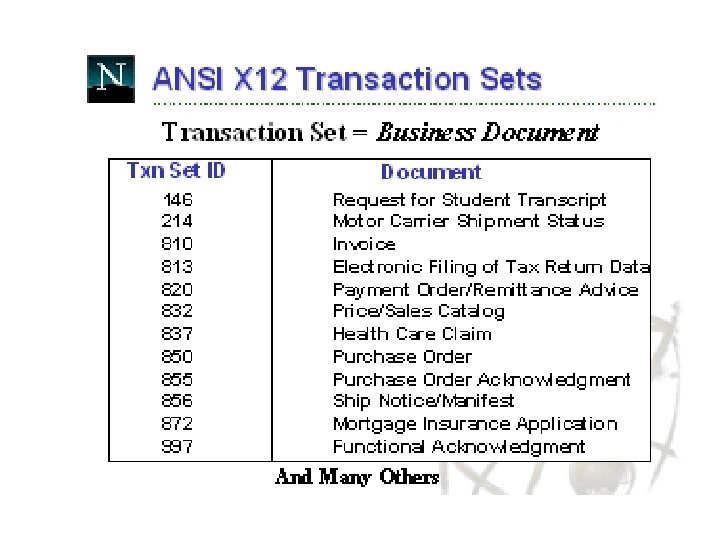
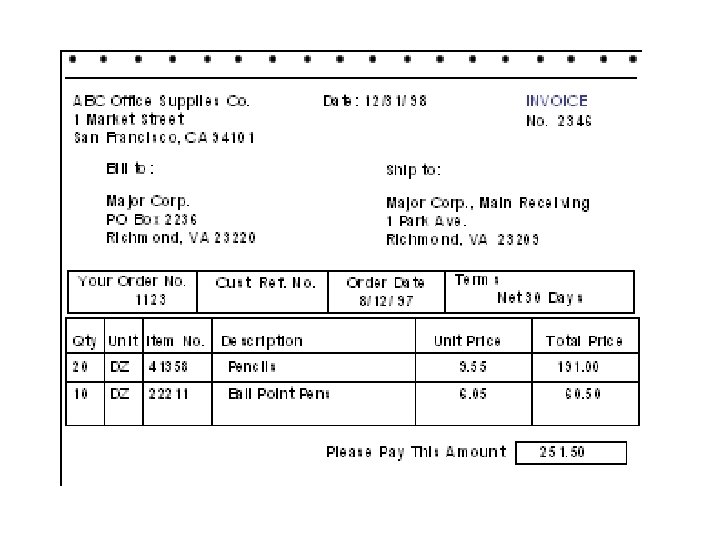
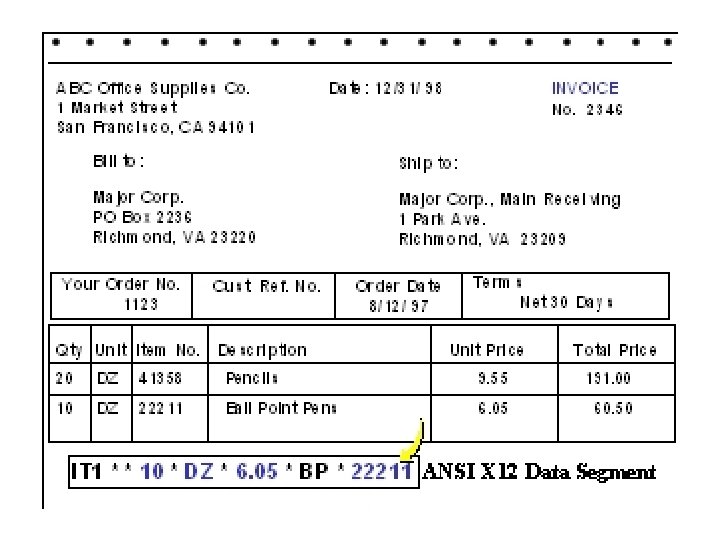
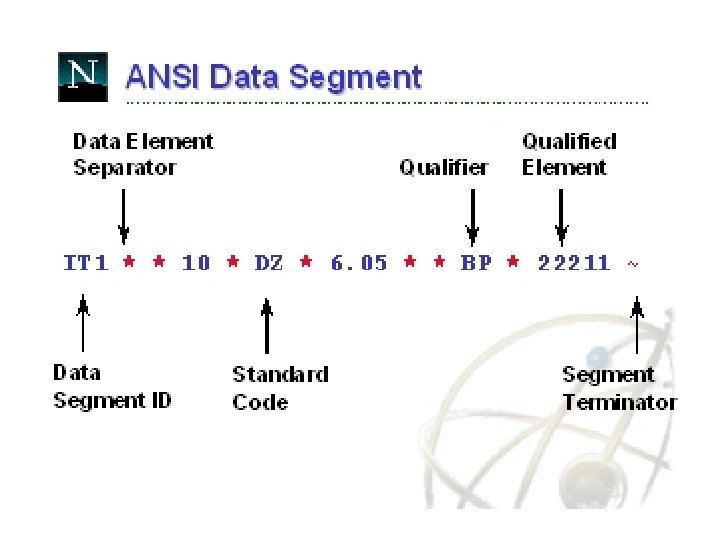
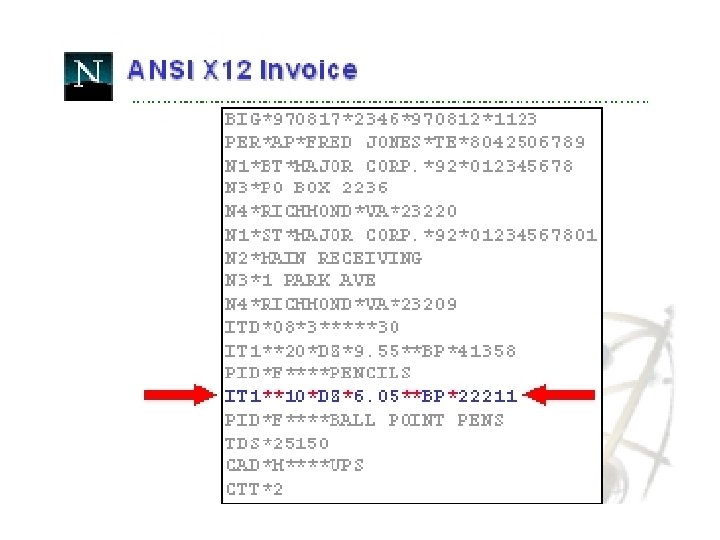
 Translate In-house Data to Common Standard • Translation process – Data fields in business applications are mapped to corresponding fields in EDI documents • Two Common EDI Standards – ANSI X 12 in North America – EDIFACT outside North America • Following examples taken from: – http: //developer. netscape. com/docs/presentations/xpert/edi. html
Translate In-house Data to Common Standard • Translation process – Data fields in business applications are mapped to corresponding fields in EDI documents • Two Common EDI Standards – ANSI X 12 in North America – EDIFACT outside North America • Following examples taken from: – http: //developer. netscape. com/docs/presentations/xpert/edi. html

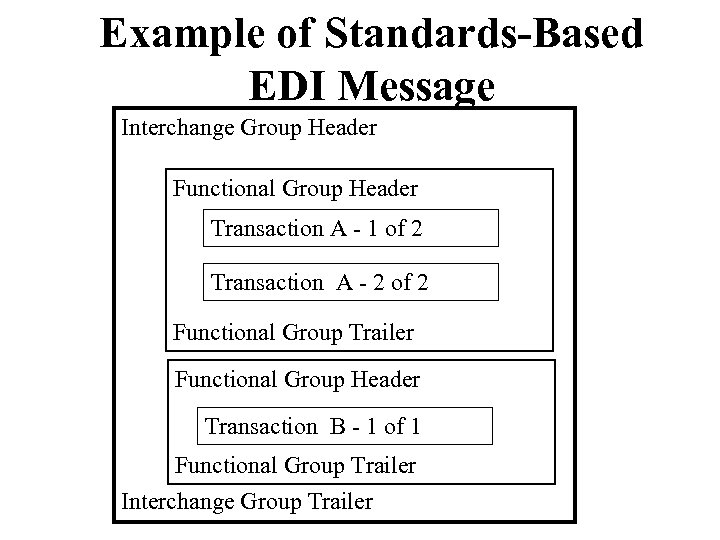 Example of Standards-Based EDI Message Interchange Group Header Functional Group Header Transaction A - 1 of 2 Transaction A - 2 of 2 Functional Group Trailer Functional Group Header Transaction B - 1 of 1 Functional Group Trailer Interchange Group Trailer
Example of Standards-Based EDI Message Interchange Group Header Functional Group Header Transaction A - 1 of 2 Transaction A - 2 of 2 Functional Group Trailer Functional Group Header Transaction B - 1 of 1 Functional Group Trailer Interchange Group Trailer
 EDI Network Options
EDI Network Options
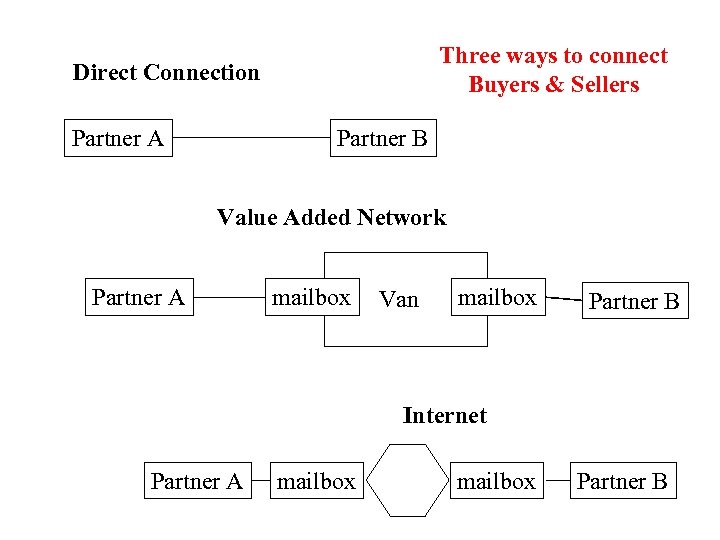 Three ways to connect Buyers & Sellers Direct Connection Partner A Partner B Value Added Network Partner A mailbox Van mailbox Partner B Internet Partner A mailbox Partner B
Three ways to connect Buyers & Sellers Direct Connection Partner A Partner B Value Added Network Partner A mailbox Van mailbox Partner B Internet Partner A mailbox Partner B
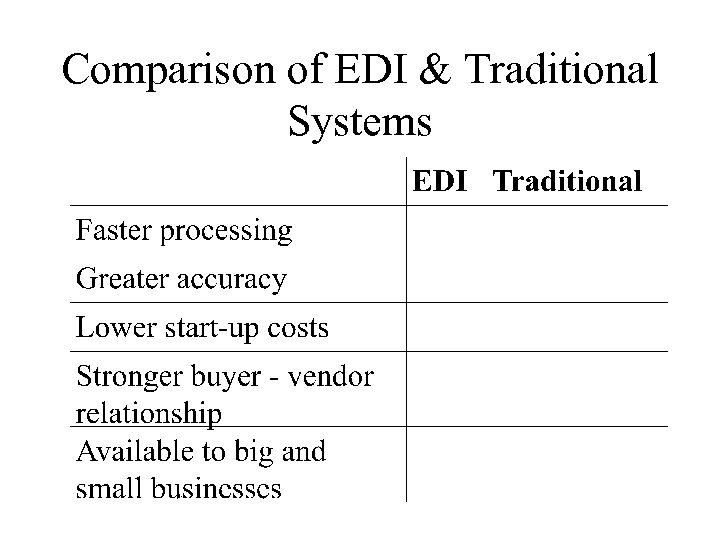 Comparison of EDI & Traditional Systems
Comparison of EDI & Traditional Systems
 What can go wrong with EDI? What are the controls?
What can go wrong with EDI? What are the controls?
 POS & Scanners
POS & Scanners
 Retail POS Systems • Captures and collects sales information at time of sale. • Technologies that are important for this: – Bar codes – Scanners & PCs – Off the shelf software
Retail POS Systems • Captures and collects sales information at time of sale. • Technologies that are important for this: – Bar codes – Scanners & PCs – Off the shelf software
 Bar Codes Identify Products
Bar Codes Identify Products
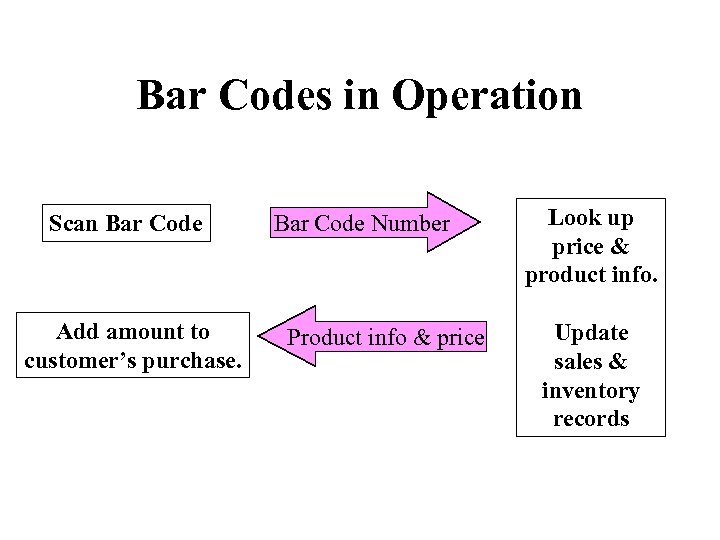 Bar Codes in Operation Scan Bar Code Add amount to customer’s purchase. Bar Code Number Product info & price Look up price & product info. Update sales & inventory records
Bar Codes in Operation Scan Bar Code Add amount to customer’s purchase. Bar Code Number Product info & price Look up price & product info. Update sales & inventory records
 • Use POS data to track sales and manage inventory. • A few of the changes K Mart made: – Eliminate use of retail inventory method. – Ability to make inquiries of data as the day proceeds. – Find adjust overstocked / understocked stores.
• Use POS data to track sales and manage inventory. • A few of the changes K Mart made: – Eliminate use of retail inventory method. – Ability to make inquiries of data as the day proceeds. – Find adjust overstocked / understocked stores.
 • JC Penney sends POS data to VF Corp. , maker of Lee and Wrangler jeans. • VF watches flow of stock and automatically updates a particular item once the quantity reaches an agreed-upon point. • VF uses a flexible manufacturing, allowing many small production runs.
• JC Penney sends POS data to VF Corp. , maker of Lee and Wrangler jeans. • VF watches flow of stock and automatically updates a particular item once the quantity reaches an agreed-upon point. • VF uses a flexible manufacturing, allowing many small production runs.
 Some Advantages of POS • Better customer service. Faster. Fewer errors with proper controls. • More accurate inventory counting and control. • Increased productivity through automated systems. • Opportunity to integrate with EDI for improved replenishment time.
Some Advantages of POS • Better customer service. Faster. Fewer errors with proper controls. • More accurate inventory counting and control. • Increased productivity through automated systems. • Opportunity to integrate with EDI for improved replenishment time.
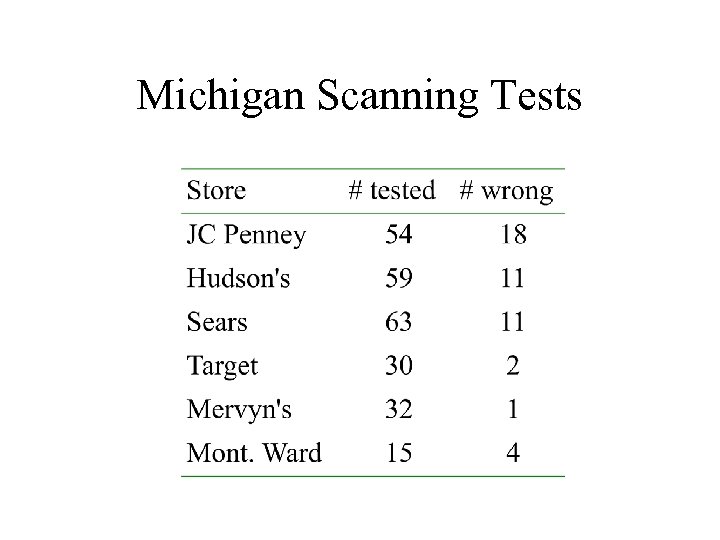 Michigan Scanning Tests
Michigan Scanning Tests
 Scanners and POS - What can go wrong? What are the controls?
Scanners and POS - What can go wrong? What are the controls?
 Using XML to Define Documents and XBRL for Business Reporting
Using XML to Define Documents and XBRL for Business Reporting
 A Web Page
A Web Page
 HTML That Created A Web Page
HTML That Created A Web Page
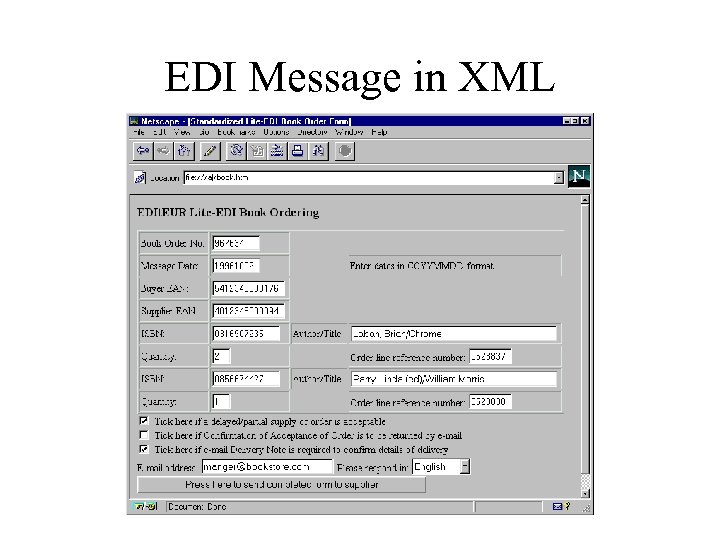 EDI Message in XML
EDI Message in XML
 XBRL • XML based framework for exchange of financial information. • Example: –
XBRL • XML based framework for exchange of financial information. • Example: –
 XML Tags: The Key •
XML Tags: The Key •
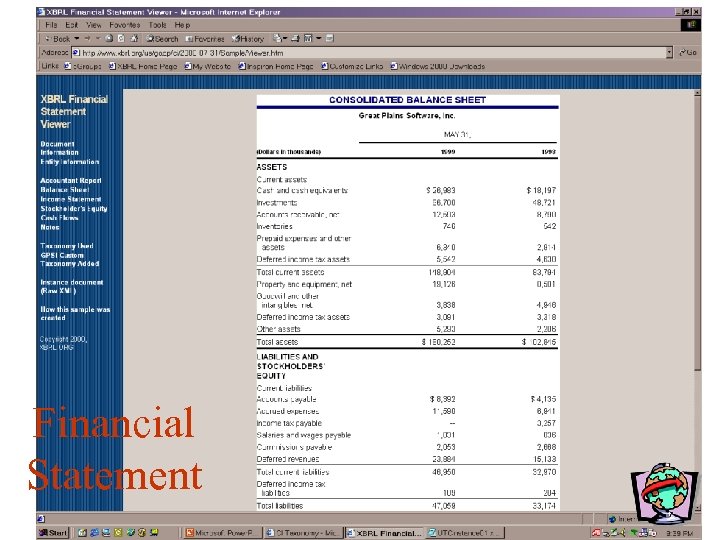 Financial Statement
Financial Statement
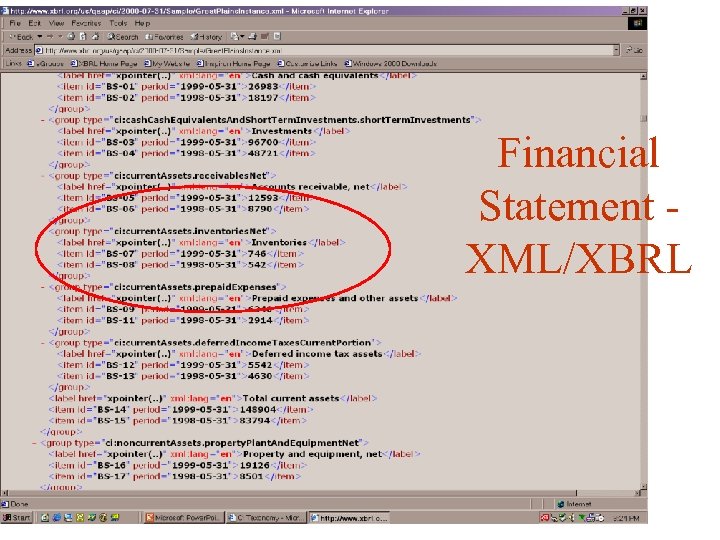 Financial Statement XML/XBRL
Financial Statement XML/XBRL
 Summary • Operation of EDI • Operation of POS systems • Use of XML and XBRL
Summary • Operation of EDI • Operation of POS systems • Use of XML and XBRL


