9a33ea60f1c148fba864fe68420c1481.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 31

Eczema in children Hugo Van Bever Department of Pediatrics National University Singapore APAPARI Workshop, Hanoi, May 2008
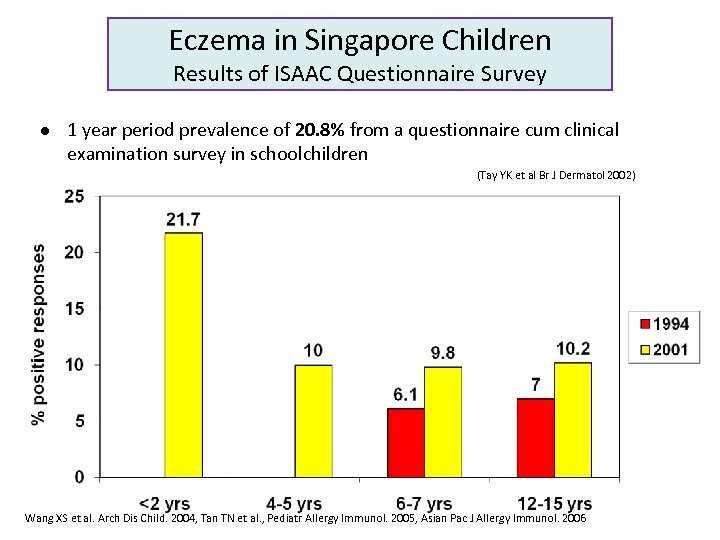
Eczema in Singapore Children Results of ISAAC Questionnaire Survey l 1 year period prevalence of 20. 8% from a questionnaire cum clinical examination survey in schoolchildren (Tay YK et al Br J Dermatol 2002) Wang XS et al. Arch Dis Child. 2004, Tan TN et al. , Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2005, Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol. 2006
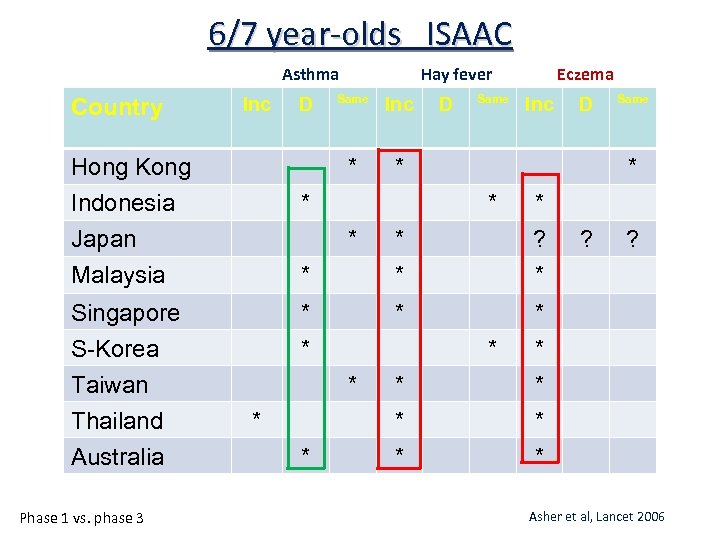
6/7 year-olds ISAAC Asthma Country Inc * * ? * Same * * * * D * * Inc * * D Same Eczema * * Japan Malaysia Phase 1 vs. phase 3 D Same * Inc Hong Kong Indonesia Singapore S-Korea Taiwan Thailand Australia Hay fever * * * ? ? Asher et al, Lancet 2006
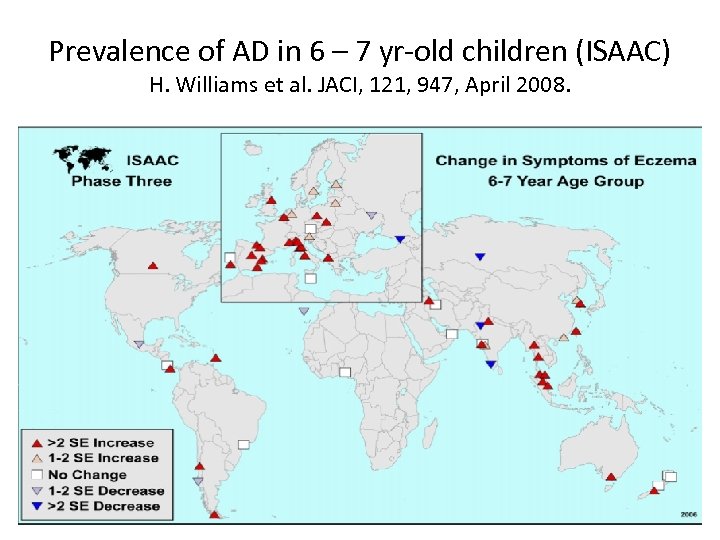
Prevalence of AD in 6 – 7 yr-old children (ISAAC) H. Williams et al. JACI, 121, 947, April 2008.
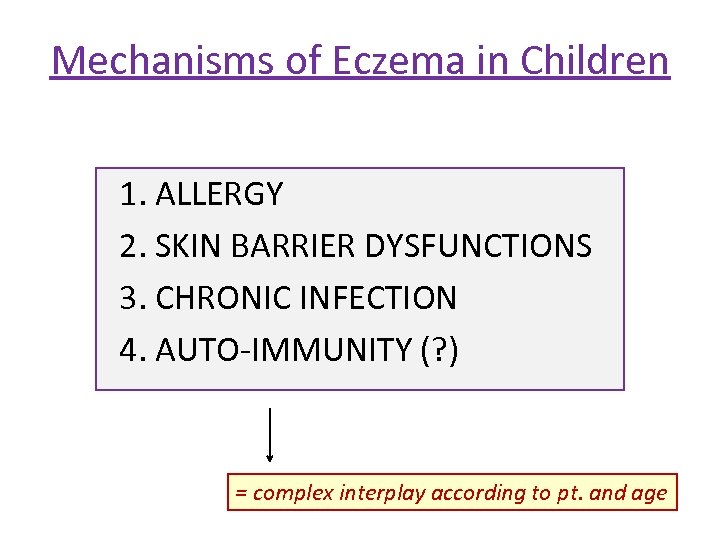
Mechanisms of Eczema in Children 1. ALLERGY 2. SKIN BARRIER DYSFUNCTIONS 3. CHRONIC INFECTION 4. AUTO-IMMUNITY (? ) = complex interplay according to pt. and age
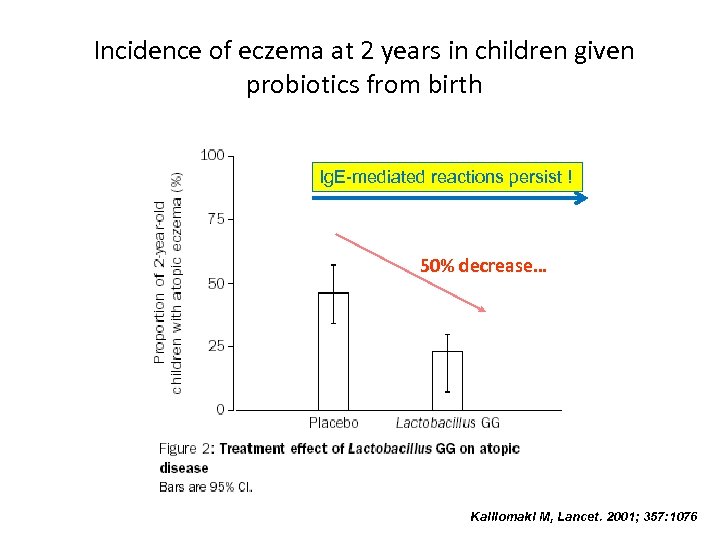
Incidence of eczema at 2 years in children given probiotics from birth Ig. E-mediated reactions persist ! 50% decrease… Kalliomaki M, Lancet. 2001; 357: 1076
AD and BMT 1. Complete correction of the Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome by allergenic bone-marrow transplantation. Parkman et al. NEJM 1978, 298, 921. 2. Transfer of atopy following bone marrow transplantation. Bellou A, et al. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 1997, 78, 513.

Atopic dermatitis 1. SKIN DISORDER 2. ALLERGIC DISEASE 3. Combination ?
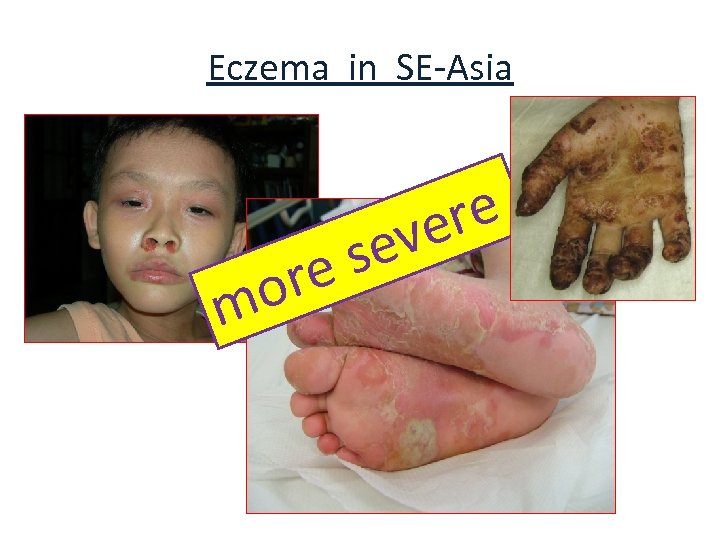
Eczema in SE-Asia or m re ve se e

The Asian Skin 1. Ethnic differences in the pattern of skin diseases seen in a dermatology department – atopic dermatitis is more common among Asian referrals in Leicestershire. Sladden et al. Clin Exp Dermatol 1991, 16, 348. UK 2. The effect of lifestyle on wheeze, atopy, and bronchial hyperreactivity in Asian and white children. Carey et al. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1996, 154, 537. US 3. Atopic dermatitis in children in the United States, 1997 – 2004: visit trends, patient and provider characteristics, and prescribing patterns. Horii et al. Pediatrics 2007, 120, e 527. US AD in Asians… 1. more common 2. more severe (? )

Is atopic dermatitis, an allergic disease ? B S, YE … T U
Eczema SKIN BARRIER DYSFUNCTIONS
New perspectives on epidermal barrier dysfunction in atopic dermatitis: Gene–environment interactions. Michael J Cork et al. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2006, 118, 3 – 21. “… on the importance of epidermal barrier dysfunction in genetically predisposed individuals …”
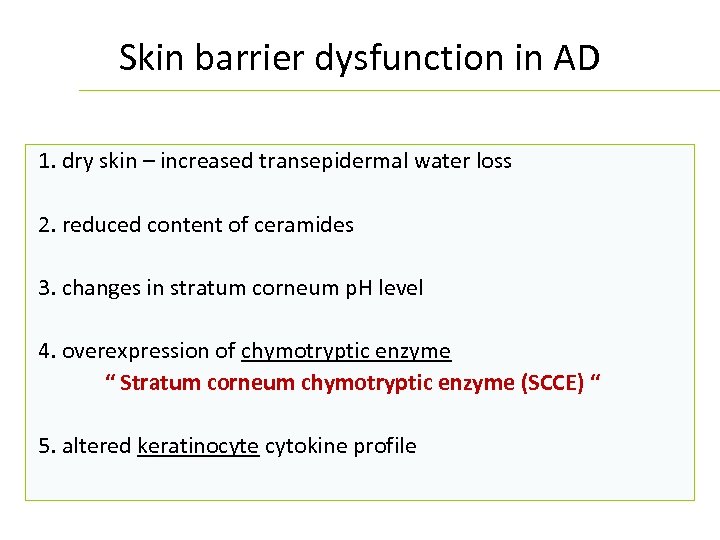
Skin barrier dysfunction in AD 1. dry skin – increased transepidermal water loss 2. reduced content of ceramides 3. changes in stratum corneum p. H level 4. overexpression of chymotryptic enzyme “ Stratum corneum chymotryptic enzyme (SCCE) “ 5. altered keratinocyte cytokine profile

Two (of the many) new players in eczema… 1. Chymotrypsin (SCCE) 2. Filaggrin
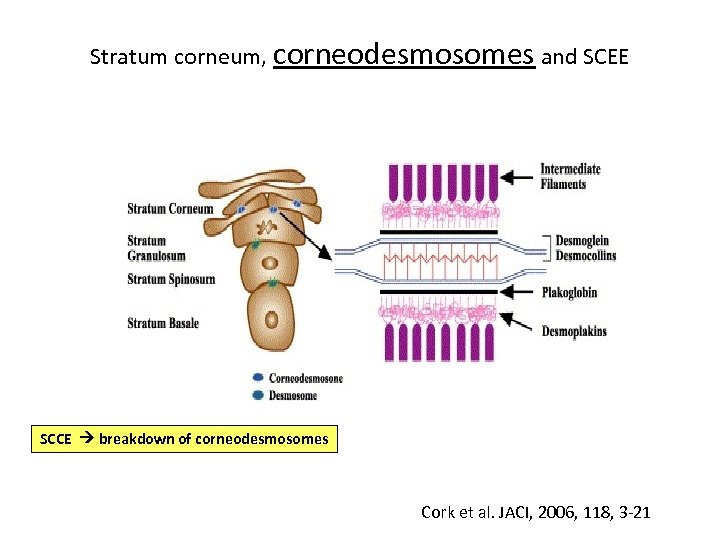
Stratum corneum, corneodesmosomes and SCEE SCCE breakdown of corneodesmosomes Cork et al. JACI, 2006, 118, 3 -21
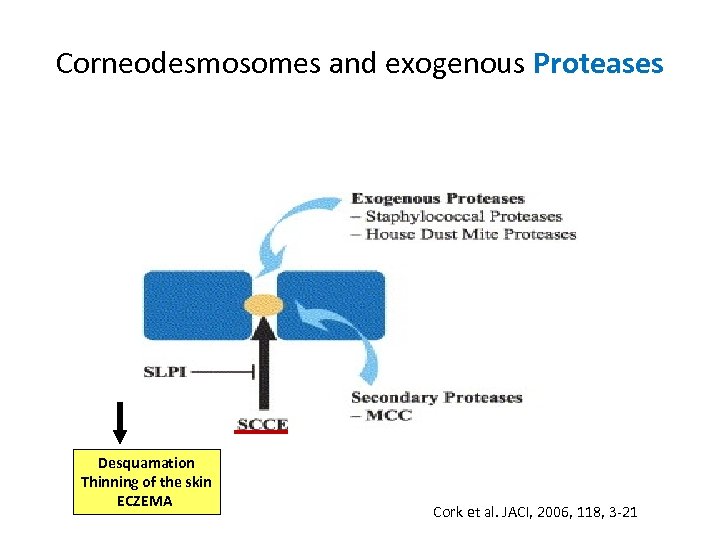
Corneodesmosomes and exogenous Proteases Desquamation Thinning of the skin ECZEMA Cork et al. JACI, 2006, 118, 3 -21
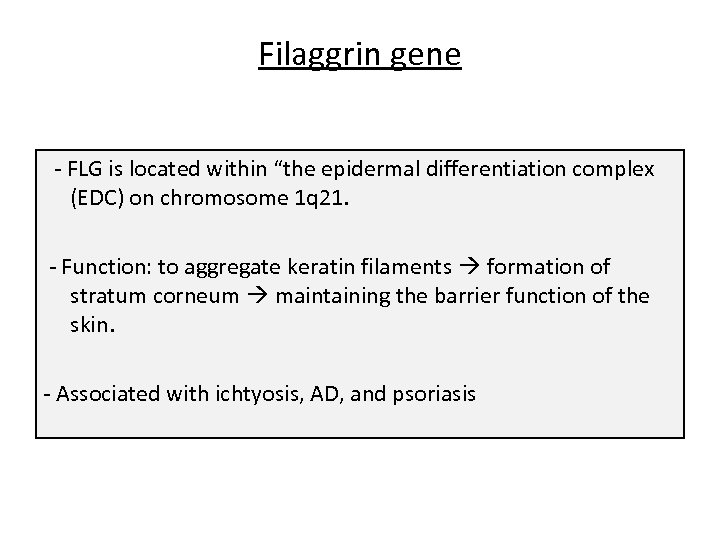
Filaggrin gene - FLG is located within “the epidermal differentiation complex (EDC) on chromosome 1 q 21. - Function: to aggregate keratin filaments formation of stratum corneum maintaining the barrier function of the skin. - Associated with ichtyosis, AD, and psoriasis
JACI 2007, 120, 1406 – 1412.
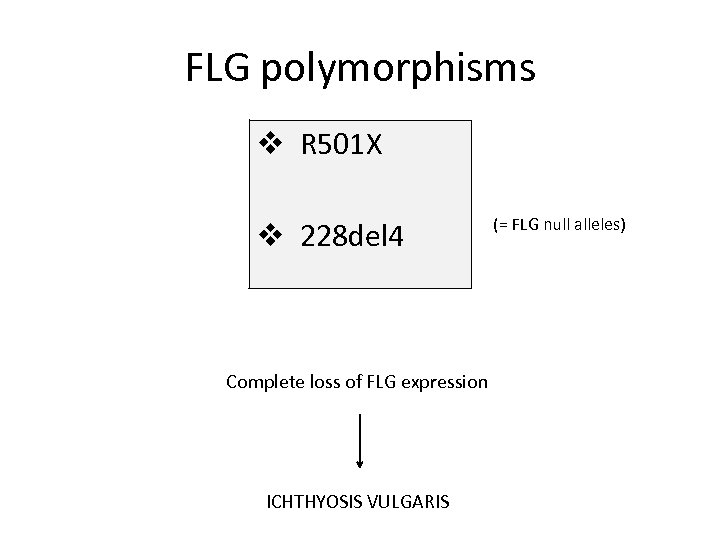
FLG polymorphisms v R 501 X v 228 del 4 Complete loss of FLG expression ICHTHYOSIS VULGARIS (= FLG null alleles)
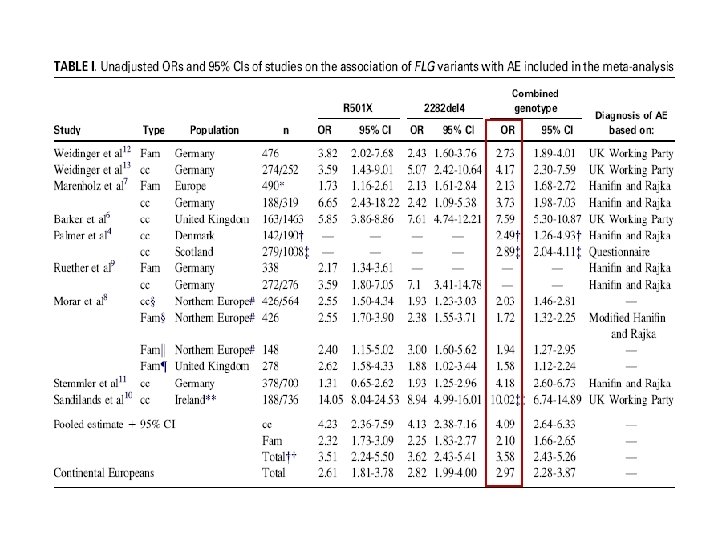
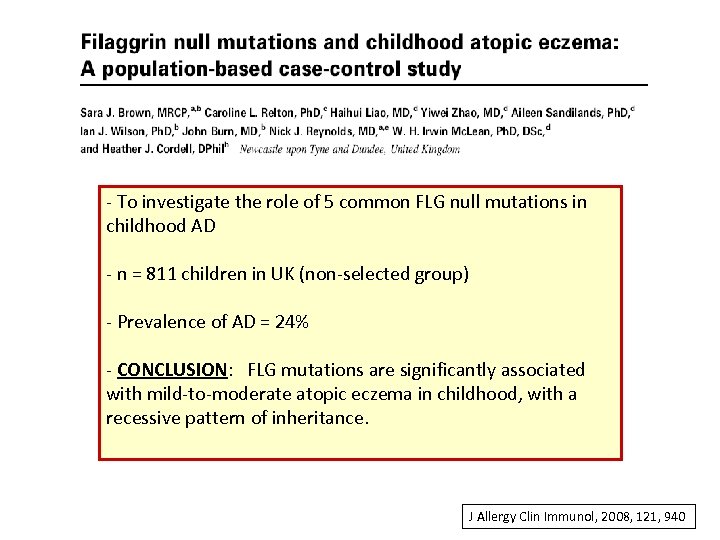
- To investigate the role of 5 common FLG null mutations in childhood AD - n = 811 children in UK (non-selected group) - Prevalence of AD = 24% - CONCLUSION: FLG mutations are significantly associated with mild-to-moderate atopic eczema in childhood, with a recessive pattern of inheritance. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2008, 121, 940
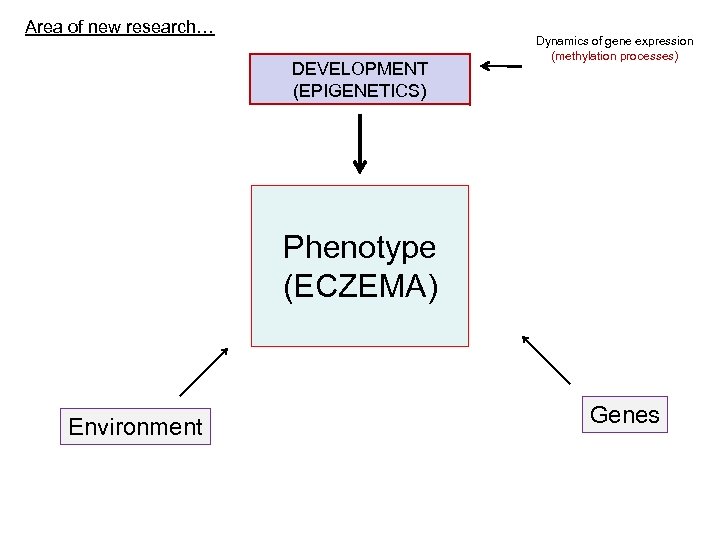
Area of new research… DEVELOPMENT (EPIGENETICS) Dynamics of gene expression (methylation processes) Phenotype (ECZEMA) Environment Genes
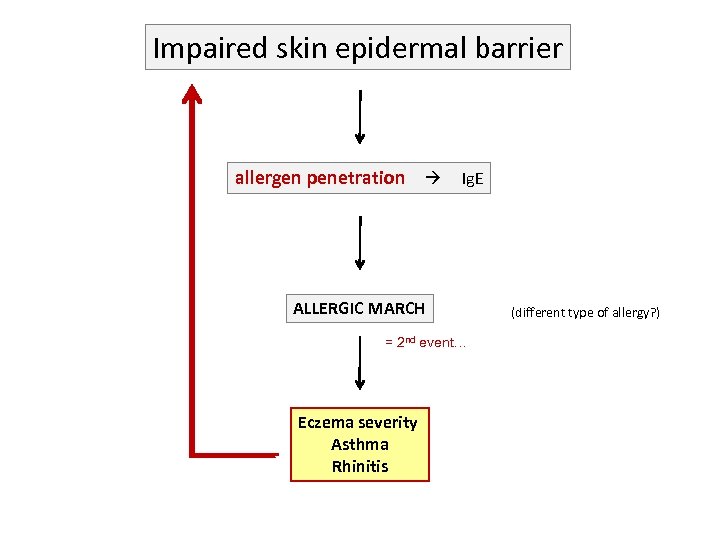
Impaired skin epidermal barrier allergen penetration Ig. E ALLERGIC MARCH = 2 nd event… Eczema severity Asthma Rhinitis (different type of allergy? )
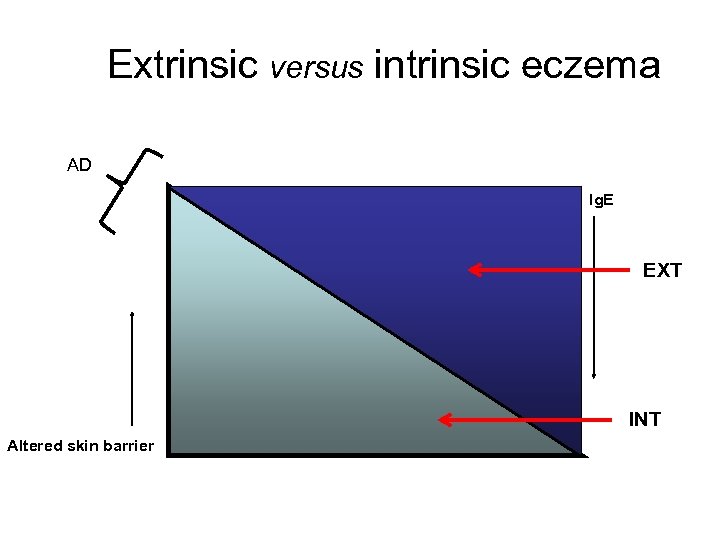
Extrinsic versus intrinsic eczema AD Ig. E EXT INT Altered skin barrier
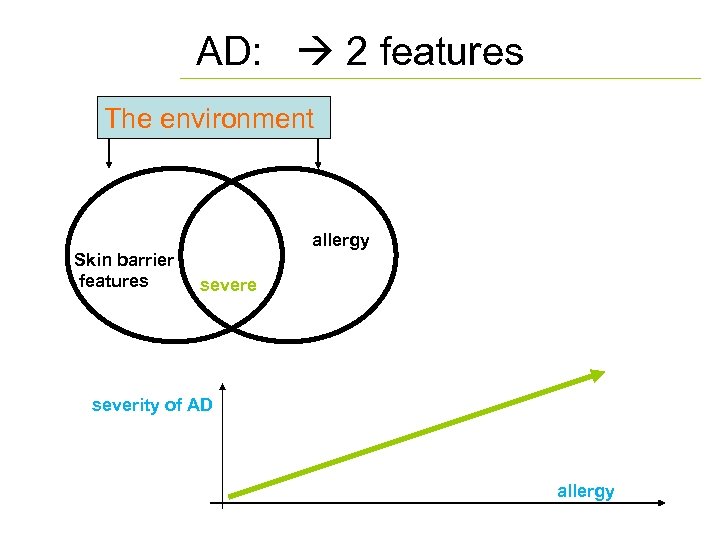
AD: 2 features The environment Skin barrier features allergy severe severity of AD allergy
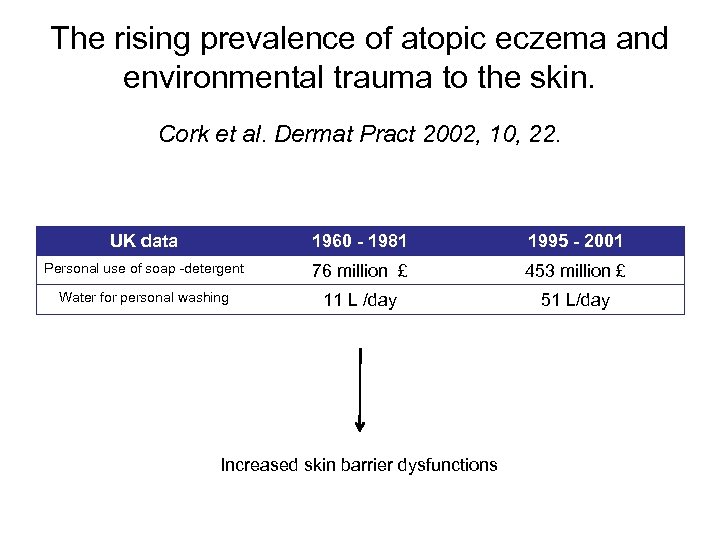
The rising prevalence of atopic eczema and environmental trauma to the skin. Cork et al. Dermat Pract 2002, 10, 22. UK data 1960 - 1981 1995 - 2001 Personal use of soap -detergent 76 million £ 453 million £ Water for personal washing 11 L /day 51 L/day Increased skin barrier dysfunctions
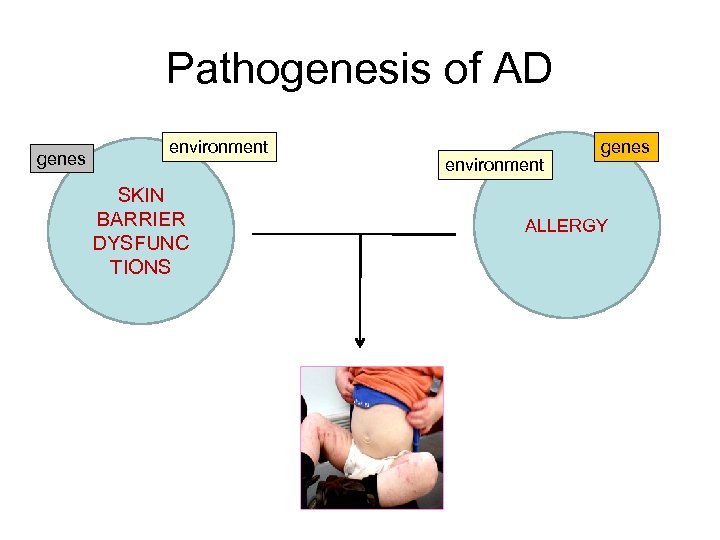
Pathogenesis of AD genes environment SKIN BARRIER DYSFUNC TIONS environment genes ALLERGY
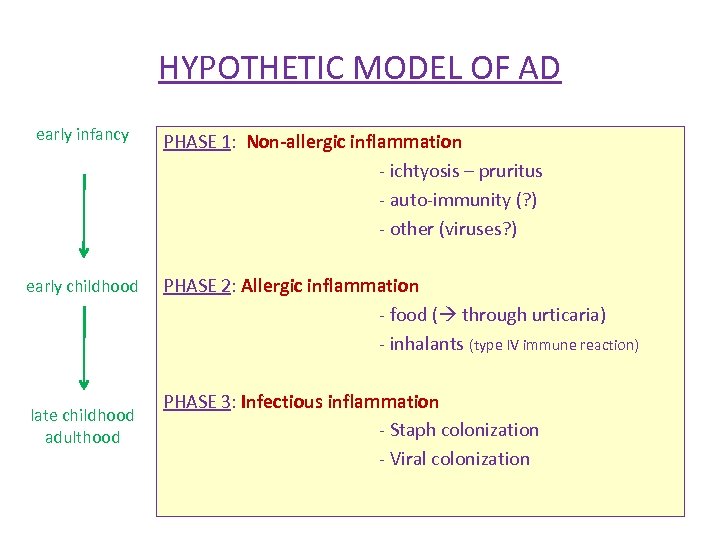
HYPOTHETIC MODEL OF AD early infancy early childhood late childhood adulthood PHASE 1: Non-allergic inflammation - ichtyosis – pruritus - auto-immunity (? ) - other (viruses? ) PHASE 2: Allergic inflammation - food ( through urticaria) - inhalants (type IV immune reaction) PHASE 3: Infectious inflammation - Staph colonization - Viral colonization
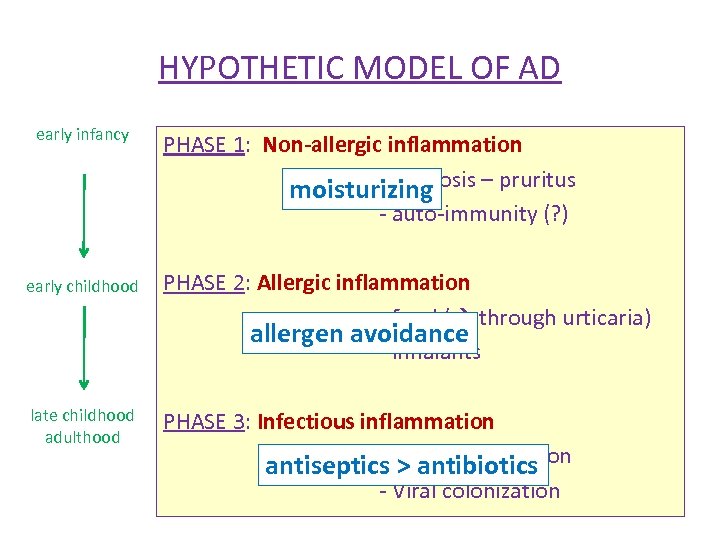
HYPOTHETIC MODEL OF AD early infancy PHASE 1: Non-allergic inflammation - ichtyosis – pruritus moisturizing - auto-immunity (? ) early childhood PHASE 2: Allergic inflammation - food ( through urticaria) allergen avoidance - inhalants late childhood adulthood PHASE 3: Infectious inflammation - > antibiotics antiseptics Staph colonization - Viral colonization

Conclusion… 1. Complex disease different types 2. Not only allergy… there is more 3. More studies on “start” of AD 4. Treatment: according to age
9a33ea60f1c148fba864fe68420c1481.ppt