Ec&Biz Lecture 2.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 29

Economy and Business Lecture 2 : Global Dimensions of Management 9/e - Chapter 5

Study Questions Ø What are the international business challenges of globalization? Ø What are multinational corporations and what do they do? Ø What is culture and how does it relate to global diversity? Ø How do management practices transfer across cultures? Management 9/e - Chapter 5 2

Study Question 1: What are the international business challenges of globalization? Ø Key concepts in the challenges of globalization: l Global economy l Globalization l International management l Global manager Management 9/e - Chapter 5 3

Study Question 1: What are the international business challenges of globalization? ü Global economy l ü Resource supplies, product markets, and business competition are worldwide, rather than local Globalization l The process of growing interdependence of these components in the global economy Management 9/e - Chapter 5 4

Study Question 1: What are the international business challenges of globalization? ü International management l ü Management in organizations with business interests in more than one country Global manager l Informed about international developments l Transnational in outlook l Competent in working with multicultural people l Aware of regional developments in a changing world Management 9/e - Chapter 5 5

Study Question 1: What are the international business challenges of globalization? ü International businesses l ü Conduct for-profit transactions of goods and services across national boundaries Reasons why businesses go international: l Profits l Customers l Suppliers l Capital l Labor Management 9/e - Chapter 5 6

Study Question 1 What are the international business challenges of globalization? Ø Market entry strategies involve the sale of goods or services to foreign markets but do not require expensive investments. Ø Types of market entry strategies: l Global sourcing l l Exporting Importing Licensing agreement Franchising Management 9/e - Chapter 5 7
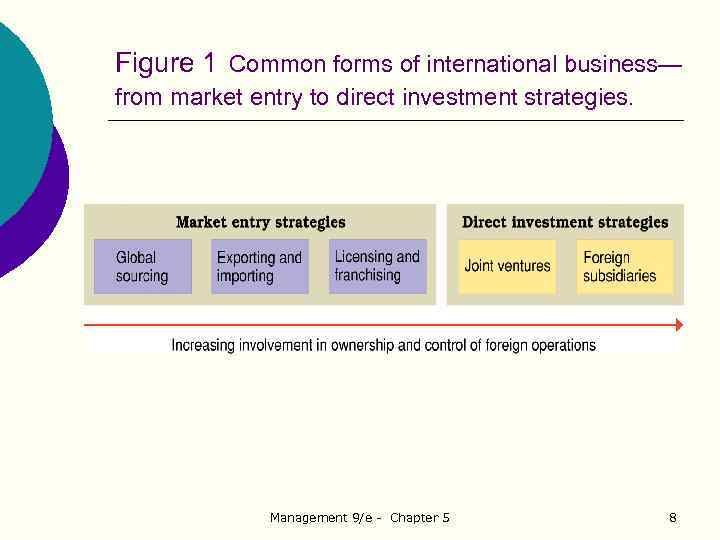
Figure 1 Common forms of international business— from market entry to direct investment strategies. Management 9/e - Chapter 5 8

Study Question 1 What are the international business challenges of globalization? Ø Direct investment strategies require major capital commitments but create rights of ownership and control over foreign operations. Ø Types of direct investment strategies: l Joint ventures l Foreign subsidiaries Management 9/e - Chapter 5 9

Study Question 1 What are the international business challenges of globalization? Ø Criteria for choosing a joint venture partner: l Familiarity with your firm’s major business. l Strong local workforce. l Future expansion possibilities. l Strong local market for partner’s own products. l Good profit potential. l Sound financial standing. Management 9/e - Chapter 5 10

Study Question 1 What are the international business challenges of globalization? Ø Complications in the global business environment: l Environment is complex, dynamic, and highly competitive. l Global business executives must deal with differences in the environment of business in different countries. l World Trade Organization resolves trade and tariff disputes among countries. l Protectionism can complicate global trading relationships. Management 9/e - Chapter 5 11

Study Question 2: What are multinational corporations and what do they do? Ø A multinational corporation (MNC) is a business with extensive international operations in more than one foreign country. Management 9/e - Chapter 5 12

Study Question 2: What are multinational corporations and what do they do? Ø Mutual benefits for host country and MNC: l Shared growth opportunities l Shared income opportunities l Shared learning opportunities l Shared development opportunities Management 9/e - Chapter 5 13

Study Question 2: What are multinational corporations and what do they do? Ø Host country complaints about MNCs: l Excessive profits l Domination of local economy l Interference with local government l Hiring the best local talent l Limited technology transfer l Disrespect for local customs Management 9/e - Chapter 5 14

Figure 5. 2 What should go right and what can go wrong in MNC-host country relationships. Management 9/e - Chapter 5 15

Study Question 2: What are multinational corporations and what do they do? Ø MNC complaints about host countries: l Profit limitations l Overpriced resources l Exploitative rules l Foreign exchange restrictions l Failure to uphold contracts Management 9/e - Chapter 5 16

Study Question 2: What are multinational corporations and what do they do? Ø Ethical issues for MNCs: l Corruption — illegal practices that further one’s business interests. l Sweatshops — employing workers at low wages for long hours and in poor working conditions. l Child labor — full-time employment of children for work otherwise done by adults. l Sustainable development — meeting current needs without compromising future needs. Management 9/e - Chapter 5 17

Study Question 3: What is culture and how does it relate to global diversity? Ø Culture l The shared set of beliefs, values, and patterns of behavior common to a group of people. Ø Culture shock l Ø Cultural intelligence l Ø Confusion and discomfort a person experiences in an unfamiliar culture. The ability to adapt and adjust to new cultures Ethnocentrism l Tendency to consider one’s own culture as superior to others. Management 9/e - Chapter 5 18

Study Question 3: What is culture and how does it relate to global diversity? Ø Stages in adjusting to a new culture: l Confusion l Small victories l The honeymoon l Irritation and anger l Reality Management 9/e - Chapter 5 19

Study Question 3: What is culture and how does it relate to global diversity? Ø Popular dimensions of culture: l Language ¡ l l Interpersonal space Time orientation ¡ l l Low-context cultures and high-context cultures Monochronic cultures and polychronic cultures Religion Contracts and agreements Management 9/e - Chapter 5 20

Study Question 3: What is culture and how does it relate to global diversity? Ø Values and national cultures (Hofstede): l Power distance l Uncertainty avoidance l Individualism-collectivism l Masculinity-femininity l Time orientation Management 9/e - Chapter 5 21
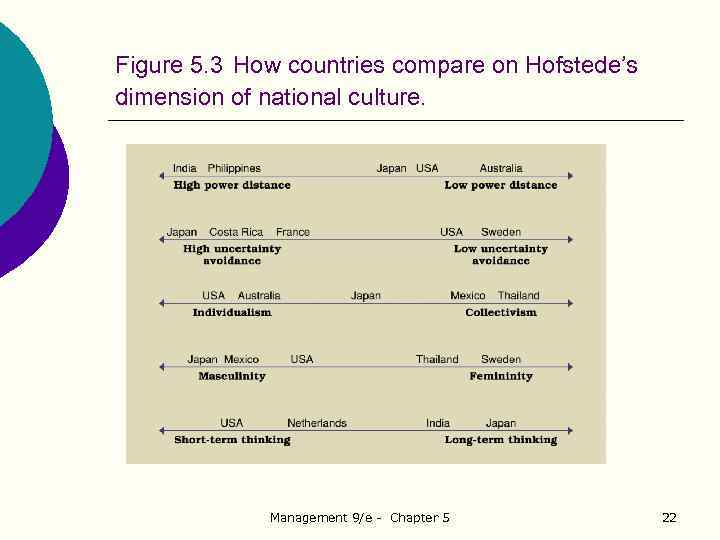
Figure 5. 3 How countries compare on Hofstede’s dimension of national culture. Management 9/e - Chapter 5 22

Study Question 3: What is culture and how does it relate to global diversity? Ø Project GLOBE (Global Leadership and Organizational Behavior Effectiveness) l Researches the leadership, organizational practices, and diversity among world cultures. Power distance ¡ Uncertainty avoidance ¡ Gender egalitarianism ¡ Future orientation ¡ Management 9/e - Chapter 5 23

Study Question 3: What is culture and how does it relate to global diversity? l Project GLOBE’s nine dimensions continued ¡ Institutional collectivism ¡ In-group collectivism ¡ Assertiveness ¡ Performance orientation ¡ Humane orientation Management 9/e - Chapter 5 24
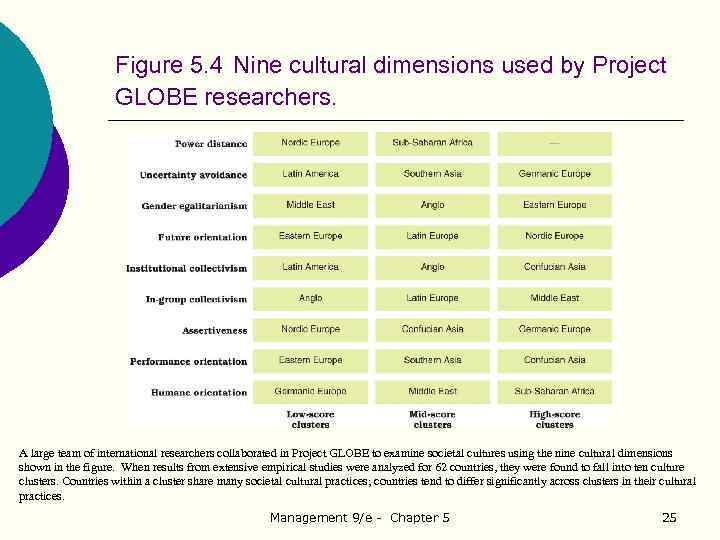
Figure 5. 4 Nine cultural dimensions used by Project GLOBE researchers. A large team of international researchers collaborated in Project GLOBE to examine societal cultures using the nine cultural dimensions shown in the figure. When results from extensive empirical studies were analyzed for 62 countries, they were found to fall into ten culture clusters. Countries within a cluster share many societal cultural practices; countries tend to differ significantly across clusters in their cultural practices. Management 9/e - Chapter 5 25

Study Question 3: What is culture and how does it relate to global diversity? Ø Understanding cultural differences (Trompenaars): l l l Relationships with people: ¡ Universalism versus particularism ¡ Individualism versus collectivism ¡ Neutral versus affective ¡ Specific versus diffuse ¡ Achievement versus prescription Attitudes toward time — sequential and synchronic views. Attitudes toward environment — inner-directed and outer-directed cultures. Management 9/e - Chapter 5 26

Study Question 4: How do management practices transfer across cultures? Ø Comparative management l How management systematically differs among countries and/or cultures. Ø Global managers l Need to successfully apply management functions across international boundaries. Management 9/e - Chapter 5 27

Study Question 4: How do management practices transfer across cultures? Ø Are management theories universal? l U. S. management theories may be ethnocentric. ¡ Participation and individual performance are not emphasized as much in other cultures. l Not all Japanese management practices can be applied successfully abroad. Management 9/e - Chapter 5 28

Study Question 4: How do management practices transfer across cultures? Ø Global organizational learning: l Companies can and should learn from each other. l Readiness for global organizational learning varies based on managerial attitudes. ¡ ¡ Polycentric attitudes ¡ l Ethnocentric attitudes Geocentric attitudes Be alert, open, inquiring, but always cautious. Management 9/e - Chapter 5 29
Ec&Biz Lecture 2.ppt